Overview:
To convert A1C to glucose levels, one must first obtain the A1C percentage and then apply the conversion formula: eAG (mg/dL) = (A1C × 28.7) - 46.7, allowing for an understanding of average blood glucose over the preceding months. The article outlines this process step-by-step, emphasizing the significance of interpreting the results for effective diabetes management and the potential health implications associated with various A1C levels.
Introduction
Managing diabetes effectively hinges on a clear understanding of A1C levels, a critical metric that reflects average blood glucose over time. As diabetes prevalence continues to rise, with recent statistics showing a significant portion of the population affected, the importance of monitoring A1C cannot be overstated.
This article delves into the essentials of A1C testing, its implications for health, and the necessary steps for converting A1C results into actionable insights.
With the support of T2DSolutions, individuals can access valuable resources and community support to navigate their diabetes management journey, ensuring they remain informed and empowered to make healthier choices.
Understanding A1C: The Key to Diabetes Management
As part of our dedication to assisting newly diagnosed patients, T2D Solutions is thrilled to launch a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 health education and community support. This hub will showcase educational articles, community support groups, and tools for tracking A1C to glucose levels, offering valuable resources for effective management of blood sugar. Understanding A1C to glucose levels, which is commonly referred to as glycated hemoglobin, is essential for managing blood sugar levels.
This test acts as a crucial indicator of A1C to glucose levels over the preceding two to three months, expressed as a percentage. Elevated percentages indicate a decline in blood sugar control. Recent analysis indicates that the prevalence of the condition is at 14.3% among the population, highlighting the significance of tracking A1C values.
The American Diabetes Association recommends maintaining an A1C level below 7% in 2024 to significantly reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. As noted by the American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, 'there remains strong consensus that establishing a uniform approach to diagnosing GDM will benefit people with GDM, caregivers, and policymakers.' Understanding the implications of your A1C results in relation to glucose levels is essential for effective management, as these results inform treatment strategies and necessary lifestyle modifications.
For instance, individuals who have experienced acute pancreatitis should undergo screening for blood sugar issues within 3–6 months, as pancreatic-related conditions can often be misdiagnosed as Type 2. By regularly tracking A1C readings and understanding the correlation of A1C to glucose levels, and utilizing the resources available through T2D Solutions, patients can better manage their glucose and make informed choices to enhance their overall health outcomes. Stay tuned for more resources and support from T2D Solutions.
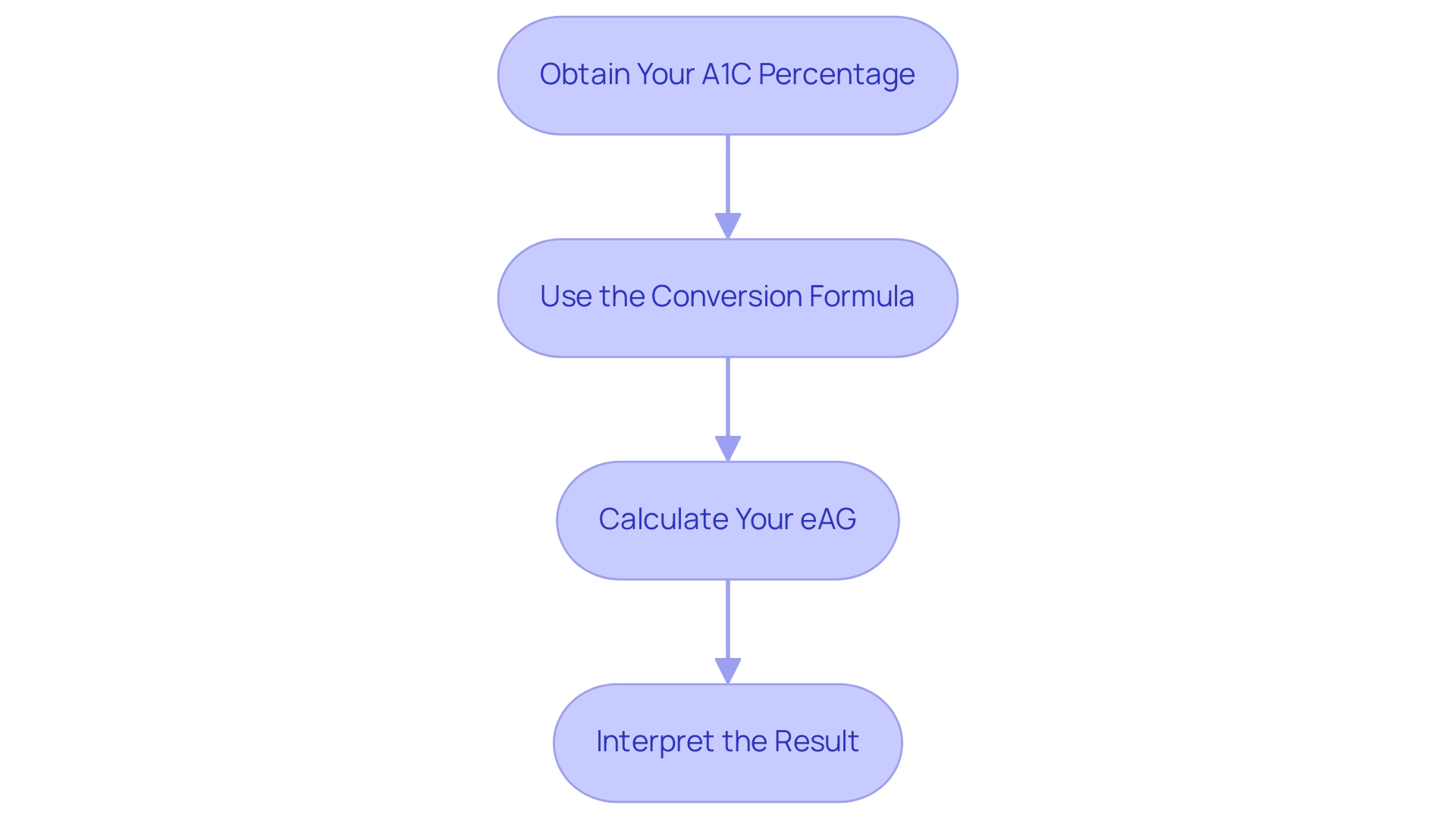
Step-by-Step Guide to Converting A1C to Glucose Levels
To convert A1C to estimated average glucose (eAG), follow these systematic steps:
- Obtain Your A1C Percentage: This value is typically provided by your healthcare provider following a blood test.
- Use the Conversion Formula: The formula for converting A1C to eAG is as follows: eAG (mg/dL) = (A1C × 28.7) - 46.7.
- Calculate Your eAG: For instance, if your A1C is 7%, the calculation would be: eAG = (7 × 28.7) - 46.7, resulting in an eAG of approximately 158.9 mg/dL.
- Interpret the Result: This eAG value signifies your average blood glucose readings over the past months, providing important insight into your condition control approach. Comprehending your eAG can assist in assessing the efficacy of your treatment strategy and guide essential modifications.
At T2DSolutions, we acknowledge the significance of tracking A1C to glucose levels and eAG values in the care of individuals with health conditions related to blood sugar. Our upcoming platform will provide resources and tools to help you better understand these conversions and their implications for your health. According to findings from the ACCORDION follow-up, there was no difference in total mortality after a total of 9 years, underscoring the importance of consistent monitoring over time.
Heather Grey, a specialist in blood sugar conditions, highlights the importance of grasping these conversions: 'Knowing your eAG can enable you to take control of your health.' Furthermore, the UKPDS Post-Trial Monitoring study demonstrated that effective management of A1C to glucose levels can lead to significant reductions in myocardial infarctions and total mortality over 20 years, illustrating the long-term health benefits of maintaining appropriate blood sugar levels. With T2DSolutions, you will have access to comprehensive education on managing your condition and community support to assist you on your journey.
Interpreting A1C Results: What They Mean for Your Health
As part of our dedication to assisting newly diagnosed patients, T2D Solutions is introducing a comprehensive resource hub centered on Type 2 and Type 3 conditions education and community support. This hub will provide a variety of features, including educational materials, community support forums, and expert consultations to assist you in managing your health journey. A1C results are crucial for assessing the relationship of A1C to glucose levels and are categorized as follows:
- Normal: An A1C below 5.7% indicates normal blood sugar levels.
- An A1C to glucose levels ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% suggests an increased risk of progressing to the condition known as prediabetes.
- A diagnosis of diabetes is confirmed with an A1C to glucose levels of 6.5% or higher.
Understanding these categories is vital for individuals to evaluate their health risks and make informed decisions regarding lifestyle modifications, including dietary adjustments that can influence A1C to glucose levels, enhanced physical activity, or medication modifications.
The 2024 Standards of Care emphasize the importance of these categories, with the American Diabetes Association noting that many recommendations have been revised to reflect new evidence. As stated by the American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, 'The 2024 Standards of Care contains, in addition to many minor changes that clarify recommendations or reflect new evidence, more substantive revisions detailed below.' This understanding is especially crucial as recent findings have emphasized the prevalence of prediabetes and significantly affecting overall health outcomes.
For instance, the glucose-independent racial difference in A1C is approximately 0.3 percentage points, indicating variations in A1C levels among different populations. Furthermore, individuals diagnosed with gestational glucose intolerance (GDM) should receive lifelong screening for prediabetes and type 2 conditions to allow for early intervention. The financial burdens linked to this health condition in the United States hit an estimated $413 billion in 2022, highlighting the need for prompt intervention and treatment approaches.
We encourage you to subscribe to remain informed and empowered in your journey of health control as we keep offering more resources and information.

The Importance of Regular A1C Monitoring for Diabetes Control
Regular A1C monitoring is essential for effective management of blood sugar due to several key factors:
- Tracking Progress: Consistent testing provides critical insights into how well your management plan is performing, enabling both you and your healthcare provider to stay informed about your glycemic control.
- Adjusting Treatment: When A1C readings indicate a relationship between A1C to glucose levels that falls outside the target range, timely adjustments to your treatment plan can be implemented, ensuring optimal management of your condition.
- Preventing Complications: Regular monitoring is crucial in mitigating long-term complications associated with high blood sugar, particularly regarding the relationship of A1C to glucose levels, including heart disease, kidney damage, and vision problems. In 2020, the hospitalization rate for hypoglycemia was noted at 2.2 per 1,000 adults with blood sugar disorders, underscoring the importance of preventive measures.
As T2DSolutions launches as your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 metabolic condition education and community support, it aims to empower newly diagnosed patients with the knowledge needed for effective self-management. Current recommendations suggest that individuals with this condition should have their A1C tested at least twice a year, with the latest guidelines for 2024 advocating for more frequent testing—up to four times a year—if there are changes in your treatment plan or if your A1C to glucose levels are above target. The American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee highlights the significance of such monitoring, stating,
The use of CGM devices should be considered from the outset of the diagnosis of the condition that necessitates insulin treatment.
This viewpoint strengthens the importance of continuous glucose monitoring in evaluating glycemic patterns, as illustrated in a case study that shows how CGM devices offer valuable information for improving health strategies. Furthermore, it is crucial to include sleep health practices, as Recommendation 5.51 indicates that encouraging good sleep habits can significantly affect A1C to glucose levels and overall wellness. Stay connected with T2D Solutions by subscribing for updates on new content and resources designed for your health management journey.
Expect to find articles, tips, and community support designed to help you navigate your condition effectively.
![]()
Common Questions About A1C Testing and Conversion
Below are some frequently asked questions regarding A1C testing and conversion, brought to you by Td Solutions, your new resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support:
-
How often should I get my A1C tested? Generally, it is advisable to undergo testing every three months if you are adjusting your treatment plan. For individuals whose measurements are stable, testing twice a year is sufficient.
-
What is the difference between A1C and daily blood glucose tests? The A1C test offers an average blood sugar reading over the past two to three months, in contrast to daily blood glucose tests that reflect your current A1C to glucose levels at the time of testing.
-
Can I convert A1C to glucose amounts myself? Yes, you can calculate your estimated Average Glucose (eAG) using the conversion formula included in this guide. This enables you to comprehend your glucose readings in relation to the A1C to glucose levels.
-
What if my A1C is high? If your A1C readings are elevated, it is essential to discuss with your healthcare provider about possible modifications to your treatment plan. This discussion could result in a more efficient approach to enhance your A1C levels.
Considering that 41.0% of men and 32.0% of women have prediabetes based on their fasting glucose or A1C to glucose levels, regular A1C testing becomes crucial for early detection and control of the condition. The American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee emphasizes the importance of establishing a uniform approach to diagnosing conditions such as Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM), which can ultimately benefit patients, caregivers, and policymakers. This consensus reflects a broader trend in managing diabetes-related conditions, including the alignment of liver disease management with other professional societies, ensuring comprehensive care for patients with these conditions.
Additionally, the case study titled 'Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management' highlights how A1C testing plays a vital role in managing diabetes alongside kidney health, emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach to patient care.
At T2D Solutions, we are committed to supporting you on your diabetes journey. Subscribe now to stay informed about the latest resources, tips, and community support available to help you manage your condition effectively.
Conclusion
Regular monitoring of A1C levels is essential for effective diabetes management. Understanding A1C, its implications, and the conversion to estimated average glucose (eAG) empowers individuals to take control of their health. With A1C categorized into normal, prediabetes, and diabetes ranges, it provides a clear framework for evaluating one’s health status and making informed lifestyle adjustments.
The significance of consistent testing cannot be overstated. It allows for tracking progress, adjusting treatment plans, and preventing long-term complications associated with diabetes. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, the need for regular A1C testing becomes increasingly urgent. Utilizing the resources and support offered by T2DSolutions enhances the ability to navigate this journey effectively.
In conclusion, staying informed about A1C levels and utilizing available educational resources are vital steps towards better diabetes management. By prioritizing regular monitoring and understanding test results, individuals can make proactive choices that lead to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life.



