Overview
While Type 2 diabetes is not congenital like Type 1 diabetes, it’s important to recognize that genetic predispositions can significantly increase the likelihood of developing it later in life. It's understandable to feel concerned about this possibility. Studies show that while you may inherit a predisposition, environmental factors and lifestyle choices are crucial in determining your health journey. In fact, having a family history of diabetes can double your risk of developing the condition.
You're not alone in navigating these concerns. Many individuals share similar experiences, and it's vital to explore how lifestyle changes can make a difference. Remember, seeking support and resources can empower you on this path to better health. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
The origins of Type 2 diabetes can often be misunderstood, leading to a common misconception about its congenital nature. It's important to recognize that while this condition typically manifests later in life due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors, the question of whether one can be born with a predisposition to it remains compelling. Understanding the interplay between genetics, lifestyle choices, and early life influences can illuminate pathways to prevention and management. This understanding can prompt critical discussions about how individuals can navigate their health risks.
What insights can we glean from the latest research on genetic markers and risk factors? These insights could reshape our approach to this prevalent condition, helping us realize that you're not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way as you seek to understand and manage your health.
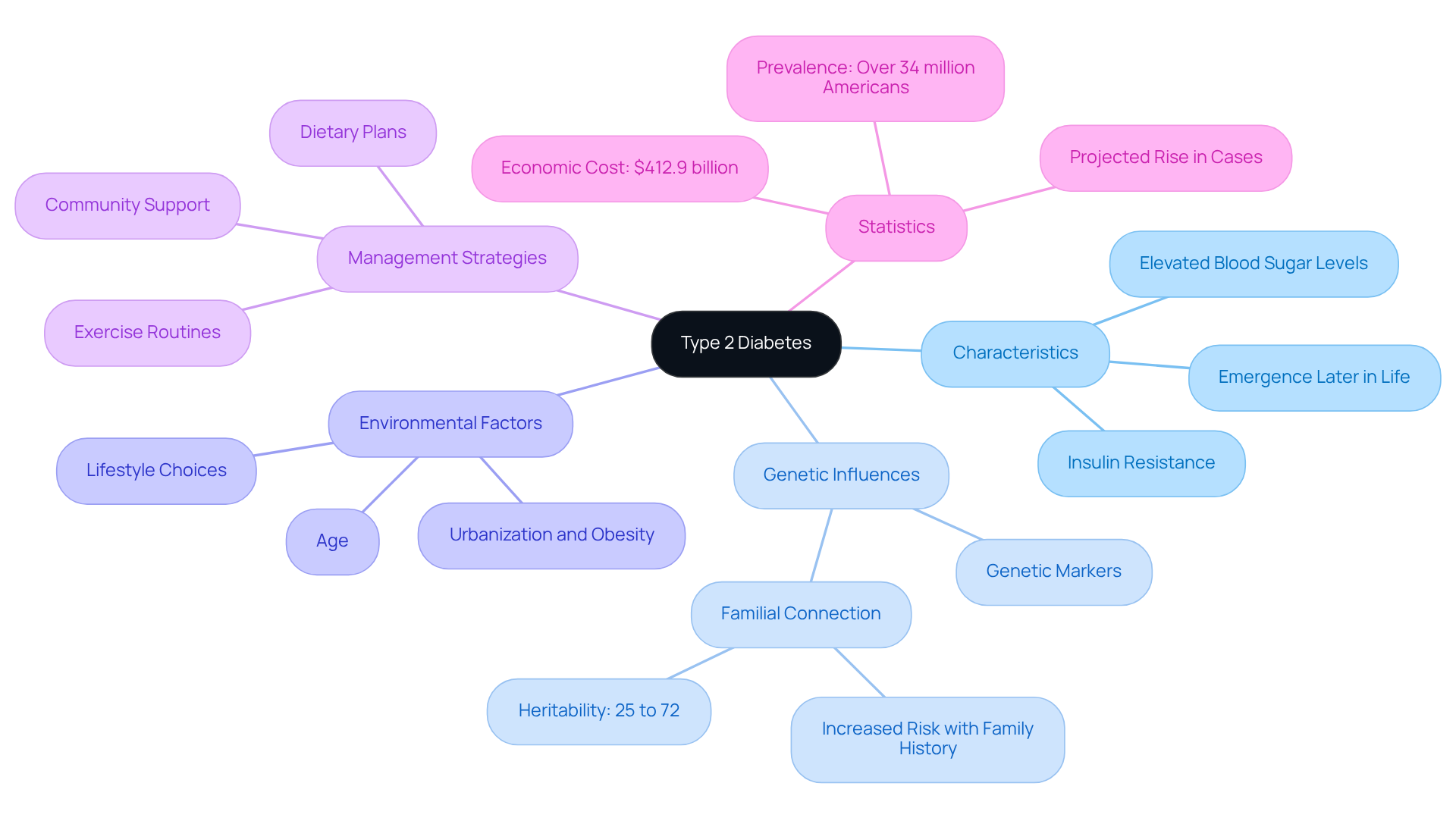
Defining Type 2 Diabetes: Can It Be Congenital?
Condition 2 is primarily characterized by insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels. Unlike the first type, which is an autoimmune condition often identified in childhood, the second type typically emerges later in life. While it may not be accurate to suggest that can you be born with type 2 diabetes, genetic predispositions can significantly increase the likelihood of developing it.
Studies suggest that roughly 25% to 72% of the heritability of this second form of diabetes can be attributed to genetic influences, indicating a strong familial connection. For instance, individuals with a family history of blood sugar issues face a heightened risk; research indicates that having a close relative with the condition can double the chance of developing it. Additionally, environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and age play crucial roles in its onset.
Therefore, while a child may inherit a genetic predisposition, it raises the question: can you be born with type 2 diabetes if they do not inherit the disease itself at birth? Recent studies have uncovered various genetic markers associated with the second type of diabetes, highlighting the importance of understanding these factors in managing the condition.
As researchers in blood sugar regulation note, the interplay between genetic predisposition and lifestyle choices emphasizes the complexity of managing this condition. It’s important to recognize that proactive measures can help mitigate risks, even for those who are genetically predisposed.
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive resources and community support to help individuals navigate these complexities. By offering educational materials and fostering a supportive community, T2DSolutions is committed to empowering those impacted by the second form of diabetes to take proactive steps in their health management.
Moreover, it’s crucial to acknowledge that over 90% of individuals with this condition have Type 2 diabetes, and the number of Americans affected by this illness is anticipated to rise significantly over the next decade. The economic burden of this condition is substantial, with the total cost of diagnosed cases in the United States reaching $412.9 billion in 2022. This underscores the urgent need for effective management strategies.
Furthermore, disparities in diabetes prevalence among different racial and ethnic groups highlight the multifaceted nature of this condition, necessitating tailored approaches to prevention and care. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Understanding Onset and Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes
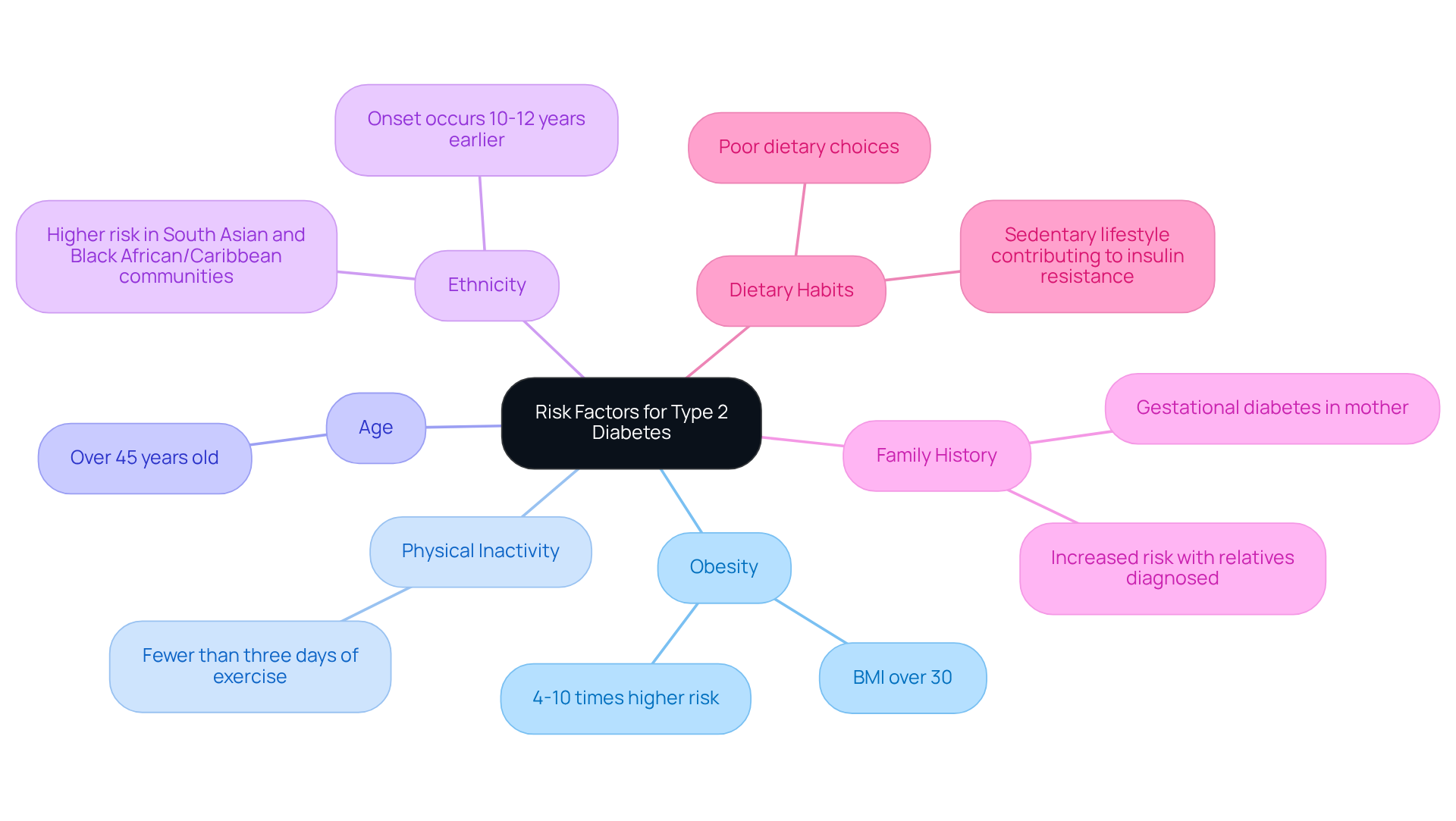
The onset of Type 2 Diabetes is influenced by a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. It's important to understand that obesity plays a significant role, with individuals categorized as obese (BMI over 30) facing a 4-10 times greater likelihood of developing this condition. Physical inactivity can further increase this risk, particularly for those who engage in fewer than three days of exercise each week. Additionally, age is a crucial factor; individuals over 45 are at a heightened risk. Research shows that non-insulin-dependent diabetes can occur roughly 10-12 years earlier in South Asian and Black African and Caribbean communities compared to other ethnic backgrounds.
Family history also has a significant impact, as individuals with relatives diagnosed with diabetes experience a notable increase in their own risk. Moreover, children born to mothers who had gestational diabetes are at an elevated risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes later in life. Poor dietary habits and sedentary lifestyles contribute to insulin resistance, a key characteristic of this disease.
Understanding these risk factors is essential for taking proactive steps toward prevention. Lifestyle modifications—such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting a balanced diet—can significantly reduce the chances of developing this chronic condition. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. By recognizing the various factors that influence the onset of Type 2 Diabetes, you can take meaningful actions toward better health. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Implications of Early Diagnosis and Management Strategies
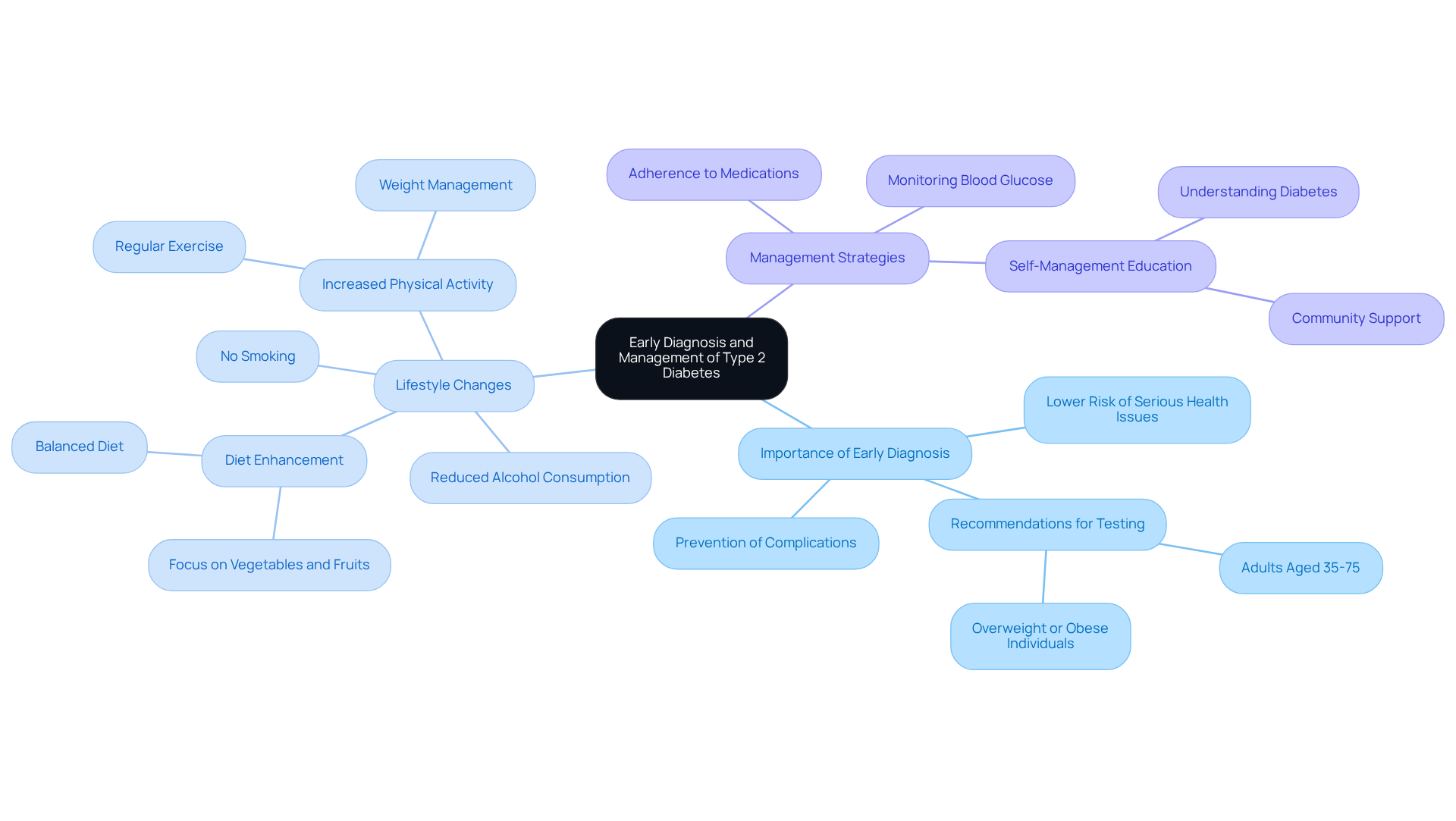
Early diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes is essential for effective management and the prevention of complications. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but when identified promptly, you can adopt lifestyle changes—like enhancing your diet and increasing physical activity—that can significantly lower blood sugar levels. For instance, regular exercise not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also improves insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for blood sugar control.
Management strategies should include:
- Consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels
- Adherence to prescribed medications
- Education on self-management techniques
Engaging in these practices early on greatly enhances your likelihood of maintaining normal blood sugar levels and averting complications like cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and neuropathy. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; early intervention promotes a proactive health strategy, enabling you to take control of your condition management.
Healthcare providers stress that lifestyle changes, such as refraining from smoking and reducing alcohol consumption, are essential elements of a thorough care strategy for managing blood sugar. By implementing these strategies, newly diagnosed patients can significantly improve their health outcomes and quality of life.
T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource hub, offering education and community support to help you navigate your diabetes management journey. We are here to [support you every step of the way](https://t2dsolution.com).
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes, while not congenital in the traditional sense, is significantly influenced by genetic predispositions that can increase your risk of developing the condition later in life. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by the interplay of genetics, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices. Recognizing these influences is vital for effective management and prevention.
Key insights reveal that:
- A family history of diabetes
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Age
are critical factors contributing to the likelihood of developing Type 2 diabetes. Early diagnosis and proactive management strategies, including lifestyle modifications and consistent monitoring, can lead to better health outcomes and a reduced risk of complications. The economic burden of this condition, alongside disparities in prevalence among different communities, emphasizes the urgency for tailored prevention and management approaches.
Ultimately, recognizing the multifaceted nature of Type 2 diabetes is essential for empowering you to take control of your health. By embracing proactive measures, seeking support, and staying informed about risk factors, you can significantly mitigate your risk and improve your quality of life. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. The path may be challenging, but with the right resources and community support, it is possible to navigate the complexities of Type 2 diabetes effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Type 2 Diabetes primarily characterized by?
Type 2 Diabetes is primarily characterized by insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels.
How does Type 2 Diabetes differ from Type 1 Diabetes?
Unlike Type 1 Diabetes, which is an autoimmune condition often identified in childhood, Type 2 Diabetes typically emerges later in life.
Can you be born with Type 2 Diabetes?
It is not accurate to suggest that one can be born with Type 2 Diabetes; however, genetic predispositions can significantly increase the likelihood of developing it later in life.
What role do genetics play in the development of Type 2 Diabetes?
Studies suggest that roughly 25% to 72% of the heritability of Type 2 Diabetes can be attributed to genetic influences, indicating a strong familial connection.
How does having a family history of Type 2 Diabetes affect an individual's risk?
Individuals with a family history of blood sugar issues face a heightened risk; having a close relative with the condition can double the chance of developing Type 2 Diabetes.
What factors contribute to the onset of Type 2 Diabetes?
Environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and age play crucial roles in the onset of Type 2 Diabetes.
What recent findings have been made regarding genetic markers and Type 2 Diabetes?
Recent studies have uncovered various genetic markers associated with Type 2 Diabetes, emphasizing the importance of understanding these factors in managing the condition.
How can individuals manage their risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes?
Proactive measures, including lifestyle choices, can help mitigate risks, even for those who are genetically predisposed to the condition.
What is the current prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes in the United States?
Over 90% of individuals with diabetes have Type 2 Diabetes, and the number of Americans affected by this illness is expected to rise significantly over the next decade.
What is the economic impact of Type 2 Diabetes in the United States?
The total cost of diagnosed cases of Type 2 Diabetes in the United States reached $412.9 billion in 2022, highlighting the substantial economic burden of the condition.
Why is it important to consider racial and ethnic disparities in diabetes prevalence?
Disparities in diabetes prevalence among different racial and ethnic groups highlight the multifaceted nature of Type 2 Diabetes, necessitating tailored approaches to prevention and care.



