Overview
Understanding the differences between Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and Type 2 is important, especially for those navigating this journey. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that requires lifelong insulin therapy. It often presents with sudden symptoms, which can be overwhelming. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance. Many people find that they can manage it initially through lifestyle changes and oral medications, leading to a more gradual onset of symptoms.
It's completely natural to have questions and concerns about these conditions. You're not alone in this journey. Many individuals have walked this path and found support through shared experiences. Remember, seeking help and resources is a positive step forward. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
In the realm of chronic health conditions, diabetes mellitus presents a complex and increasingly prevalent challenge that affects many lives. With two primary forms—Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes—understanding their distinctions is crucial for effective management.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that requires lifelong insulin therapy because the body cannot produce the hormone. In contrast, Type 2 diabetes often develops gradually, marked by insulin resistance that can sometimes be managed with lifestyle changes and oral medications.
As diabetes rates surge, particularly among youth and diverse populations, the urgency for education and intervention has never been greater. It’s understandable to feel overwhelmed by this information, but you are not alone in this journey.
This article delves into the definitions, symptoms, treatment approaches, and lifestyle impacts associated with both types of diabetes. We aim to offer essential insights and support for patients and healthcare providers alike, reassuring you that we are here to support you every step of the way.
Define Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 and Type 2
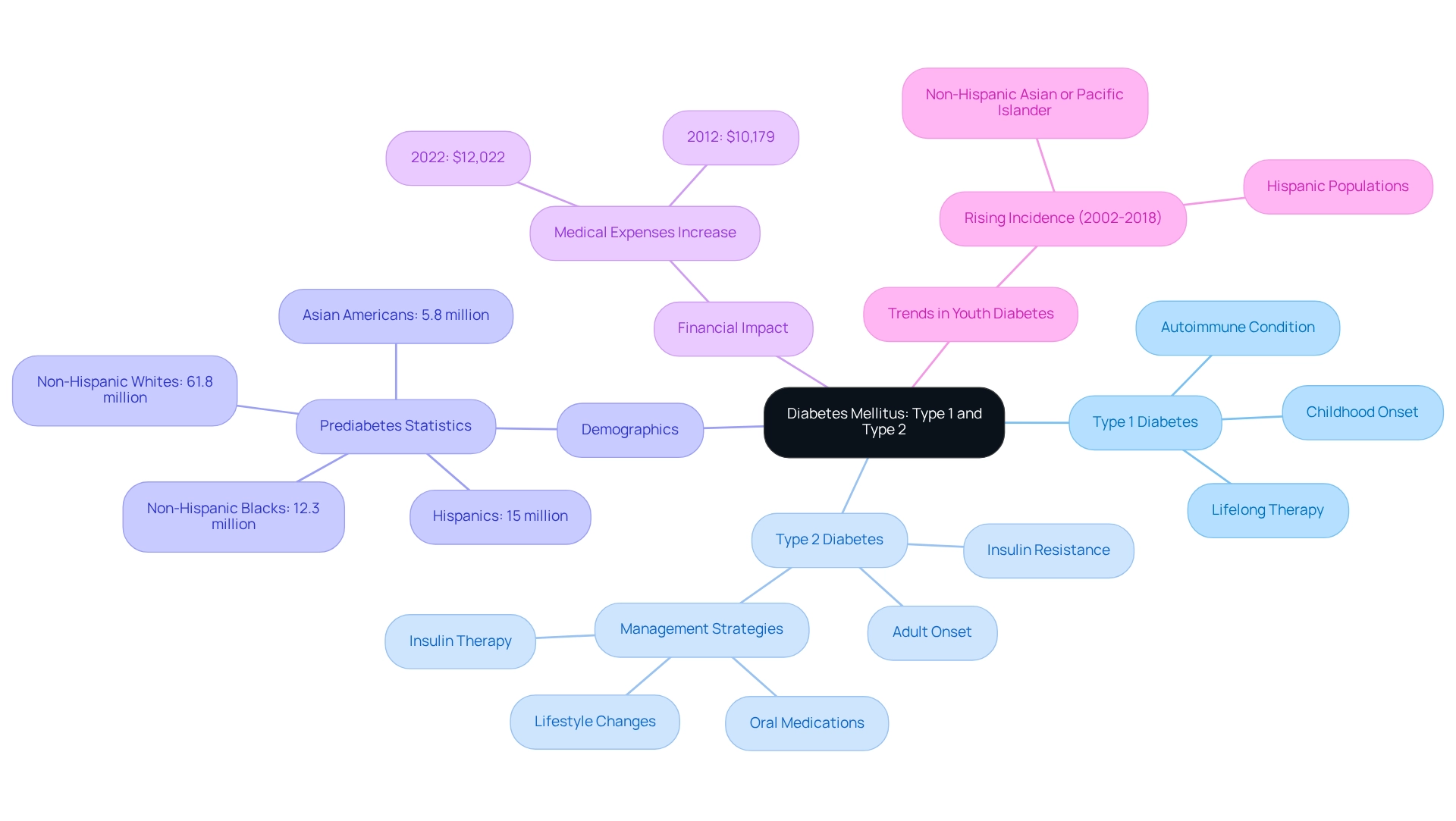
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to providing essential resources and support for individuals managing diabetes. Diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 is a long-lasting metabolic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can arise from inadequate hormone production or inefficient hormone use.
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D), a type of diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2, is primarily an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the beta cells in the pancreas that produce glucose-regulating hormones, often resulting in little to no hormone production. This condition typically manifests in childhood or adolescence and necessitates lifelong hormone therapy. Conversely, diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 is characterized by the body’s resistance to insulin, which means the cells do not respond effectively to the hormone, often alongside a gradual decrease in hormone production. T2D usually develops in adults, especially those with risk factors such as obesity and a sedentary lifestyle. Management often starts with lifestyle changes and oral medications, which may delay the need for insulin therapy.
Recent studies reveal a troubling rise in related health issues, with 8.0% of U.S. adults diagnosed with such conditions showing non-HDL cholesterol levels of 190 mg/dL or higher. This statistic underscores the importance of monitoring cholesterol levels as part of managing these health concerns. Moreover, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention highlights a significant number of adults with diagnosed prediabetes:
- 61.8 million non-Hispanic whites
- 15 million Hispanics
- 12.3 million non-Hispanic Blacks
- 5.8 million Asian Americans
This situation emphasizes the urgent need for education and intervention.
Additionally, the incidence of diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 among youth has risen notably from 2002 to 2018, particularly in non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander and Hispanic populations. The case study "Trends in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in Youth (2002-2018)" highlights this trend, reinforcing the pressing need for early intervention and education to mitigate long-term health complications associated with diabetes.
The financial impact of treating diabetes is also significant; additional medical expenses per individual increased from $10,179 to $12,022 between 2012 and 2022. This is a crucial consideration for newly diagnosed patients as they navigate their treatment options. At T2DSolutions, we strive to empower patients with the knowledge and tools necessary for effective management of their condition. You're not alone in this journey—we are here to support you every step of the way.
Compare Symptoms of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
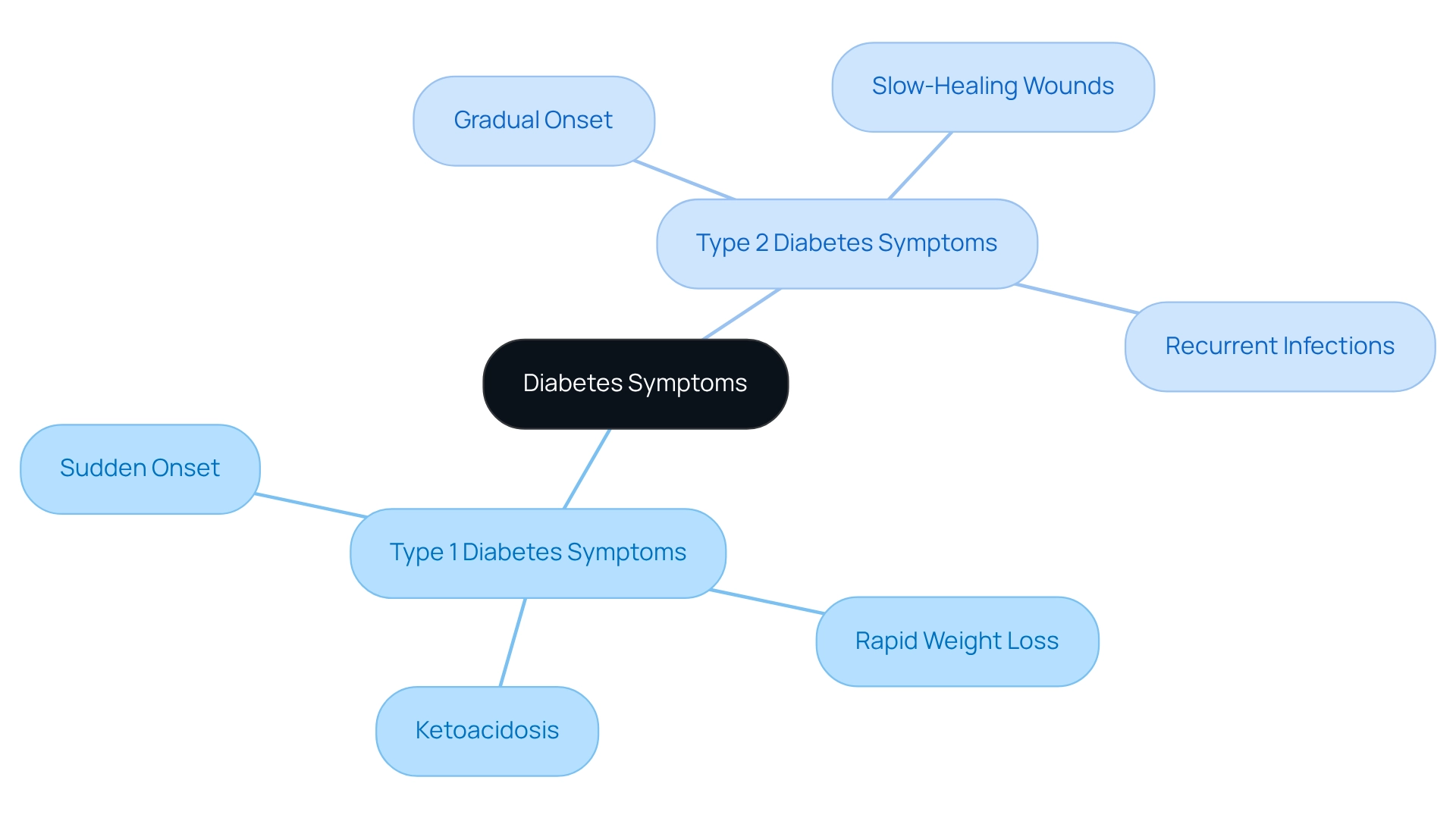
The signs of diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 can feel overwhelming, as they share similarities such as heightened thirst, frequent urination, tiredness, and blurred vision. It's important to recognize that the onset and severity of these symptoms can differ significantly. For instance, Condition 1 often presents with sudden and intense symptoms, including rapid weight loss and the potential for ketoacidosis, which can be life-threatening. On the other hand, symptoms of form 2 tend to develop more gradually and may be less noticeable, leading to delayed diagnosis.
Individuals with form 2 may experience slow-healing wounds and recurrent infections, which can easily be mistaken for other health issues. This can be particularly concerning, as understanding these differences is crucial for timely intervention. Did you know that approximately 16,000 new cases of form 1 occur each year among individuals aged 20 to 44 in the U.S.? This statistic highlights the importance of recognizing early symptoms and seeking help.
Moreover, those with insulin-dependent conditions often face an 8- to 13-year shorter life expectancy compared to those without. This underscores the significance of early diagnosis and management. Healthcare professionals emphasize that understanding these differences can empower you to take action. For example, studies indicate that early reduction of HbA1c levels in individuals with Type 1 can significantly lower the risk of microvascular complications, reinforcing the need for timely diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies.
Real-life experiences illustrate the necessity of identifying symptoms. A patient may initially dismiss heightened thirst and fatigue as stress-related, only to discover later that these were early signs of the condition. Conversely, symptoms of variety 2 might be overlooked for years, leading to more serious health challenges. It's particularly alarming that non-Hispanic Black children have shown the highest occurrence of Type 2 conditions over the years, highlighting the need for awareness across different populations.
By understanding the unique characteristics of each type, we can work together—patients and healthcare providers alike—to ensure effective management and improve health outcomes. Remember, you're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Contrast Treatment Approaches for Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
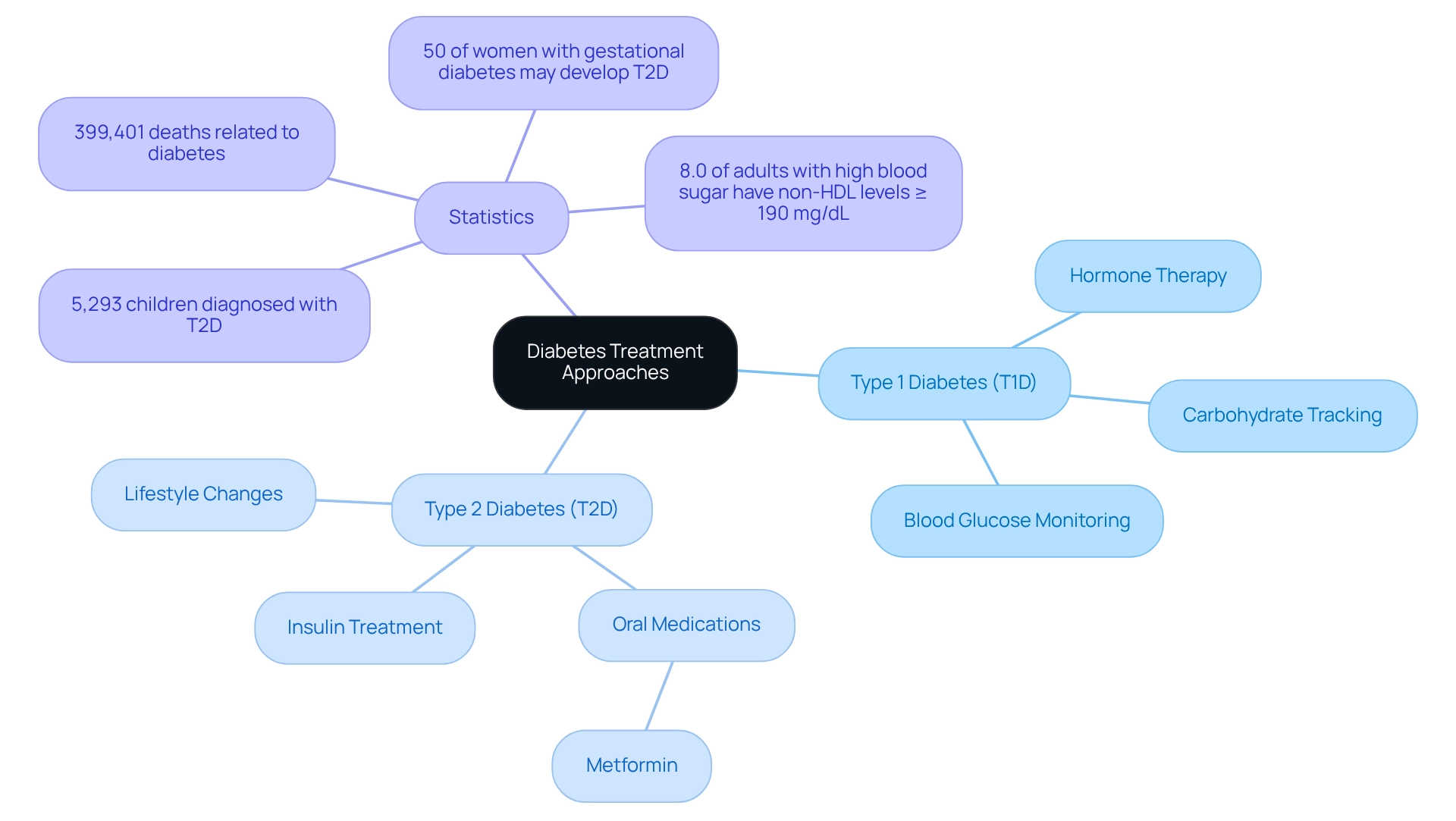
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to providing valuable resources that help you understand and manage diabetes. For those with Type 1 diabetes (T1D), management primarily revolves around hormone therapy, as individuals with this condition cannot produce insulin. Typically, patients require several daily injections or the use of a pump to effectively control their blood glucose levels. In addition to hormone therapy, essential management methods include tracking carbohydrate intake and consistently assessing blood glucose levels to ensure optimal regulation.
On the other hand, the journey of managing Type 2 diabetes (T2D) often starts with lifestyle adjustments. These may include dietary changes and increased physical activity, all aimed at improving insulin responsiveness. Research shows that these lifestyle interventions can significantly impact blood glucose levels and enhance overall health. If these changes alone do not yield the desired results, healthcare providers may prescribe oral medications like metformin to help manage blood sugar levels. As T2D progresses, some patients may also require insulin treatment to achieve adequate glycemic control.
The rising prevalence of Type 2 diabetes is concerning, especially among younger individuals. In fact, 5,293 children and teenagers aged 10 to 19 years have been identified with this condition. Treatment options are influenced by various factors, including the patient's age, the duration of the condition, and any existing health issues. Recent data indicates that in 2021, diabetes was noted as a primary or contributing factor in 399,401 death certificates, underscoring the urgent need for effective management strategies. Additionally, a troubling 8.0% of adults with diagnosed high blood sugar levels had a non-HDL cholesterol level of 190 mg/dL or greater, highlighting the importance of comprehensive care that addresses both blood glucose and heart health.
It's important to note that approximately 50% of women who experience gestational high blood sugar may later develop Type 2 diabetes, which emphasizes the need for awareness regarding risk factors associated with this condition. Recent advancements in treatment options for diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 reflect a dynamic landscape in management. Ongoing research continues to explore innovative technologies and therapies aimed at improving patient outcomes. For instance, current treatment strategies for T1D focus on optimizing blood glucose control and minimizing complications, with insulin remaining central to therapy.
As our understanding of diabetes evolves, so too do the strategies employed to manage it effectively. We strive to ensure that patients receive the most current care tailored to their unique needs. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. T2DSolutions is here to support you with the latest information and resources to help you manage your condition effectively.
Examine Lifestyle Impacts on Diabetes Management
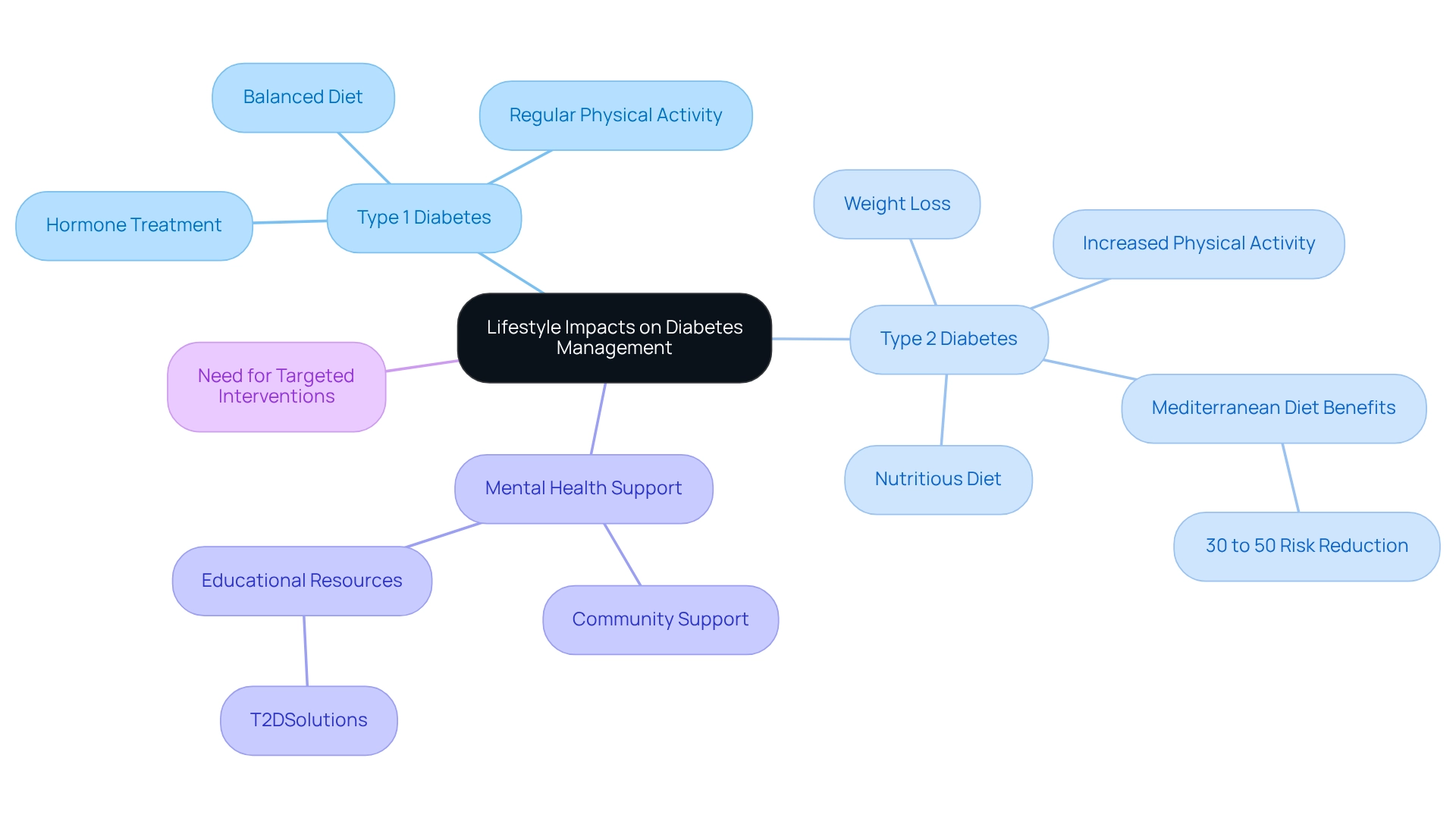
Lifestyle decisions play a crucial role in managing both forms of blood sugar conditions. For those facing form 1 blood sugar issues, embracing a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity are vital for effective glucose control and enhancing hormone treatment. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but know that these lifestyle changes can make a significant difference.
In contrast, for individuals managing Type 2 blood sugar conditions, lifestyle changes serve as the primary approach. Evidence shows that weight loss, increased physical activity, and a nutritious diet can greatly enhance insulin sensitivity and glycemic control. For instance, the PREDIMED study revealed that a Mediterranean diet, rich in extra virgin olive oil or nuts, led to a remarkable 30% to 50% reduction in the likelihood of developing Type 2 conditions among high-risk individuals. This underscores the power of dietary changes in your journey.
Moreover, a systematic review highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions to address the rising prevalence of diabetes-related issues, reinforcing the importance of lifestyle changes. Current statistics indicate that many patients struggle with maintaining physical activity levels. Changes in Apolipoprotein B, measured in mg/dL, reflect the cardiometabolic health impacts of these lifestyle adjustments.
Mental health support is equally essential for both types, as the stress of managing a chronic condition can lead to emotional challenges. You're not alone in this journey; engaging in community support and utilizing educational resources, such as those offered by T2DSolutions, can empower you to make informed lifestyle choices. T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource hub, providing educational materials and community support tailored specifically for newly diagnosed patients.
By prioritizing diet and exercise, you can significantly influence your diabetes management and enhance your quality of life. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Diabetes mellitus, which includes both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, presents significant challenges that call for urgent awareness and effective management. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that requires lifelong insulin therapy. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes is often manageable through lifestyle changes and oral medications. The rising rates of diabetes, particularly among youth and diverse populations, underscore the critical need for early intervention and education.
Understanding the symptoms of each type is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. Type 1 diabetes typically manifests with sudden and severe symptoms, while Type 2 diabetes symptoms develop more gradually, often resulting in delayed care. Recognizing these differences is crucial for fostering effective collaboration between healthcare providers and patients.
The approaches to treatment vary significantly: insulin is vital for managing Type 1 diabetes, whereas Type 2 diabetes often begins with lifestyle modifications aimed at improving insulin sensitivity. The financial implications of diabetes management further highlight the necessity for comprehensive care that addresses both blood glucose control and overall health.
Lifestyle choices play a fundamental role in managing diabetes. Individuals with Type 1 can benefit from a balanced diet and regular exercise alongside their insulin therapy, while those with Type 2 may achieve significant improvements through lifestyle changes. Moreover, mental health support and community resources are essential in empowering individuals on their diabetes journey.
Ultimately, being informed and proactive in diabetes management can lead to better health outcomes and an enhanced quality of life. With the right knowledge and resources, you can effectively navigate your diabetes and make informed decisions that positively impact your well-being. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; support is available every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2?
Diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 is a long-lasting metabolic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can result from inadequate hormone production or inefficient hormone use.
What is Type 1 Diabetes (T1D)?
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) is primarily an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the beta cells in the pancreas that produce glucose-regulating hormones, often leading to little to no hormone production. It typically manifests in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong hormone therapy.
How does diabetes mellitus type 2 differ from type 1?
Diabetes mellitus type 2 (T2D) is characterized by the body's resistance to insulin, meaning the cells do not respond effectively to the hormone. It usually develops in adults, particularly those with risk factors like obesity and a sedentary lifestyle, and management often begins with lifestyle changes and oral medications.
What are the recent statistics regarding health issues related to diabetes in the U.S.?
Recent studies show that 8.0% of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes have non-HDL cholesterol levels of 190 mg/dL or higher, highlighting the importance of monitoring cholesterol levels in managing diabetes.
How many adults in the U.S. are diagnosed with prediabetes, and what are the statistics by demographic?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that 61.8 million non-Hispanic whites, 15 million Hispanics, 12.3 million non-Hispanic Blacks, and 5.8 million Asian Americans are diagnosed with prediabetes.
What trend has been observed in the incidence of diabetes among youth from 2002 to 2018?
There has been a notable rise in the incidence of diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 among youth, particularly in non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander and Hispanic populations, emphasizing the need for early intervention and education.
What is the financial impact of treating diabetes?
The additional medical expenses per individual for treating diabetes increased from $10,179 to $12,022 between 2012 and 2022, which is an important consideration for newly diagnosed patients.
How does T2DSolutions support individuals managing diabetes?
T2DSolutions is dedicated to providing essential resources and support for individuals managing diabetes, empowering them with knowledge and tools for effective management of their condition.



