Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, A1C testing stands as a pivotal tool for assessing long-term blood sugar control. This critical metric not only offers insights into an individual's average glucose levels over the past two to three months but also serves as a barometer for potential complications related to diabetes.
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, understanding the implications of A1C results has never been more essential. From guiding treatment adjustments to empowering patients with knowledge, the significance of regular A1C monitoring cannot be overstated.
This article delves into the importance of A1C, the relationship between A1C and average blood glucose levels, and the various factors influencing these readings, providing a comprehensive overview for individuals navigating their diabetes journey.
Understanding A1C: Importance and Implications for Diabetes Management
A1C, also known as glycated hemoglobin, is a crucial blood test that provides a snapshot of the A1C to blood sugar conversion, reflecting average blood sugar levels over the preceding two to three months. Expressed as a percentage, this metric serves as a critical indicator of blood sugar control; higher percentages suggest a greater risk of complications related to the condition. For individuals managing blood sugar levels, particularly those who are newly diagnosed, understanding the A1C to blood sugar conversion is essential, as it not only helps evaluate their risk for potential complications but also guides necessary adjustments in treatment protocols.
T2DSolutions is dedicated to offering extensive resources and assistance for health control, including the significance of A1C monitoring. As part of our launch, we will provide educational resources, community assistance, and tools specifically tailored for blood sugar control. A significant trend observed since 2008 shows a decreasing incidence of the condition, currently at 8.4 per 1,000 adults, emphasizing the importance of A1C monitoring in improving health outcomes.
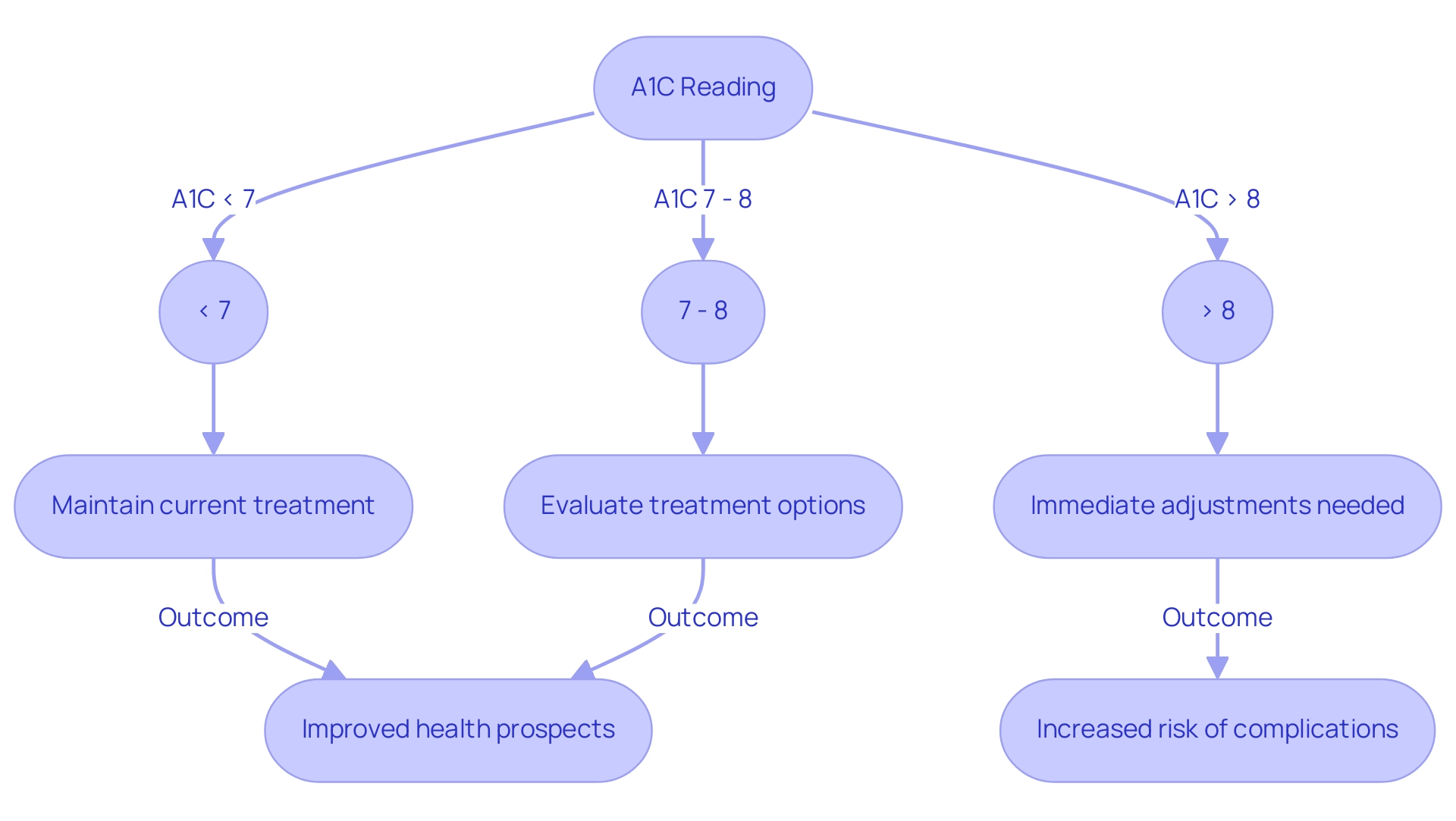
Typically, an A1C reading of 7% or higher indicates the need for adjustments in blood sugar control strategies, particularly in relation to A1C to blood sugar conversion. Regular monitoring of A1C measurements facilitates timely interventions, which can lead to improved long-term health prospects, especially in relation to A1C to blood sugar conversion. Recent studies have shown that keeping A1C levels within the suggested range greatly decreases the occurrence of complications related to the condition, highlighting the significance of A1C to blood sugar conversion in effective control of the illness.
Additionally, a case study reveals that the prevalence of undiagnosed blood sugar issues increases with age, rising from 1.3% in adults ages 20–39 to 6.8% in those aged 60 and older, highlighting the critical need for early detection and management. Furthermore, experts like Ms. Krohe from Novo Nordisk Inc. emphasize that consistent A1C monitoring is instrumental in the A1C to blood sugar conversion, which helps in tailoring individualized treatment plans and optimizing patient care. We invite you to subscribe to T D Solutions to stay updated on the latest resources and support available for your health journey.
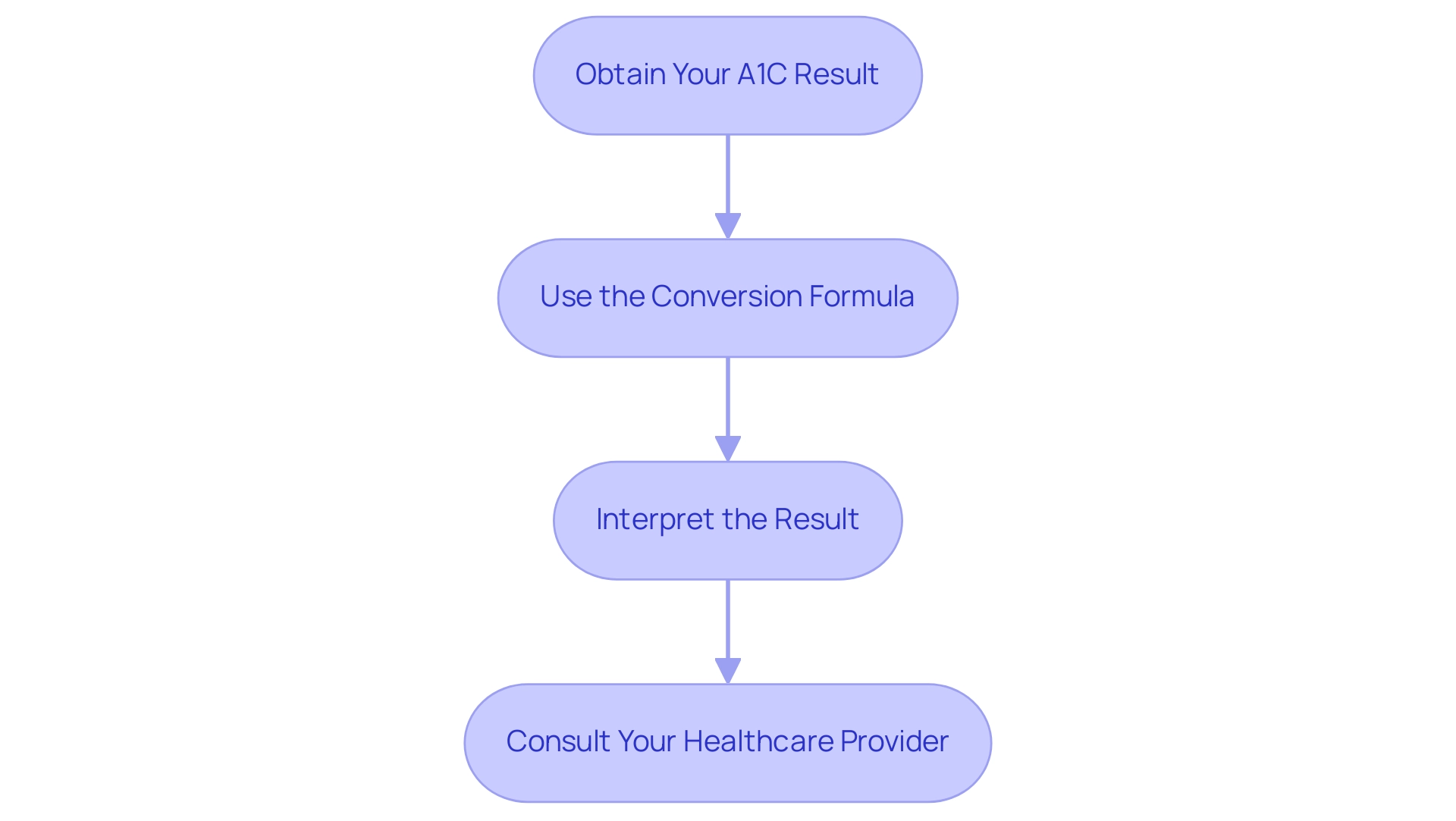
Step-by-Step Guide to Converting A1C to Blood Glucose
To convert A1C to estimated average blood glucose (eAG), adhere to the following steps:
- Obtain Your A1C Result: Start by ensuring you have your most recent A1C test result, which is typically expressed as a percentage.
- Use the Conversion Formula: Utilize the formula: eAG (mg/dL) = (A1C × 28.7) - 46.7. For instance, if your A1C is 7%, the calculation would be: (7 × 28.7) - 46.7 = 158.9 mg/dL.
- Interpret the Result: The eAG value you obtain reflects your average blood glucose level over the past three months, providing insight into your overall glycemic control. It's important to note that the ACOG recommends thresholds of 130, 135, or 140 mg/dL for the 1-hour 50-g glucose tolerance test, which can help in understanding the A1C to blood sugar conversion of your results.
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: It is crucial to discuss your results with your healthcare provider to grasp their implications on your health and to make any necessary adjustments to your management plan. Regular consultations are vital, especially if there are changes in your condition or treatment, as insulin regimens may need adjustment based on factors such as steroid dosing. As Chuck Henderson, CEO of the ADA, states, "At the ADA, we are focused on improving the quality of care for anyone who lives with blood sugar conditions, prediabetes, or who is at risk of developing blood sugar issues, particularly through A1C scale conversion." This emphasizes the significance of comprehending the A1C to blood sugar conversion in managing your condition effectively.
Additionally, T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource hub for education and support related to blood sugar management. We encourage you to explore T2 Solutions for more information on managing your condition effectively and to stay updated with new resources that can assist you in your journey.
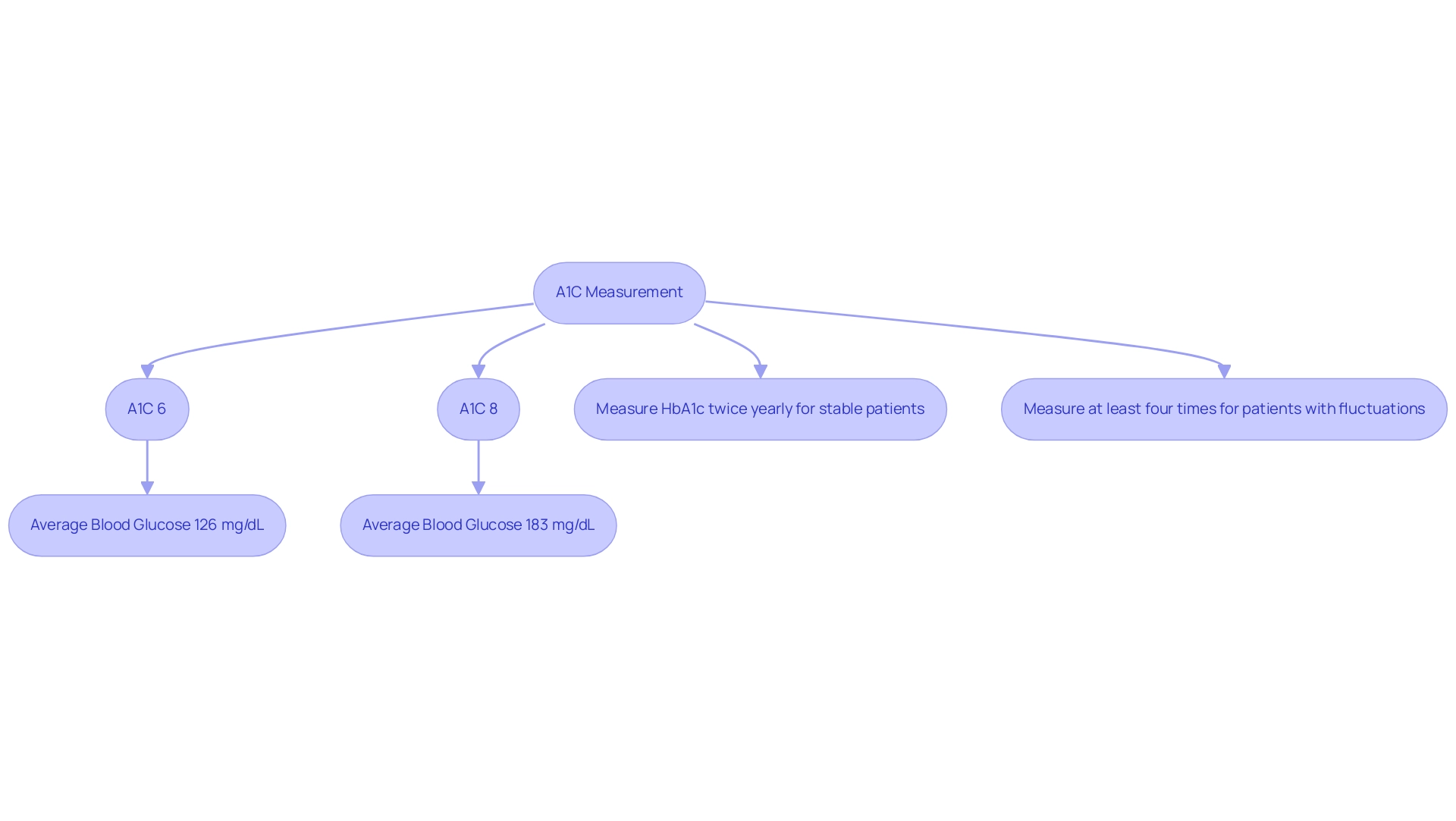
The Relationship Between A1C and Average Blood Glucose Levels
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your extensive source for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar control. As a brand new site, we are dedicated to providing valuable insights and support for newly diagnosed patients. A1C readings function as a crucial measure for the a1c to blood sugar conversion, providing important insights into managing the condition over time.
According to ADA guidelines:
- HbA1c values should be measured twice yearly in stable patients
- At least four times in patients with glucose fluctuations
Research indicates a significant correlation wherein each 1% increase in A1C to blood sugar conversion is associated with an approximate rise of 30 mg/dL in average blood glucose. This relationship is crucial for newly diagnosed patients managing their condition, as maintaining A1C within established target ranges can substantially mitigate the risk of complications.
For example, the a1c to blood sugar conversion indicates that:
- An A1C of 6% correlates with an average blood glucose concentration of approximately 126 mg/dL
- An A1C of 8% reflects an average of around 183 mg/dL
Understanding these values empowers patients to make informed treatment decisions and emphasizes the importance of regular monitoring. Moreover, a research titled 'Impact of Elevated Biomarkers on Diabetes Diagnosis' revealed that having increased amounts of both fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c is linked to a high positive predictive value for diagnosing the condition and risk of complications.
As pointed out by Vivian Fonseca, 'Translating the hemoglobin A1C assay results into actionable health strategies is essential for effective control of the condition,' guiding individuals towards maintaining optimal A1C levels and minimizing potential health risks. Stay tuned for more resources and insights as we continue to develop T2D Solutions into a supportive community for education on diabetes-related issues. Don’t forget to subscribe to receive updates and be notified when new content is published!
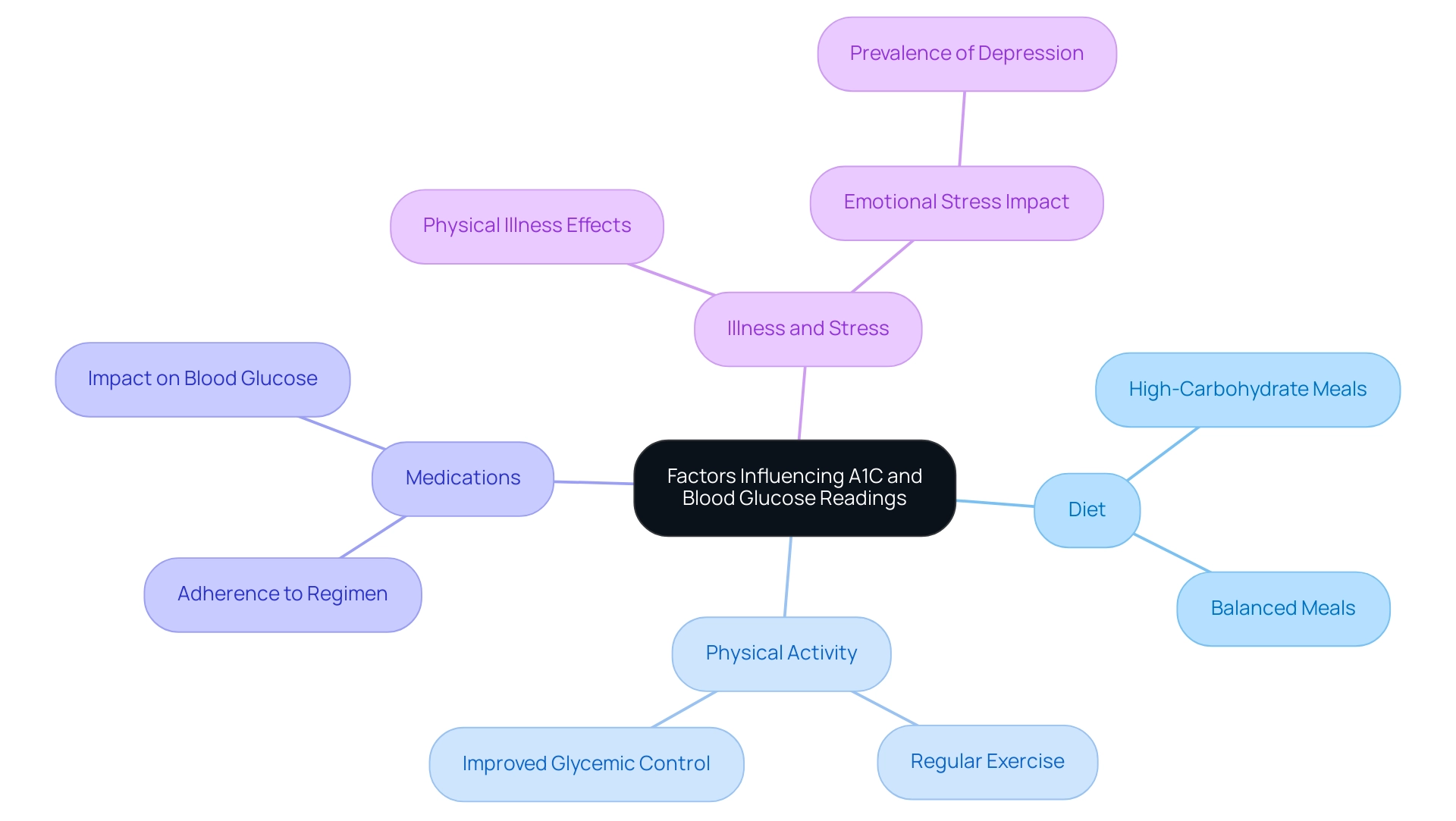
Factors Influencing A1C and Blood Glucose Readings
Multiple factors significantly influence the a1c to blood sugar conversion and blood glucose readings, necessitating careful consideration in diabetes management.
-
Diet: The consumption of carbohydrates plays a pivotal role in determining blood glucose amounts. High-carbohydrate meals can cause noticeable spikes in blood glucose, while balanced meals with suitable portions of carbohydrates can help sustain stable amounts.
Nutritionists emphasize that a well-rounded diet is foundational for effective glucose control. -
Physical Activity: Regular exercise is essential for controlling blood sugar, as it not only reduces blood glucose amounts but also aids in enhancing A1C over time. Integrating physical activity into daily routines has been demonstrated to improve overall glycemic control, making it a vital element of care for those with the condition.
-
Medications: Various diabetes medications can directly affect blood glucose control and, by extension, A1C values. Following prescribed medication regimens is critical for achieving optimal treatment outcomes.
-
Illness and Stress: Physical illness and emotional stress have been identified as significant contributors to elevated blood glucose readings, thereby affecting A1C results.
Significantly, the occurrence of depression among individuals with type 1 conditions is two to three times greater than in the general population, emphasizing the emotional factors that can complicate care. It is essential for individuals to track their glucose levels during times of illness or increased stress to comprehend their effect on overall health control. By acknowledging and tackling these aspects, individuals can take proactive measures toward effective condition oversight, improving their quality of life and overall health.
T2DSolutions is dedicated to offering extensive resources for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar control, providing educational materials and community support to empower patients in their health journey. As we prepare to launch, we invite you to subscribe to our updates to stay informed about our resources and community support. This way, you can be among the first to access valuable information tailored for newly diagnosed patients.
As Dr. William H. Herman states, 'Address correspondence and reprint requests to William H. Herman, MD, Diabetes Prevention Program Coordinating Center, Biostatistics Center, George Washington University, 6110 Executive Blvd., Suite 750, Rockville, MD 20852.' Moreover, the clinical importance of HbA1c in the context of a1c to blood sugar conversion acts as a marker of overall glycemic regulation, indicating the average blood sugar readings over the previous three months, rendering it essential for overseeing blood sugar care and evaluating long-term glucose regulation.
The Importance of Regular A1C Testing and Monitoring
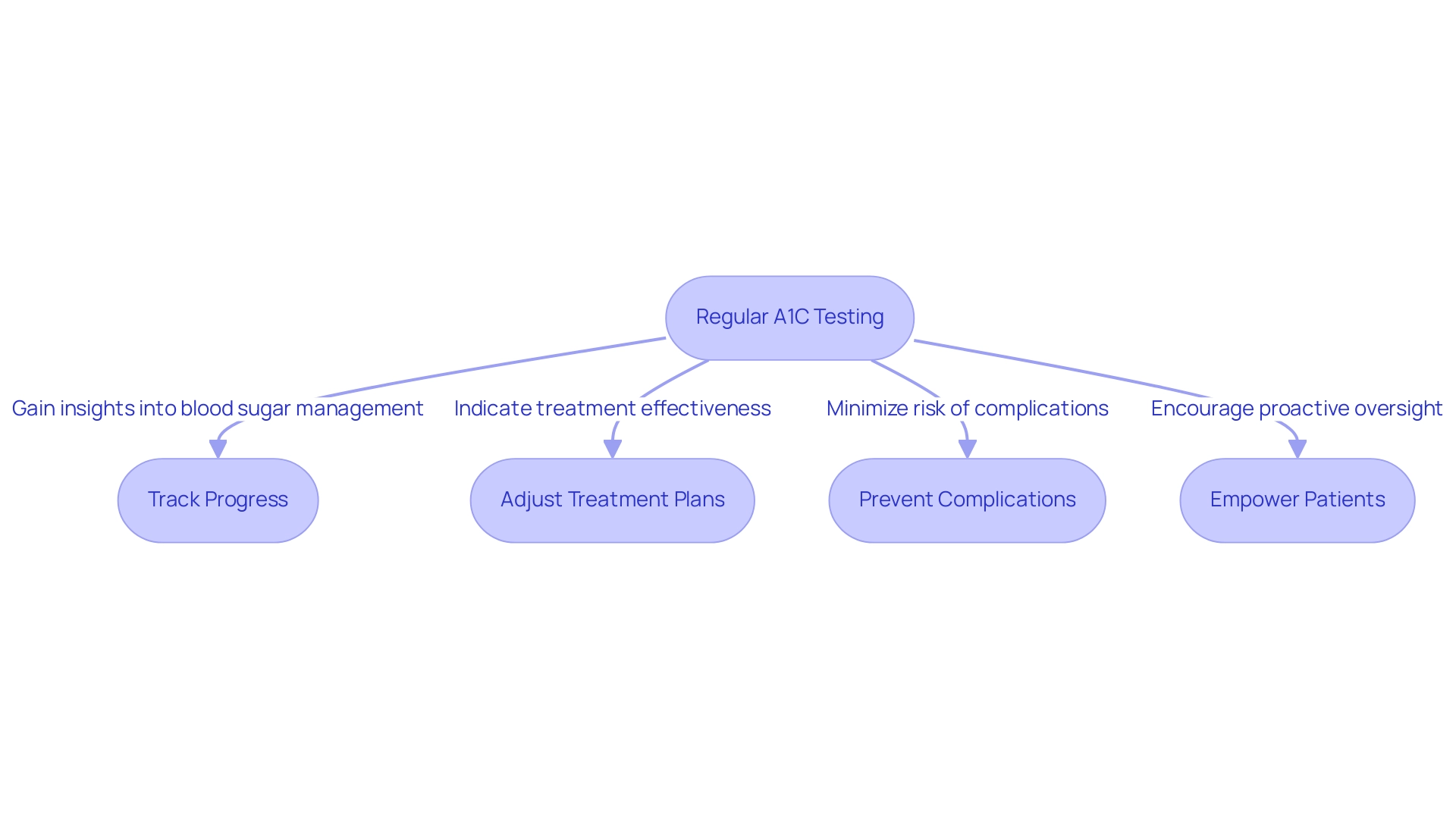
Launching T2DSolutions as a new resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, we emphasize that regular testing for A1C to blood sugar conversion is a cornerstone of effective diabetes care, offering numerous advantages for individuals coping with this condition. It facilitates the following:
- Track Progress: By monitoring A1C levels, individuals gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of their blood sugar management over time.
- Adjust Treatment Plans: A1C results play a vital role in the a1c to blood sugar conversion process, serving as indicators of whether current treatment strategies are effective, necessitating potential adjustments to optimize care.
- Prevent Complications: Keeping A1C levels within recommended target ranges is crucial for effective a1c to blood sugar conversion, which minimizes the risk of diabetes-related complications, including neuropathy and cardiovascular diseases. Significantly, the lowest HbA1c control rate (<8.0%) recorded was only 55.3% for Commercial HMO in 2015, emphasizing ongoing difficulties in A1C oversight.
- Empower Patients: Regular testing instills a sense of agency in individuals, equipping them with essential knowledge about their condition and encouraging proactive oversight.
Andrew Georgiou emphasizes, "Regular testing for A1C to blood sugar conversion is essential for effective management of the condition, as it provides critical insights that can guide treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes." The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals with the condition should have their A1C tested at least twice a year, as this is important for understanding the a1c to blood sugar conversion, with increased frequency suggested if there are changes to their treatment plans. Additionally, a recent study underscored the relationship between adherence to testing frequency and improved patient outcomes, reinforcing the importance of consistent monitoring.
As T2DSolutions continues to develop, we will provide additional resources and tools to assist newly diagnosed patients in managing their A1C levels effectively, including guidance on a1c to blood sugar conversion. Our upcoming features will include personalized tracking tools, educational materials, and community support forums to help you take control of your health and make informed decisions regarding your diabetes management.
Conclusion
Understanding A1C is crucial for effective diabetes management, as it provides a clear reflection of average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. Regular monitoring of A1C not only helps in tracking progress and adjusting treatment plans but also plays a significant role in preventing complications associated with diabetes. The established correlation between A1C levels and average blood glucose is vital for patients to understand, empowering them to make informed decisions about their health.
Numerous factors influence A1C readings, including:
- Diet
- Physical activity
- Medications
- Emotional well-being
Recognizing these elements allows individuals to adopt proactive strategies that enhance their overall health and quality of life. Furthermore, the commitment to regular A1C testing is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management, providing the insights necessary for optimizing treatment and improving patient outcomes.
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, the importance of A1C monitoring cannot be overstated. Staying informed and engaged in diabetes management is essential for individuals navigating their health journeys. Utilizing available resources, such as T2DSolutions, can provide valuable support and education, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and a more empowered approach to managing diabetes.



