Overview
Understanding how to convert blood glucose levels to A1C can be a crucial step in managing your diabetes. You can use the formula A1C (%) = (Blood Sugar Level + 46.7) / 28.7 to estimate your A1C percentage based on your average blood sugar readings. This knowledge empowers you to monitor your blood sugar control over time.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by these numbers, but grasping this conversion is vital for effective diabetes management. By keeping track of your A1C, you can make informed decisions regarding your treatment plans. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way, helping you navigate your path to better health.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding A1C levels is pivotal for maintaining optimal health. A1C, a blood test that reflects average blood sugar levels over the previous two to three months, serves as a vital indicator of how well you are managing your diabetes.
With the rising prevalence of diabetes and the associated healthcare costs, the importance of regular A1C monitoring cannot be overstated. It’s understandable to feel overwhelmed, but this article delves into the intricacies of A1C, exploring its implications for treatment effectiveness and the connection between blood glucose and A1C levels.
We will also discuss practical methods for converting glucose readings to A1C percentages. By equipping you with essential knowledge and tools, we aim to empower you to take charge of your diabetes management and improve your overall quality of life.
Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Understanding A1C: What It Is and Why It Matters
A1C, or hemoglobin A1C, is an essential blood test that evaluates the average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, represented as a percentage. This percentage shows the ratio of hemoglobin molecules that have sugar attached to them. Higher A1C readings indicate worse blood sugar management and an increased risk of diabetes-related complications. For individuals managing diabetes, understanding the blood glucose to A1C conversion is vital, as it serves as a key indicator of the effectiveness of treatment plans and lifestyle modifications.
Consistent observation of measurements for blood glucose to A1C conversion is crucial for long-term glucose management. It not only provides insight into how effectively blood sugar has been managed but also aids in determining necessary modifications in care. In 2025, the significance of A1C monitoring remains paramount, with studies showing that 8.0% of adults with diagnosed conditions had a non-HDL measurement of 190 mg/dL or greater.
This statistic underscores the necessity for effective management strategies, as elevated non-HDL levels can be linked to heightened cardiovascular risk, further complicating the management of blood sugar.
Recent research highlights the stability of blood sugar disorder incidence rates among U.S. adults from 2000 to 2021, with a notable decline in new diagnoses since 2008. This trend indicates enhancements in glucose control prevention and management strategies, emphasizing the importance of monitoring blood glucose to A1C conversion in these efforts. The case study titled 'Trends in Diabetes Incidence Among Adults' illustrates that while overall incidence rates remained relatively stable, the decline in new diagnoses suggests that effective practices for blood glucose to A1C conversion monitoring and management are becoming more prevalent among patients.
Furthermore, professional viewpoints emphasize the importance of A1C testing and the blood glucose to A1C conversion for individuals with blood sugar issues. David F. Williamson, PhD, from the Hubert Department of Global Health at Emory University, states, "A1C Level and Future Risk of Diabetes: A Systematic Review" highlights the predictive value of A1C levels in assessing future risk of the condition. It is not merely a number; it reflects the cumulative impact of daily choices and medical interventions on blood sugar control.
By understanding the blood glucose to A1C conversion and its implications, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their condition, ultimately enhancing their quality of life and reducing the risk of complications.
Additionally, emotional distress associated with managing blood sugar levels can significantly affect patients' overall well-being. Regular A1C monitoring, which involves blood glucose to A1C conversion, can alleviate some of this distress by providing patients with a clearer understanding of their blood sugar control, allowing them to make informed decisions about their health. T2DSolutions is dedicated to offering resources, practical advice, and expert perspectives to improve management and quality of life, enabling individuals to navigate their health journey with confidence.
As a new resource center for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community assistance, T2DSolutions will provide valuable content and tools to help individuals effectively manage their A1C readings through blood glucose to A1C conversion.
The Connection Between Blood Glucose Levels and A1C
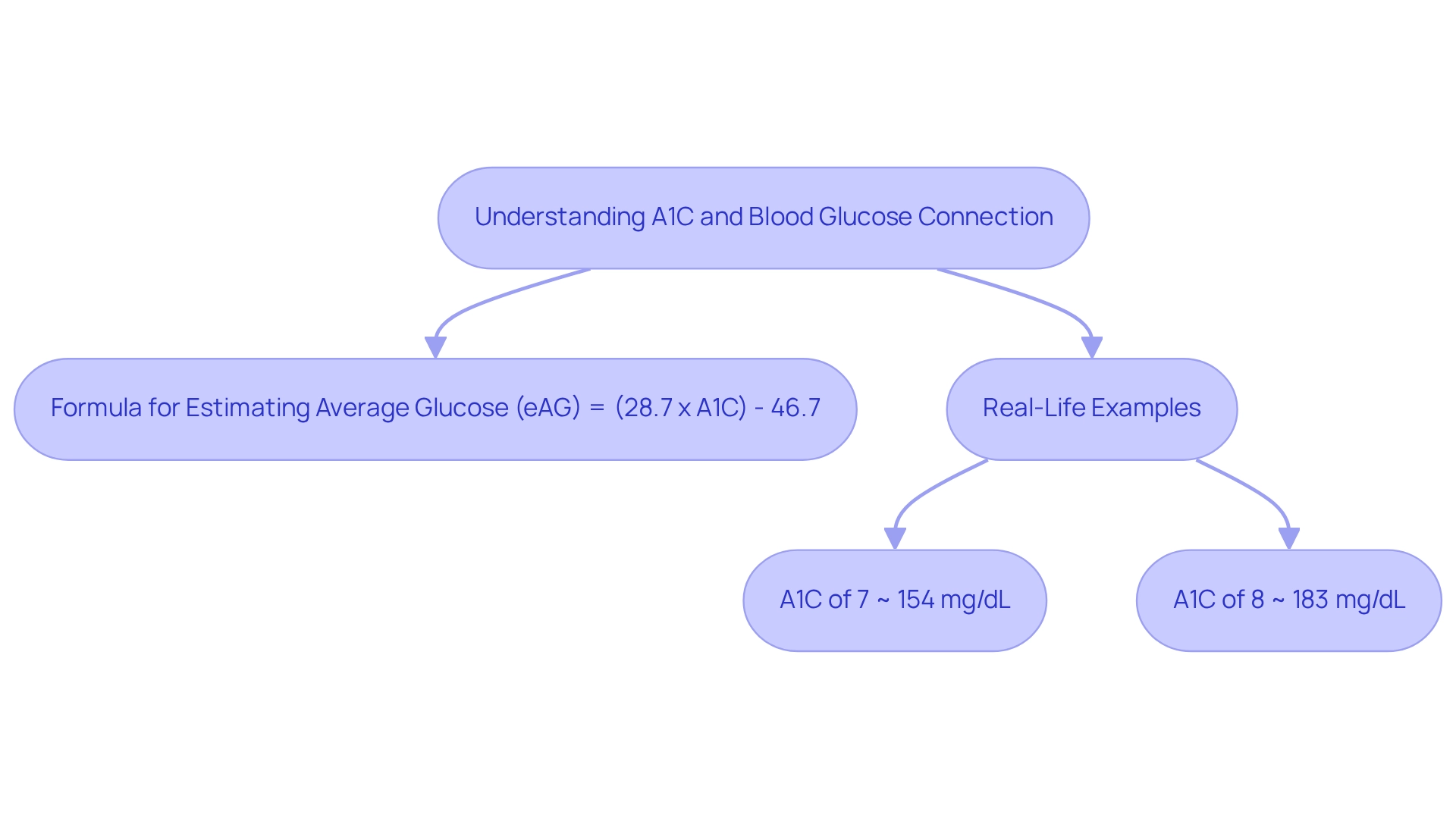
The connection between blood sugar concentrations and A1C highlights the importance of blood glucose to A1C conversion. A1C serves as a crucial measure of average blood sugar amounts over time. You might find it helpful to know that this relationship can be quantified using the formula: Estimated Average Glucose (eAG) = (28.7 x A1C) - 46.7. This means that for each percentage point rise in A1C, the average blood sugar concentration increases by roughly 28.7 mg/dL.
Understanding this is essential for anyone managing diabetes. It emphasizes how daily blood sugar monitoring directly impacts the blood glucose to A1C conversion, which can lead to more effective diabetes management. You're not alone in navigating this; many are on the same path.
Recent studies have shown that individuals facing both short- and long-term complications encounter diabetes-related costs that are nearly 123% higher than those without complications. This statistic underscores the significance of maintaining ideal blood sugar concentrations to avoid complications and manage healthcare costs efficiently. By proactively managing blood sugar levels, you can significantly reduce your risk of complications and related expenses.
Real-life examples can be quite illuminating: a patient with an A1C of 7% typically has an average blood glucose level indicating about 154 mg/dL, while an A1C of 8% relates to roughly 183 mg/dL. These examples reinforce the importance of regular monitoring and the proactive management of blood glucose levels.
Experts in blood sugar management stress the importance of understanding A1C results and their implications for patient care. For instance, Eyth E. notes, 'Hemoglobin A1c is a valuable tool in managing blood sugar conditions and other glycemic control disorders, but it functions best in an interprofessional healthcare team environment to be effective.' This highlights the necessity of collaboration among healthcare providers to ensure accurate interpretation of A1C results and to support you on your management journey.
Moreover, certain medical conditions can interfere with A1C testing, leading to inaccurate results. A case study on the limitations of A1C testing shows that healthcare providers must interpret these results carefully and verify them with plasma sugar samples. This is crucial to avoid misdiagnosis and ensure proper management of blood sugar conditions. It reinforces the need for a comprehensive approach to diabetes care, where accurate testing and interpretation are paramount.
Additionally, recent discoveries suggest that a higher BMI is associated with an increased chance of having both fasting plasma levels and HbA1c elevated together. This information provides wider context regarding factors affecting blood sugar and A1C values, which is important for those who have recently been diagnosed to consider in their management plans.
In conclusion, understanding the connection between blood sugar amounts and the blood glucose to A1C conversion is vital for effective management of the condition. By recognizing how daily blood sugar amounts impact this conversion, you can take proactive steps to uphold your health and prevent complications. T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource hub for diabetes education, offering support and information to help you navigate your management journey. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Methods for Converting Blood Glucose to A1C
Managing blood glucose levels can feel overwhelming, but various efficient techniques can help you convert those levels to A1C results. One of the most widely used formulas is:
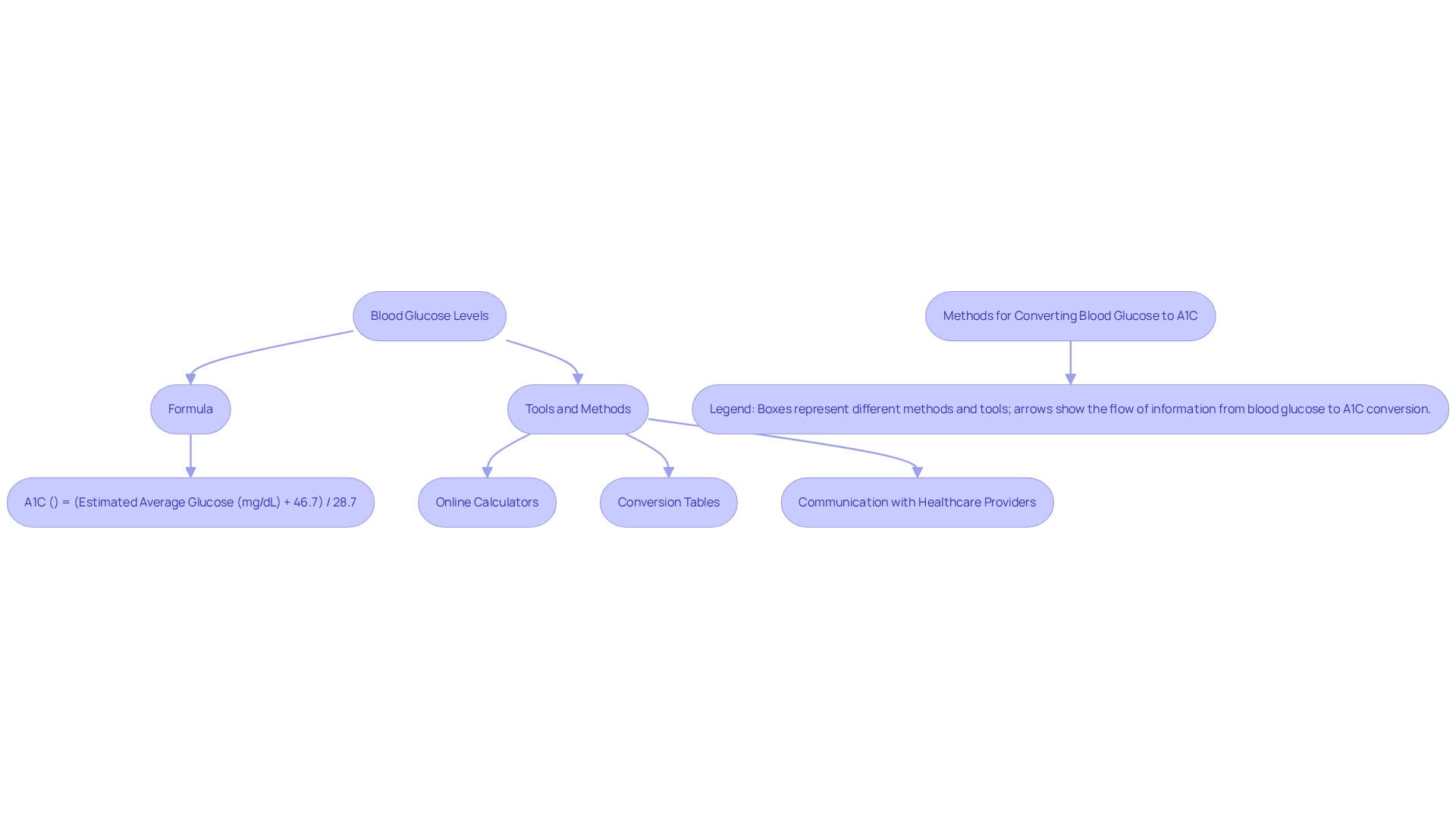
A1C (%) = (Estimated Average Glucose (mg/dL) + 46.7) / 28.7.
This straightforward formula offers a simple way to estimate A1C based on your average sugar concentrations.
If math isn’t your strong suit, don’t worry! Numerous online calculators and conversion charts are readily available, making it easier for you to perform these calculations without needing advanced mathematical skills. You’re not alone in this journey; many individuals find these tools incredibly helpful.
For those who prefer a more visual representation, conversion tables can be particularly beneficial. These tables show the connection between different blood sugar readings and their associated A1C percentages, allowing you to consult and understand your sugar management quickly.
Research backs the precision of these online calculators, revealing that roughly 90% of individual patients' calculated estimated average sugar levels (eAG) fell within ±15% of the study-wide calculated average sugar levels. This level of accuracy underscores the reliability of these tools in aiding diabetes management, especially for newly diagnosed patients learning to navigate their condition.
Healthcare experts emphasize the importance of using these techniques to enhance communication between patients and providers regarding sugar management. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) has introduced the estimated average sugar (eAG) concept to improve this dialogue, allowing A1C results to be reported in familiar units. This initiative aims to enhance your understanding and care. As David Schoenfeld, PhD, from Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, highlights, "Effective communication about blood sugar management is crucial for empowering patients in their care for diabetes."
In practice, many have found success using these tools to manage their condition effectively. For example, a case study emphasized the use of an eAG/A1C conversion calculator, which facilitated enhanced conversations about sugar management between healthcare providers and patients. This cooperative method not only improves comprehension but also enables you to engage actively in your health management, leading to better health outcomes.
By utilizing these various methods and tools for blood glucose to A1C conversion, you can gain valuable insights into your diabetes management, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Step-by-Step Guide to Convert Blood Glucose to A1C
To convert your blood glucose level to A1C, follow these steps:
- Obtain Your Blood Sugar Measurement: Start by using your glucometer to check your blood sugar measurement. Remember to note whether the measurement is in mg/dL or mmol/L.
- Use the Conversion Formula: If your blood sugar is in mg/dL, apply the formula: A1C (%) = (Blood Sugar Level + 46.7) / 28.7. For readings in mmol/L, convert to mg/dL by multiplying by 18.015, then use the same formula.
- Calculate Your A1C: Perform the calculation to determine your A1C percentage. For instance, if your blood glucose level is 180 mg/dL, the calculation would be: (180 + 46.7) / 28.7 = 7.9% A1C.
- Interpret Your Results: Compare your A1C result to the recommended targets for managing blood sugar levels, which are typically below 7% for most adults. Understanding these targets is essential for effective blood sugar management.
- Consult with Your Healthcare Provider: Discuss your results with your healthcare provider to understand their implications for your health management plan. Seeking advice from a licensed dietitian can also offer important assistance in effectively managing blood sugar. As Sarah Bullard, MS, RD, highlights, "Understanding your A1C is crucial for effective management of the condition."
In a study involving 507 participants, researchers established a strong linear connection between A1C values and estimated average blood sugar (eAG), reinforcing the significance of precise A1C calculations in managing health. This relationship is consistent across various demographic groups, making it a reliable tool for understanding and managing diabetes. The research named 'Translating the A1C Assay Into Estimated Average Sugar Values' emphasizes how A1C can be represented in the same units as self-monitoring sugar measurements, further reinforcing its importance.
Common mistakes in blood glucose to A1C conversion include miscalculating the blood glucose level or misunderstanding the conversion formula. By following these steps carefully, you can avoid these pitfalls and gain a clearer understanding of your health management. Remember, accurate A1C calculations are essential for tailoring your treatment plan and achieving better health outcomes.
For additional resources and assistance concerning blood sugar management, consider visiting T2DSolutions. You're not alone in this journey, and there are many resources available to support you.

Common Questions About A1C Conversion
-
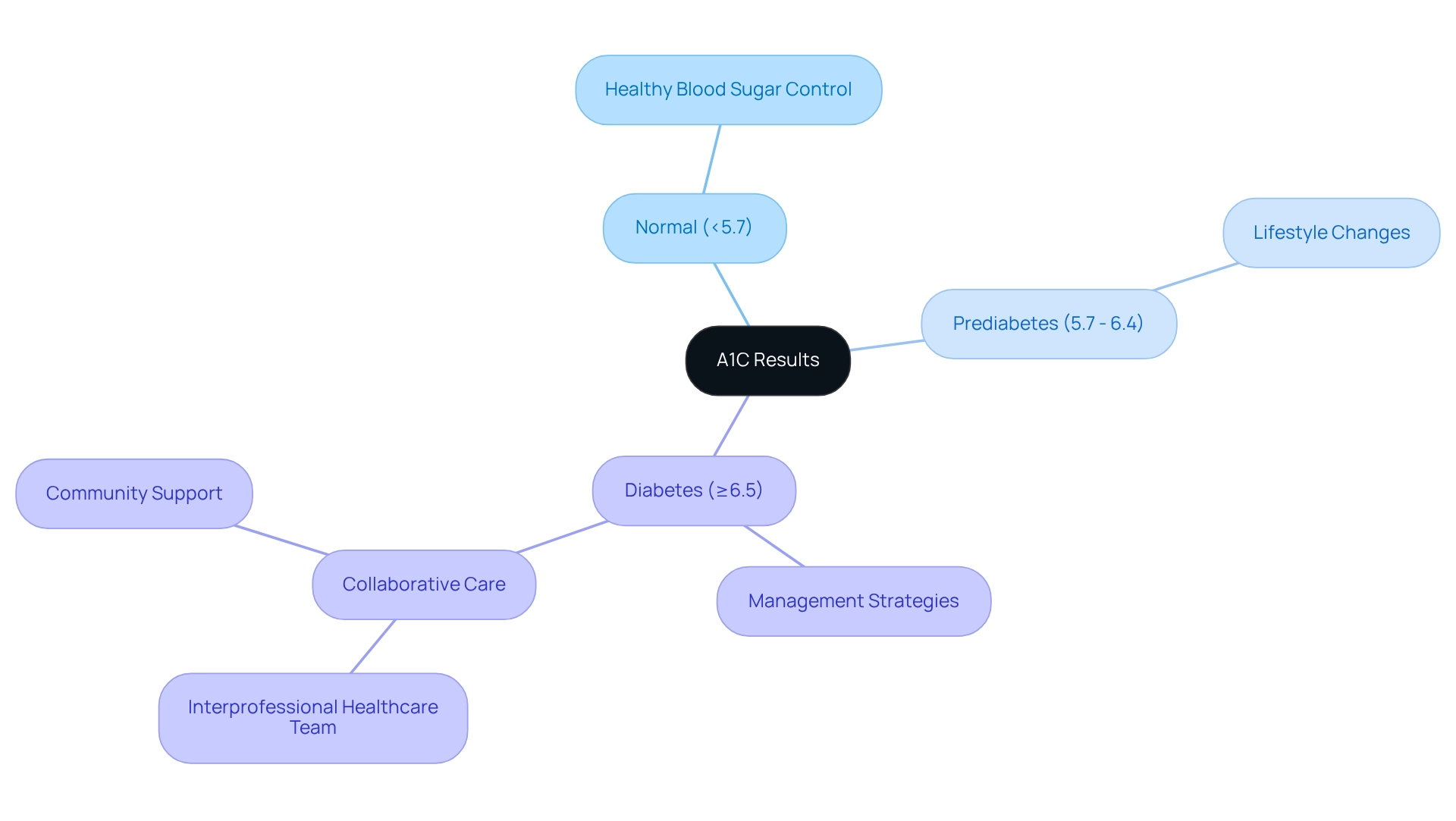
What is the normal range for A1C? A normal A1C level is considered to be below 5.7%. Levels from 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or above is diagnostic for the condition. Understanding these ranges is crucial for early intervention and management. Research indicates that an A1C cutoff of 5.6% has merely a 31% positive predictive value for identifying individuals at risk of developing the condition in the future. Early preventive intervention is essential to mitigate this risk and improve health outcomes.
-
How often should I check my A1C? For most individuals diagnosed with diabetes, it is advised to have A1C readings tested at least twice a year. However, depending on personal health situations and changes in treatment, more frequent testing may be necessary to ensure effective blood sugar management.
-
Can I perform a blood glucose to A1C conversion to determine my blood sugar? Yes, you can convert A1C values to estimated average glucose (eAG) using the formula: Estimated Average Glucose (mg/dL) = (A1C x 28.7) - 46.7. This conversion helps patients understand their blood sugar measurements in a familiar context, facilitating improved management decisions.
-
What factors can affect my A1C results? Several factors can influence A1C results, including conditions like anemia, certain medications, and variations in hemoglobin. It is vital to discuss any potential issues with your healthcare provider to ensure accurate interpretation of your A1C results.
-
Frequently asked questions about A1C conversion clarified by specialists: Experts often address questions related to A1C monitoring, emphasizing the importance of understanding how lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, can impact A1C readings. For instance, following dietary guidelines that favor whole, unprocessed foods while avoiding refined carbohydrates can significantly assist in controlling blood sugar levels. As Eyth E. notes, "Hemoglobin A1c is a valuable tool in managing diabetes mellitus and other glycemic control disorders, but it functions best in an interprofessional healthcare team environment to be effective."
-
Real-world examples addressing A1C monitoring concerns: Many individuals have successfully managed their A1C readings through consistent monitoring and lifestyle adjustments. For example, a patient who embraced a balanced diet and increased physical activity reported a decrease in their A1C from 7.2% to 6.8% over six months, showcasing the effectiveness of proactive management strategies. This highlights the importance of community support and shared experiences in achieving better health outcomes.
-
Frequently asked questions about A1C measurements in 2025: As we progress through 2025, patients are increasingly interested in the latest guidelines and recommendations for A1C monitoring. Staying informed about recent studies and professional insights is essential for effective management of blood sugar conditions, especially as new findings emerge regarding the connection between A1C values and overall health outcomes.
The Importance of Regular A1C Monitoring in Diabetes Management
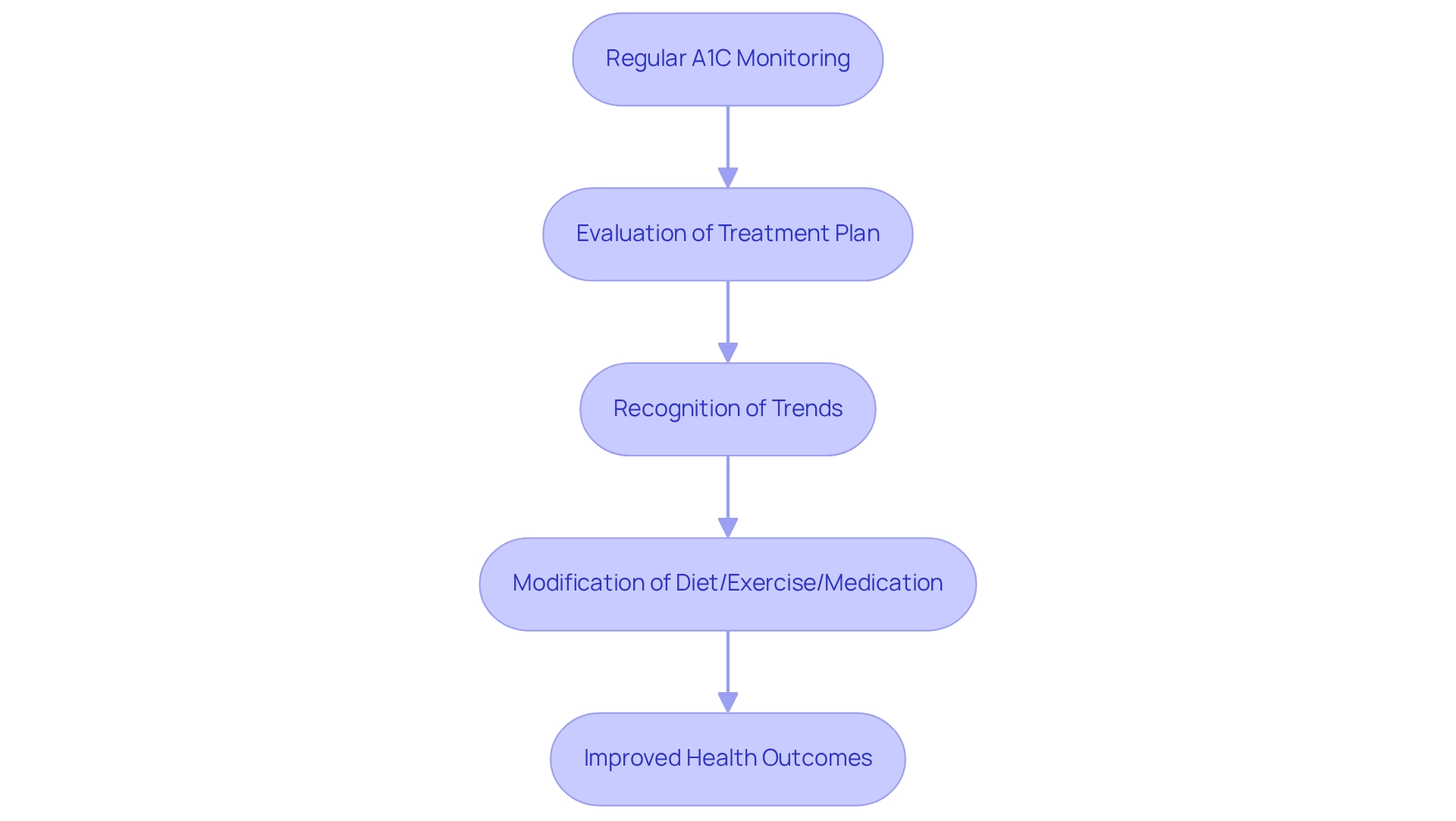
Regular A1C monitoring is essential for effective diabetes management. It provides a comprehensive view of the blood glucose to A1C conversion for long-term control. This metric allows you and your healthcare provider to evaluate the effectiveness of your treatment plan over time. Studies have shown that individuals who consistently track their A1C readings can recognize trends that guide important modifications to their diet, exercise, and medication routines.
At T2DSolutions, we understand that keeping A1C measurements within target ranges is vital. Doing so can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage. Research indicates that individuals with well-managed A1C levels experience fewer complications, which underscores the importance of regular monitoring. A recent study titled "Effectiveness of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Uncontrolled Diabetes" highlighted the benefits of CGM devices, showing significant improvements in glycemic control among patients transitioning from self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) to CGM.
This shift not only enhances daily management but also contributes to better long-term outcomes. Experts in the field emphasize that regular monitoring of blood glucose to A1C conversion is crucial for modifying your treatment for blood sugar management. According to endocrinologist Naik R., "Hemoglobin A1c is a valuable tool in managing blood sugar conditions and other glycemic control disorders, but it functions best in an interprofessional healthcare team environment to be effective." Tracking A1C levels provides critical insights that help tailor treatment strategies to your individual needs.
This proactive approach is supported by the latest findings, which suggest that consistent monitoring can lead to improved health outcomes and a reduction in diabetes-related complications. While the study on CGM devices shows promising results, it is important to note its limitations, including a small sample size and lack of a control group. These factors call for further research to validate these findings.
In summary, the importance of regular A1C monitoring cannot be overstated. It acts as a foundation of glucose regulation, allowing you to take control of your health and collaborate with your healthcare team to attain optimal outcomes.
For additional resources and assistance in managing your condition, visit T2DSolutions. We invite you to subscribe for updates on new content and tools available for recently diagnosed patients. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Interpreting Your A1C Results: What They Mean for Your Health
Understanding the conversion of blood glucose to A1C results is essential for effectively managing your health. An A1C level below 5.7% is classified as normal, indicating healthy blood sugar control. If your levels fall between 5.7% and 6.4%, this signals prediabetes, highlighting the importance of making proactive lifestyle changes to prevent progression to a more serious condition.
A diagnosis is confirmed with an A1C of 6.5% or higher, which necessitates a comprehensive management strategy tailored to your individual needs. For those already diagnosed, the general recommendation is to aim for an A1C below 7%. This target significantly reduces the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Evidence supports that lower A1C values correlate with improved health outcomes, especially in the context of blood glucose to A1C conversion. For instance, a multivariate analysis revealed that A1C accounted for 7.4% of the variance in insulin action, while fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and 2-hour plasma glucose explained 10.3% and 13.8%, respectively. This highlights the importance of these measures in understanding overall glycemic control.
As Eyth E. notes, "Hemoglobin A1c is a valuable tool in managing diabetes mellitus and other glycemic control disorders, but it functions best in an interprofessional healthcare team environment to be effective." Discussing your blood glucose to A1C conversion results with your healthcare provider is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan. This collaboration can help set realistic health goals and adjust management strategies as needed.
As you progress in managing your glucose levels, staying informed about the implications of your blood glucose to A1C conversion can empower you to take charge of your health effectively. In 2025, understanding the significance of your A1C results is more crucial than ever, especially as the occurrence of type 2 conditions continues to rise, with over 5,293 children and adolescents identified in recent years. The additional medical expenses related to this health condition have also increased considerably, from $10,179 to $12,022 per individual from 2012 to 2022, underscoring the necessity of effective oversight.
Engaging with your healthcare team and utilizing accessible resources, like those provided by T2DSolutions, can enhance your management journey. T2DSolutions is dedicated to community and collaboration, serving as a valuable resource hub for diabetes education and support. They provide newly diagnosed patients with the tools and information needed to manage their condition effectively. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding A1C levels is crucial for effective diabetes management, serving as a vital indicator of long-term blood sugar control. It's important to recognize the significance of regular A1C monitoring, as it plays a key role in evaluating treatment effectiveness and guiding necessary adjustments in care. With the right knowledge and tools, you can take proactive steps to manage your diabetes, ultimately enhancing your quality of life and reducing the risk of complications.
The connection between blood glucose levels and A1C highlights the necessity for daily monitoring and management. By acknowledging how fluctuations in glucose impact A1C results, you can make informed decisions about your health and adopt strategies that promote better outcomes. Additionally, practical methods for converting glucose readings to A1C percentages empower you to engage actively in your diabetes care.
In summary, regular A1C testing is not merely a routine check; it is an essential component of a comprehensive diabetes management plan. As diabetes prevalence continues to rise, understanding and utilizing A1C levels effectively becomes increasingly crucial. Resources like T2DSolutions offer valuable support and education, ensuring you are equipped to navigate your diabetes journey with confidence and competence. Remember, taking charge of your health through informed decision-making can lead to a brighter, healthier future for you and others living with diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is A1C and why is it important?
A1C, or hemoglobin A1C, is a blood test that measures the average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, expressed as a percentage. It indicates how well blood sugar is being managed and helps assess the risk of diabetes-related complications.
How does A1C relate to blood glucose levels?
The A1C test reflects the ratio of hemoglobin molecules with sugar attached. A higher A1C percentage indicates poorer blood sugar management. The relationship between A1C and average blood glucose can be quantified using the formula: Estimated Average Glucose (eAG) = (28.7 x A1C) - 46.7.
Why is monitoring A1C levels crucial for individuals with diabetes?
Consistent monitoring of A1C levels is vital for long-term glucose management as it helps determine the effectiveness of treatment plans and lifestyle changes. It also provides insight into necessary modifications in care to prevent complications.
What trends have been observed in diabetes diagnoses from 2000 to 2021?
There has been a stability in blood sugar disorder incidence rates among U.S. adults, with a notable decline in new diagnoses since 2008. This suggests improvements in glucose control prevention and management strategies.
What are the potential risks associated with high A1C levels?
Higher A1C levels indicate worse blood sugar management, which can increase the risk of diabetes-related complications and cardiovascular issues, as evidenced by elevated non-HDL cholesterol levels.
How can emotional distress impact individuals managing blood sugar levels?
Managing blood sugar can cause emotional distress, which affects overall well-being. Regular A1C monitoring can help alleviate this distress by providing clarity on blood sugar control, enabling better health decisions.
What role does T2DSolutions play in diabetes management?
T2DSolutions is a resource center dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community assistance, offering valuable content and tools to help individuals manage their A1C readings effectively.
What factors can interfere with A1C testing accuracy?
Certain medical conditions can affect A1C testing results, leading to inaccuracies. It is important for healthcare providers to interpret A1C results carefully and verify them with plasma sugar samples to avoid misdiagnosis.
How do body weight and A1C levels relate?
Recent findings suggest that a higher Body Mass Index (BMI) is associated with an increased likelihood of having elevated fasting plasma levels and HbA1c, highlighting additional factors that can influence blood sugar and A1C values.
