Overview:
To convert blood glucose levels from mg/dl to mmol/l, one must multiply the mg/dl value by 0.0555, which allows for accurate interpretation of glucose readings across different measurement systems. The article emphasizes the importance of this conversion for effective diabetes management, particularly for individuals traveling internationally or engaging with healthcare professionals who use mmol/l, thereby ensuring better communication and understanding of their health status.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of blood glucose management is essential for individuals living with diabetes, particularly in understanding the various measurement units used globally. The distinction between milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) and millimoles per liter (mmol/l) is not merely academic; it has practical implications for effective diabetes care.
This article delves into the significance of these units, offering insights into their conversion and the contexts in which they are most relevant:
- Traveling abroad
- Interpreting medical literature
The ability to convert and understand these measurements is critical for informed decision-making. Additionally, practical tips for accurate blood glucose monitoring and a wealth of resources for ongoing education are provided to empower individuals on their diabetes management journey.
Understanding Blood Glucose Measurement Units: mg/dl vs. mmol/l
Blood sugar levels are primarily measured in two units: mg/dl to mmol/l and millimoles per liter (mmol/l). In the United States, mg/dl is the standard measurement, whereas the conversion from mg/dl to mmol/l is more widely used internationally. Grasping these units is essential for efficient diabetes management, as they indicate the concentration of sugar in the bloodstream.
For those newly diagnosed, it is essential to know that the conversion from mg/dl to mmol/l indicates that:
- 1 mg/dl of sugar is approximately equivalent to 0.0555 mmol/l.
This conversion factor, which converts mg/dl to mmol/l, is essential for interpreting sugar level readings across various regions and contexts. With global diabetes prevalence on the rise, nearly 50% of the increase attributed to changing demographic profiles, comprehending these measurement units becomes increasingly important.
Additionally, the low blood sugar index (LBGI) is utilized to assess hypoglycemia risk based on self-monitoring of blood sugar (SMBG) data; however, it may underestimate risk when continuous sugar monitoring (CGM) data is used. This underscores the necessity for accurate interpretation of glucose levels. A case study on hypoglycemia in the control of blood sugar levels reveals that severe hypoglycemia is often associated with the duration of the condition and socioeconomic status, rather than solely relying on hemoglobin A1c (HbA) levels.
Thus, understanding the conversion from mg/dl to mmol/l can significantly empower individuals in effectively managing their condition. At&T Solutions, we are dedicated to offering extensive resources, including educational materials and community support initiatives, to help newly diagnosed patients in navigating their health journey. Stay tuned for our latest updates and resources that will further support your understanding and management of diabetes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Converting mg/dl to mmol/l
To transform sugar levels from mg/dl to mmol/l, follow these detailed steps:
- Identify Your Blood Glucose Level: Begin with the reading you wish to convert, usually expressed in mg/dl.
- Utilize the Conversion Factor: To convert the value from mg/dl to mmol/l, multiply the mg/dl value by 0.0555.
- For instance, if your blood glucose level registers at 180 mg/dl, the calculation would be: 180 mg/dl × 0.0555 = 9.99 mmol/l.
- Execute the Calculation: Employ a calculator or perform the computation manually to determine the mmol/l equivalent.
- Using the prior example, 180 mg/dl translates to approximately 9.99 mmol/l.
- Round the Result: Depending on your specific requirements, you may choose to round the result to one or two decimal places for ease of use. In this case, the result rounds to 10.0 mmol/l.
- Document the Conversion: It is advisable to keep a record of your conversions for future reference, particularly if you are consistently tracking your sugar levels.
- Understand Risk Levels: It's important to recognize that sugar levels can indicate varying risk levels for hyperglycemia. Cutoff points are identified at 4.5 and 9 mmol/L, which separate low, moderate, and high risk for hyperglycemia.
- Consider Post-operative Context: If you are managing diabetes after surgery, be aware that sugar levels exceeding 13.5 mmol/L require testing for urine ketones, with positive results necessitating monitoring every 4 hours.
By following these steps, you can accurately convert your serum measurements to mmol/l from mg/dl, which is crucial for effective diabetes management. Ongoing sugar monitoring is advised since it offers insights into daily fluctuations in sugar levels, as noted by Sarah Jayawardene, MS:
Utilizing a continuous sugar monitor is the favored approach for measuring and tracking sugar levels, as it illustrates how your personal levels change on a daily basis.
Moreover, progress in sugar monitoring technology, such as the Development of Continuous Glucose-EGA (CG-EGA), emphasizes the significance of precise level tracking.
The CG-EGA permits a thorough assessment of clinical accuracy across various glucose levels, improving the overall management of the condition. As we launch T2DSolutions, we aim to provide comprehensive resources, such as educational guides and interactive tools, alongside community support forums for individuals managing their health care. These resources will assist you in keeping your sugar levels within healthy limits and making informed choices regarding your health.
Common Scenarios for Converting Blood Glucose Levels
Transforming serum sugar levels from mg/dl to mmol/l is essential in various situations that can greatly influence management of sugar-related conditions:
-
Traveling Abroad: When visiting nations that utilize mmol/l, it is essential to convert your sugar level readings accordingly. This conversion ensures that you manage your condition effectively and avoid potential health risks. Notably, a case study revealed that only 7.9% of diabetic travelers carried identification for their condition, indicating a gap in preparedness that could jeopardize their safety while traveling.
-
Reading Medical Literature: A substantial portion of medical studies and guidelines employs mmol/l as the standard measurement unit. Being proficient in converting your measurements allows you to accurately interpret this information, which is vital for informed healthcare decisions.
-
Communicating with Healthcare Providers: If your healthcare team predominantly uses mmol/l for monitoring, the ability to convert your readings from mg/dl to mmol/l enhances communication and ensures a clear understanding of your blood glucose levels. The likelihood of visiting a physician increases with trip duration, with an odds ratio of 2.253, emphasizing the importance of being well-prepared.
-
Using Different Glucometers: Different glucometers may display results in either mg/dl or mmol/l. Familiarity with the conversion process aids in maintaining consistency in your monitoring, which is crucial for effective management of the condition.
By understanding these scenarios, you can enhance your confidence in handling the condition, ensuring you are well-prepared for various situations that may occur. As healthcare professionals often emphasize, being informed and prepared can significantly enhance your ability to manage your condition effectively while traveling.
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to supporting you on this journey.
Our platform will provide extensive resources, including educational materials, community support, and tools specifically designed for Type 2 and Type 3 management. Subscribe now to stay updated on our launch and access valuable information tailored to your needs.
Tips for Accurate Blood Glucose Monitoring
As part of T2DSolutions' commitment to supporting newly diagnosed patients in managing their diabetes, we present essential tips for accurate blood glucose monitoring and effective diabetes management:
-
Use a Quality Glucometer: Invest in a reliable and accurate glucometer tailored to your specific needs. Regular calibration, as per the manufacturer’s guidelines, is crucial for maintaining accuracy. Recent evaluations have shown that devices like the OneTouch UltraEasy achieved 91% accuracy within ±20%/15 mg/dL, underscoring the importance of selecting a high-quality meter.
-
Follow Testing Protocols: Adhering to established testing protocols is vital. Always wash your hands thoroughly before testing to prevent contamination of the sample, ensuring more accurate results. Additionally, it's important to note that 95% of measured sugar results should fall within ±10 mg/dL to mmol/l of lab reference values for concentrations less than 100 mg/dL and within 10% for concentrations equal to or greater than 100 mg/dL, highlighting the standards for accuracy in monitoring.
-
Keep a Logbook: Recording your blood glucose readings, along with details such as the time of day, food intake, and physical activity, is a beneficial practice. This log will assist you in recognizing patterns and making informed choices concerning your health care.
-
Consult with Your Healthcare Team: Regular discussions with your healthcare provider about your readings and any concerns are essential. This collaborative method enables prompt modifications to your strategy based on your unique needs and responses.
-
Stay Informed: Ongoing learning about blood sugar control is essential. Stay informed about the latest tools, techniques, and advancements in glucometer technology that can enhance your care. As M.A.K. noted, comprehending the statistics and reliability of your glucometer is essential for effective oversight.
-
Learn from Case Studies: Reviewing case studies, such as the "Accuracy Evaluation of Five Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems," can provide insight into the real-world performance of glucometers. This multicenter study evaluated the accuracy of various devices under daily routine conditions, offering valuable context for your own monitoring practices.
At T2DSolutions, we are committed to offering resources, tools, and community support to assist you in managing your condition effectively. Sign up for our newsletter to remain informed about the newest details and resources offered at T2DSolutions, empowering you on your health journey. By applying these strategies, you can greatly enhance your overall health control, preparing yourself to navigate different situations with assurance and precision.
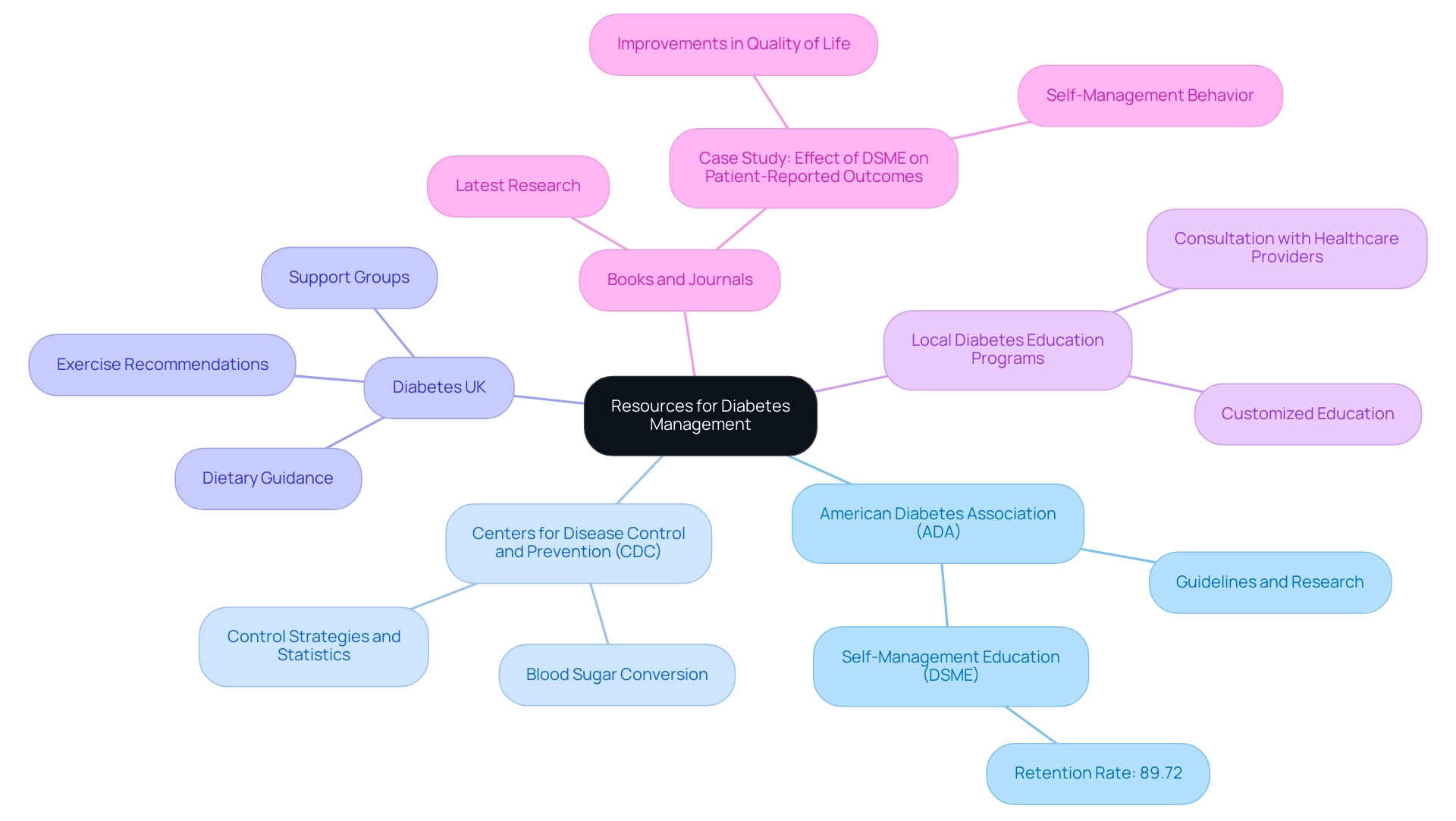
Resources for Further Learning
For individuals seeking to enhance their understanding of blood glucose management and overall diabetes care, the following resources are invaluable, and T2DSolutions is here to support you in utilizing them effectively:
- American Diabetes Association (ADA): The ADA serves as a cornerstone for those navigating health challenges, offering extensive guidelines, research findings, and educational materials that are crucial for effective care. Their commitment to providing up-to-date information helps empower patients to make informed decisions regarding their health. Notably, studies have shown that self-management education (DSME) programs have a retention rate of about 89.72%, highlighting their effectiveness in supporting patients.
-
Website: www.diabetes.org
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC is a vital source for information on blood sugar regulation, including control strategies and statistics that help in understanding the conversion from mg/dl to mmol/l. Their data-driven approach assists individuals in comprehending the broader context of health management, particularly the significance of converting mg/dl to mmol/l and making lifestyle changes.
-
Website: www.CDC.gov/diabetes
-
Diabetes UK: This organization offers a variety of comprehensive resources centered on managing the condition, including dietary guidance, exercise recommendations, and access to support groups. Their efforts play a significant role in fostering a community of support for individuals with this condition.
-
Website: www.diabetes.org.uk
-
Local Diabetes Education Programs: Numerous hospitals and clinics provide customized education programs aimed at addressing individual needs. Consulting with healthcare providers can lead to recommendations for programs that fit specific objectives and learning preferences. As Ehab Mudher Mikhael from the Department of Clinical Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, University of Baghdad, notes, "This review study aimed to determine the effectiveness and factors affecting the success of DSME programs in T2DM patients living in ME countries," underscoring the importance of these educational initiatives.
-
Books and Journals: Engaging with reputable literature on blood sugar management, including both practical guides and scientific journals, allows individuals to stay informed about the latest research and best practices in the field. A relevant case study titled "Effect of DSME on Patient-Reported Outcomes" assessed changes in patient-reported outcomes, including quality of life and self-management behavior, and found significant improvements resulting from these programs.
By actively utilizing these resources and connecting with T2DSolutions, patients can significantly improve their knowledge and skills in managing diabetes effectively. We encourage you to visit our website for more tailored support and educational materials, leading to better health outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of blood glucose measurement units, particularly the difference between mg/dl and mmol/l, is paramount for individuals managing diabetes. This article has highlighted the importance of these units in various contexts, including traveling abroad and interpreting medical literature, where accurate conversions are essential for effective diabetes management. The step-by-step guide provided ensures that individuals can confidently convert their glucose readings, while the scenarios outlined emphasize the practical applications of this knowledge.
Furthermore, the tips for accurate blood glucose monitoring reinforce the necessity of using quality glucometers, adhering to testing protocols, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers. Engaging with reliable resources, such as the American Diabetes Association and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, can significantly enhance an individual’s understanding and management of their condition.
In conclusion, empowerment through knowledge is crucial in diabetes care. By mastering the conversion between mg/dl and mmol/l, utilizing accurate monitoring techniques, and leveraging educational resources, individuals can take proactive steps toward effective diabetes management. This comprehensive approach not only aids in daily decision-making but also fosters a greater sense of control over one’s health journey.



