Overview
The main focus of this article is to guide you in calculating A1C for effective diabetes management. Understanding how to calculate A1C is vital; it involves averaging your blood glucose readings over a two to three-month period using a specific formula. This process is not just about numbers—it's about empowering you to take control of your health.
Calculating A1C is important because it guides treatment and lifestyle adjustments, helping to prevent complications associated with diabetes. You're not alone in this journey; many have walked this path and found ways to thrive. We are here to support you every step of the way as you navigate these important aspects of your health.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding the A1C test is pivotal for ensuring optimal health outcomes. This essential diagnostic tool measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, offering a comprehensive view of your glycemic control. With the rising prevalence of diabetes globally, including millions affected in Germany alone, the importance of regular A1C monitoring cannot be overstated. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by this information, but grasping how A1C levels correlate with average blood glucose—and the factors influencing them—can empower you to make informed decisions about your treatment plan.
As healthcare professionals emphasize the significance of personalized A1C goals, this knowledge can truly make a difference in your diabetes management journey. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. By taking proactive steps, you can improve your quality of life and feel more in control of your health. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Understanding the A1C Test: Importance and Purpose
The A1C test, often referred to as the hemoglobin A1C test, is a vital tool in managing diabetes. It helps assess average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, expressed as a percentage. This percentage indicates the proportion of hemoglobin molecules in the blood that have glucose attached. Understanding this test is crucial for managing blood sugar effectively, enabling both healthcare professionals and patients to make informed choices about treatment strategies.
Consistent tracking of A1C values is essential for preventing diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular conditions and nerve damage. Research shows that maintaining A1C levels below 7% significantly reduces the risk of these issues. In Germany, where over 7.2 million individuals were diagnosed with diabetes as of 2014, effective management strategies like A1C testing are critical for improving health outcomes in such a large population.
Moreover, standardizing HbA1c measurement is vital for obtaining reliable results when calculating A1C. The analytical variation in glucose measurement is less than the biological variation, which highlights the challenges in achieving accurate A1C results across different laboratories and instruments. This underscores the importance of consistent testing methods in managing blood sugar effectively.
Real-world examples illustrate the positive impact of A1C testing on patient outcomes. For instance, a case study revealed that 31.9% of adults with diabetes were physically inactive, defined as engaging in less than 10 minutes of moderate or vigorous activity per week. This inactivity emphasizes the need to incorporate physical activity into blood sugar management plans, which can be tailored by using A1C results to create individualized strategies.
Expert opinions further reinforce the significance of the A1C test. Experts like Vaag emphasize that improving glycemic management in individuals with type 2 diabetes may be more critical than addressing dyslipidemia for preventing both microvascular and macrovascular complications. This perspective highlights that calculating A1C is not just a diagnostic tool but a cornerstone of comprehensive care for those managing blood sugar conditions.
In conclusion, understanding the A1C test and calculating A1C is essential for patients who have recently received a diagnosis. It serves as a key indicator of blood sugar control, guiding lifestyle changes and treatment adjustments that can lead to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. T D Solutions is dedicated to providing resources and support for patients navigating their health journey, ensuring you have the information needed to appreciate the importance of A1C testing and its implications for your well-being.
How the A1C Test Works: Mechanisms and Measurements
Calculating A1C is an essential tool in managing blood sugar levels. This test measures the percentage of glucose that has bonded to hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells. As blood sugar levels increase, more glucose attaches to hemoglobin, which is crucial for determining A1C percentages. Typically, this test is performed using a blood sample drawn from a vein or via a finger prick, with results expressed as a percentage.
Elevated A1C percentages indicate that blood sugar management may not be adequate, making the calculation of A1C vital for effectively controlling the condition.
For instance, an A1C level of 6.5% or higher suggests diabetes, while values between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes. Understanding these thresholds is particularly important for newly diagnosed patients, as it aids in interpreting results and making informed lifestyle adjustments. Recent studies highlight that maintaining A1C levels of 6.5% or lower is especially critical for pregnant women with Type 1 diabetes, underscoring the test's significance across different patient demographics.
As noted by the Cleveland Clinic, whether you’ve been living with this condition for years or are newly diagnosed, having experts you can trust is essential.
At T2DSolutions, we strive to be that trusted resource. Our platform is dedicated to providing comprehensive information on blood sugar control, including the importance of the A1C test. The mechanism behind calculating A1C is straightforward yet effective: it reflects average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, offering a long-term view of blood sugar management.
This information is particularly relevant considering that around 31.9% of adults with this condition are categorized as physically inactive. This highlights the need for lifestyle changes that can positively impact A1C levels. Furthermore, women who experienced gestational issues should be evaluated for glucose imbalance no later than 12 weeks after giving birth, emphasizing the importance of calculating A1C. By understanding how the A1C test works and its implications, individuals can take proactive steps in their health journey.
Stay informed with the latest resources and information by subscribing to T2DSolutions. We are dedicated to supporting you on your health journey.
A1C Levels and Average Blood Glucose: What You Need to Know
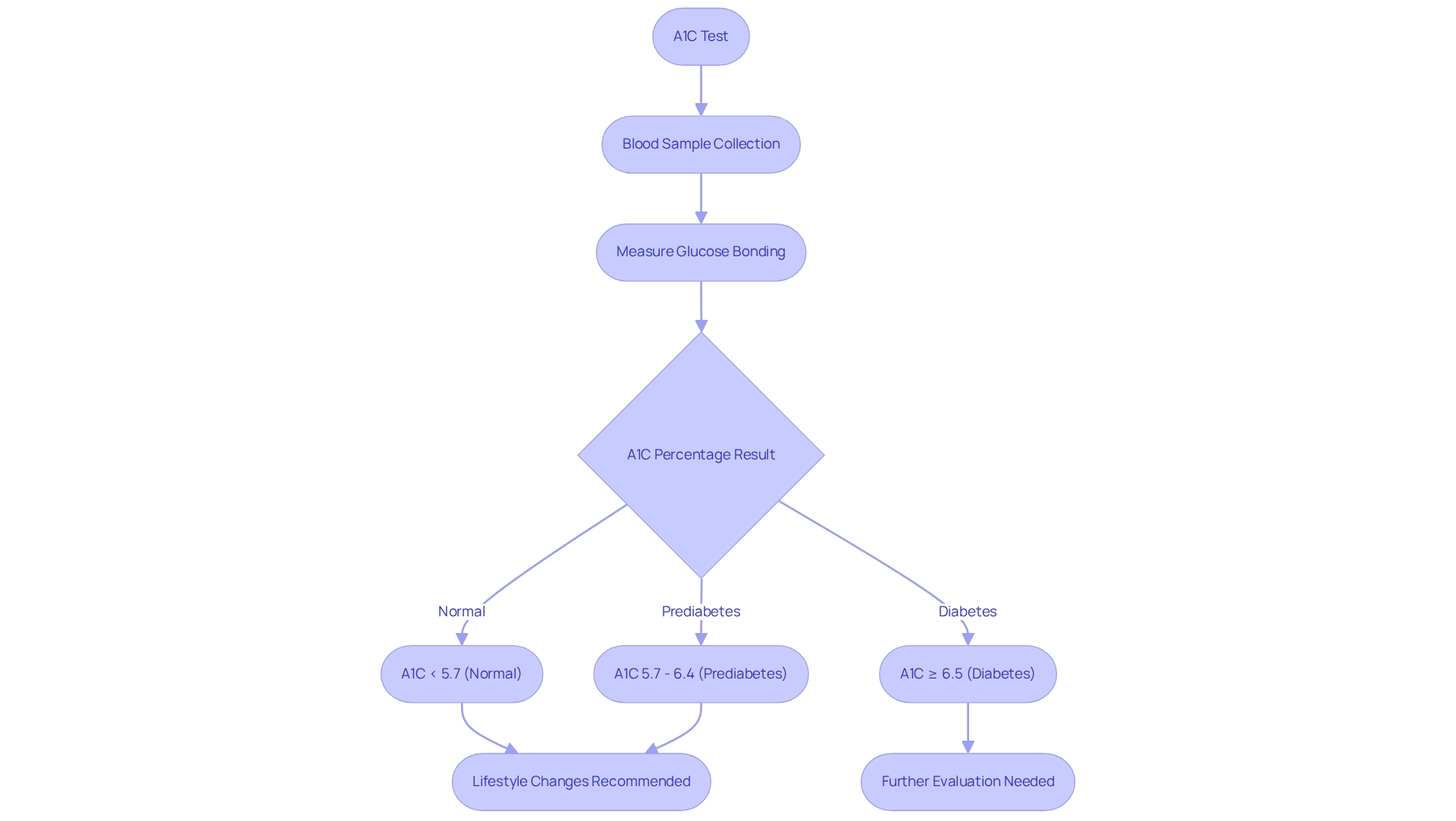
A1C readings are fundamentally connected to average blood sugar readings, making this relationship vital for effective management of your condition. The American Diabetes Association outlines a straightforward conversion formula: estimated average glucose (eAG) in mg/dL = (28.7 x A1C) - 46.7. For example, an A1C of 7% relates to an average blood glucose concentration of roughly 154 mg/dL.
This connection isn't just theoretical; it has important implications for individuals managing their blood sugar levels. By understanding how A1C readings relate to blood sugar management over time, you can make informed choices regarding your treatment approaches.
At T2DSolutions, we strive to equip you, especially if you’re newly diagnosed, with the information and tools essential for effective health control. Consistent tracking of both A1C and daily blood glucose measurements is crucial for calculating A1C and provides a thorough perspective on blood sugar management. Recent research has shown that individuals who actively engage in calculating A1C readings alongside their daily measurements tend to achieve better overall management of their condition.
For instance, a study involving 507 patients highlighted the importance of point-of-care testing (POCT) for HbA1c, which allows for timely adjustments in treatment based on rapid results. However, it’s important to note that the study had limitations, including a small sample size and potential selection bias due to patient characteristics. The findings indicated a significant degree of agreement between POCT HbA1c measurements and laboratory tests, reinforcing the reliability of these methods in clinical settings.
As mentioned in the research publication, 'GMI derived by isCGM or eAG derived by conventional SMBG systems, along with the POCT-HbA1c measurements, demonstrated a strong degree of agreement; hence, we suggest them as possible methods for diabetes monitoring, particularly when a quick result is required or with individuals experiencing uncontrolled diabetes or undergoing intensive insulin therapy.'
Moreover, current statistics reveal that A1C levels can provide insights into average blood glucose levels across different patient populations. For instance, an A1C of 6% typically correlates with an average blood glucose of about 126 mg/dL, while an A1C of 8% corresponds to approximately 183 mg/dL. Understanding these correlations empowers you to set realistic goals for your blood sugar management.
Expert opinions further emphasize the significance of this relationship. Endocrinology experts recommend regular A1C testing for calculating A1C as a method to evaluate long-term glucose management, especially for individuals on intensive insulin therapy or facing uncontrolled blood sugar levels. By integrating A1C monitoring into your routine, you can enhance your understanding of your condition and improve your overall health outcomes.
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to offering the resources and assistance you need to manage your journey effectively. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Step-by-Step Guide: Calculating A1C from Average Glucose
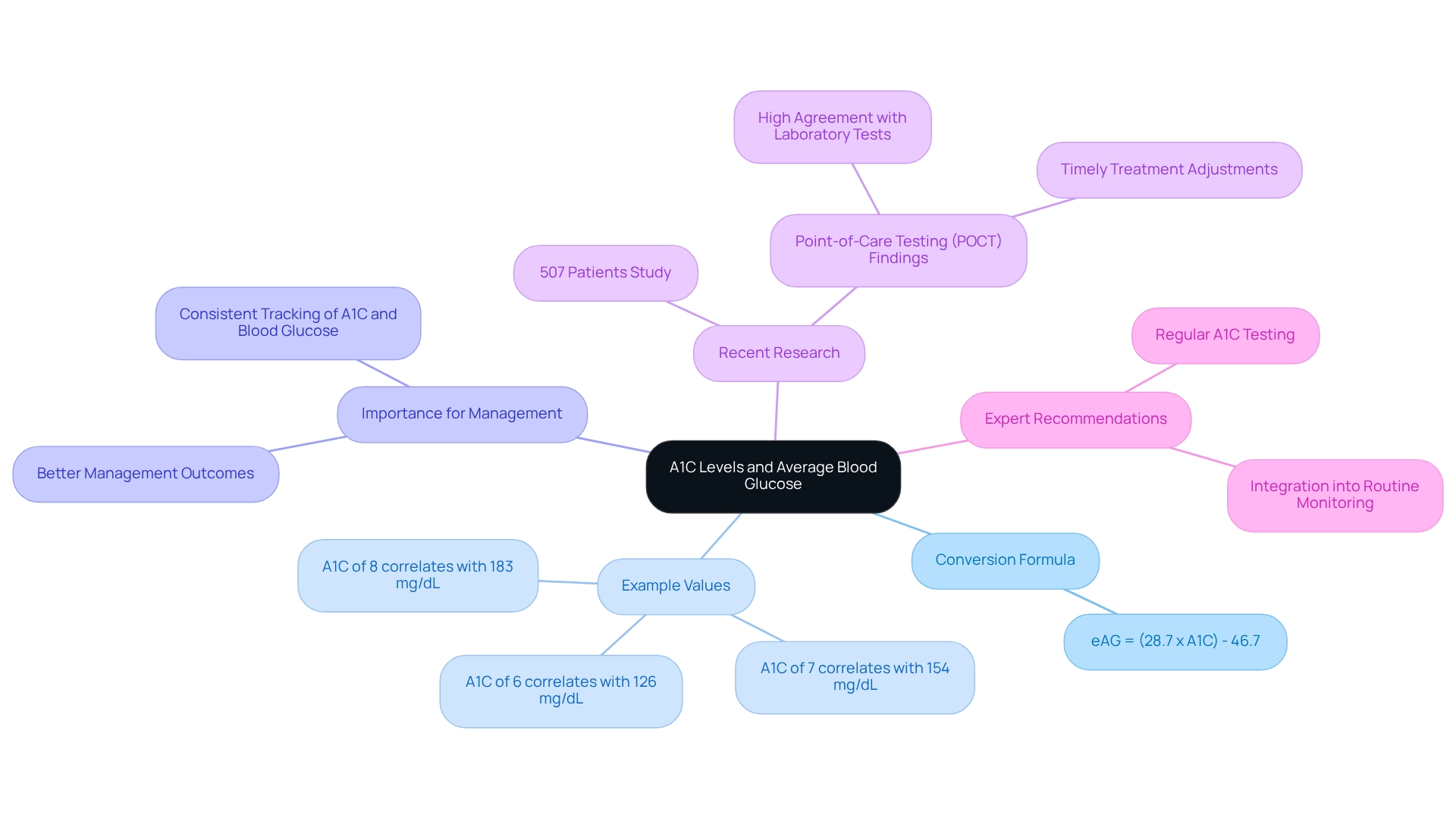
To calculate your A1C from average glucose readings, please follow these supportive steps:
-
Gather Your Average Glucose Data: Start by collecting your daily blood glucose readings over the last two to three months. Using a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor will help you gather the most accurate data.
-
Calculate the Average: Next, sum all your glucose readings and divide this total by the number of readings you have. This average is crucial for understanding your overall blood sugar control and can help you feel more in control of your health.
-
Use the Conversion Formula: Now, apply the formula A1C (%) = (Average Glucose (mg/dL) + 46.7) / 28.7. For example, if your average glucose is 150 mg/dL, you would calculate it as (150 + 46.7) / 28.7, resulting in an A1C of approximately 6.9%.
-
Interpret Your Results: Finally, compare your calculated A1C with the recommended targets. A good starting point for average glucose is under 154 mg/dL, with a standard deviation under 50 mg/dL. Regularly assessing your A1C can assist you in tracking your condition and making important adjustments to your treatment strategy.
Understanding your A1C is vital, as it reflects your average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. This metric is essential for evaluating your health control and can empower you to make informed choices about your well-being. As Richard M. Bergenstal, MD, emphasizes, "The overall objective is to make or keep the curve as narrow and flat as possible within the designated target range."
It’s important to recognize the significant prevalence of diabetes, with 1.2 million Americans newly diagnosed in 2021. This highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions and education. Moreover, the average medical costs for individuals with diagnosed health conditions related to diabetes are 2.6 times greater than they would be without the illness, underscoring the financial implications of effective management. Additionally, blood glucose test outcomes may vary during pregnancy, with elevated readings early on suggesting possible type 1 or type 2 issues.
By remaining informed and proactive, you can effectively manage your condition and enhance your quality of life.
At T2DSolutions, we are here to support newly diagnosed patients. Our commitment includes providing educational materials, community support, and tools for calculating A1C and tracking glucose levels. Stay connected with us for more resources and support on your health journey.
Setting A1C Goals: Recommended Targets for Diabetes Management
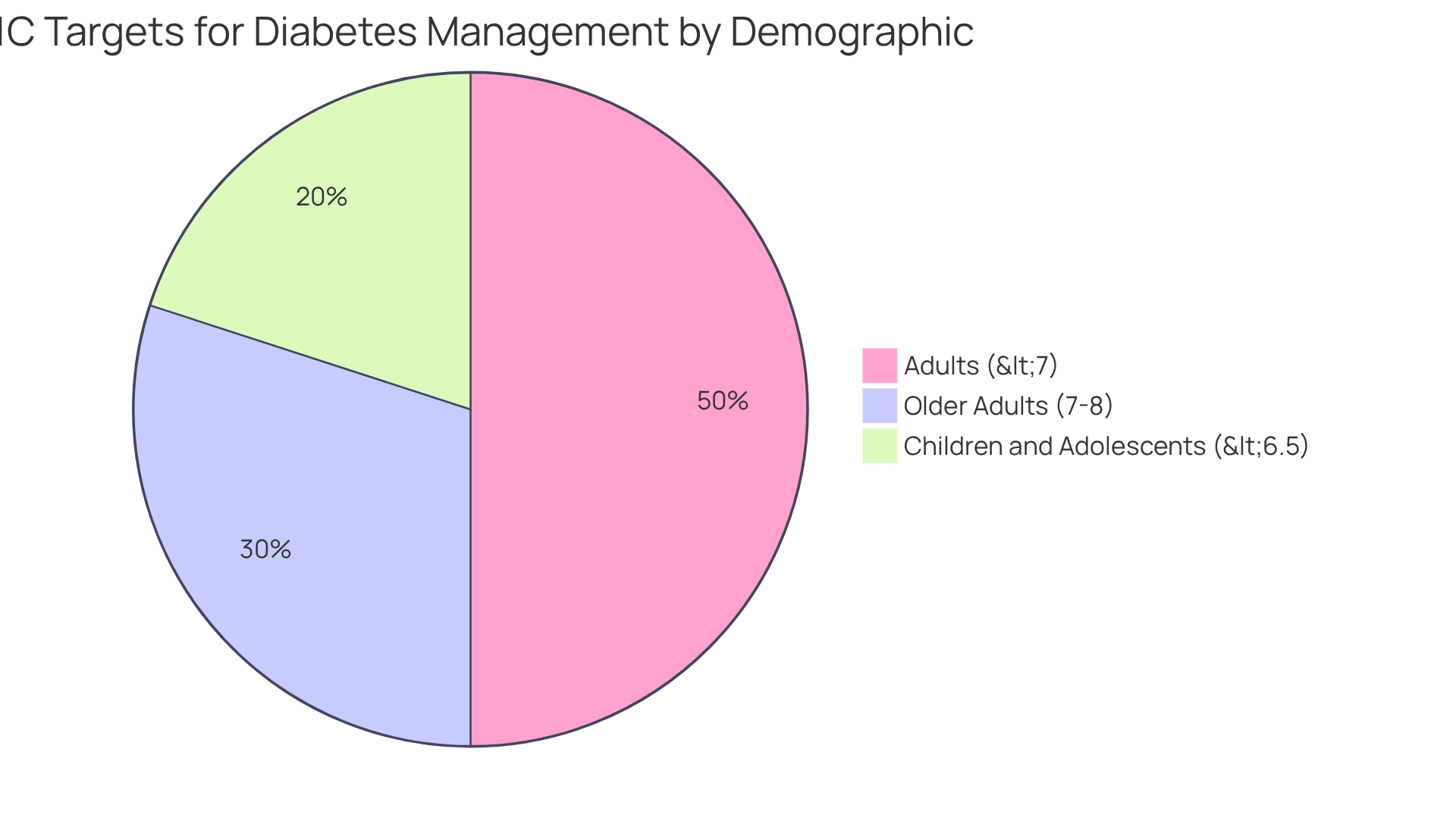
Calculating A1C targets is essential for effectively managing diabetes, and it's important to understand how these targets can vary based on individual circumstances. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) offers specific recommendations tailored to different demographics:
- For most adults with diabetes: An A1C level of less than 7% (53 mmol/mol) is generally considered optimal for managing diabetes effectively.
- For older adults or those with complex health issues: A more lenient target of 7% to 8% may be appropriate, tailored to individual health circumstances and preferences.
- For children and adolescents: An A1C goal of less than 6.5% (48 mmol/mol) is often recommended to ensure optimal health outcomes during these formative years.
These targets should be personalized, taking into account your unique health conditions, risk factors, and treatment plans. For instance, a recent case study titled "Trends in Incidence of Diagnosed Diabetes Among Adults" highlighted that while the overall incidence of diagnosed conditions among U.S. adults has remained stable, variations exist across different counties. This underscores the need for customized public health interventions that resonate with your specific situation.
It's also important to recognize that severe hypoglycemia was significantly more likely in participants assigned to the intensive glycemic control arm across various trials. This emphasizes the risks associated with different management strategies, reminding us that every journey is unique.
Regular consultations with healthcare providers are crucial for adjusting these goals as needed. The ADA stresses the importance of shared decision-making in this process, allowing for a collaborative approach that enhances your engagement and self-efficacy. As Neda Laiteerapong observed, "Future research is required to examine the long-term impacts of establishing personalized glycemic goals in adults with this condition." This ensures that guidelines remain relevant and effective for varied patient groups.
At T2DSolutions, we are here to support you every step of the way. We strive to offer resources and assistance for individuals calculating A1C objectives, helping newly diagnosed patients understand and effectively manage their condition. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we are here to help you navigate these important decisions.
Factors Affecting A1C Levels: Lifestyle and Health Considerations
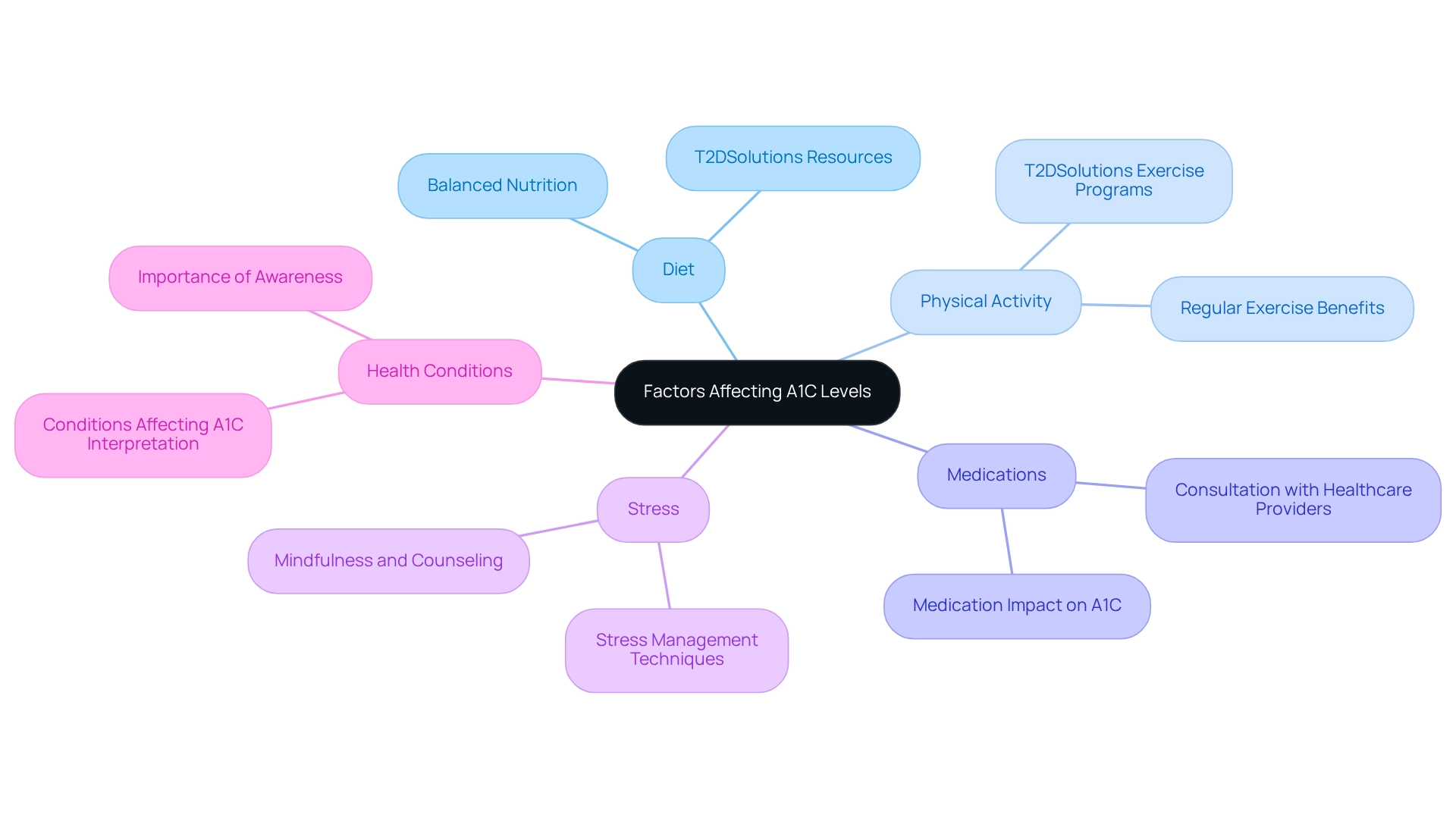
A range of factors can notably affect A1C values, which are essential for efficient diabetes management. Understanding these components can empower individuals to take proactive measures in their care:
-
Diet: A diet rich in sugars and carbohydrates can lead to increased blood glucose levels, subsequently raising A1C. Recent research highlights that dietary choices play a crucial role in managing A1C values, with balanced nutrition being vital for optimal health outcomes. T2DSolutions provides resources and advice on nutritious eating practices designed for managing blood sugar.
-
Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise is one of the most effective ways to lower blood sugar. Physical activity not only aids in calculating A1C but also contributes to overall well-being. Many patients who incorporate regular exercise into their routines report significant improvements in their A1C results. T2DSolutions offers exercise advice and programs tailored for individuals with diabetes.
-
Medications: Various diabetes medications can influence blood glucose regulation, thus affecting A1C readings. It’s important for patients to discuss their medication regimens and the significance of calculating A1C with healthcare providers to ensure optimal management strategies are in place. T2DSolutions can assist in understanding medication choices and their effects on A1C.
-
Stress: Increased stress can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, negatively impacting A1C. Managing stress through mindfulness, yoga, or counseling can be beneficial in maintaining stable glucose levels. T2DSolutions provides materials for stress management designed specifically for individuals managing diabetes.
-
Health Conditions: Certain health issues, such as anemia and kidney disease, can skew A1C results by affecting hemoglobin levels. Being aware of these conditions is crucial for accurate interpretation of A1C readings. Statistics reveal that nearly 47.4% of U.S. adults with diagnosed diabetes have an A1C value of 7.0% or higher, underscoring the importance of understanding and managing these influencing factors. Notably, an individual with blood sugar readings consistently around 154 mg/dL may have an A1C of 7%, emphasizing the need to calculate A1C values based on blood sugar levels. Additionally, a recent study identified limitations such as the lack of dietary pattern data and the necessity to evaluate mental and emotional conditions, which can affect HbA1c readings.
By understanding how diet, exercise, medications, stress, and health conditions influence A1C readings, individuals can make informed choices that enhance their control over their condition and overall quality of life, especially when calculating A1C. As R.A.P. highlighted, patients should discuss calculating A1C with their healthcare providers to improve their blood sugar management strategies. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; T2DSolutions is here to support you every step of the way.
Improving Your A1C: Practical Tips and Strategies
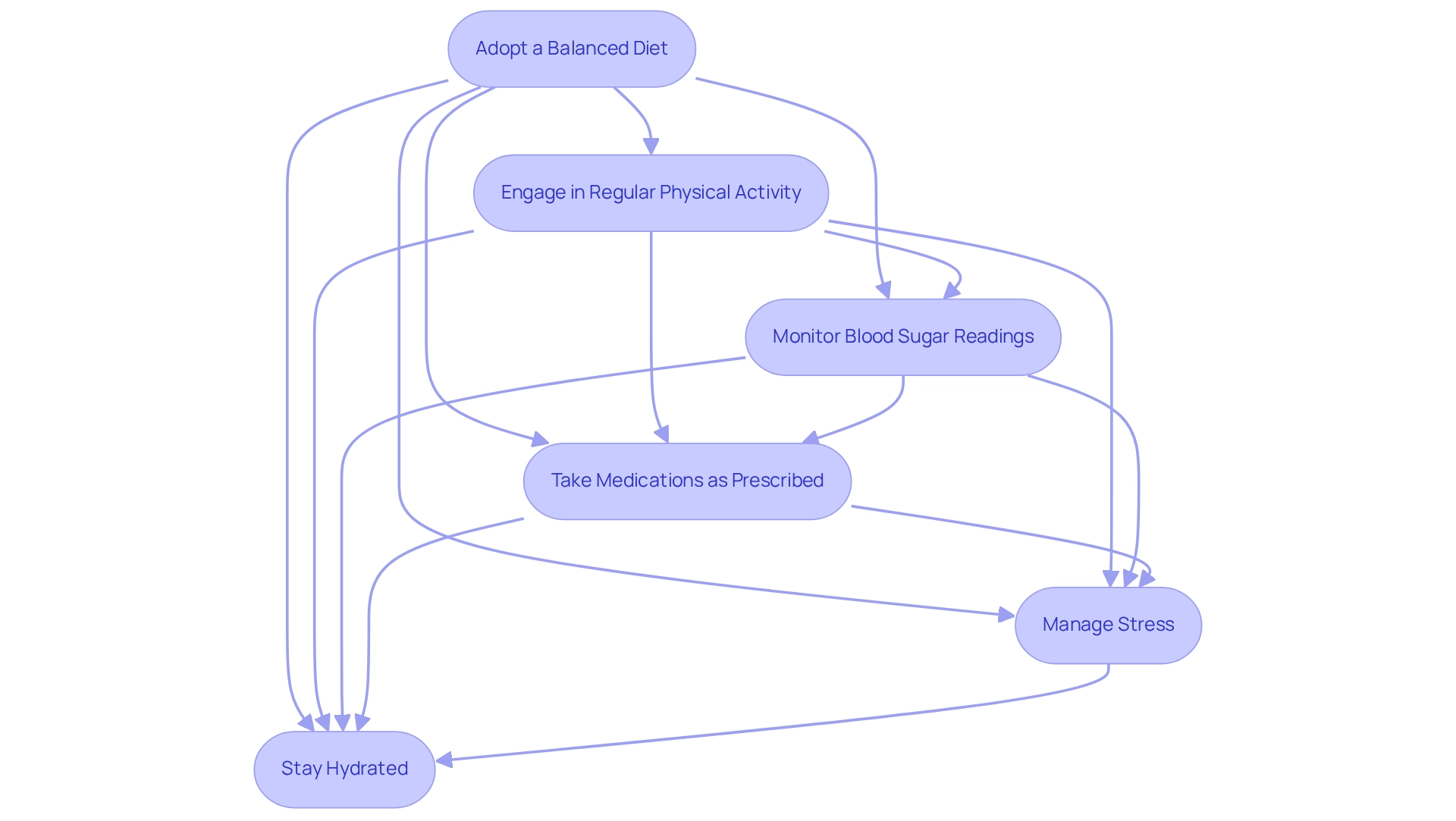
To effectively improve your A1C levels, consider implementing the following strategies, supported by T2DSolutions, your new resource hub for diabetes education and management:
-
Adopt a Balanced Diet: Prioritize whole foods such as fresh vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Reducing the intake of processed foods that are high in sugars and unhealthy fats can significantly impact your blood sugar control.
-
Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Activities such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming not only improve physical fitness but also aid in better blood sugar control.
-
Monitor Blood Sugar Readings: Regularly checking your blood glucose readings is crucial. This practice aids in calculating A1C by helping you understand how various foods and activities influence your A1C, allowing for more informed dietary and lifestyle choices.
-
Take Medications as Prescribed: Following your healthcare provider's advice concerning medications for blood sugar control is crucial for effective oversight. Consistency in medication can lead to improved A1C outcomes.
-
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact blood sugar readings. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help maintain emotional well-being and improve overall diabetes management.
-
Stay Hydrated: Consuming sufficient quantities of water is essential for sustaining optimal blood sugar concentrations. Proper hydration supports metabolic processes and can aid in better glucose regulation.
Applying these strategies can result in notable enhancements in calculating A1C readings over time. For instance, studies indicate that individuals who adopt a balanced diet and engage in regular physical activity can see a reduction in A1C levels, which can be assessed through calculating A1C, by as much as 1% to 2% within a few months. Moreover, the financial consequences of this condition emphasize the significance of efficient handling strategies; the total projected expenses related to this illness in the U.S. hit $413 billion in 2022, stressing the necessity for proactive actions to enhance health results and lower healthcare expenses.
As L. Jiang noted, "Manuscript preparation was supported in part by National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (R21DK108187, L. Jiang; and 1P30DK092923, S.M. Manson)." By concentrating on these useful suggestions and techniques for calculating A1C, individuals can make significant progress toward controlling their A1C levels.
It is also essential to recognize that managing this condition is a collective journey, emphasizing the importance of community and collaboration in achieving better health outcomes. T2DSolutions is here to support you on this journey.
The Importance of Regular A1C Monitoring: Staying on Track
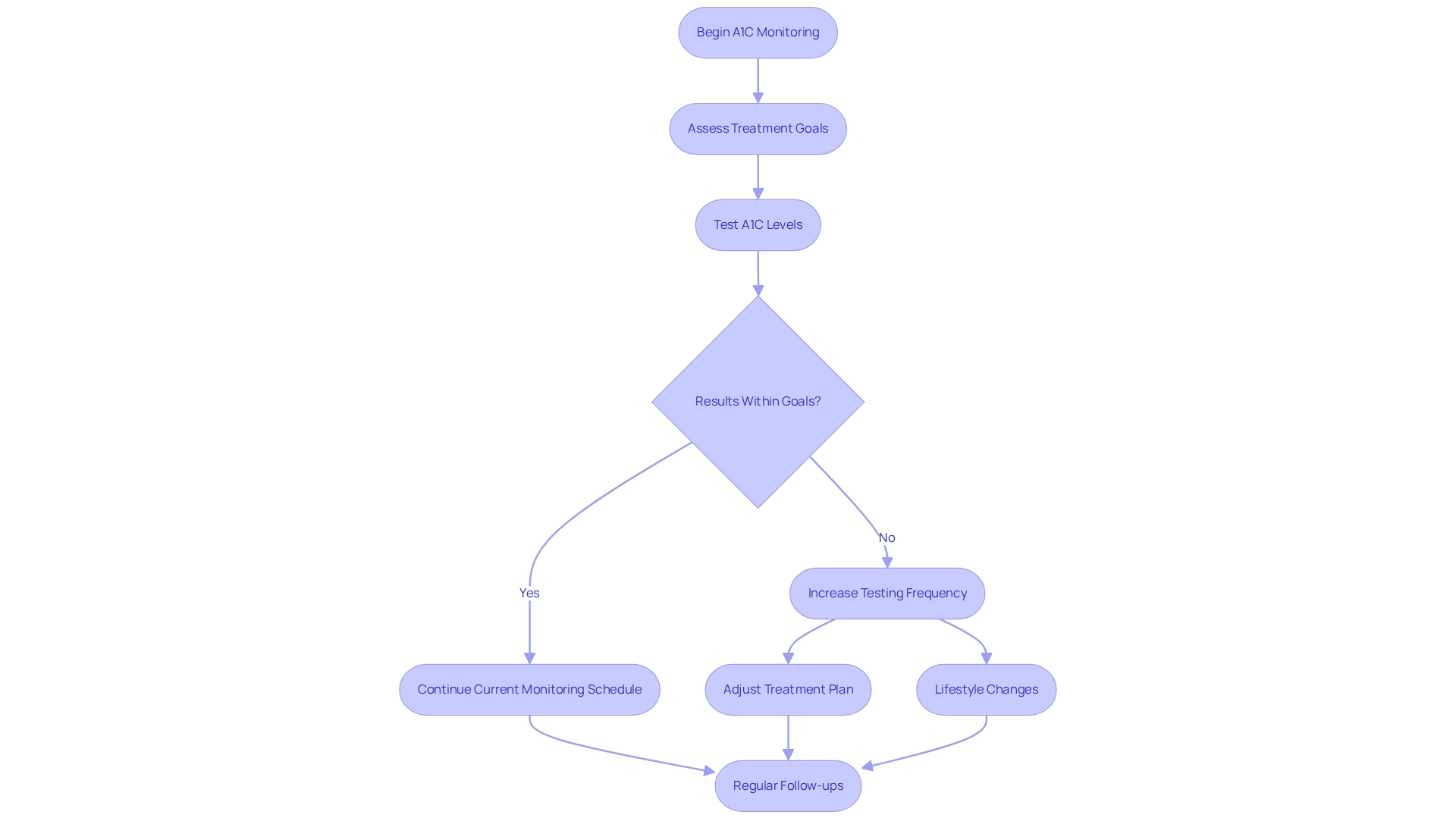
Frequent monitoring, especially calculating A1C, is essential for effective health oversight. It provides both individuals and healthcare professionals with a clear view of blood sugar regulation over time. At T2DSolutions, we understand how important this monitoring is, particularly for those who are newly diagnosed. The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals with diabetes consider having their A1C levels tested at least twice a year if they are meeting their treatment goals.
However, if your treatment plan changes or if you're having difficulty meeting your goals, more frequent testing is advisable. This proactive approach to monitoring, including calculating A1C, helps recognize trends in blood sugar readings, allowing for timely adjustments to treatment plans and lifestyle changes.
Statistics highlight the importance of regular A1C monitoring: approximately 39.5% of adults with diagnosed conditions have a non-HDL cholesterol measurement of 130 mg/dL or greater. This underscores the need for careful oversight to prevent complications associated with both cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Additionally, recent studies indicate that consistent A1C calculations can lead to significant improvements in overall management of diabetes. For example, research by Helminen et al. revealed that increased HbA1c concentrations could serve as an early indicator for clinical type 1 diabetes in genetically susceptible children, suggesting that tracking A1C figures can help identify at-risk individuals promptly.
Expert insights further emphasize the significance of calculating A1C through regular testing. Gregory J. Norman, a leading researcher in glucose management, noted that even among patients using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) who did not start insulin therapy, there was a notable improvement in A1C levels. He stressed that consistent monitoring can lead to better health outcomes, regardless of the treatment approach, highlighting the critical role of A1C calculations in effectively managing blood sugar levels.
With the increasing prevalence of diabetes, including 18,169 newly diagnosed cases of type 1 in children and adolescents under 20 during 2017-2018, T2 Solutions is dedicated to providing resources and support for A1C testing frequency in 2025, focusing on individualized care. Frequent evaluations are vital to ensure optimal control of blood sugar levels. By following these guidelines and prioritizing A1C calculations, you can significantly enhance your ability to manage your condition effectively and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
At T2DSolutions, we offer educational materials and support to help newly diagnosed patients navigate their diabetes management journey. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is essential for effective diabetes management and can significantly impact your overall health. By regularly monitoring your A1C levels, which reflect average blood sugar control over the past two to three months, you can make informed decisions about your treatment plan. The A1C test not only helps in assessing your current glucose control but also guides you in making lifestyle changes, adjusting medications, and setting personalized goals.
Key factors influencing A1C levels include:
- Your diet
- Physical activity
- Medication adherence
- Stress management
- Any underlying health conditions
By adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress effectively, you can positively influence your A1C levels. Understanding the relationship between A1C and average blood glucose levels empowers you to establish realistic targets and take proactive steps in your diabetes management journey.
In a world where diabetes prevalence continues to rise, the importance of regular A1C monitoring cannot be overstated. Timely testing allows for adjustments in your treatment and helps prevent complications associated with diabetes. As experts emphasize the significance of personalized A1C goals, it becomes clear that informed decisions and a proactive approach to health can lead to an improved quality of life. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; by leveraging available resources and support, you can navigate your diabetes journey with confidence and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C test, measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, expressed as a percentage. It is crucial for managing diabetes, as it helps healthcare professionals and patients make informed treatment decisions and prevent complications.
How does the A1C percentage relate to blood sugar management?
The A1C percentage indicates the proportion of hemoglobin molecules in the blood with glucose attached. Maintaining A1C levels below 7% significantly reduces the risk of complications such as cardiovascular issues and nerve damage.
What are the typical A1C level thresholds for diabetes and prediabetes?
An A1C level of 6.5% or higher suggests diabetes, while levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes. Understanding these thresholds is essential for newly diagnosed patients to interpret their results and adjust their lifestyle accordingly.
How is the A1C test performed?
The A1C test is typically performed using a blood sample drawn from a vein or via a finger prick. The results are then expressed as a percentage.
Why is standardization of HbA1c measurement important?
Standardizing HbA1c measurement is vital for obtaining reliable results, as the analytical variation in glucose measurement is less than the biological variation. This consistency is crucial for effective blood sugar management across different laboratories and instruments.
What role does physical activity play in managing A1C levels?
Physical activity is important for managing blood sugar levels. A study showed that 31.9% of adults with diabetes were physically inactive, highlighting the need to incorporate exercise into blood sugar management plans.
What do experts say about the significance of the A1C test?
Experts emphasize that improving glycemic management, particularly in individuals with type 2 diabetes, is critical for preventing complications. The A1C test is seen as a cornerstone of comprehensive care for managing blood sugar conditions.
How can patients benefit from understanding their A1C results?
Understanding A1C results helps patients make informed lifestyle changes and treatment adjustments, leading to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life.
