Overview
An A1C level of 6.6% indicates a diagnosis of diabetes, as it exceeds the critical threshold of 6.5%, reflecting consistently elevated blood glucose levels over the previous months. The article emphasizes that understanding this value is crucial for implementing necessary lifestyle changes and potential medication adjustments to mitigate the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Introduction
Understanding A1C levels is crucial for effective diabetes management, as these measurements provide insights into long-term blood sugar control. The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, evaluates average glucose levels over the past two to three months, making it a vital tool for both patients and healthcare providers. Results are categorized into ranges that indicate normal, prediabetic, or diabetic status, guiding treatment decisions and lifestyle modifications.
Regular monitoring of A1C levels empowers individuals to take proactive steps in their health journey, reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. This article delves into the significance of A1C testing, the implications of various A1C levels, and the lifestyle and medication strategies that can help individuals achieve optimal glycemic control.
Understanding the A1C Test: What It Measures and Its Importance
At a2d Solutions, we recognize the importance of understanding A1C values, particularly the a1c 6.6 meaning, for effectively managing the condition. The A1C test, officially referred to as the glycated hemoglobin test, is a vital diagnostic tool that assesses the average blood sugar concentrations over the prior two to three months, which is important for understanding the a1c 6.6 meaning. This test offers a comprehensive view of long-term glycemic control, surpassing the insights gained from daily glucose monitoring.
A1C outcomes are expressed as a percentage:
- Values under 5.7% are considered normal for individuals without the condition.
- Figures between 5.7% and 6.4% suggest prediabetes.
- A verified diagnosis of a blood sugar condition is established when A1C values reach 6.5% or above, highlighting the a1c 6.6 meaning.
Understanding the A1C 6.6 meaning is essential for effective management of the condition, allowing healthcare providers to customize treatment plans and assess the risk of complications related to the illness.
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines:
- Stable patients should have their A1C measurements taken at least twice yearly.
- Those with glucose fluctuations require testing a minimum of four times annually.
As Roopa Naik emphasizes, 'Hemoglobin A1C is a valuable tool in managing blood sugar disorders and other glycemic control issues, but it functions best in an interprofessional healthcare team environment to be effective.' This collaboration is essential to ensure that the implications of A1C levels are fully understood and appropriately addressed in patient care.
Furthermore, it is important to note that further research is needed to explore the association of A1C with long-term clinical outcomes in initially nondiabetic populations. A case study titled 'Strengths and Limitations of A1C as a Diagnostic Tool' highlights the strengths of using A1C for screening, including its high repeatability and specificity for detecting undiagnosed conditions, while also addressing limitations such as the cross-sectional design and reliance on single fasting glucose measurements. T2DSolutions is dedicated to offering extensive resources and community assistance to empower individuals in their health management journey.
We invite you to subscribe to our updates to stay informed about our latest resources and community initiatives designed to support those affected by Type 2 and Type 3 conditions.
What an A1C Level of 6.6 Means for Your Health
An A1C measurement of 6.6% is indicative of diabetes, reflecting the a1c 6.6 meaning, as it surpasses the critical threshold of 6.5%. This stage indicates that glucose concentrations have been consistently elevated over the prior months, posing an increased risk for diabetes-related complications, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Nerve damage
- Kidney issues
Specifically, an A1C of 126 corresponds to an estimated average glucose of 154 mg/dL, highlighting the importance of monitoring blood glucose.
As emphasized by top specialists in the field, comprehending a1c 6.6 meaning necessitates significant lifestyle adjustments. These may include:
- Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables
- Increasing physical activity to at least 150 minutes per week
- Potentially modifying medication under the supervision of a healthcare professional
Regular follow-up testing is essential not only for monitoring A1C measurements but also for assessing the effectiveness of the implemented management strategies.
In this regard, T2DSolutions acts as a comprehensive resource for newly diagnosed patients, providing valuable education and community support customized to the needs of those managing Type 2 and Type 3 conditions. T2DSolutions provides a range of services, including:
- Educational materials
- Community forums for peer support
- Personalized guidance from healthcare professionals
According to Xuanping Zhang, 'The selection of specific thresholds, however, will ultimately depend on the interventions likely to be employed and the tradeoffs between sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value.'
Moreover, studies suggest that ethnic differences may affect health outcomes, as demonstrated in a case study highlighting disparities in cancer risk associations among various ethnic groups at comparable A1C values. Understanding the a1c 6.6 meaning empowers individuals to take proactive measures toward improving their health and minimizing the risk of complications, with T2D Solutions as a crucial partner in this journey. Testimonials from users of T2D Solutions highlight its effectiveness, with many reporting improved management of their diabetes through the resources and support provided.
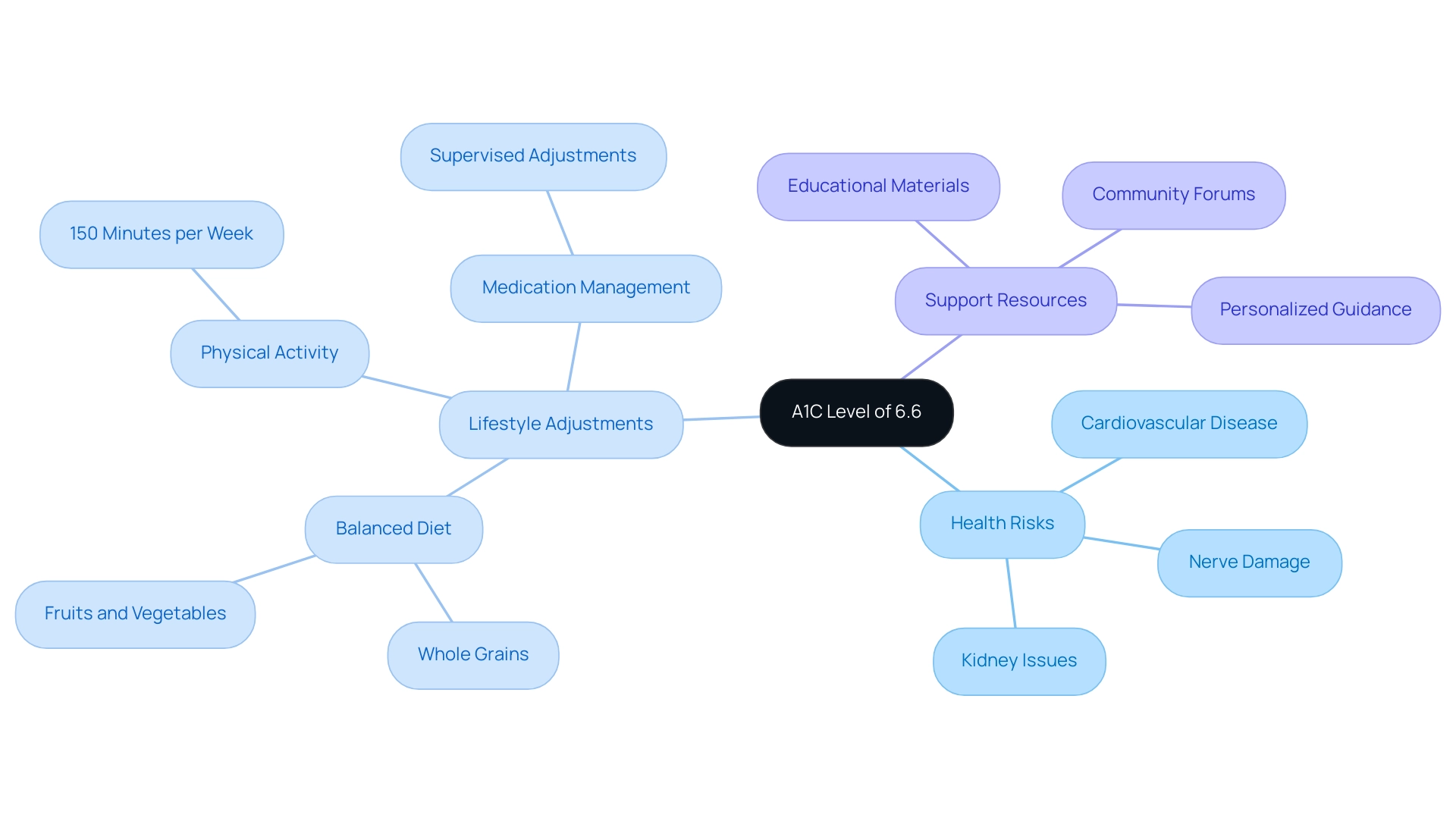
Lifestyle Changes to Lower A1C Levels
To effectively reduce A1C values, individuals can implement several key lifestyle changes:
- Balanced Diet: Prioritize whole foods, including an array of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is essential to restrict processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-carbohydrate snacks that can elevate sugar levels.
Recent research indicates that improved diet quality may also mitigate genetic influences on type 2 conditions (T2D), highlighting the significant role of nutrition in disease management. As noted, 'improved diet quality might attenuate the genetic influences on T2D.' Additionally, individuals may benefit from professional dietary counseling, such as six scheduled, 30-minute visits with a dietitian, to further tailor their nutrition plans.
T2DSolutions will offer resources and guidance to support these dietary changes.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week, such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
The inclusion of strength training exercises at least twice weekly can further improve sugar regulation. Expert opinions emphasize that consistent physical activity not only aids in lowering A1C but also contributes to overall cardiovascular health. T2DSolutions will provide exercise resources customized for individuals with blood sugar issues.
- Weight Management: For individuals who are overweight, losing even a modest 5-10% of body weight can lead to significant enhancements in sugar regulation. Case studies reveal that among adults with this condition, 47.4% recorded an A1C value of 7.0% or higher, underscoring the importance of weight management in care and the need for effective lifestyle changes.
T2DSolutions will feature weight management programs and support.
- Consistent Monitoring: Regularly checking glucose measurements is essential for understanding how various foods and activities influence individual sugar responses.
This practice helps tailor dietary and exercise routines effectively.
- Stress Management: Employ stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga.
Stress has been demonstrated to negatively influence blood sugar rates, making stress management a crucial aspect of managing this condition. By adopting these lifestyle changes, individuals can experience improved A1C readings, which relate to the a1c 6.6 meaning, and enhanced overall health. T2DSolutions aims to be a comprehensive resource for newly diagnosed patients, offering tools and community support to assist in these lifestyle changes.
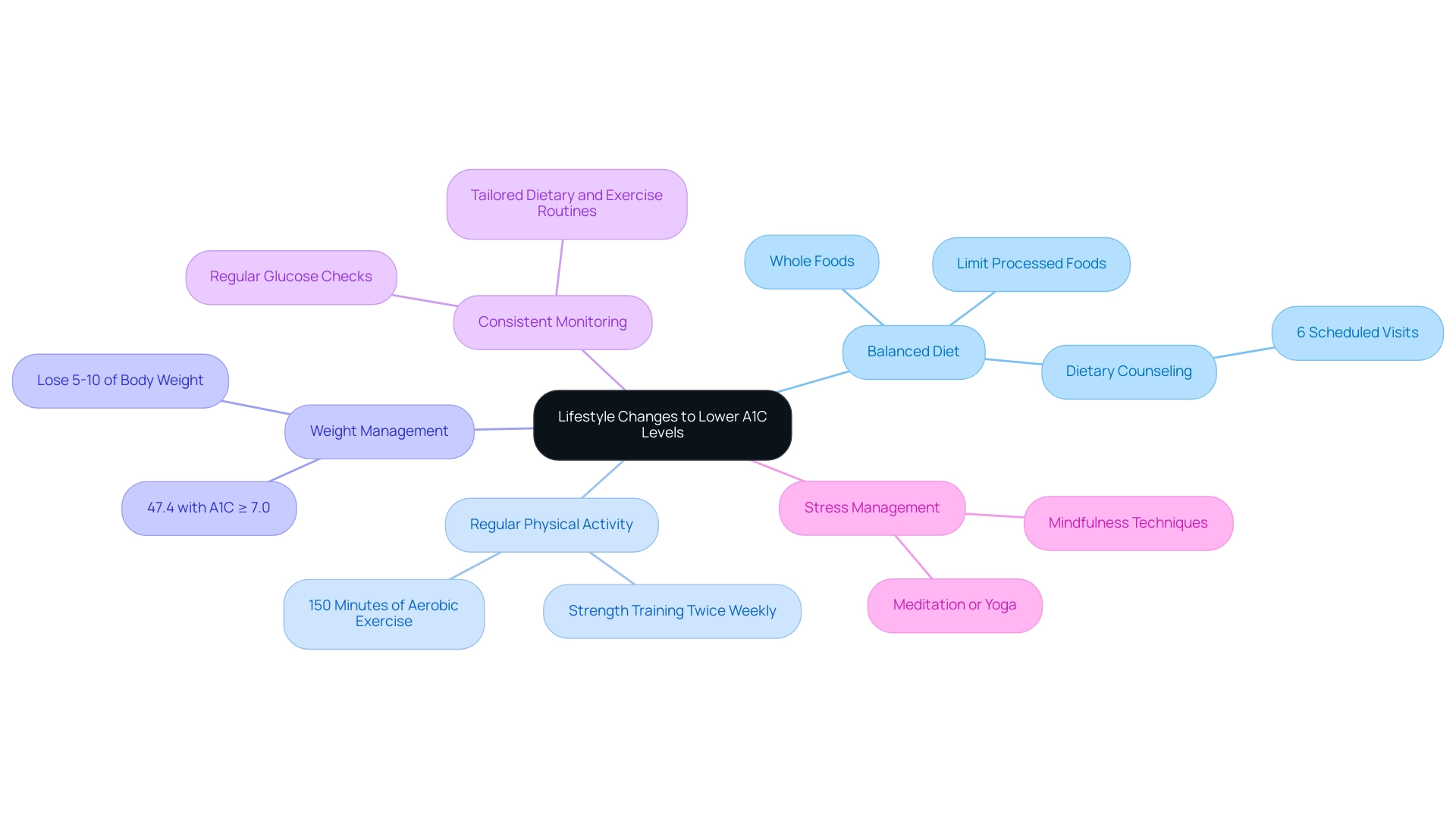
The Role of Medication in A1C Management
As you navigate your condition management journey, understanding your A1C values is crucial. For individuals presenting with an A1C reading of 6.6%, knowing the A1C 6.6 meaning may indicate that the initiation of medication is essential for achieving improved glucose control. The primary classes of diabetes medications include:
-
Metformin: This is typically the first-line therapy, functioning by reducing glucose production in the liver and enhancing insulin sensitivity. It is particularly notable for its safety profile, being appropriate for patients with estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR) of 30 mL/min/1.73 m² or higher. However, it is important to note that certain medications do not reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease or prevent loss of renal function.
-
Sulfonylureas: These medications stimulate the pancreas to increase insulin production, thereby reducing sugar levels.
-
DPP-4 Inhibitors: This class assists in lowering sugar levels without causing weight gain, making them a favorable option for many patients.
-
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These agents promote insulin secretion in response to meals and may aid in weight loss, although the mechanisms behind their weight loss effects are not fully understood, involving both central and peripheral pathways.
-
Insulin Therapy: In certain cases, insulin injections may be necessary for effective blood sugar management. A relevant study, the GRADE trial, compared the effects of adding different hypoglycemic agents to metformin therapy and suggested that treatment with liraglutide has beneficial effects on cardiovascular disease, although results should not be viewed as definitive proof of GLP-1 receptor agonists reducing cardiovascular disease incidence in low-risk populations.
It is crucial for patients to collaborate closely with their healthcare providers to create a personalized medication plan that addresses their specific needs while also monitoring potential side effects. As noted by healthcare professionals, a tailored approach is vital for effective management of the condition. For further support and resources, Td Solutions offers a hub for education and community support, helping newly diagnosed patients understand their options and manage their condition effectively.
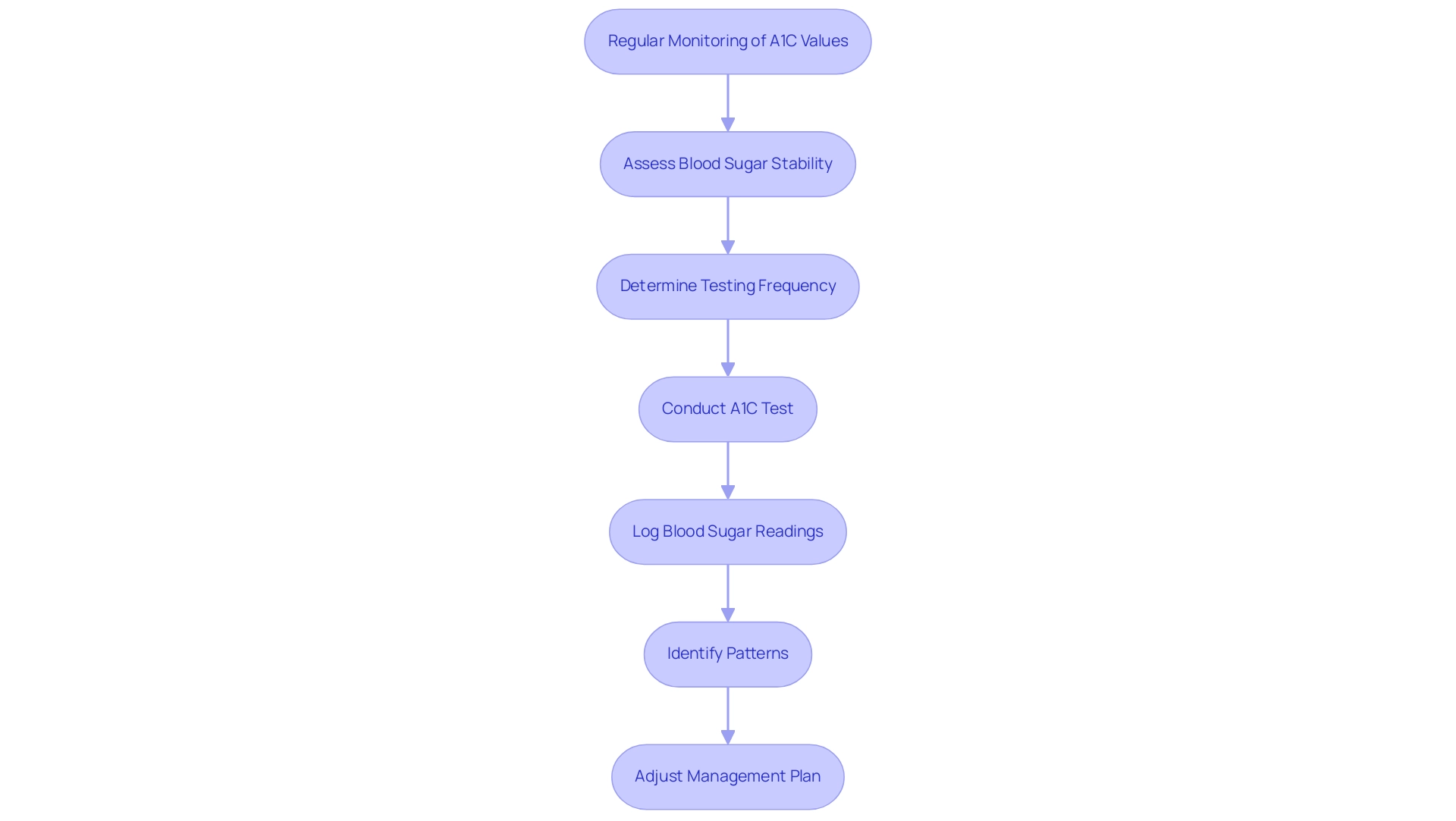
Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up Testing
Regular monitoring of A1C values is essential for individuals diagnosed with diabetes or prediabetes to grasp the a1c 6.6 meaning. Current guidelines suggest that patients with stable blood sugar readings should be aware of the a1c 6.6 meaning and undergo an A1C test at least twice a year. However, for those with elevated A1C levels or recent changes in treatment, it may be important to understand a1c 6.6 meaning, which could warrant more frequent testing.
According to insights from Edmonton Laboratories, HbA1c should be used to monitor glycemic control only in patients identified as having the condition. It is inappropriate to use HbA1c to screen for the condition in asymptomatic patients. Along with A1C tests, daily glucose monitoring, as recommended by healthcare professionals, plays a crucial role in effective management of the condition.
Keeping a meticulous log of blood sugar readings can help identify patterns, allowing for timely adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication regimens. The examination of patient demographics revealed that the median adherence rate for individuals with type 2 conditions was only 50%, with an average of 1.6 tests per year, which falls short of the recommended frequency. This low adherence rate has been linked to poorer patient outcomes, as evidenced by the CKD incidence in the low adherence group being 2.0%, compared to 3.7% in the moderate and 3.8% in the high adherence groups.
These findings underscore the necessity for consistent follow-up appointments with healthcare teams to evaluate overall health, address challenges, and understand the a1c 6.6 meaning to adapt management plans accordingly. Furthermore, longitudinal trends in HbA1c values and related complications underscore the critical importance of regular monitoring and adherence over time, reinforcing the need for stricter compliance with guidelines in management. As you navigate your diabetes journey, T2 Solutions will serve as your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support.
T2DSolutions offers a variety of resources, including educational articles, community forums, and personalized support, providing you with the knowledge and tools necessary to manage your health effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding A1C levels is a fundamental aspect of diabetes management, providing critical insights into long-term blood sugar control. The A1C test not only helps diagnose diabetes but also aids in monitoring the effectiveness of treatment strategies. With an A1C level of 6.6% indicating diabetes, individuals are encouraged to make significant lifestyle changes, including:
- Adopting a balanced diet
- Increasing physical activity
to improve their health outcomes.
Medication also plays a pivotal role in achieving optimal A1C levels. Various classes of diabetes medications, such as Metformin and GLP-1 receptor agonists, can assist in managing blood sugar levels effectively. However, it is essential for patients to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets their specific needs.
Regular monitoring of A1C levels is crucial for all individuals with diabetes or prediabetes. Adhering to testing guidelines and maintaining consistent follow-up appointments can lead to better health outcomes and reduced risk of complications. Utilizing resources such as T2DSolutions can empower patients to take charge of their diabetes management journey, ensuring they have the necessary tools and support to navigate their condition successfully.
In conclusion, understanding and managing A1C levels is vital in the fight against diabetes. By combining lifestyle changes, appropriate medication, and consistent monitoring, individuals can significantly improve their overall health and minimize the risks associated with diabetes. Taking proactive steps today can lead to a healthier tomorrow.



