Overview
The article outlines four essential steps for meal planning that can help you effectively manage type 2 diabetes. These steps focus on:
- Carbohydrate counting
- Understanding the glycemic index
- Portion control
- Creating balanced meals
We understand that navigating these strategies can feel overwhelming, but practical tips are provided to help you personalize your meal plans.
By implementing these strategies through careful shopping and preparation, you can maintain flexibility and monitor your progress. This adaptability is crucial for aligning with your individual health goals. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way. Together, these strategies ensure a comprehensive approach to dietary management.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of meal planning for type 2 diabetes can feel overwhelming. Yet, it is essential for effective glucose management and overall well-being. By understanding key components like:
- carbohydrate counting
- glycemic index
- portion control
you can transform your dietary habits into a powerful tool for health. However, the real challenge is creating a personalized meal plan that not only meets your nutritional needs but also fits seamlessly into your lifestyle.
It's understandable to wonder: how can you strike the perfect balance between health and enjoyment while managing diabetes? You're not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to support you every step of the way.
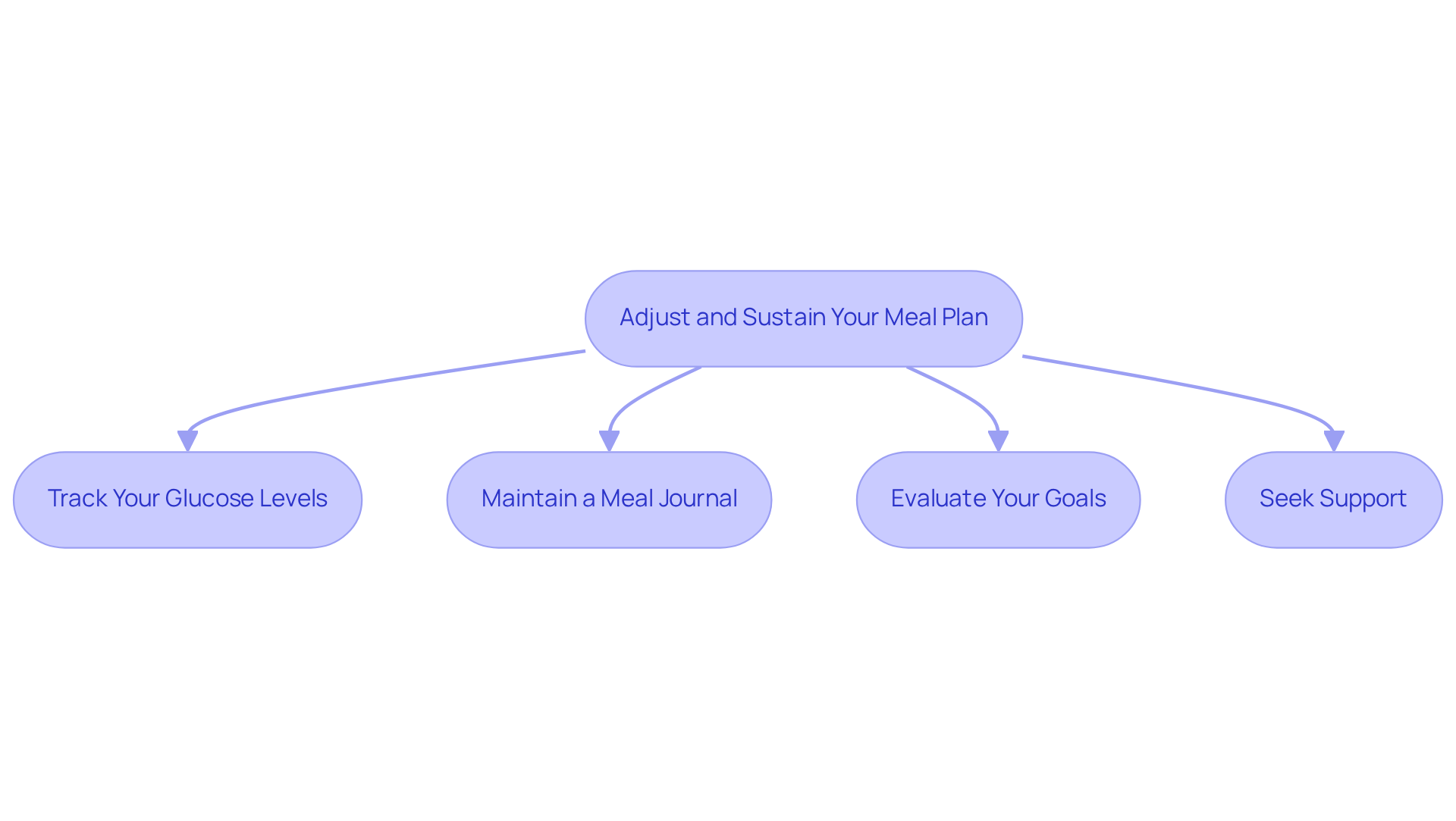
Understand the Basics of Meal Planning for Type 2 Diabetes
Eating for type 2 diabetes is essential for effectively managing glucose levels, and it's completely understandable to feel a bit overwhelmed. Familiarizing yourself with the following key concepts can significantly enhance your dietary choices and empower you on this journey:
-
Carbohydrate Counting: Recognizing carbohydrates in foods is vital, as they have the most substantial impact on blood sugar. Aim for a consistent carbohydrate intake at each meal, ideally between 45 to 60 grams per meal and 15 to 20 grams per snack. This practice assists in keeping stable glucose levels, helping you feel more in control.
-
Glycemic Index (GI): Understanding the glycemic index of items is important. The GI categorizes carbohydrates according to their impact on glucose levels, with lower GI items promoting more stable glucose stability. Including low-GI items in your diet can help reduce spikes in blood sugar, facilitating better management of your condition.
-
Portion Control: Proper portion sizes are critical in diabetes management. Utilizing measuring cups or a food scale can ensure you are not overeating. A recommended strategy is to use a 9-inch plate, filling half with non-starchy vegetables, a quarter with lean protein, and the remaining quarter with whole grains or starchy vegetables. Remember, you're not alone in this process; many find this method helpful.
-
Balanced Meals: Strive for a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats in each meal. This balance not only encourages fullness but also helps in sustaining stable glucose levels. For instance, pairing carbohydrates with proteins can slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, further stabilizing blood sugar levels.
By incorporating these principles into your dietary planning for eating for type 2 diabetes, you can take proactive steps toward managing your Type 2 Diabetes effectively. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
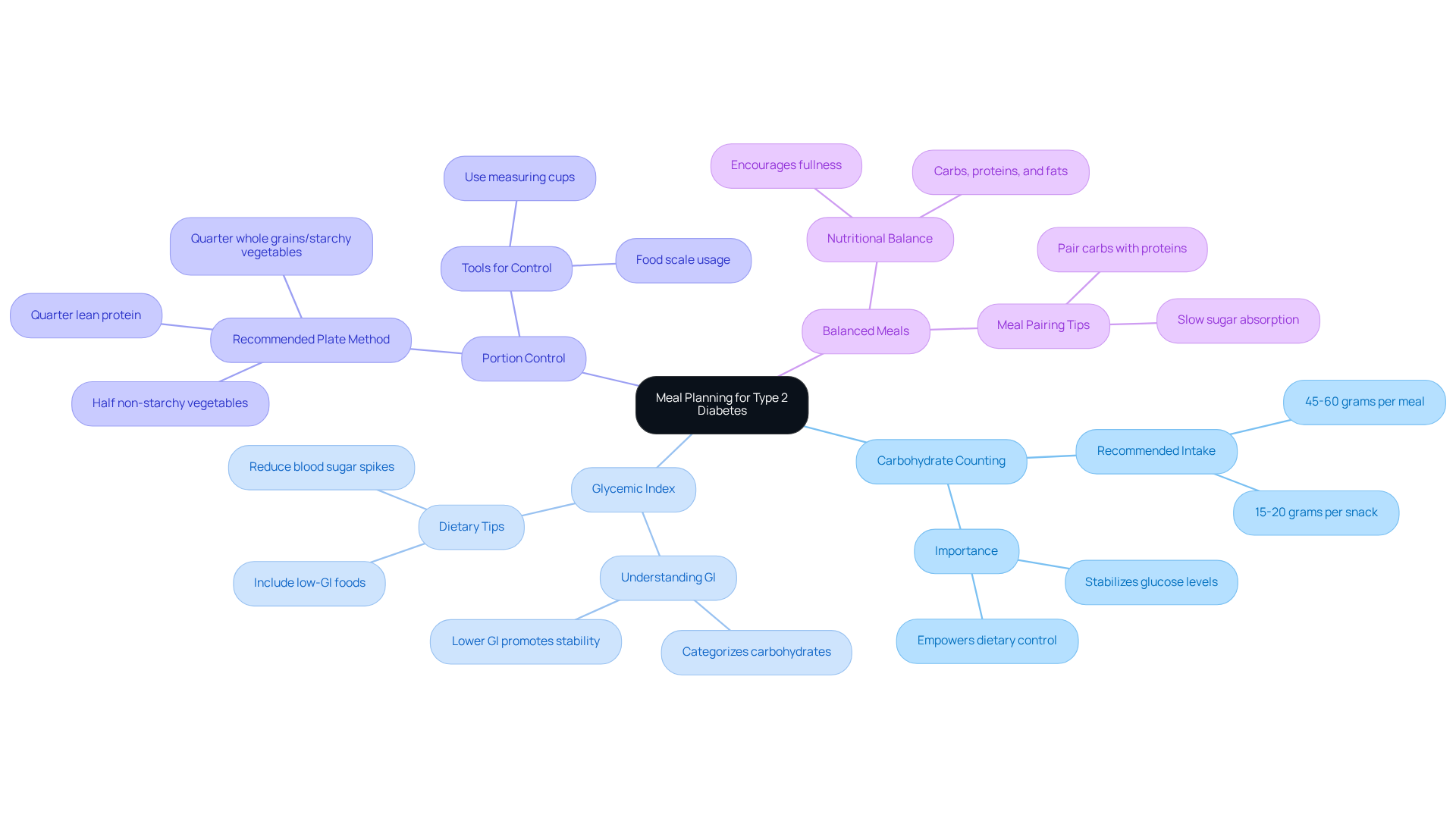
Create Your Personalized Meal Plan: Key Strategies and Tips
Creating a personalized meal plan for eating for type 2 diabetes can feel overwhelming, but you're not alone in this journey. Here are some key strategies to help you take control of your health while enjoying the process:
-
Assess Your Dietary Preferences: Start by reflecting on your likes, dislikes, dietary restrictions, and cultural preferences. This evaluation is essential for developing a dining plan that is not only effective but also enjoyable and sustainable.
-
Set Health Goals: Clearly define your health objectives, such as weight loss, improved blood glucose control, or enhanced energy levels. It's understandable to feel uncertain, but studies suggest that individuals with specific health goals are more likely to stick to their dietary plans, making this step crucial for your success.
-
Choose Recipes Wisely: Select recipes that align with both your dietary preferences and health goals. Aim for dishes that are rich in fiber, low in added sugars, and packed with healthy fats. This thoughtful approach not only supports blood sugar management but also contributes to your overall well-being.
-
Plan for Variety: Incorporate a diverse range of foods to ensure you receive a broad spectrum of nutrients and to avoid food fatigue. Rotating different proteins, vegetables, and whole grains throughout the week can keep your meals engaging and fulfilling.
-
Utilize a Food Planning Template: Consider creating a weekly food planning template that outlines your breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks. This visual aid can simplify grocery shopping and help you stay organized, making it easier to stick to your plan.
By following these strategies, you can create a customized dietary plan for eating for type 2 diabetes that meets your nutritional needs and supports your journey in managing the condition effectively. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
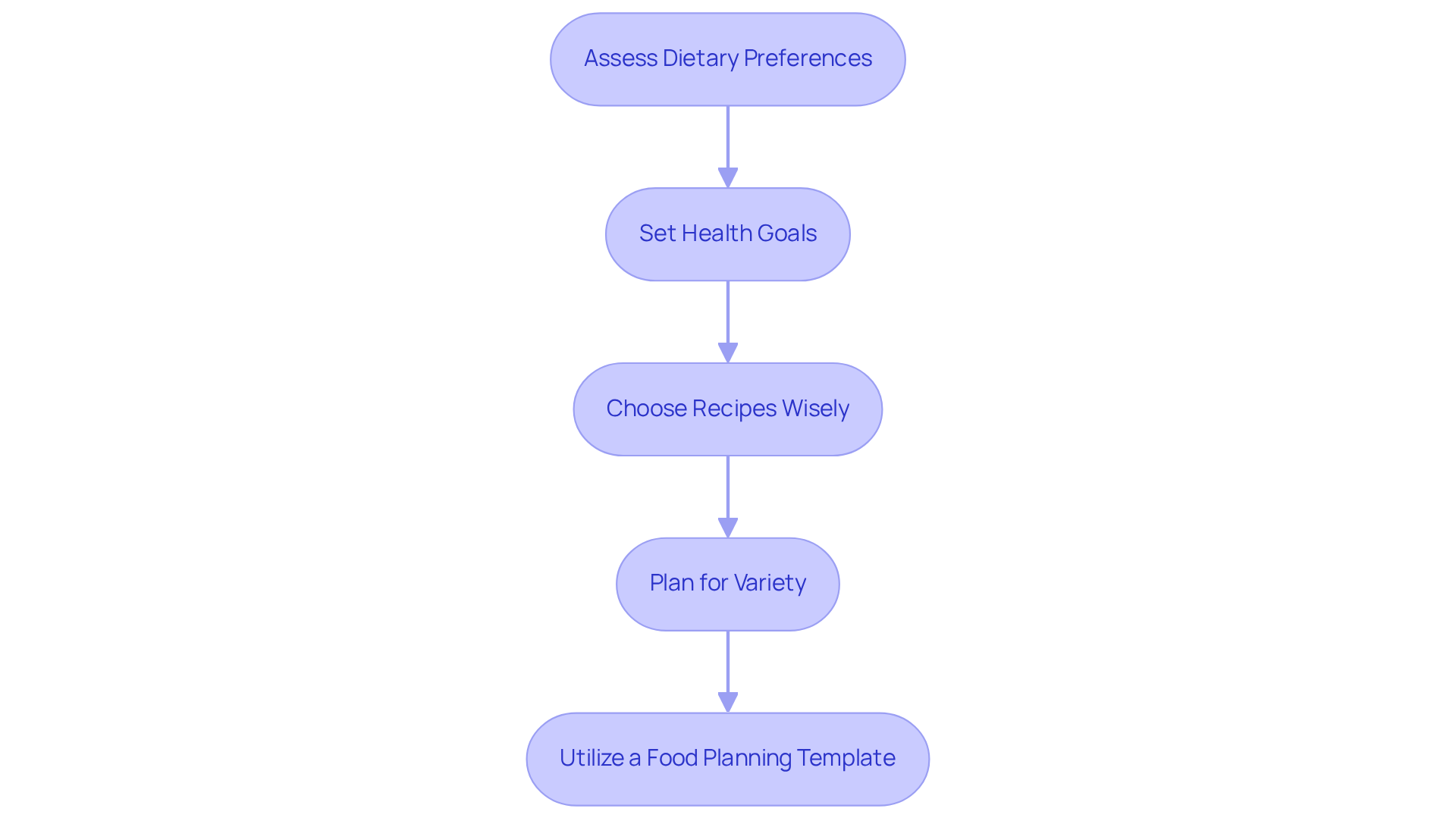
Implement Your Meal Plan: Shopping and Preparation Steps
To implement your meal plan effectively, let's take this journey together by following these compassionate steps:
-
Create a Shopping List: Start by compiling a shopping list based on your dining plan. Include all the ingredients you need, and consider organizing the list by grocery store sections. This small step can save you time and reduce stress during your shopping experience.
-
Choose Fresh and Whole Foods: Prioritize fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It’s understandable to feel tempted by processed foods, but remember that these often contain high levels of sugar and unhealthy fats. Choosing whole foods can nourish your body and uplift your spirit.
-
Food Preparation: Dedicate some time each week to prepare dishes in advance. This could mean chopping vegetables, cooking grains, or batch-cooking proteins. Storing food in portioned containers makes it easy to access healthy meals when you need them most. You're taking a proactive step toward self-care!
-
Stay Adaptable: Life can be unpredictable, and that’s okay. Be ready to modify your dining plan according to seasonal produce or unforeseen occurrences. Flexibility is key to staying on track without feeling restricted. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
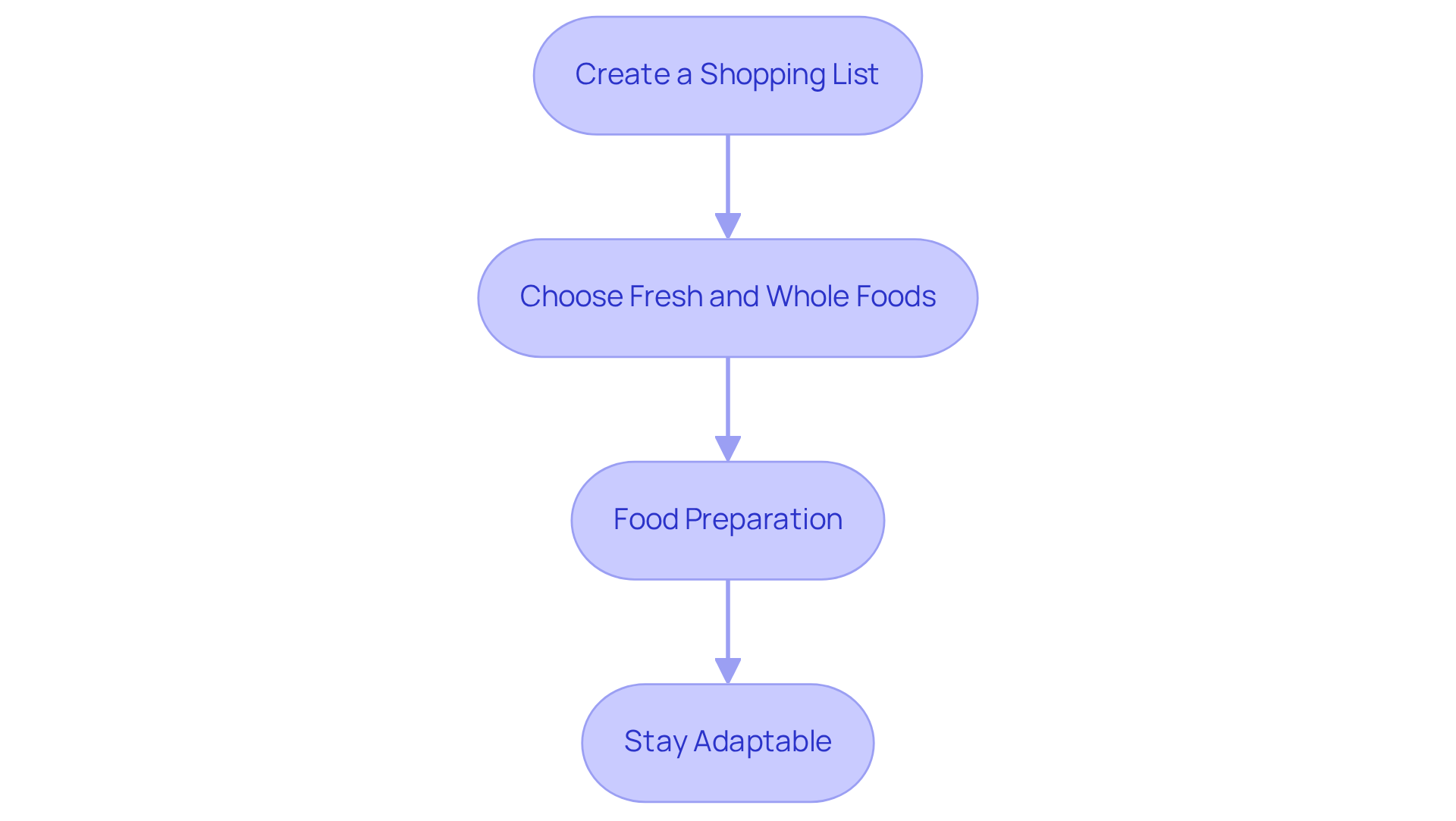
Adjust and Sustain Your Meal Plan: Monitoring and Modifications
To effectively adjust and sustain your meal plan, consider these compassionate strategies:
-
Track Your Glucose Levels: Regularly measuring your glucose levels is essential for understanding how various meals affect your readings. It's completely normal to feel overwhelmed by this process, but this practice helps identify patterns, enabling you to make informed adjustments to your diet. Research shows that self-monitoring of glucose (SMBG) is crucial for managing diabetes and avoiding complications, with rates of daily SMBG rising significantly over the years. Remember, you're not alone in this journey.
-
Maintain a meal journal by recording your meal consumption and its impact on your blood sugar to gain valuable insights into eating for type 2 diabetes. It’s understandable to feel uncertain about what to eat, but studies indicate that while meal logs can impact eating patterns, they are most beneficial when paired with targeted goal-driven strategies and instruction. For example, a study discovered that merely 26.7% of participants showed a clinically meaningful reduction in hemoglobin A1c after maintaining a dietary journal, emphasizing the necessity for further assistance. We are here to support you every step of the way.
-
Evaluate Your Goals: Periodically reassess your health goals and modify your meal plan as necessary. This may involve adjusting portion sizes, experimenting with new recipes, or incorporating a broader range of ingredients. Regular evaluations can help ensure that your choices in eating for type 2 diabetes align with your health objectives and contribute to better glycemic control. It’s important to remember that adjusting your plan is a sign of progress.
-
Seek Support: Engaging with healthcare professionals, such as registered dietitians or diabetes educators, can provide personalized advice tailored to your needs. Additionally, joining a community or support group can offer motivation and encouragement, fostering a sense of connection with others facing similar challenges. As noted by diabetes educators, incorporating a food diary into your routine can facilitate discussions about lifestyle modifications and reinforce healthy eating habits. You're not alone in this journey, and together, we can navigate these challenges.
Conclusion
Eating for type 2 diabetes involves a thoughtful approach to meal planning that can significantly enhance your health and well-being. By understanding the fundamentals of carbohydrate counting, glycemic index, portion control, and balanced meals, you can take charge of your dietary choices. This proactive stance not only aids in managing blood sugar levels but also fosters a sense of empowerment in navigating daily nutrition.
Key strategies for creating your personalized meal plan include:
- Assessing your dietary preferences
- Setting clear health goals
- Selecting appropriate recipes
- Embracing variety
Implementing these strategies can transform meal planning from a daunting task into an enjoyable and sustainable practice. Furthermore, by focusing on effective shopping and preparation steps, you can simplify your journey and ensure you have the right foods on hand to support your health.
Ultimately, the path to managing type 2 diabetes through meal planning is about more than just food; it's about building a lifestyle that promotes health and well-being. Regularly monitoring your glucose levels, maintaining a meal journal, and seeking support are crucial components of this journey. Embracing these practices can lead to meaningful improvements in your health, encouraging you to take the necessary steps toward a healthier future. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is meal planning important for managing type 2 diabetes?
Meal planning is essential for managing glucose levels effectively, helping individuals feel more in control of their dietary choices and overall health.
What is carbohydrate counting and why is it important?
Carbohydrate counting involves recognizing the amount of carbohydrates in foods, as they significantly impact blood sugar levels. It is recommended to aim for 45 to 60 grams of carbohydrates per meal and 15 to 20 grams per snack to maintain stable glucose levels.
What is the glycemic index (GI) and how does it affect diabetes management?
The glycemic index categorizes carbohydrates based on their impact on blood sugar levels. Lower GI items promote more stable glucose levels, making them beneficial for managing type 2 diabetes and reducing spikes in blood sugar.
How can portion control help in managing diabetes?
Proper portion sizes are critical in diabetes management. Using measuring cups or a food scale can help prevent overeating. A suggested method is to use a 9-inch plate, filling half with non-starchy vegetables, a quarter with lean protein, and the remaining quarter with whole grains or starchy vegetables.
What constitutes a balanced meal for someone with type 2 diabetes?
A balanced meal should include a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. This balance promotes fullness and helps sustain stable glucose levels. Pairing carbohydrates with proteins can slow down sugar absorption, further stabilizing blood sugar levels.



