Overview
Achieving a normal Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) is a journey that many embark on, and it’s important to know that you’re not alone. To help you on this path, focusing on:
- Continuous glucose monitoring
- Balanced dietary choices
- Regular physical activity
- Effective stress management
can make a significant difference. These strategies are not just beneficial; they are essential for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels and improving overall health outcomes.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but remember, you have community resources and personalized care available to support you. By embracing these strategies, you can take proactive steps toward better health. We are here to support you every step of the way, encouraging you to share your experiences and connect with others who understand your journey. Together, we can foster a supportive environment that uplifts everyone involved.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding the metrics that guide effective care is paramount. One such metric, the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI), offers a clearer picture of your average blood glucose levels through continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). Unlike traditional methods, GMI provides real-time insights that can significantly impact your treatment decisions and overall health outcomes.
As the landscape of diabetes care evolves, tools like GMI and the concept of Time in Range (TIR) are becoming increasingly vital. These resources empower you to take control of your health journey. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by all the information, but remember, you're not alone in this journey.
This article delves into the nuances of GMI, explaining its calculation and comparing it with traditional A1C testing. We will also highlight the importance of community support and continuous monitoring in achieving optimal diabetes management. Together, we can navigate this path toward better health and well-being.
Understanding the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI)
At T2DSolutions, we understand the challenges faced by individuals navigating their diabetes journey, and we’re committed to providing valuable resources to support you. One important metric to assist in this process is the normal GMI, which estimates your average blood sugar levels over time based on continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data. Unlike standard A1C tests, which reflect blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, normal GMI offers a more immediate insight into your sugar control.
Normal GMI is determined using the formula:
GMI (%) = 3.31 + 0.02392 × (mean sugar level in mg/dL).
This calculation empowers those with insulin resistance to gain a clearer understanding of their sugar patterns, enabling informed decisions about their control plans.
The significance of normal GMI in managing blood sugar levels is profound. By focusing on normal GMI, you can track daily sugar variations, which is essential for effective management of your condition. At T2DSolutions, we emphasize the importance of interpreting GMI carefully, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
We encourage clinicians to rely on mean sugar values directly obtained from CGM rather than solely on GMI. This approach underscores the importance of personalized care, as individual physiological factors can influence normal GMI calculations. It’s important to note that further research is needed to refine GMI calculations based on these individual factors.
As we look ahead to 2025, the adoption of continuous glucose monitoring technology has surged, with more patients embracing CGM systems to enhance their care. Research supports this trend, highlighting the positive impact of CGM on health outcomes related to blood sugar management. For instance, a study conducted in Romania included 105 patients from Timisoara and 42 from Iasi, showcasing a diverse sample that contributes to our understanding of GMI's effectiveness.
Real-world examples illustrate the effectiveness of GMI in managing blood sugar conditions. For example, the HYPNOS study explored the relationship between CGM metrics and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and obstructive sleep apnea. While the main trial results indicated no significant effect of therapy on glycemic control, the comprehensive dataset highlighted the potential of CGM in understanding individual glucose patterns.
GS, the guarantor of this work, stated, "I had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis," reinforcing the credibility of the findings.
As the field of blood sugar control evolves, continuous studies deepen our understanding of normal GMI and its role in patient treatment. By incorporating normal GMI into your care strategies, you can manage your health journey more effectively, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and quality of life. At T2DSolutions, we are here to help those recently diagnosed comprehend these metrics and apply them effectively in their health strategies.
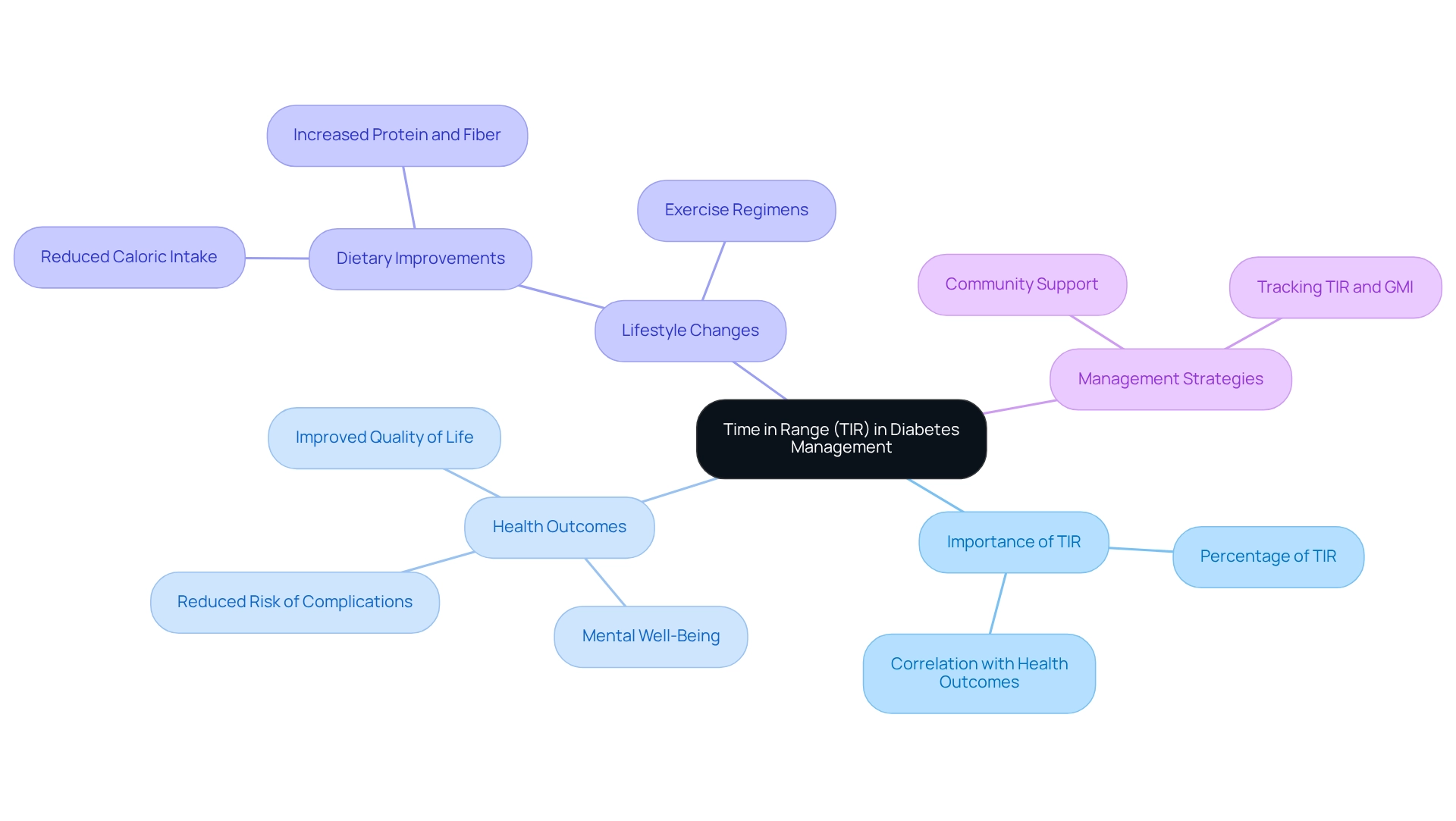
The Importance of Time in Range (TIR) in Diabetes Management
Time in Range (TIR) is a crucial measure for managing blood sugar levels. It indicates the percentage of time a person's blood sugar stays within a target range, typically between 70 and 180 mg/dL. Research shows that maintaining a high TIR is vital for reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications. For instance, individuals who achieve a TIR of at least 70% often experience significantly improved health outcomes, including a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and a better overall quality of life.
The connection between TIR and complications associated with blood sugar conditions is well-established. Higher TIR levels correlate with fewer hospitalizations and lower healthcare costs, underscoring the importance of effective blood sugar management. Recent studies indicate that patients who maintain a high TIR not only enjoy better physical health but also report enhanced mental well-being, highlighting the comprehensive benefits of diligent management of their condition.
At T2DSolutions, we recognize the importance of tracking TIR alongside the standard Glucose Management Indicator (GMI). This dual approach empowers individuals to make timely adjustments to their treatment plans and lifestyle choices, fostering a proactive attitude toward managing their health. For example, a case study involving participants who adhered to strict dietary and exercise regimens revealed a notable increase in their TIR, leading to improved health outcomes and a greater sense of empowerment in their health journey.
The study's credibility was strengthened by specific participant inclusion criteria, ensuring that only individuals with reliable data were analyzed, which enhances the validity of the findings.
As we look ahead to 2025, the emphasis on TIR continues to grow, with new research affirming its significance in treating blood sugar disorders. As individuals make dietary improvements—such as reducing caloric intake, carbohydrates, and sugars, while increasing protein and fiber—they are encouraged to prioritize maintaining their TIR for optimal health outcomes. By focusing on TIR, individuals can take meaningful steps toward effectively managing their condition and enhancing their quality of life.
As RH noted, 'GS wrote the first draft of the manuscript and RH reviewed and edited the manuscript.' This highlights the collaborative effort behind these findings. This shared journey in healthcare aligns with T2DSolutions' mission to empower individuals through shared knowledge and support, providing resources and guidance to help newly diagnosed patients navigate their health journey. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
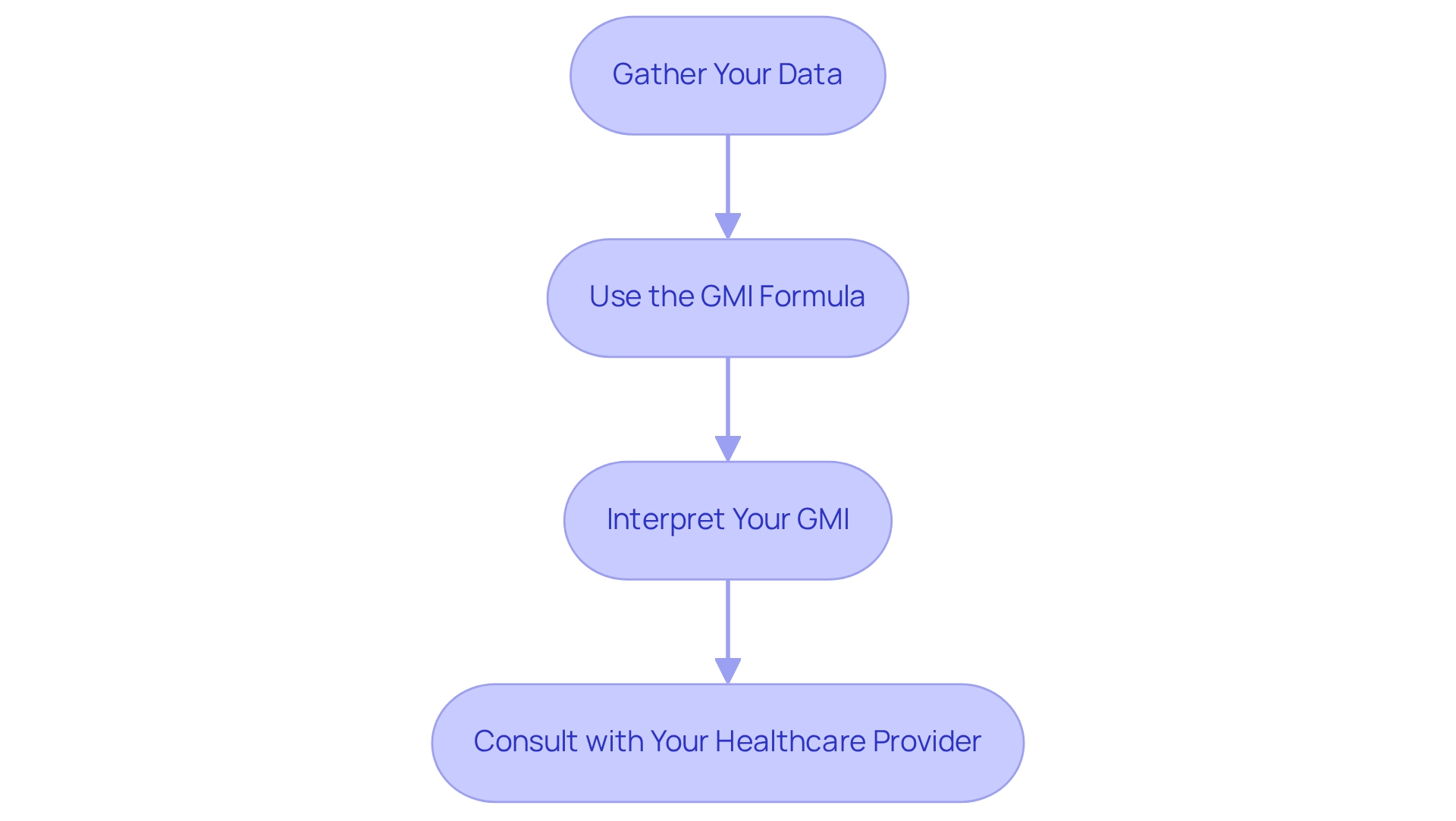
How to Calculate Your GMI: A Step-by-Step Approach
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your all-inclusive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support. Understanding your normal GMI is crucial for effective diabetes management. To help you calculate your GMI, here are some straightforward steps:
-
Gather Your Data: Start by collecting at least 14 days of continuous sugar monitoring (CGM) data. This dataset should include your average sugar levels, which are essential for precise calculation.
-
Use the GMI Formula: Apply the following formula to determine your GMI:
GMI (%) = 3.31 + 0.02392 × (mean glucose in mg/dL).
For instance, if your average glucose is 150 mg/dL, the calculation would be:
- GMI = 3.31 + 0.02392 × 150 = 3.31 + 3.588 = 6.898%.
-
Interpret Your GMI: Once you have your GMI, compare it to the normal range. A GMI below 5.7% is regarded as typical, which can assist you in evaluating your sugar control status and guide your treatment choices.
It’s important to recognize that an HbA1c of 6.5% or above signifies the condition in hospitalized patients with increased blood sugar levels exceeding 140 mg/dL, underscoring the importance of tracking normal GMI.
- Consult with your healthcare provider: Sharing your results regarding normal GMI with your healthcare provider is essential. Discuss any required modifications to your health control plan based on your findings.
Recent evidence indicates that high pre-admission glycemic control (HbA >8.0%) is linked to reduced mortality, emphasizing the significance of careful glucose oversight in clinical environments.
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to offering you the resources and assistance you need for effective control of your condition. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Explore our site for more information on GMI and other essential subjects to enhance your educational journey.
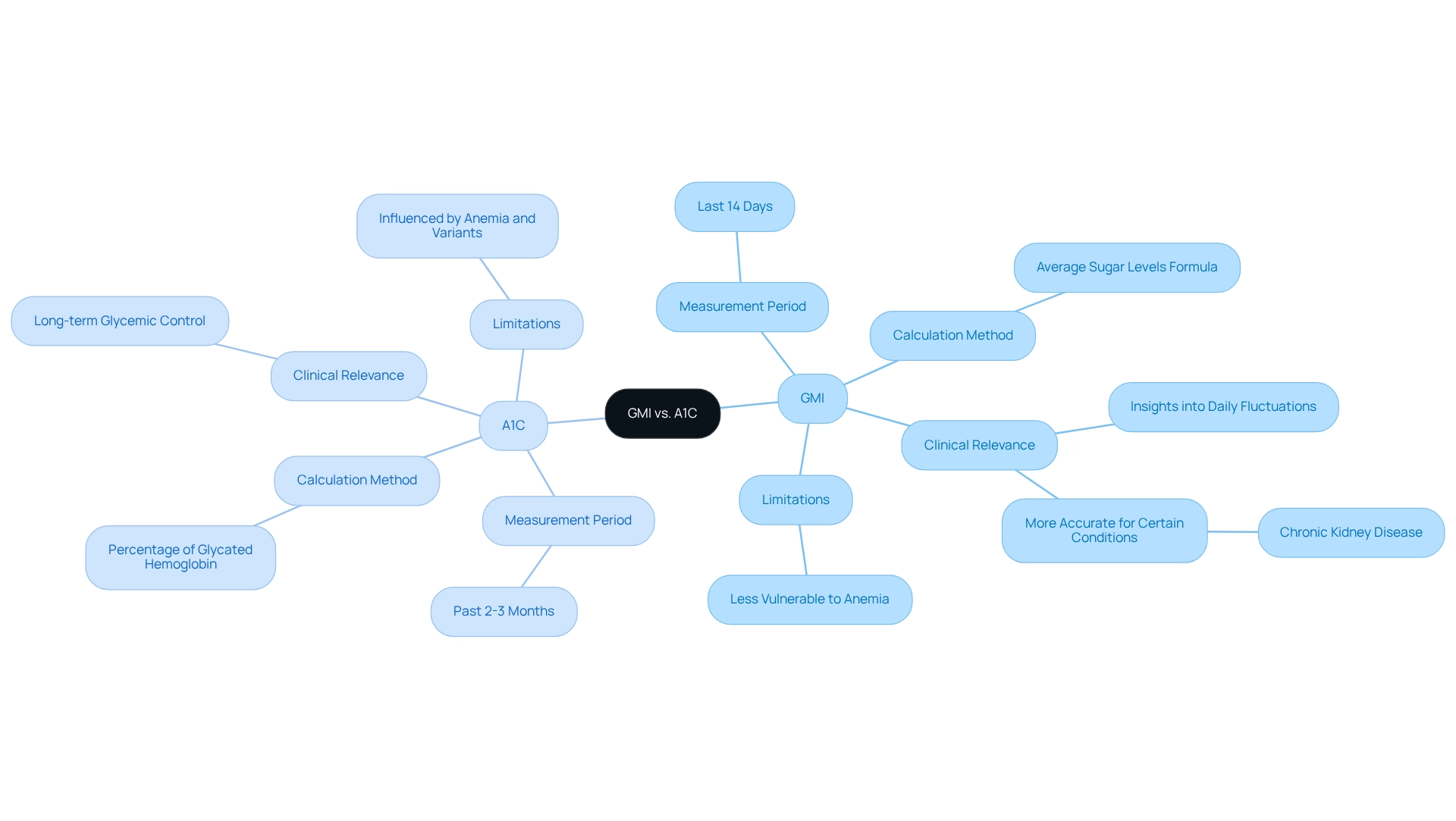
GMI vs. A1C: Understanding the Differences
Understanding the differences between normal GMI (Glucose Management Indicator) and A1C (Hemoglobin A1c) is crucial for effective diabetes management. Both metrics serve to assess glucose control, yet they do so through distinct methodologies and implications that are important for you to know.
-
Measurement Period: A1C reflects average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, providing a long-term view of glycemic control. In contrast, normal GMI offers a more immediate snapshot, derived from continuous monitoring data, typically representing the last 14 days. This immediacy can be particularly beneficial for making timely adjustments to your treatment plans.
-
Calculation Method: A1C is determined by the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, whereas GMI is obtained from average sugar levels using a specific formula. This difference in calculation can lead to variations in the results, especially for those with certain health conditions.
-
Clinical Relevance: GMI provides insights into daily sugar fluctuations that A1C may overlook. This characteristic makes normal GMI especially valuable for individuals who frequently need to fine-tune their diabetes management strategies. For instance, a recent study highlighted that up to 20% of patients exhibited nearly identical values for both HbA1c and GMI, yet discrepancies were noted in those with chronic conditions, such as chronic kidney disease. The study titled 'Comparative Analysis of GMI and HbA1c in Clinical Practice' revealed significant discordance between GMI and HbA1c in patients with a Glomerular Filtration Rate below 60 mL/min/1.73 m², suggesting that normal GMI may provide a more accurate reflection of glycemic control in this population.
-
Limitations: A1C results can be influenced by factors such as anemia or hemoglobin variants, which may distort the interpretation of sugar management. On the other hand, normal GMI is less vulnerable to these conditions, potentially offering a clearer view of your current sugar levels. It's essential to be aware of these limitations and interpret results in the context of your individual health factors. As Elizabeth Selvin from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health states, "The optimal use of CGM and its metrics in the care of patients with blood sugar issues requires knowledge of both the strengths and limitations of this groundbreaking technology."
Recent findings underscore the importance of understanding these differences. For instance, reverse correlations have been noted between the variations in normal GMI and A1C with the standard deviation and coefficient of variation of glycemia, suggesting that normal GMI may be more reactive to alterations in daily blood sugar levels.
In summary, while both A1C and normal GMI are valuable tools in managing blood sugar levels, their differences in measurement period, calculation methods, clinical relevance, and limitations highlight the need for personalized approaches in your care. By leveraging both metrics, you can achieve a more comprehensive understanding of your glucose control, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
At T2DSolutions, we are committed to providing resources and support for newly diagnosed patients. You're not alone in this journey—subscribe to our updates to stay informed about the latest information and resources for managing your condition effectively.
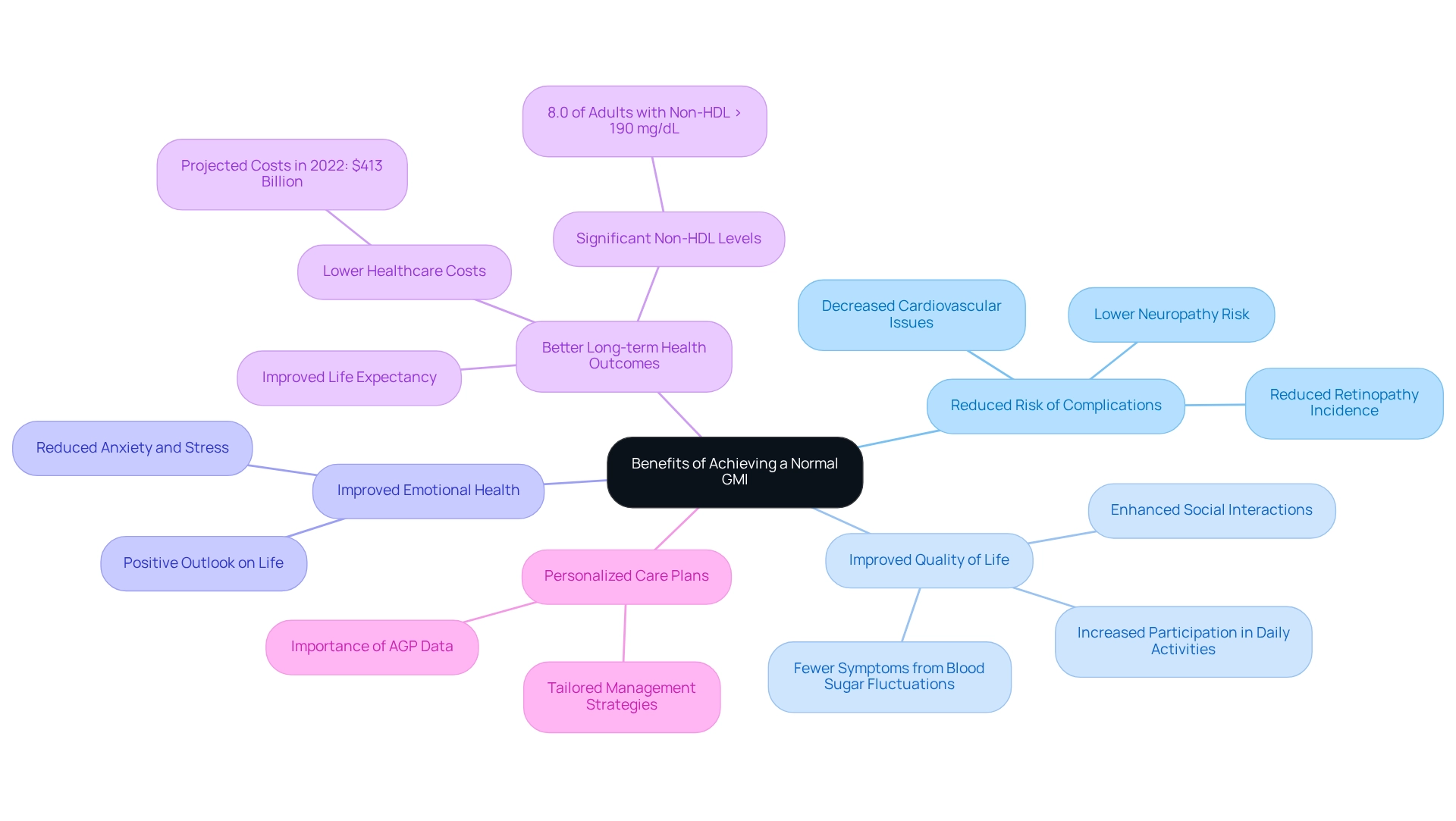
Benefits of Achieving a Normal GMI
Achieving a normal Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) offers numerous significant health benefits that can profoundly impact the lives of individuals managing diabetes.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Maintaining a normal GMI is crucial for lowering the risk of diabetes-related complications, including neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular diseases. Research shows that individuals with well-regulated sugar levels experience a significant reduction in these complications, leading to a healthier, more active lifestyle.
Many individuals who achieve a normal GMI often report improved quality of life by experiencing fewer symptoms associated with fluctuating blood sugar levels. This stability translates into a better overall quality of life, allowing for greater participation in daily activities and improved social interactions.
- Improved Emotional Health: Efficient control of blood sugar levels is crucial in alleviating the anxiety and stress frequently associated with this condition. By stabilizing blood sugar levels, individuals can experience improved mental health, fostering a more positive outlook on life.
Consistently achieving a normal GMI is associated with better long-term health outcomes. Studies show that individuals with controlled glucose levels not only face lower healthcare costs but also enjoy improved life expectancy. For example, the overall projected expenses of identified health issues related to diabetes in the U.S. hit $413 billion in 2022, emphasizing the financial advantages of efficient oversight. Furthermore, the occurrence of diagnosed blood sugar issues varies significantly across U.S. counties, ranging from 2.2 to 53.5 per 1,000 people, underscoring the importance of managing GMI in a diverse population.
Many individuals have shared inspiring stories of how achieving a normal GMI has significantly improved their quality of life. For example, one patient reported a significant reduction in fatigue and an increase in energy levels, allowing them to engage more fully with family and friends.
Research consistently demonstrates that health outcomes improve when maintaining a normal GMI, leading to a reduction in diabetes-related complications. For instance, a study revealed that 8.0% of U.S. adults with diagnosed blood sugar conditions had a non-HDL level of 190 mg/dL or above, highlighting the significance of glucose control in preventing cardiovascular problems. Furthermore, it is essential to tackle physical inactivity, as 31.9% of adults with this condition were discovered to be physically inactive, which emphasizes the necessity for enhanced activity to attain a normal GMI.
- Personalized Care Plans: As Mark Harmel, a Diabetes Care and Education Specialist, notes, "Unlike educating about an overall A1C goal of 7%, we haven't stressed the significance of new data in the Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) report, that allows us to create a more tailored care plan." This highlights the necessity for customized methods in blood sugar management.
In summary, the benefits of achieving a normal GMI extend beyond physical health, encompassing emotional well-being and overall quality of life. By prioritizing sugar management, individuals can significantly enhance their health outcomes and enjoy a more fulfilling life. You're not alone in this journey. For more resources and assistance in managing your GMI, consider exploring T2DSolutions, your comprehensive hub for education and community support related to this condition.
Practical Strategies for Maintaining a Normal GMI
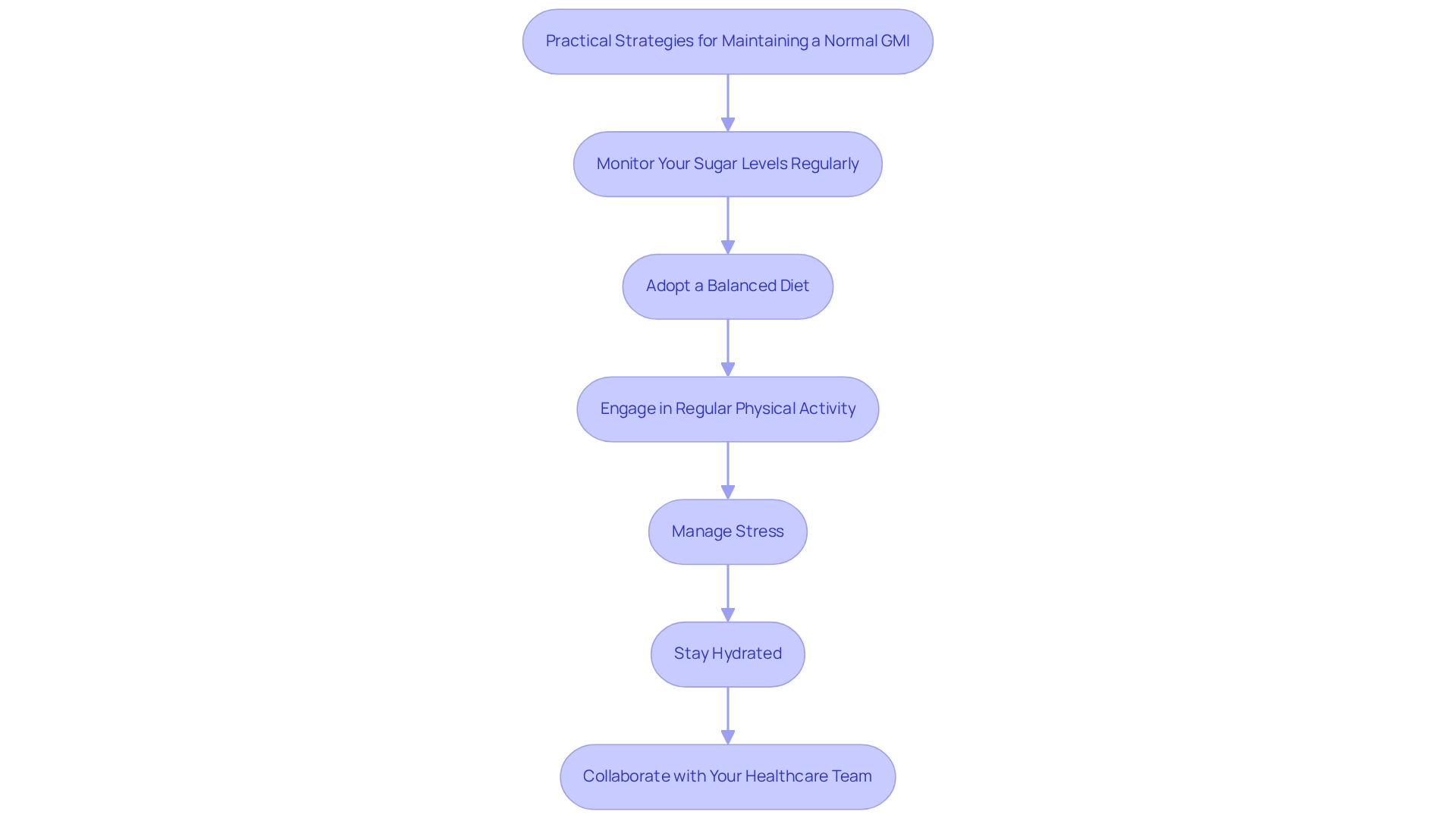
To maintain a normal GMI, consider implementing the following strategies with the support of T2D Solutions:
- Monitor Your Sugar Levels Regularly: It’s essential to keep track of your sugar levels throughout the day. You can utilize a continuous sugar monitor (CSM) or perform regular fingerstick tests. Advances in CGM technology have made it easier to understand how daily choices impact blood sugar control.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed; in Saudi Arabia, for instance, 97.3% of males and 93.1% of females were unaware of the importance of monitoring diabetes. This highlights the need for increased awareness among newly diagnosed patients. T2D Solutions offers resources and guidance on effective monitoring techniques.
-
Adopt a Balanced Diet: Emphasize a diet rich in whole foods, including a variety of vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Research suggests that dietary selections greatly affect sugar metabolism. For example, a case study on the Mediterranean diet, recognized for its richness in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, has shown that embracing this diet can enhance sugar management and lower the risk of Type 2 Diabetes. T2D Solutions provides meal planning resources to help you make informed dietary choices.
-
Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and can effectively reduce blood sugar levels. Incorporating activities you enjoy can make this goal more achievable. T2D Solutions can connect you with local exercise programs tailored for diabetes management.
-
Manage Stress: Implement stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises. Managing stress is essential, as heightened stress levels can negatively impact blood sugar regulation. T2D Solutions offers workshops and resources to help you develop effective stress management strategies.
-
Stay Hydrated: Ensure you drink plenty of water throughout the day. Proper hydration supports overall health and can aid in maintaining optimal glucose levels. T2D Solutions emphasizes the importance of hydration in managing blood sugar levels.
-
Collaborate with Your Healthcare Team: Routine discussions with your healthcare provider are crucial for modifying your health plan based on your GMI and general well-being. As Bergenstal observes, variations in sugar control may result from biological or genetic differences, making cooperative care essential for achieving improved health results. T2D Solutions promotes teamwork with healthcare experts to enhance your condition oversight.
By implementing these practical strategies and understanding that overseeing this condition is a shared journey, you can take proactive measures toward maintaining a normal GMI. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; T2D Solutions is here to support you every step of the way.
The Role of Continuous Monitoring in Achieving Normal GMI
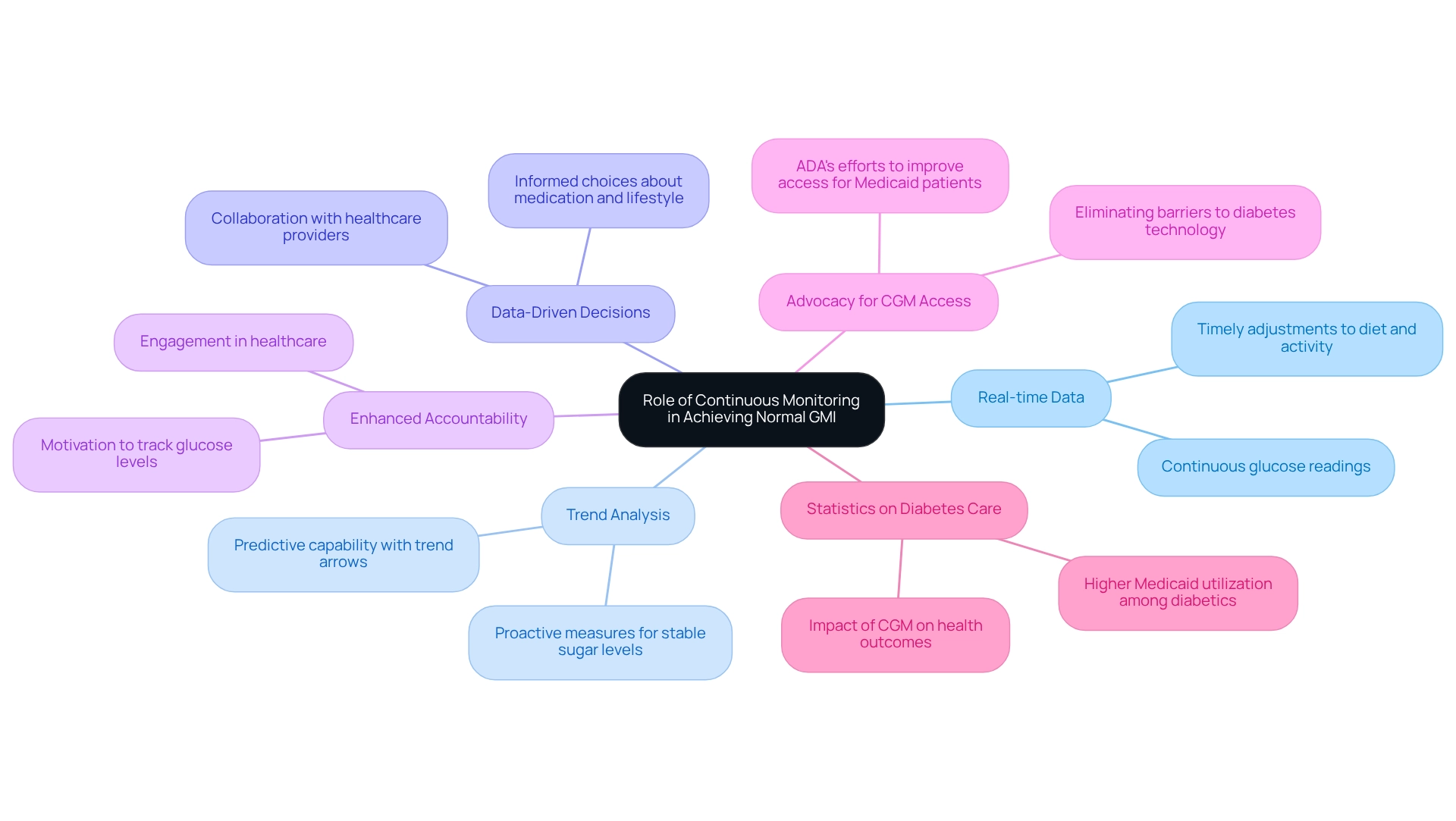
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is vital for achieving and maintaining a normal Glucose Management Indicator (GMI), offering several important advantages:
- Real-time Data: CGM systems provide continuous glucose readings, allowing individuals to monitor fluctuations throughout the day. This immediate feedback empowers timely adjustments to diet and physical activity, which is essential for effective diabetes management.
- Trend Analysis: Many CGM devices feature trend arrows that indicate whether sugar levels are rising or falling. This predictive capability helps users anticipate changes and take proactive measures, enhancing their ability to maintain stable sugar levels.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Access to comprehensive blood sugar information enables individuals to collaborate closely with healthcare providers. This partnership fosters informed choices about medication changes and lifestyle adjustments, ultimately leading to more tailored and effective strategies for managing the condition.
- Enhanced Accountability: The continuous nature of CGM encourages a greater sense of accountability among users. By consistently tracking their glucose levels, individuals are motivated to stay engaged in their healthcare, striving for improved health outcomes.
At T2DSolutions, we recognize the importance of CGM technology in managing blood sugar levels. Our platform serves as a comprehensive resource center, providing recently diagnosed patients with the information and tools they need to navigate their condition effectively. Recent trends show a growing adoption of CGM technology among individuals facing blood sugar challenges, with studies indicating that those utilizing CGM are more likely to achieve normal GMI levels.
For example, a case study highlighted the American Diabetes Association's advocacy efforts to enhance CGM access, especially for individuals on Medicaid. Their initiatives aim to eliminate barriers to essential health technology, which is crucial for improving health outcomes and reducing premature deaths. As M.E.L. noted, "Identifying populations with lower-than-expected utilization is a necessary first step in developing targeted interventions to increase CGM uptake and, ultimately, improve short- and long-term type 1 diabetes–related outcomes."
Furthermore, statistics reveal that individuals with the condition are more than twice as likely to receive healthcare through Medicaid compared to those without the condition. This underscores the importance of accessible tools for monitoring blood sugar levels, such as CGM. It highlights the critical need for enhancing CGM availability for individuals on Medicaid, reinforcing the case for CGM's significance in managing blood sugar levels.
Looking ahead to 2025, expert insights continue to emphasize the transformative impact of CGM on blood sugar control. Real-time data not only supports immediate decision-making but also contributes to long-term health improvements. As more patients share their success stories of using CGM to achieve better glucose control, the technology's role in managing the condition becomes increasingly evident, underscoring its value in the journey towards achieving normal GMI.
At T2DSolutions, we are committed to providing ongoing support and resources to help patients navigate their health journey effectively. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Leveraging Community Support for Effective Diabetes Management
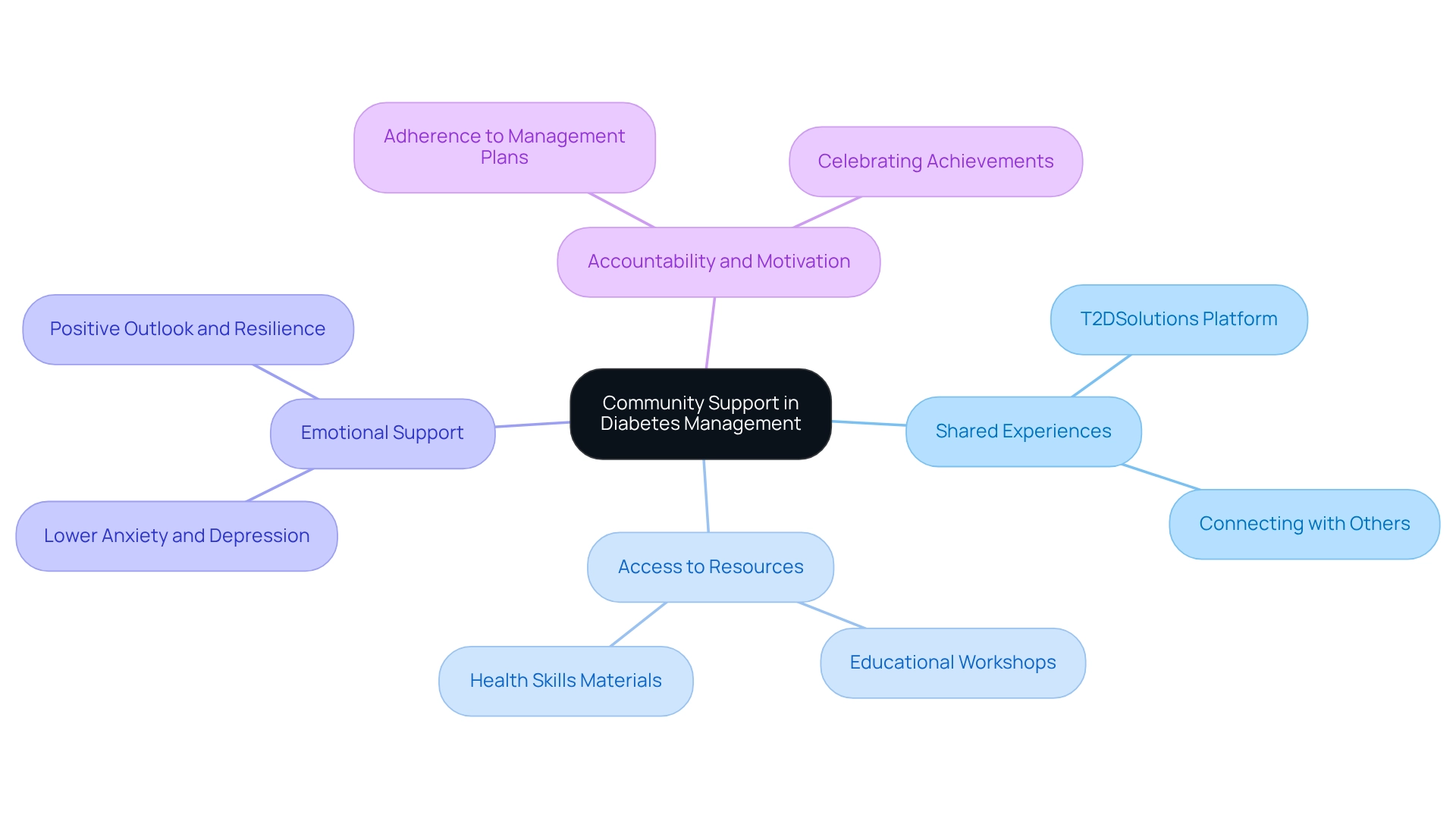
Community support is a vital aspect of effectively managing your condition, offering numerous advantages that can significantly enhance your experience.
-
Shared Experiences: Connecting with others who share your journey provides invaluable insights and motivation. These interactions can help you feel less isolated, nurturing a sense of belonging and understanding that is essential for your emotional well-being. T2DSolutions serves as a platform for individuals to share their stories and connect with one another, underscoring the importance of established support networks.
-
Access to Resources: Community groups often offer educational materials, workshops, and events designed to enhance your health skills. T2DSolutions provides a wealth of resources, equipping you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your health, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
-
Emotional Support: Engaging with a compassionate community can alleviate the emotional challenges associated with blood sugar management. Research shows that individuals who participate in support groups experience lower levels of anxiety and depression, common hurdles for those managing chronic conditions. T2DSolutions aims to foster this emotional support, which is crucial for maintaining a positive outlook and resilience.
-
Accountability and Motivation: Being part of a community increases accountability, encouraging you to adhere to your management plans. Celebrating achievements together can enhance motivation and reinforce positive behaviors. T2DSolutions encourages joining local support groups or online forums, providing a space to share experiences and strategies, enriching your overall management journey.
Recent studies reveal that community support significantly impacts glycemic management outcomes. For instance, individuals involved in peer support networks report improved glycemic control and greater adherence to treatment plans, contributing to achieving a normal glycemic index. Additionally, the age-adjusted prevalence of diagnosed conditions related to blood sugar is 12.6% among those with less than a high school education, highlighting the demographic challenges faced in community support settings.
A case study on the food environment demonstrates how access to healthy food options in community settings can affect dietary choices, especially in marginalized areas. This emphasizes the importance of community involvement in promoting healthier habits and reducing the risk of related health issues. As we move forward, the emphasis on communal support continues to grow, with specialists advocating for the integration of social determinants of health (SDOH) education in care related to these conditions.
T2DSolutions is dedicated to cultivating a workforce that promotes health equity, ensuring that everyone has access to the support they require. As the landscape of diabetes management evolves, the role of community support remains a cornerstone for achieving improved health outcomes. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively managing diabetes is a journey that involves key metrics like the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) and Time in Range (TIR). GMI offers a real-time snapshot of average blood glucose levels through continuous glucose monitoring, empowering you to make informed decisions about your treatment. On the other hand, TIR highlights the percentage of time your blood glucose remains within a target range, emphasizing its role in minimizing complications and enhancing your overall well-being.
By embracing practical strategies—such as regular glucose monitoring, maintaining a balanced diet, and engaging in physical activity—you can work towards achieving a normal GMI. Remember, community support is vital in this journey. Connecting with others provides shared experiences, resources, and emotional backing that can significantly enhance your diabetes management outcomes.
As we witness the evolution of diabetes care, integrating innovative tools like CGM technology with strong community networks empowers you to take control of your health. Prioritizing these approaches not only fosters better physical health but also nurtures emotional resilience and quality of life. By embracing these strategies and cultivating connections, you can navigate your diabetes journey with confidence, achieving lasting health improvements. You're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is normal GMI and how is it calculated?
Normal GMI (Glucose Management Indicator) estimates average blood sugar levels over time using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data. It is calculated using the formula: GMI (%) = 3.31 + 0.02392 × (mean sugar level in mg/dL).
How does normal GMI differ from standard A1C tests?
Unlike standard A1C tests that reflect blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, normal GMI provides a more immediate insight into sugar control by tracking daily sugar variations.
Why is normal GMI significant for individuals managing diabetes?
Normal GMI helps individuals track daily sugar variations, which is essential for effective management of their diabetes condition, allowing for informed decisions about their control plans.
What should clinicians rely on when interpreting GMI?
Clinicians are encouraged to rely on mean sugar values directly obtained from CGM rather than solely on GMI, as individual physiological factors can influence GMI calculations.
What is the importance of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology?
The adoption of CGM technology has surged, enhancing patient care and improving health outcomes related to blood sugar management, as supported by research.
Can you provide an example of research related to GMI and diabetes management?
The HYPNOS study explored the relationship between CGM metrics and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and obstructive sleep apnea, highlighting the potential of CGM in understanding individual glucose patterns.
What is Time in Range (TIR) and why is it important?
Time in Range (TIR) indicates the percentage of time a person's blood sugar stays within a target range, typically between 70 and 180 mg/dL. Maintaining a high TIR is vital for reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications and improving overall health outcomes.
How does tracking TIR alongside GMI benefit individuals with diabetes?
Tracking both TIR and GMI empowers individuals to make timely adjustments to their treatment plans and lifestyle choices, fostering a proactive approach to managing their health.
What lifestyle changes can help improve TIR?
Individuals are encouraged to make dietary improvements such as reducing caloric intake, carbohydrates, and sugars while increasing protein and fiber to prioritize maintaining their TIR for optimal health outcomes.
How does T2DSolutions support individuals navigating their diabetes journey?
T2DSolutions provides valuable resources, guidance, and support to help individuals, especially those recently diagnosed, understand metrics like GMI and TIR and apply them effectively in their health strategies.
