Overview
This article outlines four essential steps to help you effectively achieve your A1C goal in managing diabetes.
- First, it's important to understand the significance of A1C in your health journey.
- Next, determining a personalized target can empower you to take control.
- Implementing effective strategies tailored to your needs is crucial,
- and finally, monitoring your progress will help you stay on track.
These steps are supported by evidence that emphasizes the importance of individualized care. Remember, dietary and lifestyle adjustments can make a significant difference, and regular monitoring is key to reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
In the journey of diabetes management, understanding A1C levels is crucial. This important blood test acts as a window into your average blood sugar control over the past few months, providing insights that can greatly affect your health outcomes. As diabetes rates continue to rise across the nation, reaching and maintaining optimal A1C targets has never been more important.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but remember that effective diabetes management involves personalized strategies, dietary adjustments, and regular monitoring. Each of these elements plays a vital role in reducing the risk of complications. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of A1C, guiding you through essential steps to not only comprehend your results but also to implement actionable strategies that can enhance your overall health and well-being. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Understand A1C and Its Importance in Diabetes Management
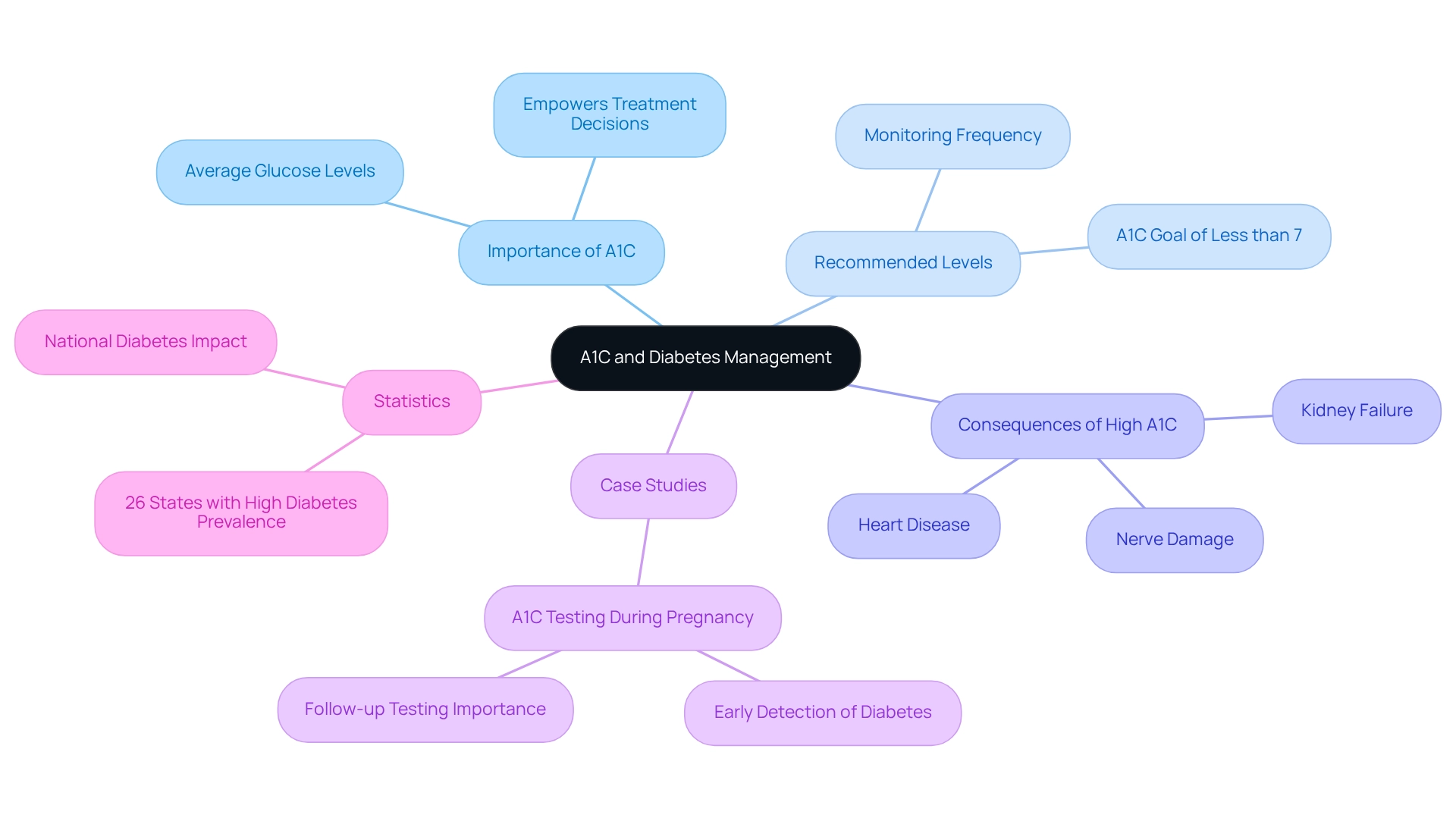
A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, is an essential test that provides valuable insight into your average glucose levels over the past two to three months, expressed as a percentage. It's understandable to feel concerned about your health; higher A1C percentages indicate poorer blood sugar control, which can lead to serious complications. The American Diabetes Association recommends that most adults with the condition aim for an A1C goal of less than 7%. Achieving and maintaining A1C levels within this range significantly reduces the risk of complications associated with high blood sugar, including heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. Understanding your A1C results is crucial for effective management. It empowers you and your healthcare team to make informed decisions regarding your treatment plan, including necessary lifestyle changes and medication adjustments.
Recent studies underscore the significance of A1C in managing blood sugar levels, demonstrating that individuals who maintain their A1C levels within the recommended range experience fewer complications and improved overall health outcomes. For instance, a case study on A1C testing during pregnancy illustrates its vital role in detecting undiagnosed blood sugar issues in women with risk factors. Early detection allows for prompt interventions, which can help prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes after pregnancy. Moreover, recent statistics reveal that 26 states and territories have a prevalence of diabetes exceeding the national average, highlighting the urgent need for effective approaches. As emphasized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, understanding how diabetes impacts our nation is essential in providing measures to mitigate its effects on American citizens.
In summary, A1C testing is not just a number; it is a crucial tool in your health care toolkit. By consistently monitoring your A1C levels and striving to achieve the A1C goal, you can significantly enhance your health and reduce the risk of complications related to diabetes. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource for individuals living with or caring for someone with blood sugar issues, offering information and support to help you navigate your care journey effectively.
Determine Your Personalized A1C Target
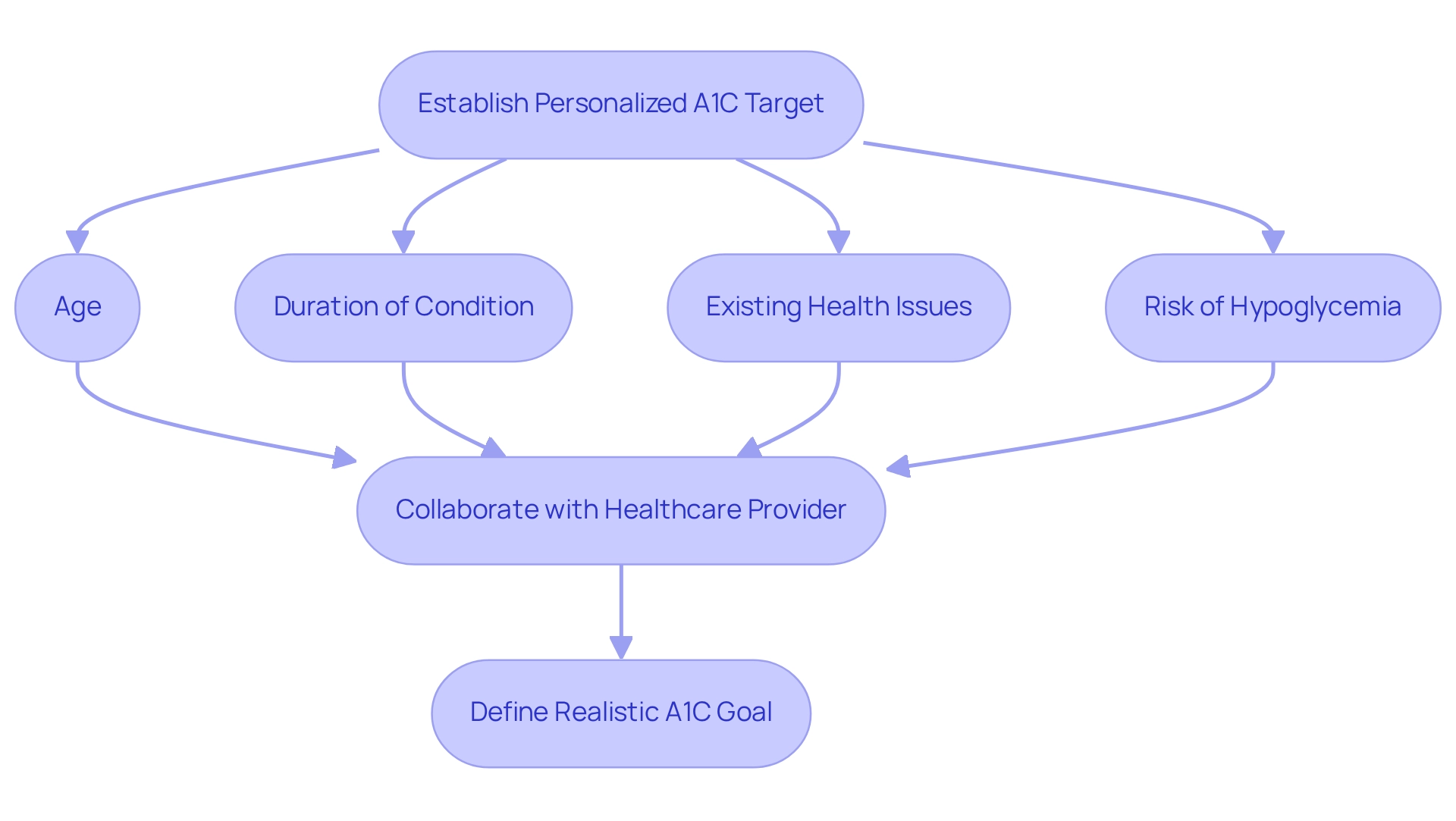
Establishing your individualized A1C goal is crucial for effectively managing your condition, and it should be a collaborative effort with your healthcare provider. Several factors influence this target, including age, duration of the condition, existing health issues, and the risk of hypoglycemia. For instance, a study conducted by Kaiser Permanente Southern California (KPSC) involving over 343,000 patients aged 55 and older highlighted that older adults, or those with a limited life expectancy, might have a higher A1C target, typically ranging from 7.5% to 8.0%. This approach helps mitigate the risks associated with low blood sugar levels.
When discussing your A1C target with your healthcare provider, it’s essential to share your complete health history and lifestyle factors, such as diet and physical activity. This joint conversation will help define a goal that not only facilitates efficient health oversight but also aligns with your overall wellness. Diabetes specialists emphasize the importance of personalizing the A1C goal based on individual circumstances, ensuring that each patient receives tailored recommendations reflecting their unique health profile. Recent findings from a study titled 'Age-Dependent Hemoglobin A1c Therapeutic Targets Reduce Diabetic Medication Changes in the Elderly' further underscore the significance of age and health status in setting A1C goals. This study indicates that modifying A1C goals according to age can lead to more effective approaches for older adults. By participating in this process with your healthcare provider, you can establish realistic and attainable A1C goals that enhance your quality of life while effectively managing your condition.
Additionally, insights from the case study 'Data-Driven Quality Improvement in Diabetes Care' demonstrate how data-driven methods can influence A1C target recommendations and improve practices in diabetes care. As Jenny Staab, PhD, noted, the guidance from various experts in this field is crucial for developing effective strategies. By incorporating these insights, you can enrich your journey in managing your condition. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Implement Strategies to Achieve Your A1C Goal
To effectively achieve your A1C goal, consider implementing the following compassionate strategies, and explore the resources available at T2DSolutions to support your journey:
-
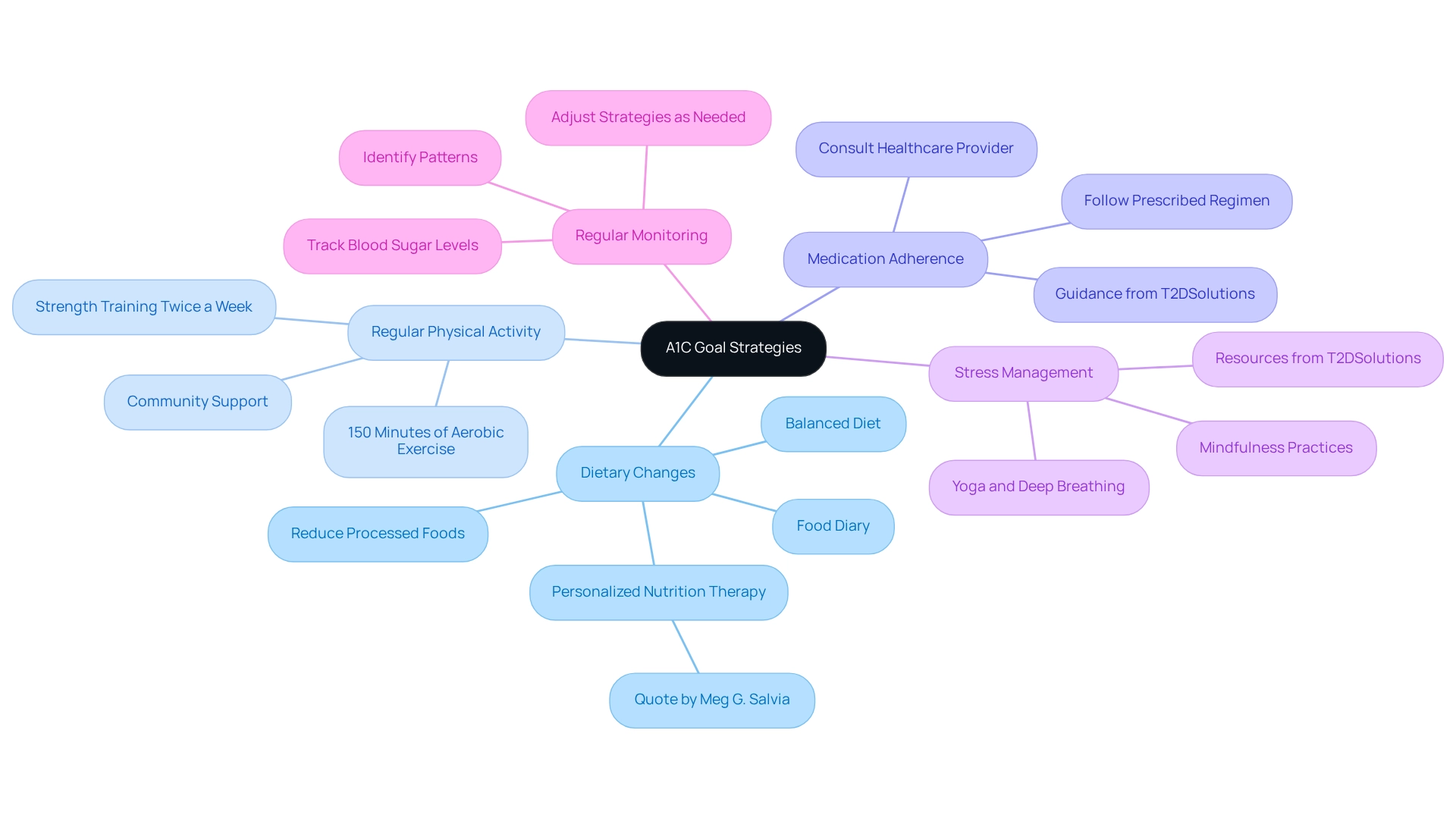
Dietary Changes: Emphasize a balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables. Reducing processed foods, added sugars, and saturated fats is crucial. Keeping a food diary can aid in tracking your intake and pinpointing areas for improvement. Research indicates that dietary modifications can significantly impact A1C levels, helping many individuals achieve their A1C goal diabetes through structured nutrition plans. However, it's understandable that dietary changes can be challenging; for instance, 42.9% of initial GLP-1 agonist users in the low-carbohydrate high-fat (LCHF) group discontinued this medication. As Meg G. Salvia states, "Providing medical nutrition therapy and customizing nutrition interventions to personal needs and situations can be a significant way physicians, dietitians, and providers can assist individuals with type 2 health conditions."
-
Regular Physical Activity: Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly, such as brisk walking or cycling. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises at least twice a week can enhance insulin sensitivity. Studies show that consistent physical activity not only aids in weight management but also contributes to better glycemic control. Remember, you’re not alone in this! T2DSolutions offers resources and community support to help you stay motivated and active.
-
Medication Adherence: Following your prescribed diabetes medication regimen diligently is essential. If you encounter side effects or have concerns, don’t hesitate to consult your healthcare provider to explore alternative options. Adhering to your medication is key for maintaining optimal glucose levels and achieving your a1c goal diabetes. T2DSolutions can provide guidance on managing medications effectively, ensuring you feel supported throughout this process.
-
Stress Management: It's important to recognize that high stress can adversely affect blood sugar levels. Engaging in stress-reducing practices such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises can be beneficial. Effectively handling stress can lead to enhanced overall health and improved diabetes control. T2DSolutions may provide tools and resources to help you with stress coping techniques, reminding you that you are not alone in navigating these challenges.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular monitoring of your blood sugar levels allows you to understand how your lifestyle choices influence your A1C goal diabetes. This practice enables prompt modifications to your strategy, ensuring you remain on course toward your goals. Regular monitoring is essential for identifying patterns and making informed decisions about your health management. T2DSolutions provides resources to help you track your progress and make necessary adjustments.
Additionally, the limitations and future research directions regarding low-carbohydrate diets suggest that further exploration is needed to understand their effectiveness in diverse populations and settings. It’s crucial to focus on the role of weight loss as a mediator in glycemic outcomes. Effective strategies for controlling blood sugar can potentially decrease glucose-lowering medications, which may assist in reducing individual and societal expenses related to type 2 conditions.
Monitor Your Progress and Adjust as Necessary
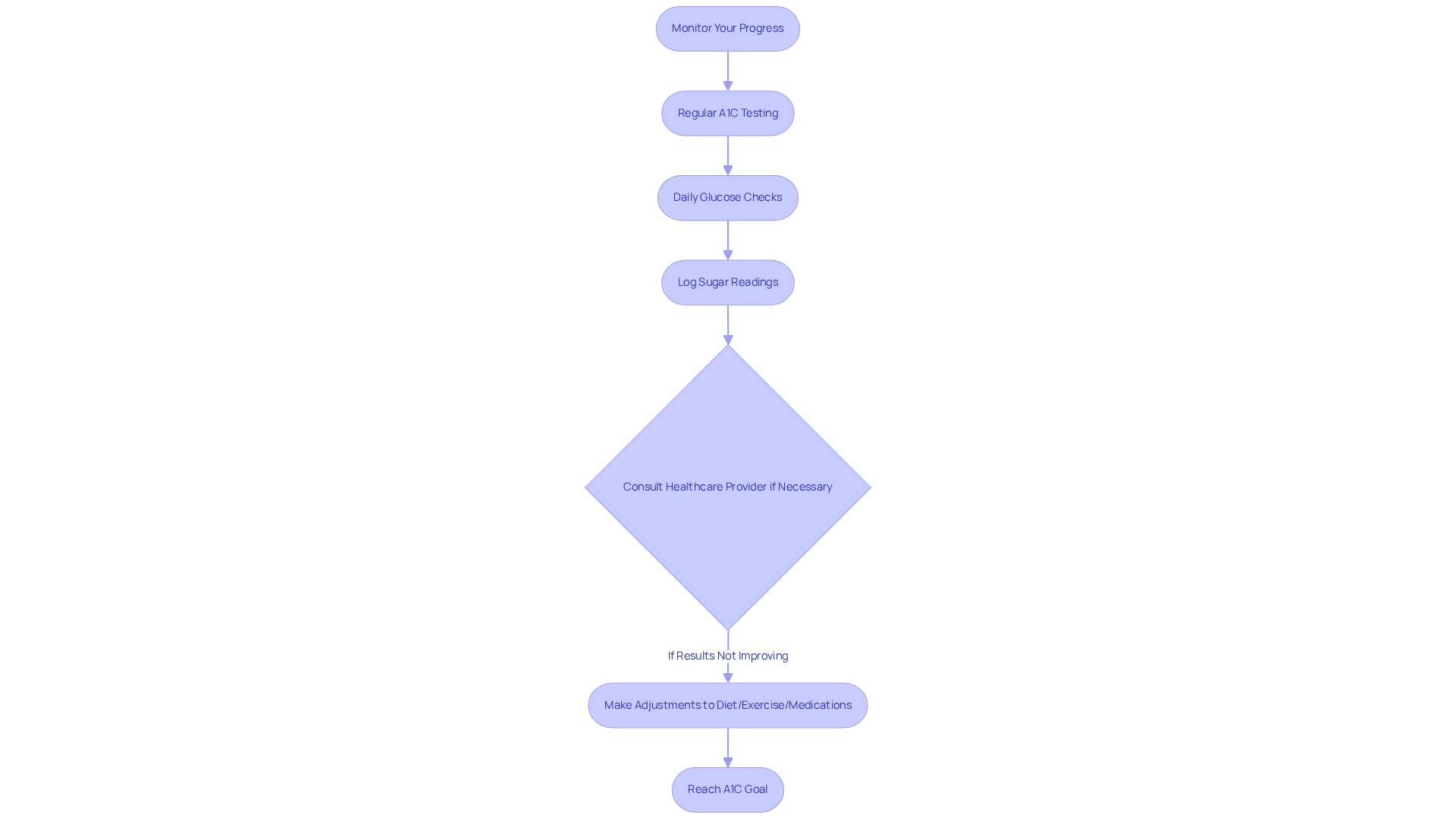
Tracking your progress is essential for effective diabetes control, which includes regular A1C testing to meet your a1c goal diabetes along with daily glucose checks. For individuals with stable A1C levels, testing should occur at least twice a year. However, it’s advisable to test more frequently when changes to your treatment plan are implemented. Keeping a thorough log of your sugar readings can help you recognize patterns and triggers that affect your glucose levels.
If your A1C results are not improving, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider to reassess your control strategies. They may recommend modifications to your diet, exercise regimen, or medications. Regular monitoring not only aids in achieving your a1c goal diabetes but also enhances your overall understanding of your condition.
Recent insights indicate that estimated average glucose (eAG) readings can provide a more relatable measure for those monitoring their blood glucose at home. These readings often reflect lower values than meter readings taken in the morning or before meals. Understanding this can empower you to make informed modifications to your healthcare. For instance, eAG can help you correlate your daily glucose readings with your A1C results, enabling more effective strategies.
It's also crucial to note that women with a history of gestational issues are at an increased risk of developing Type 2 conditions, making regular A1C monitoring even more critical for this group. As Milo Engoren mentions, "All authors revised it critically for important intellectual content and have given final approval of the version to be published," emphasizing the significance of collaborative insights in treating diabetes-related issues.
Remember, reaching your a1c goal diabetes is a journey that requires patience and persistence. Regular monitoring is a key component of that journey. T2DSolutions provides guidance on monitoring blood glucose levels and managing medication, offering the support you need to navigate this process efficiently. Explore T2DSolutions for additional resources and community support tailored to your diabetes management needs.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing A1C levels is pivotal in your journey of diabetes care. Throughout this article, we’ve highlighted the significance of A1C testing as a critical tool for monitoring your blood sugar control over time. Achieving and maintaining an A1C target below 7% can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes, including heart disease and nerve damage. Personalized A1C targets, established in collaboration with your healthcare provider, ensure that management strategies align with your unique health profile and circumstances.
Implementing effective strategies—such as dietary changes, regular physical activity, medication adherence, stress management, and ongoing monitoring—is essential for reaching your A1C goals. Each of these elements plays a vital role in fostering better health outcomes and enhancing your overall well-being. Regular progress checks and adjustments to your management plan based on A1C results and blood glucose readings are crucial for ensuring sustained success in managing diabetes.
Ultimately, understanding A1C and actively engaging in personalized management strategies empowers you to take control of your health. With resources like T2DSolutions available for support and guidance, navigating the complexities of diabetes becomes a more manageable and achievable endeavor. Prioritizing A1C management not only improves your health but also contributes to the broader goal of reducing the impact of diabetes on communities nationwide. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is A1C and why is it important?
A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, is a test that provides insight into average glucose levels over the past two to three months, expressed as a percentage. It is important because higher A1C percentages indicate poorer blood sugar control, which can lead to serious health complications.
What is the recommended A1C goal for adults with diabetes?
The American Diabetes Association recommends that most adults with diabetes aim for an A1C goal of less than 7%. Maintaining A1C levels within this range significantly reduces the risk of complications associated with high blood sugar.
How does A1C testing contribute to diabetes management?
Understanding A1C results is crucial for effective diabetes management, as it empowers individuals and their healthcare teams to make informed decisions regarding treatment plans, including lifestyle changes and medication adjustments.
What are the health risks associated with high A1C levels?
Higher A1C levels can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage.
How does A1C testing play a role during pregnancy?
A1C testing during pregnancy is vital for detecting undiagnosed blood sugar issues in women with risk factors. Early detection allows for prompt interventions to help prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes after pregnancy.
What is the current state of diabetes prevalence in the United States?
Recent statistics show that 26 states and territories have a prevalence of diabetes exceeding the national average, highlighting the urgent need for effective approaches to manage the condition.
How can individuals access support for managing blood sugar issues?
T2DSolutions is a valuable resource for individuals living with or caring for someone with blood sugar issues, offering information and support to help navigate the care journey effectively.



