Overview:
To achieve an A1C of 7.0, individuals with diabetes should focus on regular blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, medication adherence, increased physical activity, stress management, and building a support system. The article outlines practical steps and emphasizes the importance of these strategies, supported by research showing their effectiveness in managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Introduction
Understanding A1C levels is a fundamental aspect of effective diabetes management, serving as a key indicator of long-term blood sugar control. This article delves into the significance of A1C, a blood test that reflects average glucose levels over the past two to three months, and highlights the recommended target levels for adults with diabetes.
With rising diabetes diagnoses underscoring the urgency for effective management strategies, the article provides practical steps to achieve optimal A1C levels, including:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Dietary adjustments
- The importance of medication adherence
Additionally, it emphasizes the role of community support and resources available through T2DSolutions, designed to empower individuals on their diabetes journey. By exploring these critical components, readers can gain valuable insights into personalizing their diabetes management plans and improving their overall health outcomes.
Understanding A1C: What It Is and Why It Matters
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your new resource hub dedicated to empowering health management through education and community support. A1C, or glycosylated hemoglobin, is an essential blood test that assesses your average blood sugar amounts over the previous two to three months. It is represented as a percentage; higher percentages signify inadequate blood sugar control.
For most adults with high blood sugar, it is advised to maintain a target A1C of 7.0. This target is vital in reducing the risk of serious diabetes-related complications, including:
- Neuropathy
- Retinopathy
- Cardiovascular diseases
In fact, in 2017–2018, the yearly occurrence of identified cases of type 1 conditions in youth was estimated at 18,200 and 5,300 for type 2 conditions, highlighting the significance of tracking A1C values.
At T2D Solutions, we believe that comprehending your A1C levels, including A1C of 7.0, is essential for customizing your health care strategy and enabling you to make informed wellness choices. Our dedication to education and community assistance will equip you with the resources necessary to manage your health journey effectively. As we are just getting started, we encourage you to subscribe to stay updated on our offerings.
Recent studies have emphasized the predictive significance of A1C, demonstrating its usefulness in recognizing undiagnosed conditions and its function as a dependable indicator for evaluating control strategies. As mentioned in a recent study, 'A1C measure was effective and convenient for screening related to blood sugar issues,' further supporting its significance. Furthermore, a comparative research titled 'Comparison of A1C and FPG in Diabetes Screening' discovered that A1C values were a better predictor for new-onset hyperglycemia than fasting plasma glucose concentrations, enhancing the significance of A1C in managing the condition.
With T2D Solutions as your comprehensive resource, you can gain innovative insights and support tailored to managing Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes.
Practical Steps to Achieve an A1C of 7.0
-
Monitor Your Blood Sugar Regularly: It is crucial to track your blood sugar readings consistently using a glucometer. Regular monitoring allows you to gain insights into how various factors such as diet, physical activity, and medications influence your blood glucose. Aim to check your levels before meals and a couple of hours after eating to establish patterns and inform future decisions. Significantly, 94.2% of patients underwent a blood test to check for A1C 7.0, emphasizing the necessity of regular monitoring in blood sugar control. This monitoring can be further supported by resources available on T2 Solutions, which aims to educate and empower patients through informational articles and tools.
-
Adopt a Balanced Diet: Emphasize a diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables. Reducing refined sugars and processed foods is essential for managing your blood sugar effectively. Collaborating with a registered dietitian can be beneficial to develop a personalized meal plan that suits your preferences while meeting your nutritional needs. As observed by specialists in the area, balanced diets are essential for controlling blood sugar levels. Andrew D Morris, a senior lecturer, emphasizes that all authors involved in research on blood sugar conditions agree on the importance of collaborative care in achieving optimal health outcomes, a principle that T2DSolutions embodies in its mission. T2DSolutions also includes meal planning resources and recipes designed for diabetes care.
-
Manage Your Medications: Adhere strictly to your prescribed medication regimen. If you have concerns regarding side effects or the effectiveness of your medication, communicate these with your healthcare provider. They may recommend dosage adjustments or alternative medications to help you effectively achieve your A1C 7.0 target. T2DSolutions provides information on medication management and access to expert consultations to assist you in this process.
-
Increase Physical Activity: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week, which could include activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises twice a week can enhance insulin sensitivity and overall well-being, contributing positively to your blood sugar control. Resources available on T2DSolutions will guide you on how to integrate exercise into your routine effectively, including workout plans and community challenges.
-
Stay Hydrated and Limit Alcohol: Maintaining proper hydration by drinking plenty of water throughout the day is vital, as dehydration can adversely impact blood sugar. If you choose to consume alcohol, do so in moderation and always with food to mitigate the risk of hypoglycemia.
-
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can significantly affect blood sugar rates. It is beneficial to engage in stress-reducing practices such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises. Pursuing hobbies or social activities you enjoy can also serve as effective stress relievers. T2DSolutions offers community support to help you manage stress through shared experiences and resources, including forums and group activities.
-
Regular Check-Ups: Arrange regular visits with your healthcare provider to assess your A1C 7.0 levels and review your care strategy. Routine check-ups are essential for making timely adjustments to your treatment, thereby maintaining optimal diabetes control. The case study titled 'ABCs of Diabetes Management' emphasizes that only 11.1% of adults met all criteria for A1C, blood pressure, cholesterol, and smoking, illustrating the difficulties encountered in attaining optimal A1C values, such as A1C 7.0, and reinforcing the necessity for diligent management strategies. T2DSolutions aims to provide the information and support you need to navigate these challenges effectively, including access to case studies and success stories from other patients.
The Role of Carbohydrate Counting
Carbohydrate counting is a vital strategy for managing blood sugar concentrations effectively in individuals with diabetes. This method includes monitoring the amount of carbohydrates taken in meals and snacks, aiding in stabilizing blood glucose. To begin, familiarize yourself with the carbohydrate content of common foods, as this foundational knowledge is crucial.
It is recommended to maintain a consistent carbohydrate intake at each meal, which can contribute significantly to stabilizing blood sugar levels. Utilizing food labels, carbohydrate counting applications, or a comprehensive nutrition database can facilitate accurate assessment of your carbohydrate intake. Furthermore, a registered dietitian can provide invaluable assistance in developing a personalized carbohydrate plan tailored to achieve an A1C 7.0.
Recent studies, including those by Bishop et al., have discovered that patients with blood sugar issues often misestimate their carbohydrate intake, which has been linked to a higher level of A1C 7.0. This emphasizes the necessity of accurate counting. Additionally, a real-world assessment titled 'Personalized Nutritional Recommendations Based on Glycemic Responses' found that personalized recommendations improved glycemic metrics and patient-reported outcomes in individuals with type 2.
By embracing these practices, patients can enhance their condition oversight and improve overall health results. For additional resources and assistance in carbohydrate counting and health oversight, visit T2D Solutions, where you can discover tools and community support customized to your needs.
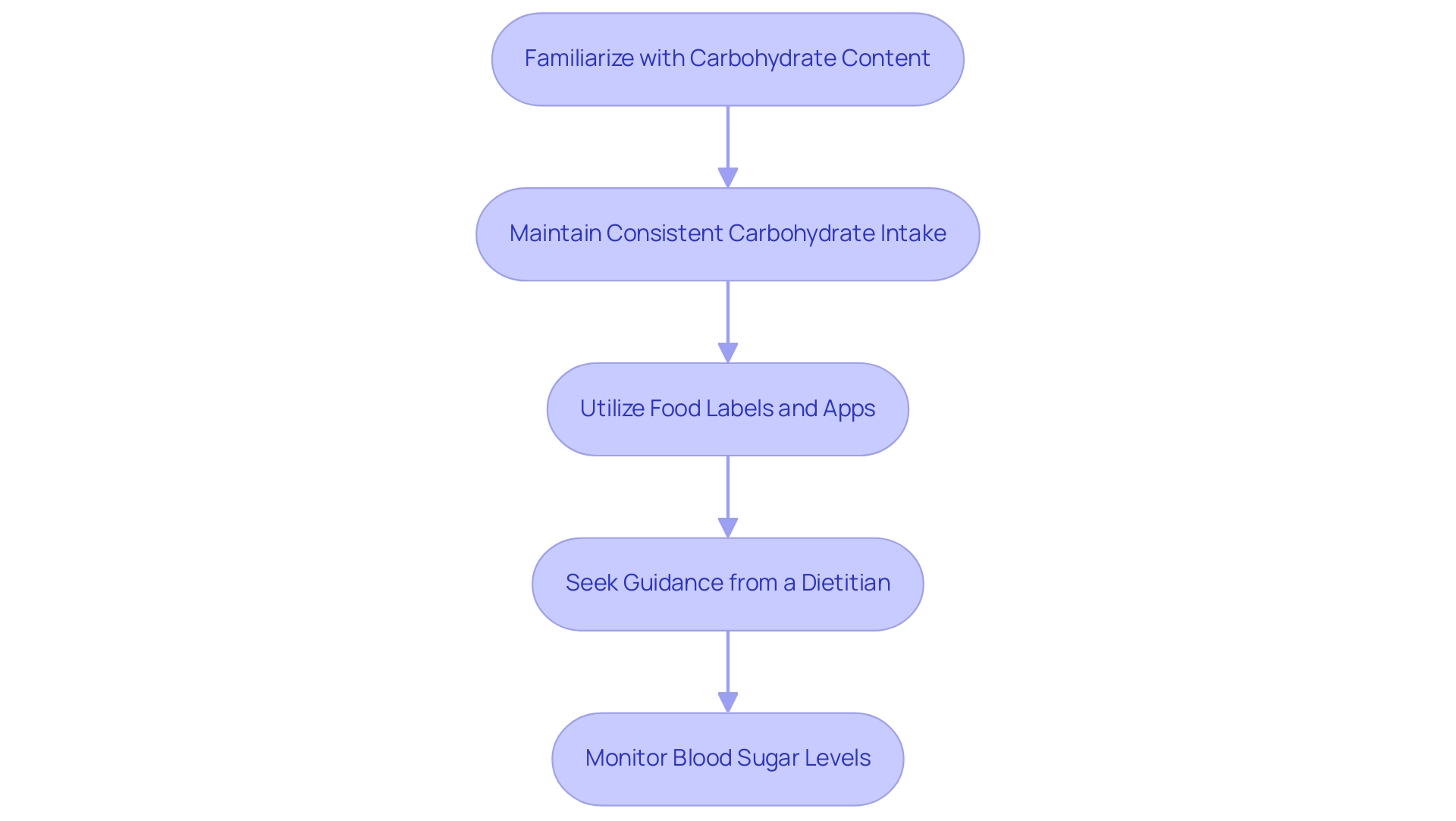
Incorporating Regular Physical Activity
Consistent physical exercise is essential for controlling blood sugar by reducing glucose amounts and enhancing insulin responsiveness. The current guidelines recommend engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly, including activities such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Additionally, it is advisable to incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week.
This approach not only builds muscle mass but also enhances glucose metabolism, which is essential for effective management of blood sugar levels, particularly in achieving A1C 7.0. Beginning with small, attainable objectives—like a daily 10-minute walk—can encourage a gradual rise in activity, making the process more manageable and sustainable. Studies show that for women, a physical activity rate of 600 METs is linked to a 25% reduced occurrence of blood sugar issues compared to inactivity.
As highlighted in recent research, increased amounts of physical activity are linked to a lower risk of developing diabetes-related conditions, which can help in achieving an A1C 7.0 level, underscoring the significance of an active lifestyle. Furthermore, the current findings provide clear scientific evidence that higher levels of physical activity are associated with a lower occurrence of A1C 7.0. It is also important to note that exercise-induced hyperglycemia can occur, particularly in individuals with type 1 conditions, and monitoring blood ketones is crucial before engaging in physical activity.
By adhering to these exercise recommendations, individuals can significantly improve their health outcomes and overall well-being. Furthermore, T2DSolutions will act as a valuable asset for newly diagnosed patients, offering continuous support and information on effective health control strategies, including the significance of physical activity. The economic consequences of handling diabetes are considerable, as additional healthcare expenses per individual have risen from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022, underscoring the significance of efficient control strategies.
Understanding the Importance of Medication Adherence
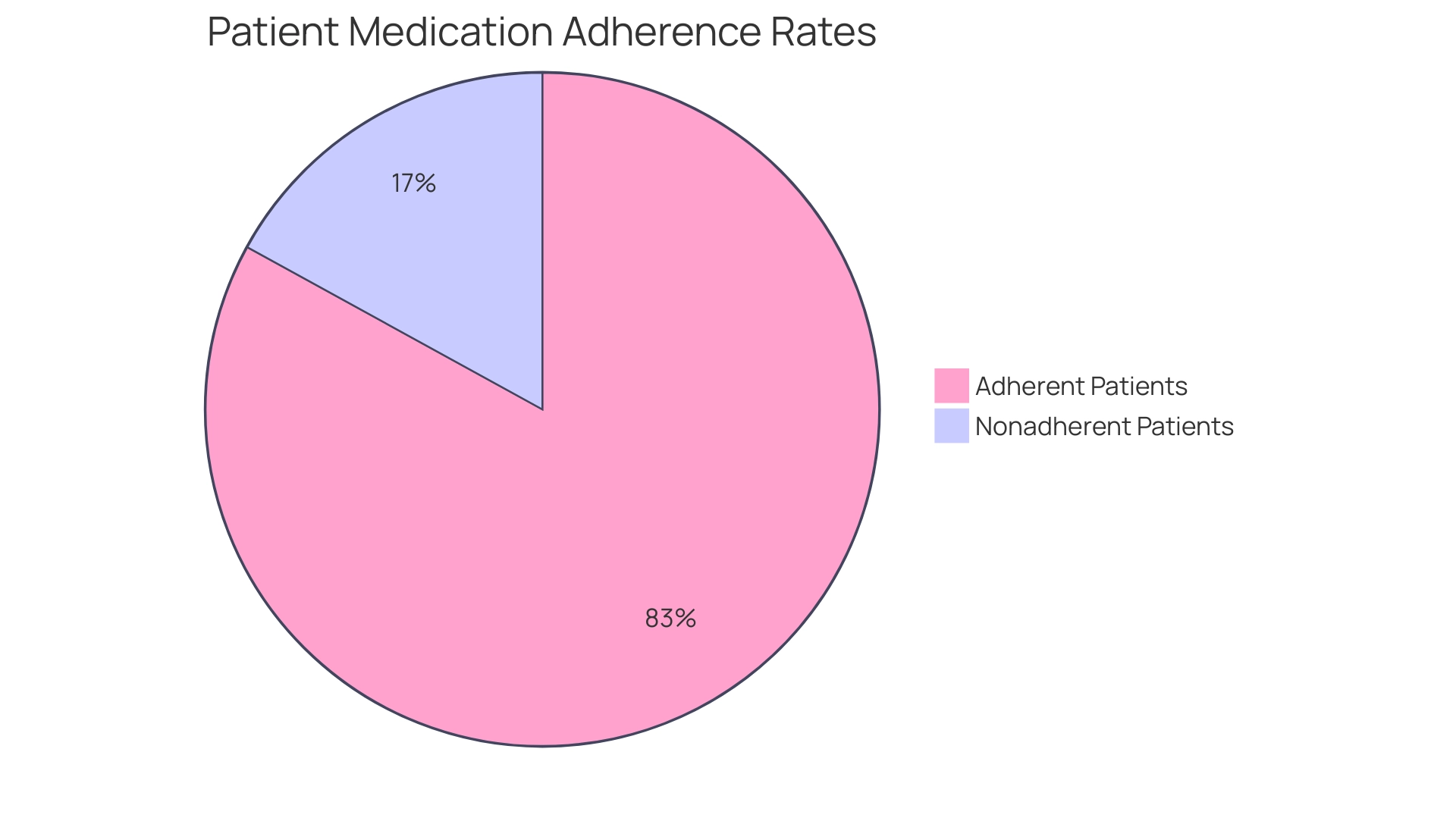
Following prescribed medications for managing blood sugar is essential for achieving and maintaining optimal levels. Research indicates that adherence rates vary significantly among patients, with studies revealing that:
- 125,404 patients (83.0%) were treated by primary care providers among adherent patients,
- 54,003 patients (80.1%) among nonadherent patients.
To enhance medication adherence, consider utilizing reminders on your smartphone or employing a pill organizer to structure your intake routine.
Should you encounter side effects or have concerns regarding your medications, it is crucial to engage in a dialogue with your healthcare provider. They can modify your treatment plan to better align with your individual needs. A case study titled 'Type of Diabetes Medication and Adherence' showed that adherence rates were compared between individuals taking oral hypoglycemic agents and those on insulin, with insulin users exhibiting significantly better adherence, evidenced by a p-value of 0.015.
Venkatarao Epari, a specialist in community medicine, highlights the significance of medication adherence, asserting that 'effective control of blood sugar necessitates not only medication, but a dedication to a holistic approach.' Furthermore, T2DSolutions is introducing a new resource center focused on informing patients about Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar control. This platform will offer a variety of educational resources, including articles, webinars, and community forums, designed to support patients in overcoming common challenges related to medication adherence.
By offering tailored approaches and a nurturing community, T2DSolutions seeks to enable patients to take charge of their health care. Remember, medication is just one part of a thorough strategy for controlling blood sugar; effective regulation of the condition also requires dietary modifications and consistent physical activity to attain the best results.
Building a Support System
Managing blood sugar levels effectively often requires more than just medical intervention; it necessitates a strong network. Research shows that five out of seven studies utilizing community and peer assistance programs have resulted in significant decreases in HbA1c levels, with many participants achieving an a1c 7.0, highlighting the tangible advantages of social backing in managing blood sugar. In fact, a meta-analysis conducted by Wheeler JA et al. has emphasized the advantageous impacts of volunteering for older adults, further stressing the significance of social assistance systems.
Becoming part of a health assistance group, whether face-to-face or virtual, allows individuals to connect with others who have similar experiences and challenges. Interacting with family and friends is equally important; informing them about the condition can improve their comprehension and capacity to assist your journey.
This dual approach not only provides emotional encouragement but also fosters accountability in managing your condition. As Wahyu Sukma Samudera, an expert in the Master of Nursing Study Program, highlights, community and peer assistance programs can significantly impact self-care behaviors and fasting blood glucose levels in individuals with Type 2 metabolic disorder. A systematic review published in Diabetes Medicine in 2012 further reinforces the effectiveness of peer assistance on health outcomes related to achieving a1c 7.0 in diabetes.
Real-world examples demonstrate that participants in such programs, like the one involving 79 eligible patients, successfully retained peer advocates, thereby establishing a continuous assistance network. This retention is directly linked to enhanced control of blood sugar levels, demonstrating the essential function of assistance systems. Therefore, seeking out and actively participating in diabetes support groups is a vital step in your diabetes management journey.
Conclusion
Maintaining optimal A1C levels is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. Understanding the significance of A1C, which reflects average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, allows individuals to tailor their management strategies effectively. The recommended target A1C level of 7.0% serves as a benchmark to minimize the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Achieving this target involves a multifaceted approach, including:
- Regular blood sugar monitoring
- Dietary modifications
- Medication adherence
- Increased physical activity
Emphasizing a balanced diet, managing carbohydrate intake, and maintaining an active lifestyle are crucial steps that can lead to significant improvements in blood glucose control. Furthermore, addressing stress and ensuring consistent healthcare follow-ups play vital roles in sustaining these health outcomes.
Community support and resources, such as those offered by T2DSolutions, further empower individuals in their diabetes journey. By connecting with peers and accessing educational materials, patients can enhance their understanding and adherence to their management plans. Ultimately, prioritizing A1C management through informed decisions and community engagement can lead to better health outcomes and improved quality of life for those living with diabetes.



