Overview:
The article provides a step-by-step guide on effectively using ICD-10 codes for diabetes screening, emphasizing the importance of accurate coding for appropriate patient treatment and management. It supports this by highlighting the significant implications of precise documentation on healthcare outcomes, such as reducing error rates in diabetes classification and enhancing insurance reimbursement processes, thus ensuring better care for individuals with diabetes.
Introduction
The realm of diabetes management is evolving, and at the heart of this transformation lies the critical role of ICD-10 coding. These alphanumeric codes are not just mere identifiers; they serve as the backbone for accurately diagnosing and documenting diabetes types, which is essential for effective patient care. With alarming statistics highlighting significant coding error rates, the need for precision in documentation has never been more pressing.
This article delves into the intricacies of ICD-10 codes, offering a comprehensive guide on their implementation, the importance of accuracy in coding practices, and recent updates that impact diabetes management. As healthcare professionals strive to enhance patient outcomes, understanding these coding classifications becomes paramount, paving the way for improved treatment strategies and resource allocation.
Understanding ICD-10 Codes: A Foundation for Diabetes Screening
ICD-10 identifiers, formally known as International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision identifiers, serve as essential alphanumeric markers for classifying medical diagnoses and procedures. In the context of diabetes screening ICD 10, these codes play a crucial role in accurately identifying specific diabetes types, such as:
- Type 1 diabetes (E10)
- Type 2 diabetes (E11)
Grasping these classification systems is essential for healthcare practitioners, as accurate documentation of conditions directly affects treatment and management approaches.
A notable statistic reveals a 42.2% error rate within glycemic control groups, which can lead to significant implications for patient care, emphasizing the necessity for enhanced accuracy in documentation to ensure appropriate treatment plans. Moreover, familiarity with the programming structure, which includes additional characters to denote complications or manifestations, is imperative for effective screening practices. As stated in a recent study, the finding that diabetes screening ICD 10 codes can accurately classify type 1 and type 2 diabetes in youth and young adults diagnosed with diabetes before age 20 years supports the use of diabetes screening ICD 10 codes for rapid and cost-efficient diabetes surveillance.
This highlights the significance of diabetes screening ICD 10 classification not only for immediate clinical care but also for ongoing research and tracking of individuals, particularly concerning the documentation of U09.9, which is essential for evaluating long-term health outcomes. Furthermore, a case study examining hyperglycemic crisis emergency visits in 2020 revealed that:
- 8.4% of cases were treated and released
- 84.4% were admitted to the hospital
This emphasizes the importance of precise ICD-10 classification in managing critical situations. As T2DSolutions launches as a new resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 health education and community support, it aims to provide newly diagnosed individuals with comprehensive information on these essential coding practices, including detailed guides and resources on understanding ICD-10 codes, ensuring they are well-informed about their health care and management strategies.
By providing educational resources and assistance, T2 Solutions will enable individuals to manage their condition effectively. Lastly, it is important to note that Springer Nature maintains neutrality regarding jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations, which is relevant when considering the credibility of the sources used in this context.
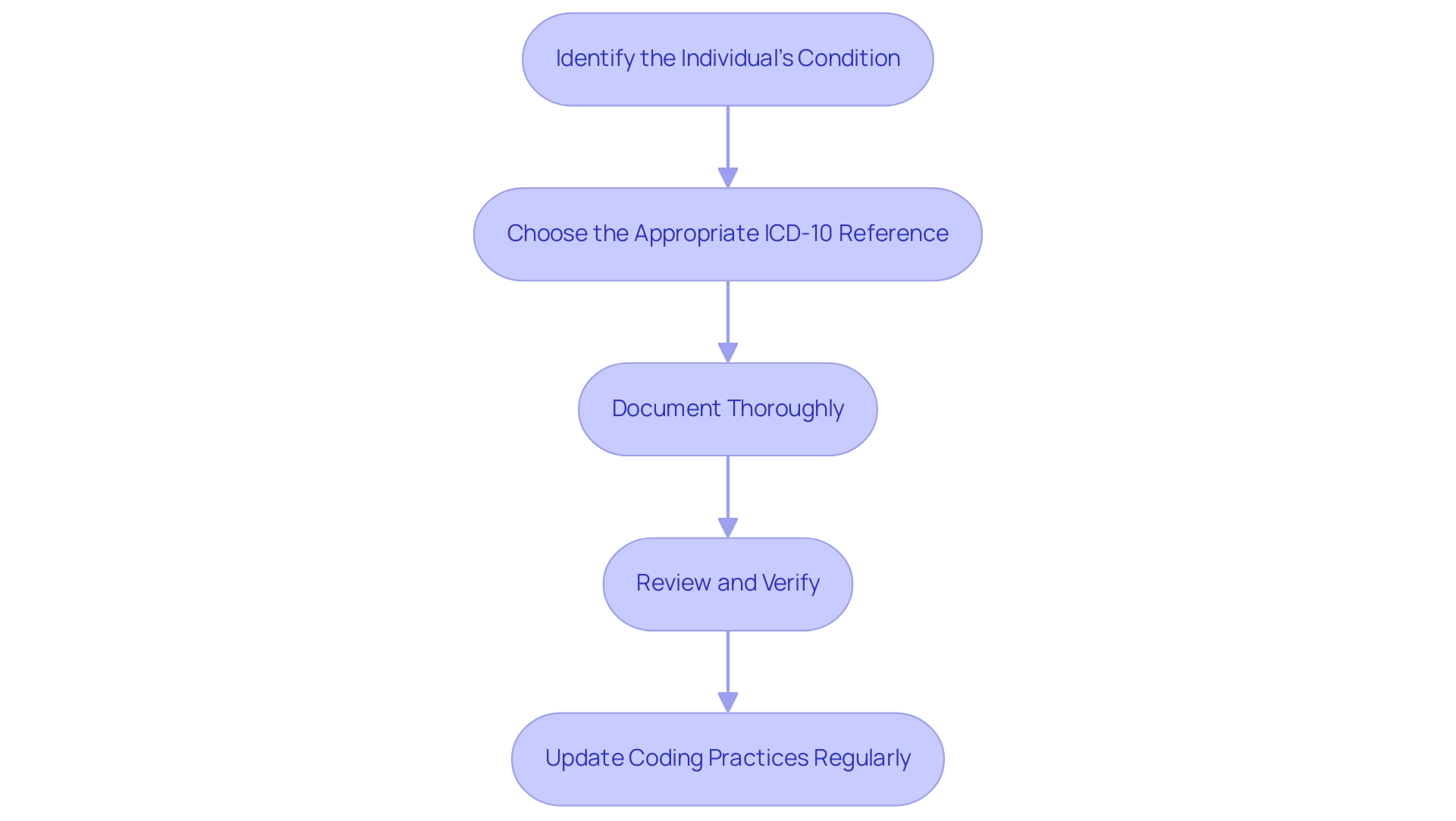
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing ICD-10 Codes for Diabetes Screening
-
Identify the Individual's Condition: Start by conducting a comprehensive assessment of the individual's medical history and current symptoms. This foundational step is crucial for establishing an accurate diabetes diagnosis and is part of the diabetes screening ICD 10, particularly given the growing evidence that comorbid conditions, such as obesity, can significantly increase the risk of diabetes complications, evidenced by a 7.59-fold increase in postpartum type 2 diabetes mellitus risk. Comprehending these risks highlights the significance of precise documentation and diagnosis in managing individuals.
-
Choose the Appropriate ICD-10 Reference: Use the ICD-10 manual or software to determine the most accurate number that represents the individual's diagnosed condition. Be attentive to any complications or specific details that may require additional characters in the programming process, ensuring that the selection aligns with the nuances of the individual's health status. As highlighted by Lipton ZC et al., advancements in diagnostic methods, such as learning to diagnose with LSTM recurrent neural networks, can further enhance the accuracy of this step.
-
Document Thoroughly: Accurately record the chosen ICD-10 identifier in the individual's medical record. It is crucial that this implementation aligns directly with the diagnosis determined during the diabetes screening ICD 10 to maintain the integrity of the individual's health documentation. Proper citation and adherence to non-commercial use guidelines, as emphasized by Bushra Khokhar, are vital in ensuring the ethical use of medical information.
-
Review and Verify: Conduct a meticulous review of the programming for accuracy. It may be advantageous to consult with programming experts to verify that the suitable instructions have been implemented, reducing the likelihood of mistakes that can result in issues with patient management and billing procedures. Real-world examples, such as the findings from the case study titled 'Validation of ICD Algorithms for Diabetes Mellitus,' demonstrate that effective practices in diabetes screening ICD 10 can significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy, achieving a sensitivity of 92.3% and specificity of 96.9%.
-
Update Coding Practices Regularly: Finally, remain vigilant about updates or modifications to ICD-10 codes. Regularly refreshing your knowledge of programming practices is vital for ensuring ongoing precision in documentation. As emphasized in the SEARCH Registry Study at Kaiser Permanente Southern California, where the application of ICD-10-CM classification was thoroughly examined, remaining informed can significantly improve classification efficiency and healthcare results.
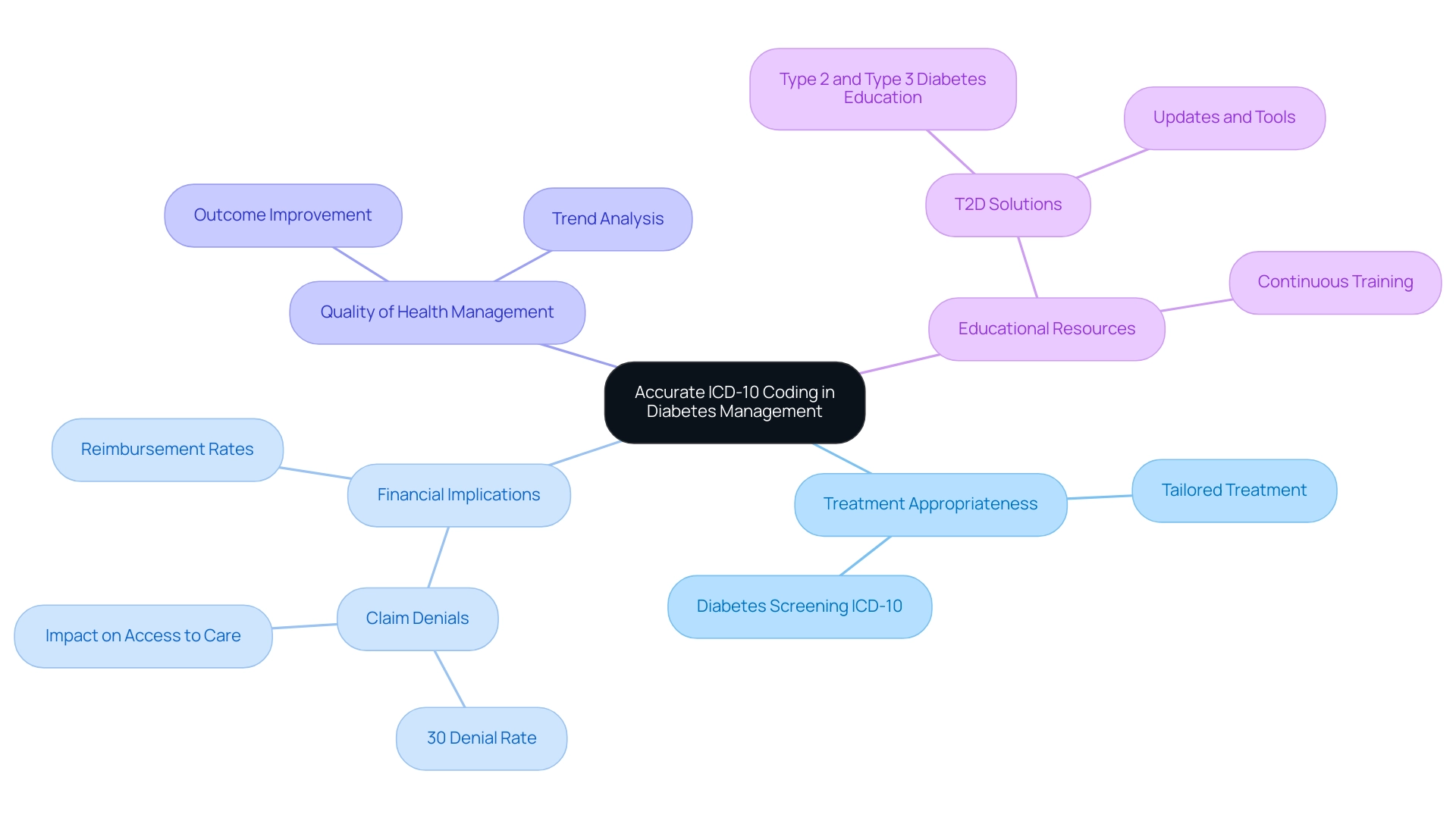
The Importance of Accurate ICD-10 Coding in Diabetes Management
Precise ICD-10 classification is essential for effective management of blood sugar levels for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures that individuals receive appropriate treatment tailored to their specific diabetes diagnosis through diabetes screening icd 10. Precise programming significantly affects reimbursement rates from insurance providers; faulty entries can result in claim denials or reduced payments, with studies indicating that nearly 30% of claims are denied due to incorrect practices.
This financial burden can severely affect individuals' access to necessary care. Moreover, accurate programming aids in the overall quality of health management by supplying valuable information for examining trends and outcomes, ultimately improving individual results. As Paul F. Hogan from The Lewin Group, Inc. states, 'Accurate documentation not only supports proper treatment but is also essential in navigating the complexities of insurance reimbursement.'
With the upcoming launch of T2D Solutions, a new resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education, individuals will soon have access to vital information and support that can aid in understanding their conditions and managing their care effectively. We encourage you to subscribe to our updates to stay informed about the latest resources and tools that will be available. Continuous training and updates on programming practices are essential for healthcare professionals to ensure accuracy in their documentation.
This diligence not only enhances care for individuals but also alleviates financial burdens linked to erroneous labeling related to diabetes screening icd 10, which can result in substantial claim denials. For instance, a case study titled 'Provider Specialty Influence on Diabetes Coding' revealed that endocrinology encounters had a T2DM sensitivity of 85.7%, compared to 91.2% for other specialties, highlighting the real-world implications of coding practices. At T2DSolutions, we aim to provide the tools and resources necessary for patients and healthcare providers alike to navigate these complexities with confidence.
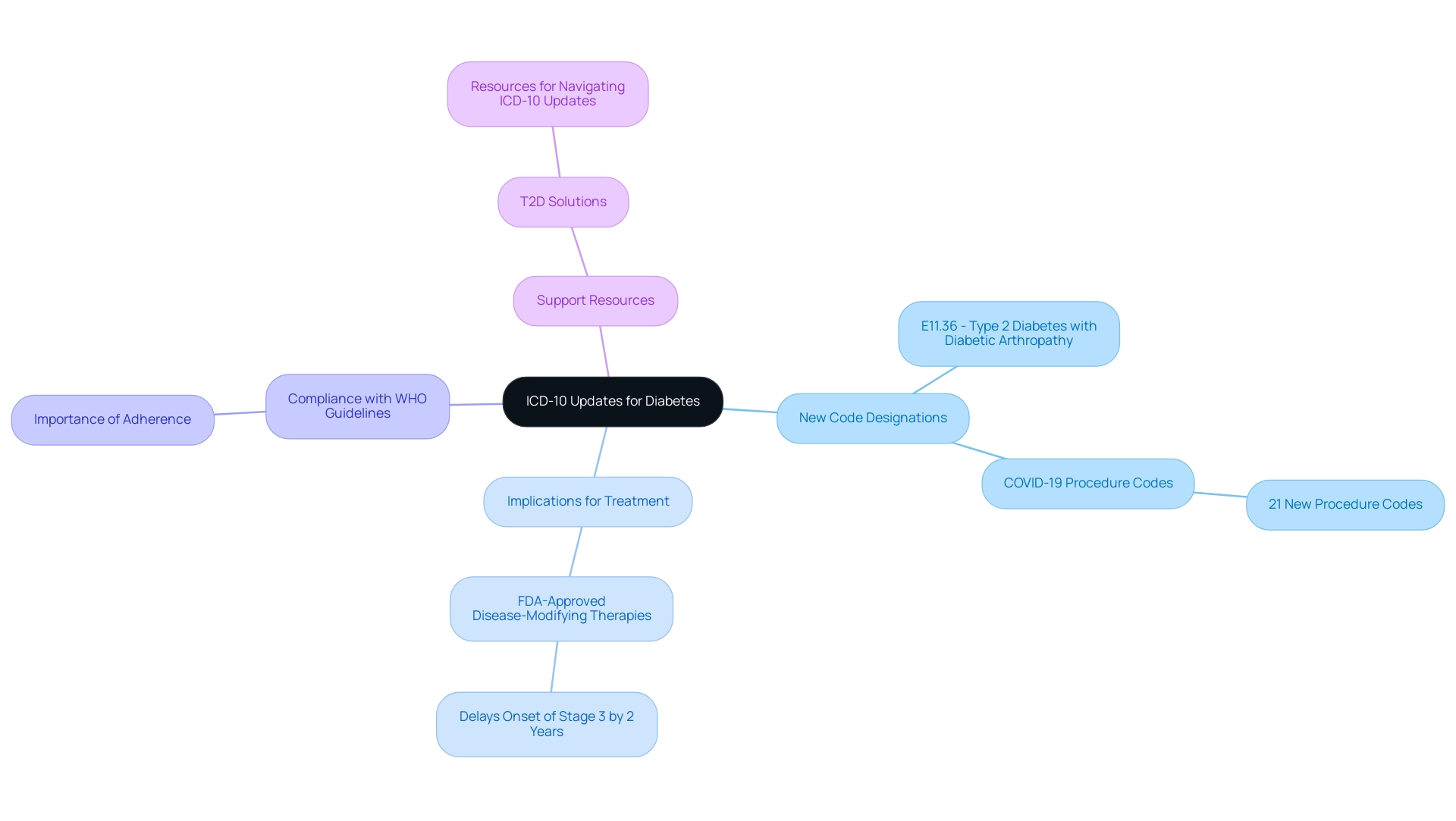
Recent Updates to ICD-10 Codes for Diabetes: What You Need to Know
Recent updates to the ICD-10 classifications for the condition have introduced a range of new designations that more precisely specify complications associated with the illness. For example, one such identifier, E11.36, specifically addresses Type 2 mellitus with diabetic arthropathy. Furthermore, the 2021 ICD-10-PCS updates incorporated new procedure classifications for COVID-19 treatments, illustrating the changing dynamics of blood sugar management amid the pandemic.
Statistics indicate that individuals diagnosed in stage 2 of the condition may be eligible for FDA-approved disease-modifying therapies, which can postpone the onset of stage 3 by an average of two years. These updates underscore the necessity for healthcare providers to be well-versed in these changes. T2D Solutions seeks to support recently diagnosed individuals by offering advice on comprehending and utilizing diabetes screening ICD 10 classifications in their management journey.
Familiarity with the official ICD-10 updates and adherence to guidelines set forth by the World Health Organization (WHO) are critical for ensuring compliance and the effectiveness of coding practices. As management of the condition progresses, it is essential that healthcare providers adjust to these revised standards to enhance care and results. As noted by health specialists, 'The integration of new codes not only enhances our ability to document complications but also supports improved treatment pathways for those we serve.'
Through T2DSolutions, individuals will find valuable resources and support to navigate these updates effectively.
Resources and Tools for Effective ICD-10 Coding in Diabetes Screening
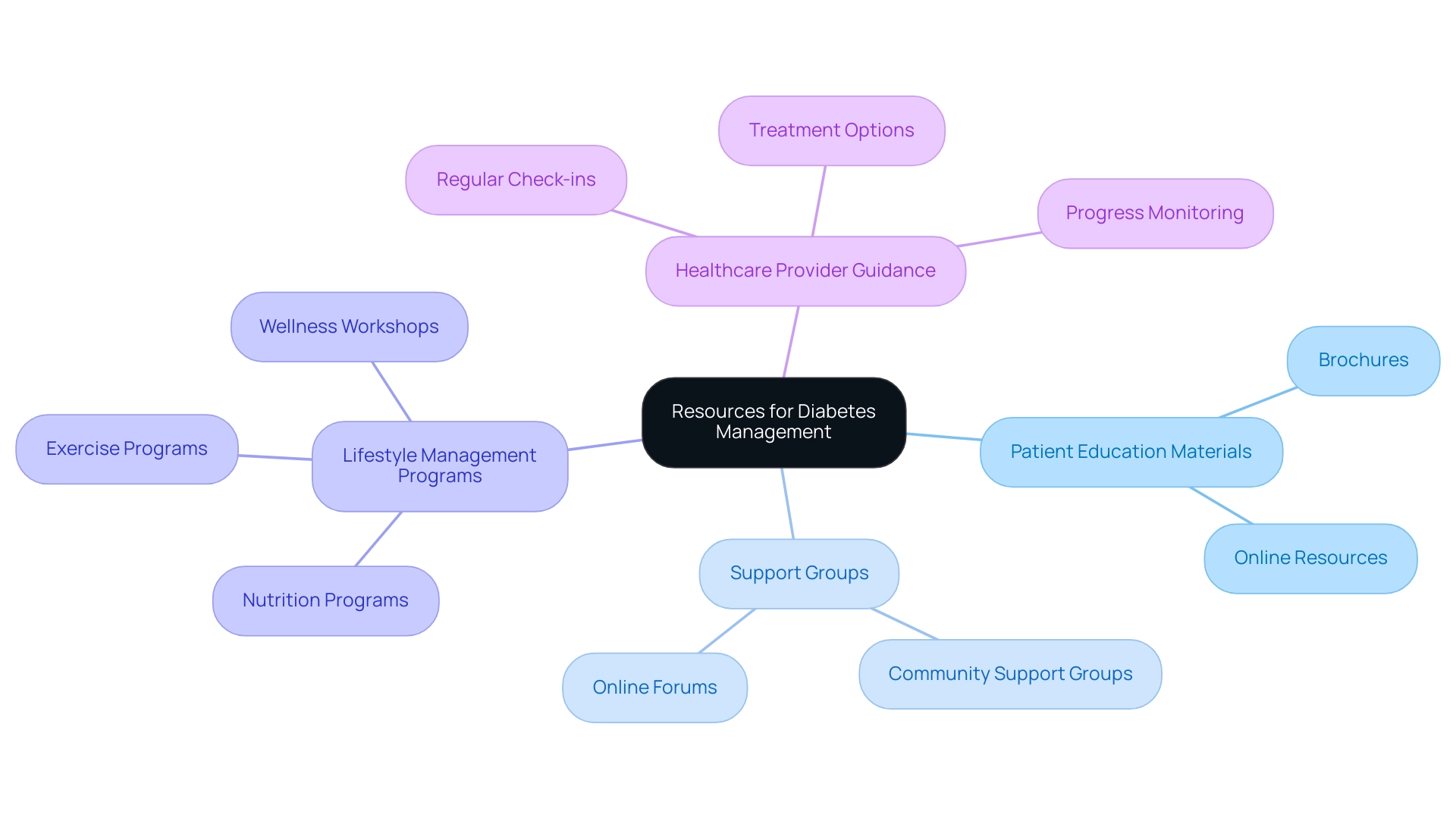
For newly diagnosed patients, comprehending management of the condition is essential. Here are some valuable resources to help you navigate your journey:
- Patient Education Materials: Look for brochures and online resources that explain the condition, its management, and the importance of regular monitoring. These materials can offer insights into what this condition means for your health and daily life.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can be incredibly beneficial. Many communities provide support groups where you can exchange experiences and gain insights from others.
- Lifestyle Management Programs: Consider enrolling in programs that emphasize nutrition, exercise, and overall wellness designed for individuals with blood sugar concerns. These programs can provide practical tips and strategies for managing your condition effectively.
- Healthcare Provider Guidance: Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider are essential. They can help you understand your treatment options, monitor your progress, and make necessary adjustments to your management plan.
By utilizing these resources, newly diagnosed patients can gain the knowledge and support needed to manage their diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
The significance of accurate ICD-10 coding in diabetes management cannot be overstated. It is essential for ensuring that patients receive the appropriate treatments tailored to their specific diagnoses. With a staggering error rate in coding practices, the need for precision in documentation is critical, not just for effective patient care but also for accurate reimbursement from insurance providers. This underscores the importance of ongoing training and adherence to updated coding practices, which can significantly enhance patient outcomes and minimize financial burdens.
Furthermore, recent updates to ICD-10 codes reflect the evolving landscape of diabetes management, allowing for more precise documentation of complications and treatment pathways. As healthcare professionals familiarize themselves with these changes, they can better navigate the complexities of diabetes care. The establishment of resources like T2DSolutions offers patients and providers vital information and support, empowering them to manage diabetes more effectively.
In conclusion, the integration of accurate ICD-10 coding practices is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. By prioritizing accuracy and staying informed about coding updates, healthcare professionals can significantly improve patient care, enhance treatment strategies, and ultimately contribute to better health outcomes for those living with diabetes.



