Introduction
Managing diabetes effectively requires a comprehensive understanding of various facets of the condition, with the A1C test serving as a cornerstone for monitoring long-term blood sugar levels. This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, best practices for maintaining healthy levels, and the role of regular medical check-ups. It also explores how technology and support networks can enhance diabetes management, alongside strategies for recognizing and responding to hypoglycemia.
By providing insights into these critical areas, individuals can empower themselves with the knowledge and resources necessary for better health outcomes in their diabetes journey.
Understanding the A1C Test: What It Measures and Its Importance
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, quantifies the percentage of hemoglobin in the bloodstream that has been modified by glucose. This examination indicates the typical blood sugar amounts over the prior two to three months, making it a vital tool for successful management of the condition. Comprehending A1C values is especially essential for newly diagnosed individuals, as it establishes the basis for informed choices in their care journey.
In the United States, the prevalence of this condition among White, non-Hispanic adults was reported at 8.5%, underscoring the need for accessible resources like T2DSolutions to educate patients about their health. For the majority of adults managing blood sugar, the target A1C goal is usually established under 7%. However, these individual goals can vary significantly, influenced by personal health circumstances and recommendations from healthcare professionals.
Frequent tracking of A1C levels for diabetics is essential, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the effectiveness of treatment strategies for blood sugar management and make required modifications. Understanding A1C levels for diabetics can empower individuals with blood sugar conditions to adopt healthier lifestyles, illustrating how everyday choices directly impact long-term health outcomes. As mentioned by Emily Phillips, a collaborative position statement from the American Diabetes Association highlights essential moments to offer self-management education and support, including the monitoring of A1C levels for diabetics.
Recent studies emphasize the significance of this test in directing treatment choices, with endocrinologists pointing out that regular monitoring of A1C levels for diabetics is essential for effective health control. Moreover, geographic differences in the prevalence of this condition indicate that individuals residing in rural regions may encounter distinct obstacles in managing their A1C levels for diabetics, further emphasizing the necessity for customized treatment approaches. T2D Solutions is dedicated to enhancing care for diabetes through education, community assistance, and comprehensive support, offering resources like informative materials and community discussions that aid newly diagnosed individuals in comprehending and regulating A1C levels for diabetics effectively.
This reinforces the role of the A1C test as a pivotal aspect of managing A1C levels for diabetics and achieving optimal health.
Best Practices for Achieving and Maintaining Healthy A1C Levels
To attain and sustain healthy A1C levels for diabetics, individuals with blood sugar issues should implement a thorough approach that includes dietary changes, physical exercise, and careful medication oversight. As you navigate your journey, T2 Solutions will serve as your comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, offering tools like meal planning guides, exercise programs, and access to community support groups.
-
Dietary Modifications: A balanced diet is essential, focusing on whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables.
-
Carbohydrate counting can be particularly effective, assisting in blood sugar control.
- Working with a dietitian can provide personalized meal plans to address individual dietary requirements, which is crucial for maintaining optimal A1C levels for diabetics.
-
A recent trial tested a low-carbohydrate diet characterized by unsaturated fat, protein, high-fiber foods, and minimal refined carbohydrates among adults with untreated prediabetes, highlighting effective dietary strategies for managing A1C levels for diabetics.
-
Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, complemented by strength training exercises twice weekly, is recommended.
-
Studies show that physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and can significantly reduce blood sugar amounts, highlighting its significance in diabetes care.
- A study highlighted that those who maintain an active lifestyle have higher odds of achieving healthier food choices, with women showing an odds ratio of 1.77 for achieving a healthy food score above the median.
-
These findings were presented in part as an abstract at the American Diabetes Association 82nd Scientific Sessions by Kirsten S. Dorans, ScD, emphasizing the critical link between physical activity and dietary choices.
-
Medication Management: Strict adherence to prescribed medications is crucial.
-
Patients should have open communication with their healthcare providers regarding any side effects or concerns, as adjustments may be necessary in response to lifestyle changes or evolving health status.
-
Monitoring Blood Sugar Concentrations: Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose concentrations provides immediate insights into how dietary choices, physical activity, and medications influence blood sugar.
-
This practice empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their daily planning strategies.
-
Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact blood sugar control.
-
Incorporating techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises into daily routines can help mitigate stress and improve overall well-being.
By implementing these best practices, individuals can take significant strides in effectively managing A1C levels for diabetics, leading to improved health outcomes and enhanced quality of life. Recent findings emphasize the importance of dietary modifications, with studies indicating that 62% of participants in low-carbohydrate diets were also on cholesterol-lowering medications. This emphasizes the interconnectedness of dietary choices and overall health oversight, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive approach to care.
As you investigate these strategies, keep in mind that T2 Solutions is here to assist you at every stage, with resources intended to improve your health journey.
The Role of Regular Medical Check-ups
Routine check-ups with healthcare professionals are crucial for the effective oversight of blood sugar conditions, and Td Solutions is here to assist you in this journey. These appointments offer a chance to evaluate a1c levels for diabetics, which serve as a key indicator of whether current strategies are yielding desired results. At T 2 Solutions, we emphasize the importance of these visits, where healthcare professionals can review blood tests, evaluate medication adherence, and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Furthermore, routine check-ups are vital for the early detection of potential diabetes-related complications, such as neuropathy and retinopathy. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, it is advised that patients with blood sugar issues visit their healthcare provider every three months if they are struggling to meet treatment goals; this interval can be extended to six months once targets are achieved. Interestingly, a statistic indicates that the unadjusted prevalence of receiving blood glucose testing among individuals with hyperlipidemia is only 44.8%, highlighting the necessity of regular check-ups to enhance testing rates and overall health oversight.
Moreover, a case study focusing on T2DM patients at moderate to high cardiovascular risk highlights the real-world implications of regular assessments, suggesting that routine visits can significantly impact health outcomes. In Ohio, females with a routine check-up had an Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR) of 1.06 for good physical health, while those with two other health conditions had an AOR of 0.35, further illustrating the correlation between regular check-ups and improved health status. To ensure optimal control of blood sugar levels, T2DSolutions advises individuals to arrange appointments at least twice a year, or more often according to their healthcare provider's recommendations.
This proactive approach not only aids in monitoring A1C levels for diabetics but also significantly impacts overall health outcomes, and we are committed to providing resources and support to help you stay on track.
Incorporating Technology in Diabetes Management
The incorporation of technology into blood sugar control provides significant advantages, especially in improving self-care routines. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide real-time information on blood sugar readings, empowering individuals to make timely adjustments to their diet and medication regimens. Recent advancements in CGM technology have been pivotal; for instance, the average monthly prescriptions for CGMs in endocrinology reached 47.4 in 2021, indicating a growing reliance on this tool among healthcare providers.
Additionally, applications for monitoring blood sugar levels play an essential role in tracking food consumption, physical activity, and glucose readings, thus offering users important insights into the trends that affect their A1C levels for diabetics. These digital resources not only empower diabetics to take proactive control of their health but also facilitate more informed discussions with their healthcare providers. Notable platforms like MySugr and Glucose Buddy illustrate user-friendly interfaces that enable thorough tracking and analysis of health management data.
As T2DSolutions launches as a new resource hub for education on the condition, it will complement these technological advancements by providing newly diagnosed patients with essential knowledge and support. Dr. Paula Chatterjee, an expert in the field, has noted that these technological advancements significantly improve patient engagement and health outcomes. Additionally, the findings from the case study on healthcare resource utilization in type 1 highlight the economic burden of managing the condition, reinforcing the need for cost-effective strategies.
The A Estrada Glycation and Inflammation Study (AEGIS) further highlights the significance of ongoing monitoring and control in attaining optimal A1C values. Overall, leveraging technology in managing the condition, alongside the educational resources offered by Td Solutions, is essential for improving care quality and achieving optimal A1C levels for diabetics.
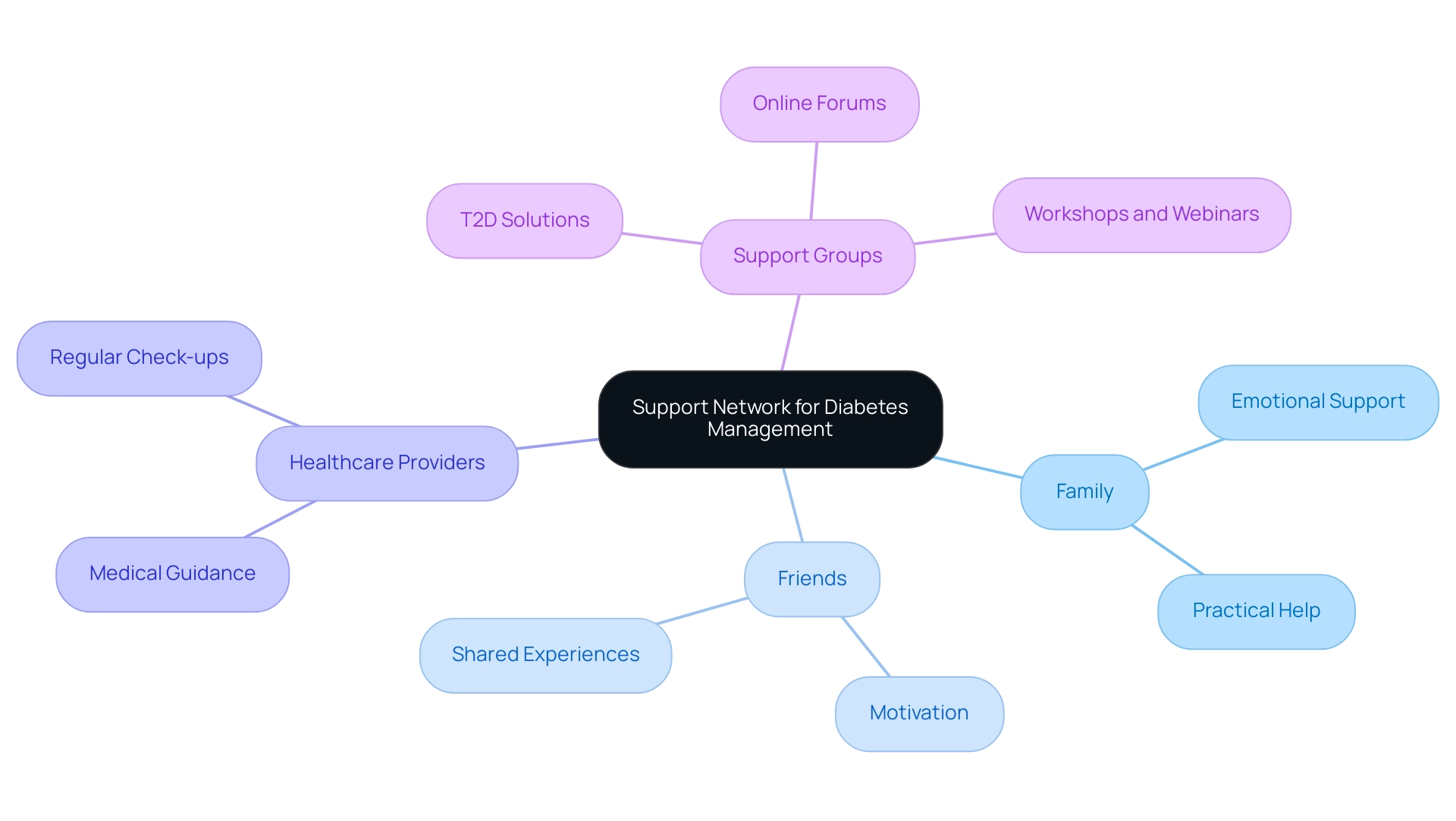
Building a Support Network
Establishing a robust support network is essential for individuals managing their condition, as it can significantly influence their ability to maintain healthy A1C levels. Assistance can originate from different sources, including family, friends, healthcare providers, and specialized support groups. Engaging with peers who understand the complexities of living with the condition fosters motivation, encouragement, and practical guidance.
For instance, the CP-HELP intervention study highlighted the positive effects of peer support on self-care behavior and fasting blood glucose levels among individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). This study demonstrated that structured education for managing blood sugar and community engagement, such as those offered by T2DSolutions, can lead to substantial improvements in health outcomes. Notably, research indicates that a 1% reduction in A1C levels for diabetics is linked to every extra 23.6 hours of contact, highlighting the influence of support networks on managing the condition.
Support groups and education classes act as invaluable platforms, allowing participants to share experiences, gain new strategies, and ease feelings of isolation. These groups, including those facilitated by T2D Solutions, can take various forms, such as in-person meetings and online forums, making them accessible to a wider audience. Active participation in these groups can enhance emotional resilience and reinforce commitment to managing the condition.
T2DSolutions intends to provide a range of resources, including workshops, webinars, and informational materials customized for individuals with Type 2 and Type 3 conditions. Retno Indarwati, a faculty member at Universitas Airlangga, emphasizes that these findings are pivotal for improving self-care behavior and blood glucose control. Furthermore, the integration of technology and telemedicine in providing education on managing blood sugar levels to rural communities presents new opportunities for support.
Individuals with blood sugar issues are urged to actively find both online and in-person groups, such as T2D Solutions, as these connections can significantly impact their journey toward effective health oversight. As T2DSolutions is just beginning, we encourage individuals to sign up for updates on forthcoming events and resources intended to aid their health journey.
Recognizing and Responding to Hypoglycemia
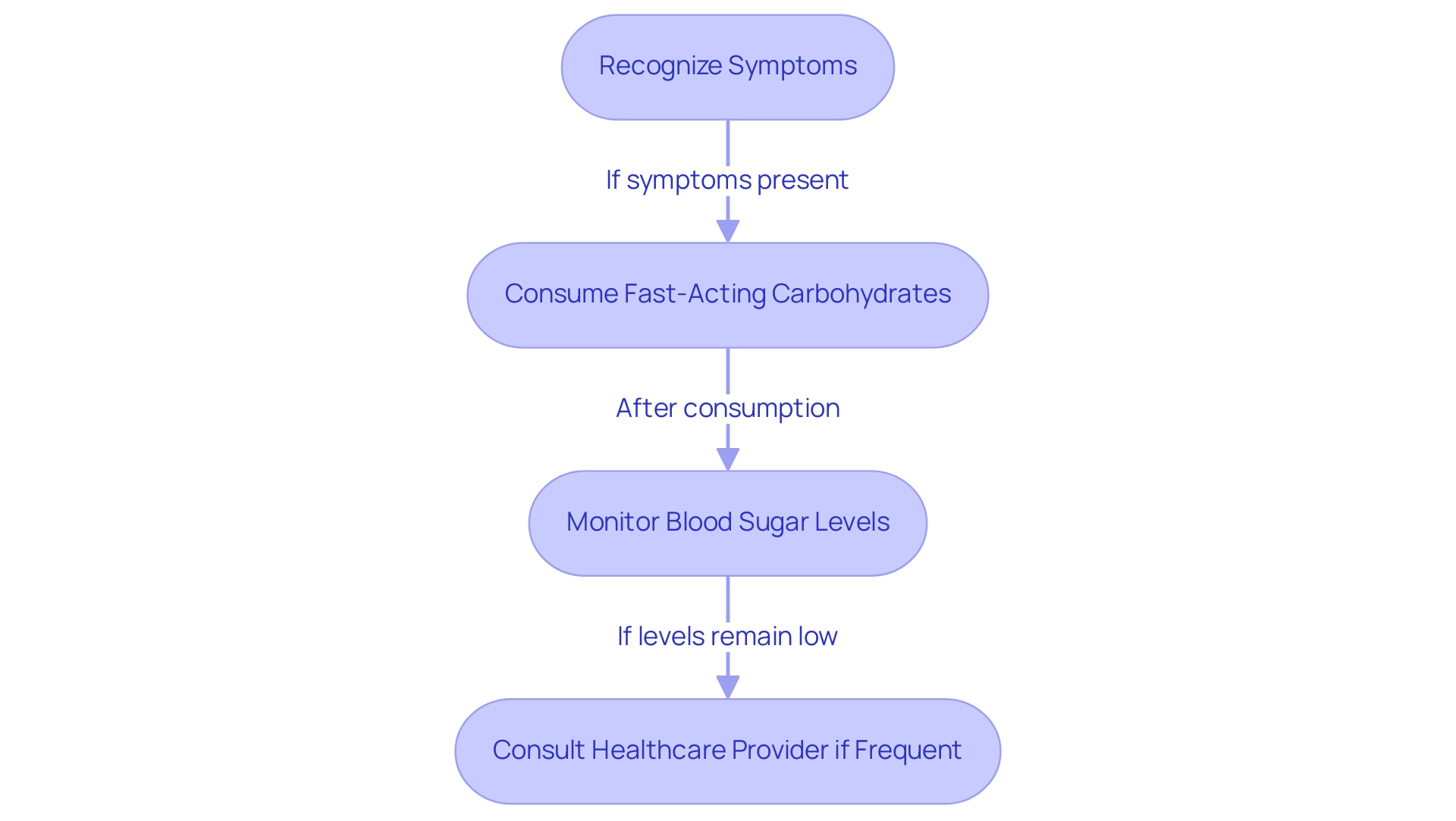
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, poses a significant risk for individuals with the condition, particularly those on insulin or certain oral medications. Recognizing the symptoms—such as sweating, dizziness, confusion, and irritability—is crucial for timely intervention. Recent studies highlight that the prevalence of hypoglycemia among diabetics remains a pressing issue, with a growing number of patients experiencing these episodes in everyday settings.
For example, a study on the epidemiology of hypoglycemia in Nigeria offered valuable information on the occurrence and handling of hypoglycemia among ambulatory type 2 diabetic patients, highlighting the need for effective strategies in diverse populations. In the broader context, statistics from 2017–2018 indicate that the annual incidence of diagnosed diabetes in youth was estimated at:
- 18,200 for type 1 diabetes
- 5,300 for type 2 diabetes
This emphasizes the importance of addressing complications like hypoglycemia. As part of the upcoming T2 Solutions resource hub, individuals will find comprehensive information on hypoglycemia control, including effective strategies to recognize and respond to low blood sugar episodes.
For effective management, individuals should always carry fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice, which can quickly raise blood sugar. In the case of hypoglycemia, consuming about 15 grams of carbohydrates can greatly help in bringing blood glucose back to safer ranges. Following an episode, it is vital to monitor blood sugar levels and consult healthcare providers if occurrences happen frequently, as this may necessitate adjustments to medication regimens or lifestyle choices.
As Dr. Afif Nakhleh observes, 'Patient education and proactive approaches are essential in empowering individuals to recognize and respond to low blood sugar episodes effectively.' Insights from healthcare professionals underscore the importance of these strategies, ensuring that individuals are well-equipped to manage hypoglycemia. T2 Solutions will serve as a vital resource for newly diagnosed patients, offering guidance and support to navigate their diabetes management journey.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing diabetes effectively hinges on several pivotal aspects, with the A1C test standing out as a fundamental tool. This test not only measures average blood sugar levels over time but also empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health. By setting personal A1C goals in consultation with healthcare providers, individuals can better navigate their diabetes care journey.
Implementing best practices such as:
- Dietary modifications
- Regular physical activity
- Medication management
is crucial for maintaining healthy A1C levels. Additionally, incorporating technology, like continuous glucose monitors, enhances self-care and enables individuals to track their progress more effectively. Regular medical check-ups further complement these efforts, providing essential opportunities for healthcare providers to assess treatment efficacy and adjust strategies as needed.
Building a robust support network is equally important, as it fosters motivation and shared experiences that can significantly impact health outcomes. Engaging with peers and utilizing community resources can bolster individuals' resilience and commitment to managing their diabetes.
Lastly, recognizing and responding to hypoglycemia is vital for preventing complications associated with low blood sugar. Armed with knowledge and resources, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively.
In conclusion, a holistic approach to diabetes management that combines education, technology, community support, and regular monitoring will lead to improved health outcomes. By embracing these strategies, individuals can empower themselves on their journey toward better health and well-being.



