Overview
This article gently explores a vital question: Are individuals born with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes? Understanding this distinction is important, especially for those navigating their diagnosis. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that is typically diagnosed in youth, while Type 2 diabetes often develops gradually in adults and is frequently linked to lifestyle factors.
Recognizing these differences can be comforting. The article details the biological distinctions, prevalence rates, and treatment approaches for each type, providing a clearer picture of what to expect. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but knowing these differences can empower you in managing your health effectively.
As you read, remember that you're not alone in this journey. Many have walked this path and found support through understanding these nuances. We encourage you to seek resources and connect with others who share similar experiences. Together, we can foster a community of support and understanding, ensuring that everyone feels heard and cared for.
Introduction
Understanding the nuances of diabetes is crucial, especially since it affects millions around the world. With approximately 30.3 million individuals in the United States alone living with this condition, it’s more important than ever to distinguish between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Each type has unique characteristics, risk factors, and management strategies that can significantly influence a person's health journey.
It's understandable to feel confused about whether these diabetes types are determined at birth or if they can develop later in life. This article delves into the key differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, providing insights that can empower you to navigate your health and treatment options more effectively. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Understand the Basics of Diabetes Types
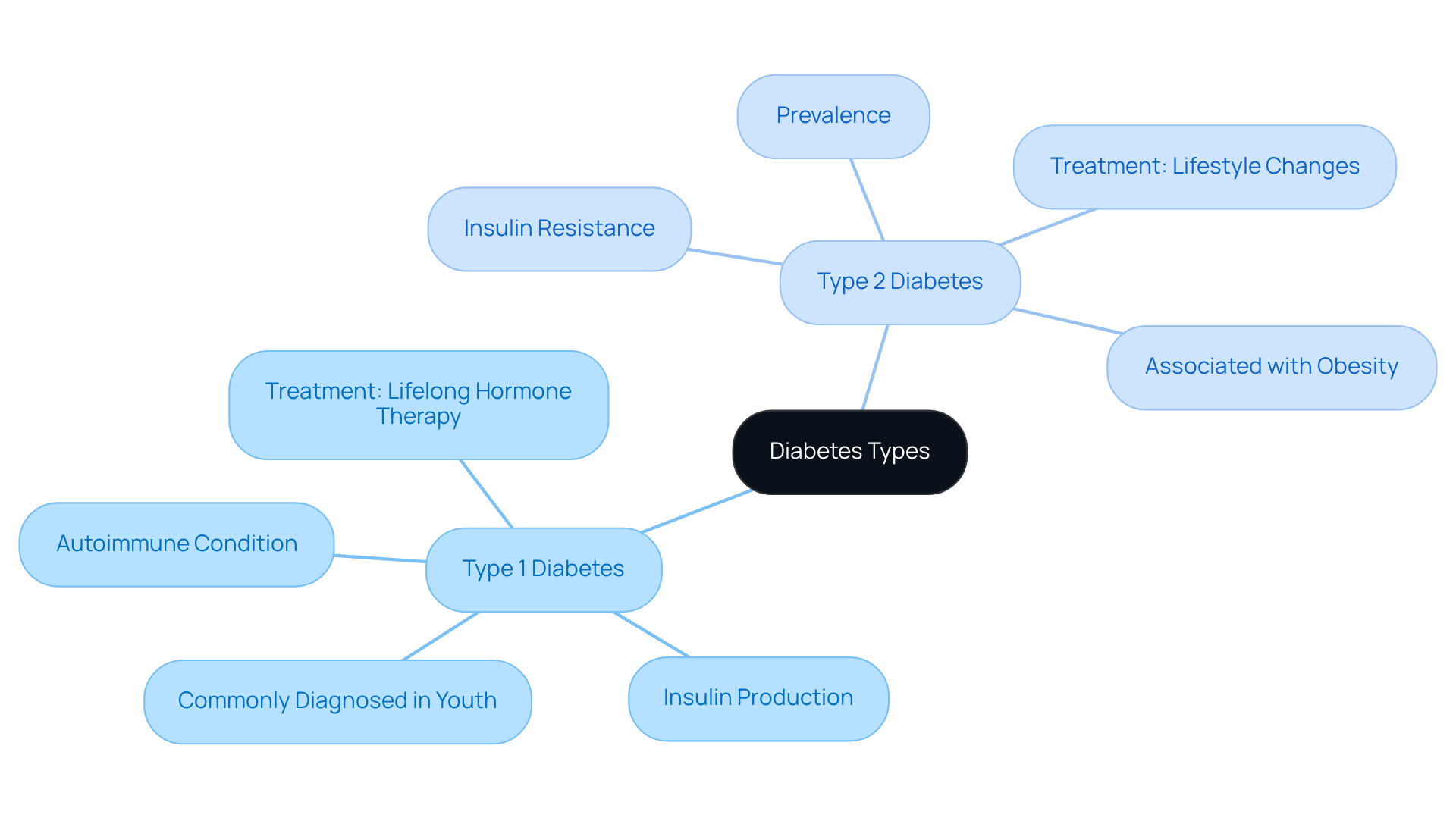
Diabetes is primarily categorized into two distinct types: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the beta cells that produce a vital hormone in the pancreas. This leads to little or no production of insulin. Often diagnosed in children and young adults, it’s commonly referred to as 'juvenile onset diabetes.' On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, meaning the body struggles to use insulin effectively. This type is more prevalent among adults and is frequently associated with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle.
Understanding these differences is important, especially when considering if you are born with type 1 or 2 diabetes, as they significantly impact treatment and management approaches. Recent statistics reveal that approximately 30.3 million individuals in the United States live with diabetes. Type 1 accounts for about 5-10% of all cases, while Type 2 comprises the majority at around 90-95%. For those diagnosed with Type 1, lifelong hormone therapy is essential, whereas individuals with Type 2 may initially manage their condition through lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, before possibly requiring insulin as the disease progresses.
Endocrinologists emphasize the importance of recognizing these distinctions, noting that treatment strategies differ significantly between the two types. For instance, managing Type 1 diabetes often focuses on precise insulin dosing and continuous glucose monitoring. In contrast, care for Type 2 diabetes frequently involves weight loss and increased physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity.
As T2DSolutions launches as a new resource hub for education and community support related to blood sugar management, individuals can find valuable information and resources to help navigate their management journey. We encourage you to explore T2DSolutions for additional insights and support, especially if you are wondering, are you born with type 1 or 2 diabetes? Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Identify Symptoms of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
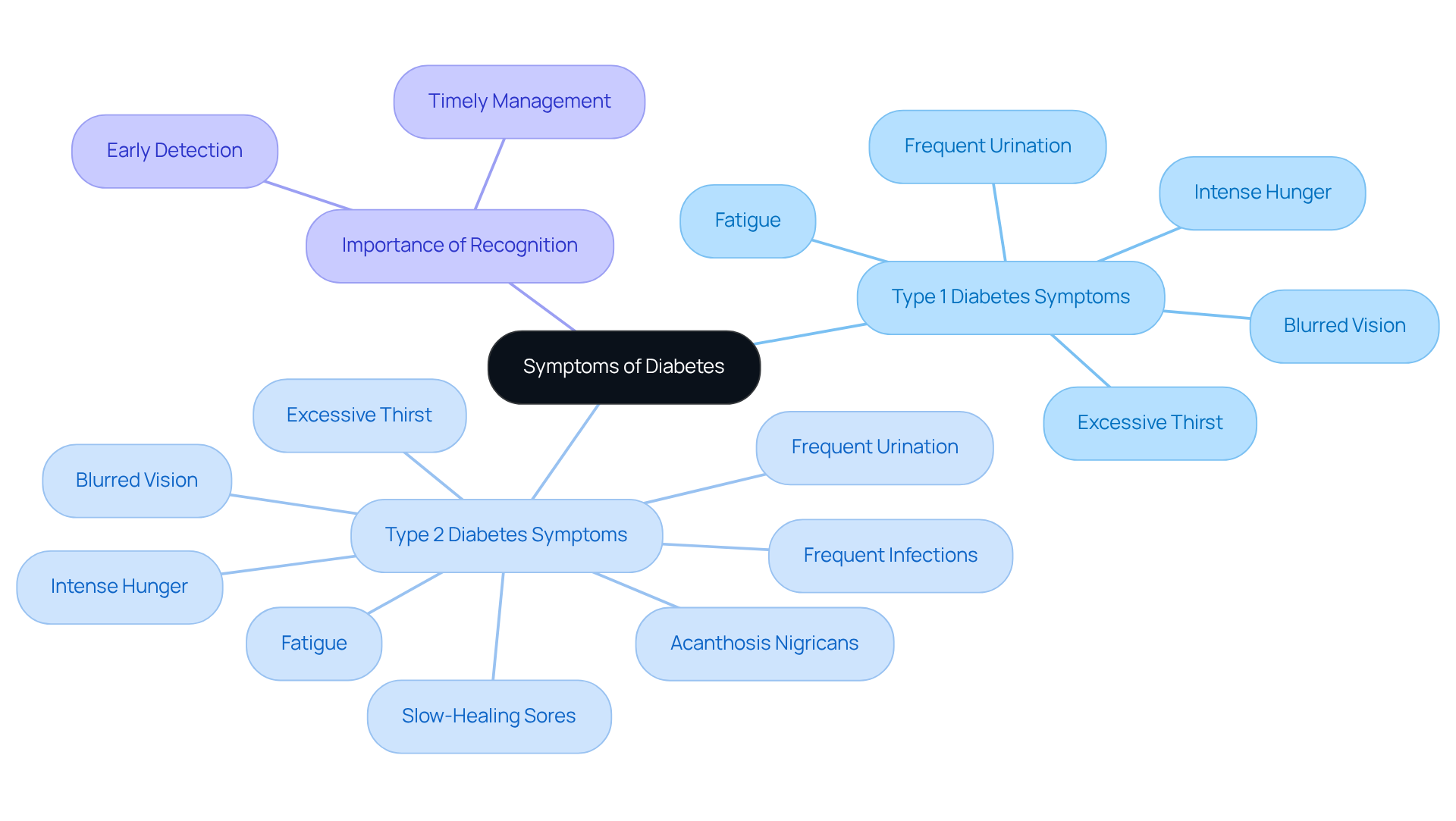
Symptoms of insulin-dependent conditions can appear quickly, often within weeks or months. You might notice excessive thirst, frequent urination, intense hunger, fatigue, and blurred vision. It's important to be aware of these signs. In contrast, the symptoms of the second variety of this condition typically emerge more gradually. While they include similar indications, they may also present slow-healing sores, frequent infections, and regions of darkened skin known as acanthosis nigricans.
In 2018, almost 1.6 million individuals in the U.S. were living with insulin-dependent conditions. This highlights the importance of recognizing these symptoms early. Some individuals may remain asymptomatic, especially in the early phases of Type 2 diabetes, which can lead to delayed diagnosis. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial because early identification allows for timely medical intervention and effective management strategies, ultimately improving health outcomes.
Moreover, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening condition that can develop swiftly in individuals with this metabolic disorder. This emphasizes the importance of recognizing symptoms. As Michelle L. Griffith, MD, points out, being aware of early symptoms can guide you in knowing when to seek care. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Assess Risk Factors and Family History
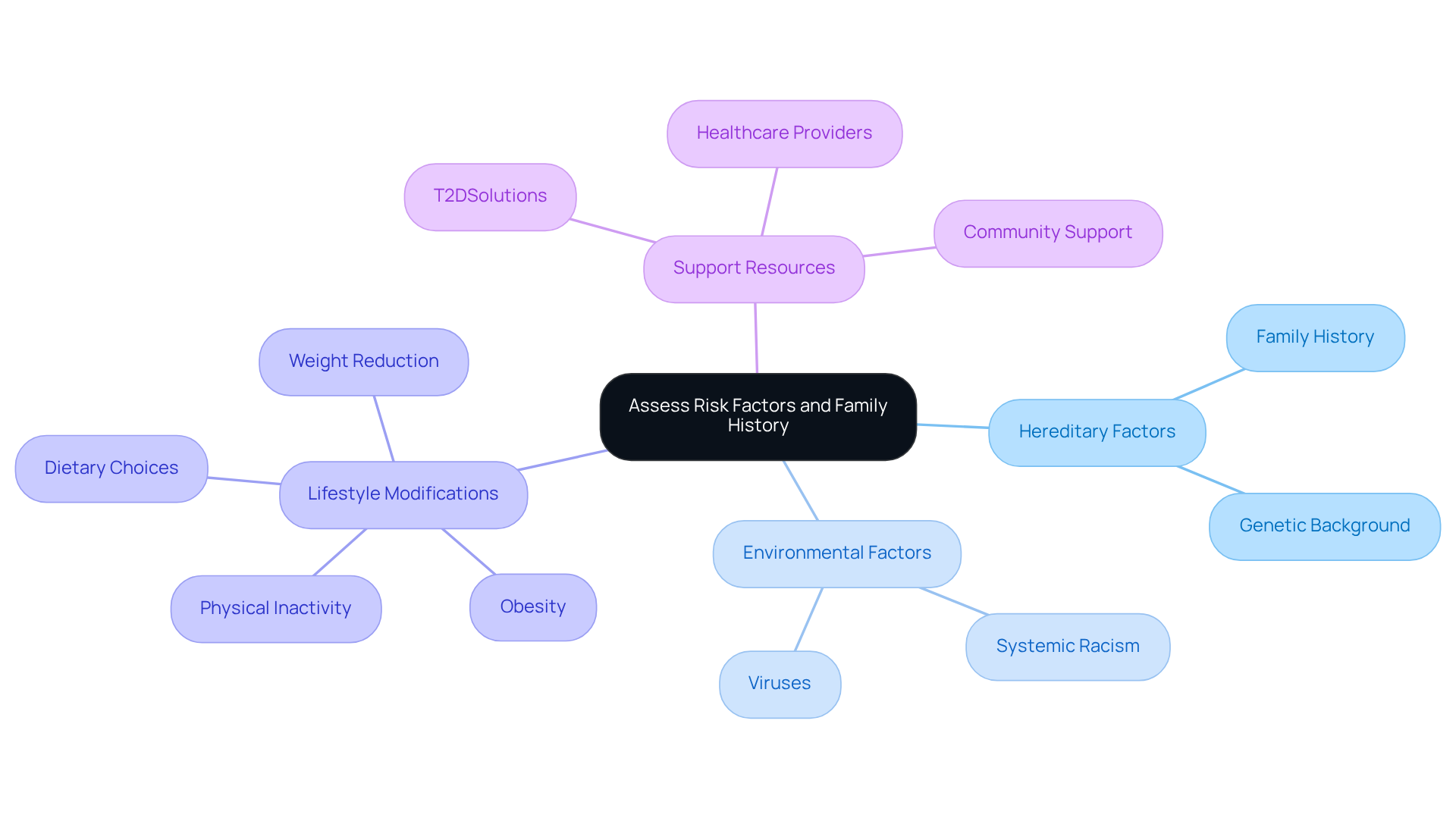
Understanding the risk elements for this condition can be challenging. It's important to know that both hereditary tendencies and environmental factors, like viruses, may contribute to its onset. In contrast, Class 2 metabolic disorder has several well-established risk factors, such as obesity, physical inactivity, age, and especially family history. If you have a family history of this condition, you are significantly more likely to develop it, which underscores the importance of understanding your genetic background.
Did you know that roughly 90-95% of Americans with this illness have the second type? The connection between rising obesity rates and the occurrence of this condition is concerning. For instance, two-thirds of fatalities in individuals with blood sugar issues are linked to cardiovascular disease. This highlights the essential need for preventive actions.
Fortunately, lifestyle modifications can make a significant difference. Even a moderate weight reduction of just five to ten pounds can lower your risk of developing Type 2. Engaging in regular physical activity and making healthier dietary choices are vital steps you can take to mitigate your risk. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; by keeping track of these risk factors and making informed lifestyle choices, you can empower yourself to seek medical advice and adopt healthier habits, ultimately improving your overall well-being.
T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource center for education and management of this condition. They provide support and information to assist you in navigating your health journey, ensuring that you have the guidance you need every step of the way.
Consult Healthcare Professionals for Diagnosis
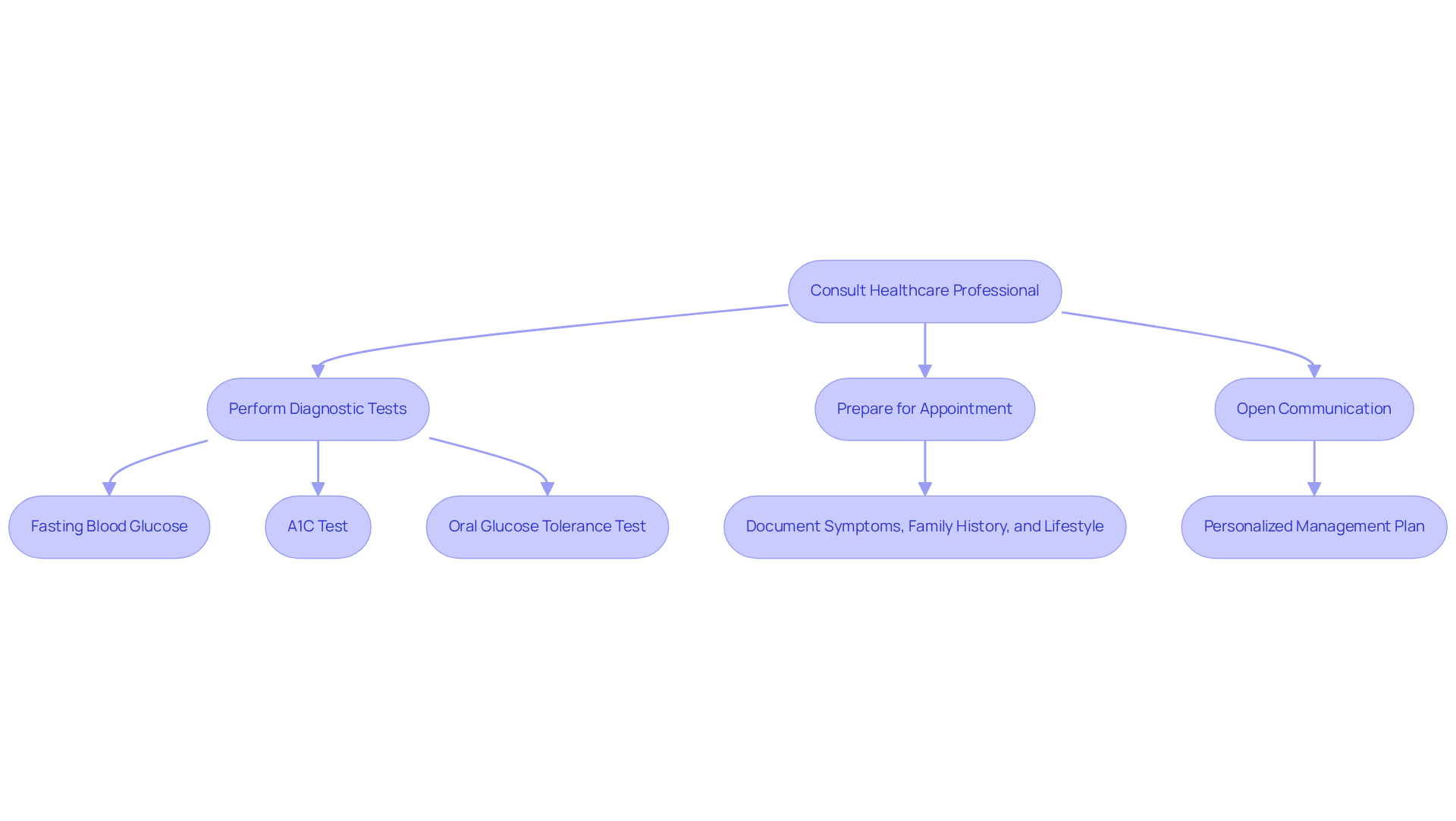
If you think that you or someone you know may have a blood sugar condition, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. They will typically perform a series of diagnostic tests—such as fasting blood glucose tests, A1C tests, and oral glucose tolerance tests—to accurately assess the situation. Preparing for your appointment by documenting any symptoms, family history, and lifestyle factors can make a significant difference in the evaluation process.
Engaging in open communication with your healthcare provider enhances the accuracy of the diagnosis and helps in developing a personalized management plan tailored to your unique needs. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Recent advancements in diabetes testing highlight the importance of timely and precise diagnosis, which can greatly impact long-term health outcomes. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes is crucial for effective management and treatment. Type 1 is primarily an autoimmune condition leading to insulin deficiency, whereas Type 2 is characterized by insulin resistance often linked to lifestyle factors. Recognizing these differences not only informs treatment choices but also empowers you to take control of your health.
Throughout this article, we’ve highlighted key points such as:
- The symptoms associated with each type
- The importance of early diagnosis
- The impact of genetic and lifestyle factors
It’s vital to consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and personalized management plans. Resources like T2DSolutions provide valuable support and guidance for those navigating their diabetes journey.
Ultimately, understanding diabetes types is not just about knowledge; it’s about taking proactive steps toward better health. By recognizing symptoms early, assessing risk factors, and seeking professional advice, you can significantly improve your management strategies. Remember, empowerment through education and support can lead to healthier choices and better outcomes. While diabetes may present challenges, informed action can pave the way for a fulfilling life. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of diabetes?
The two primary types of diabetes are Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that results in little or no insulin production, often diagnosed in children and young adults. Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance and is more common in adults, frequently associated with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle.
How does Type 1 diabetes differ from Type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes involves the immune system attacking and destroying insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, involves the body's inability to use insulin effectively. Treatment and management approaches differ significantly between the two types.
What percentage of diabetes cases are Type 1 and Type 2?
Approximately 5-10% of diabetes cases are Type 1, while Type 2 accounts for about 90-95% of all cases.
What is the typical management approach for Type 1 diabetes?
Management of Type 1 diabetes often focuses on precise insulin dosing and continuous glucose monitoring, as individuals require lifelong hormone therapy.
How is Type 2 diabetes typically managed?
Individuals with Type 2 diabetes may initially manage their condition through lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise. As the disease progresses, they may require insulin.
Why is it important to understand the differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
Understanding these differences is crucial because they significantly impact treatment and management strategies, which vary between the two types of diabetes.
What resources are available for individuals managing diabetes?
T2DSolutions is a new resource hub that offers education and community support related to blood sugar management, providing valuable information for individuals navigating their management journey.



