Overview:
To lower your A1C from 6.7, individuals should implement dietary changes, engage in regular physical activity, maintain consistent meal timing, stay hydrated, manage stress, and prioritize quality sleep. The article outlines that these lifestyle modifications, supported by research, can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and glucose regulation, ultimately aiding in achieving a healthier A1C level.
Introduction
Understanding A1C levels is essential for anyone navigating the complexities of diabetes management. An A1C reading of 6.7% indicates that blood glucose levels have been elevated over the past few months, placing individuals within the prediabetes category. This critical threshold not only highlights the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes but also underscores the importance of proactive health measures.
As diabetes continues to affect millions, with a significant portion of the adult population classified as having prediabetes, it is imperative to grasp the implications of these numbers. This article delves into effective strategies for managing A1C levels, exploring:
- Dietary changes
- Physical activity
- The role of medication when lifestyle adjustments alone are insufficient
By equipping readers with knowledge and resources, it aims to foster a comprehensive understanding of diabetes management and promote healthier outcomes.
Understanding Your A1C Level: What Does 6.7 Mean?
An A1C measurement of a1c 6.7% signifies that your average blood glucose readings have been elevated beyond normal ranges over the preceding two to three months. This measurement falls within the prediabetes category, indicating an increased likelihood of progressing to type 2 if proactive measures are not implemented. Grasping this stage is essential as it acts as a fundamental reference point for your health management strategy.
At T2DSolutions, we are committed to empowering diabetes management through education and community support. We provide a variety of resources, including:
- Educational materials
- Workshops
- Community programs
These resources are aimed at assisting you in understanding and managing your A1C values effectively. It is generally recommended to maintain an A1C level of a1c 6.7 or lower to effectively reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
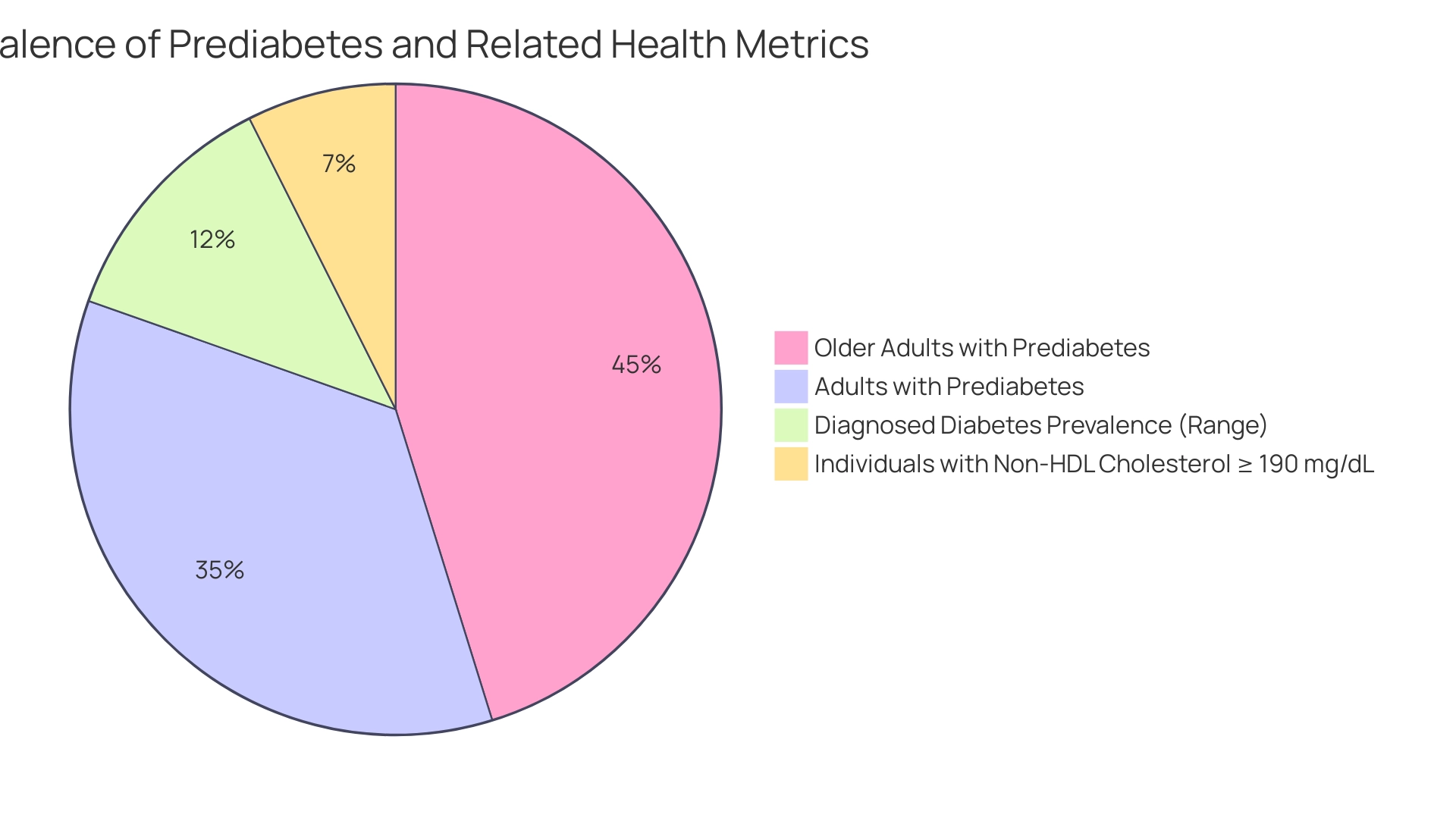
In the U.S., diagnosed prevalence of this condition among adults aged 20 years or older ranges from 4.4% to 17.9%, highlighting the widespread impact of this issue. Additionally, the number of discharges for major cardiovascular disease decreased from 1.92 million in 2019 to 1.68 million in 2020, further emphasizing the health risks linked with blood sugar regulation issues and prediabetes. With 97.6 million adults in the U.S. classified as having prediabetes, representing 38.0% of the adult population, the significance of this measure cannot be overstated.
This statistic underlines the importance of preventive actions, especially considering that among older adults aged 65 and older, the prevalence rises to 48.8%. Furthermore, 8.0% of individuals have non-HDL cholesterol values of 190 mg/dL or higher, indicating the interconnectedness of diabetes management and cardiovascular health. Thus, actively managing and monitoring your A1C measurements to achieve an a1c 6.7 is a key component in safeguarding against future health challenges, and T2D Solutions aims to provide the necessary resources and community support to assist you in this journey.
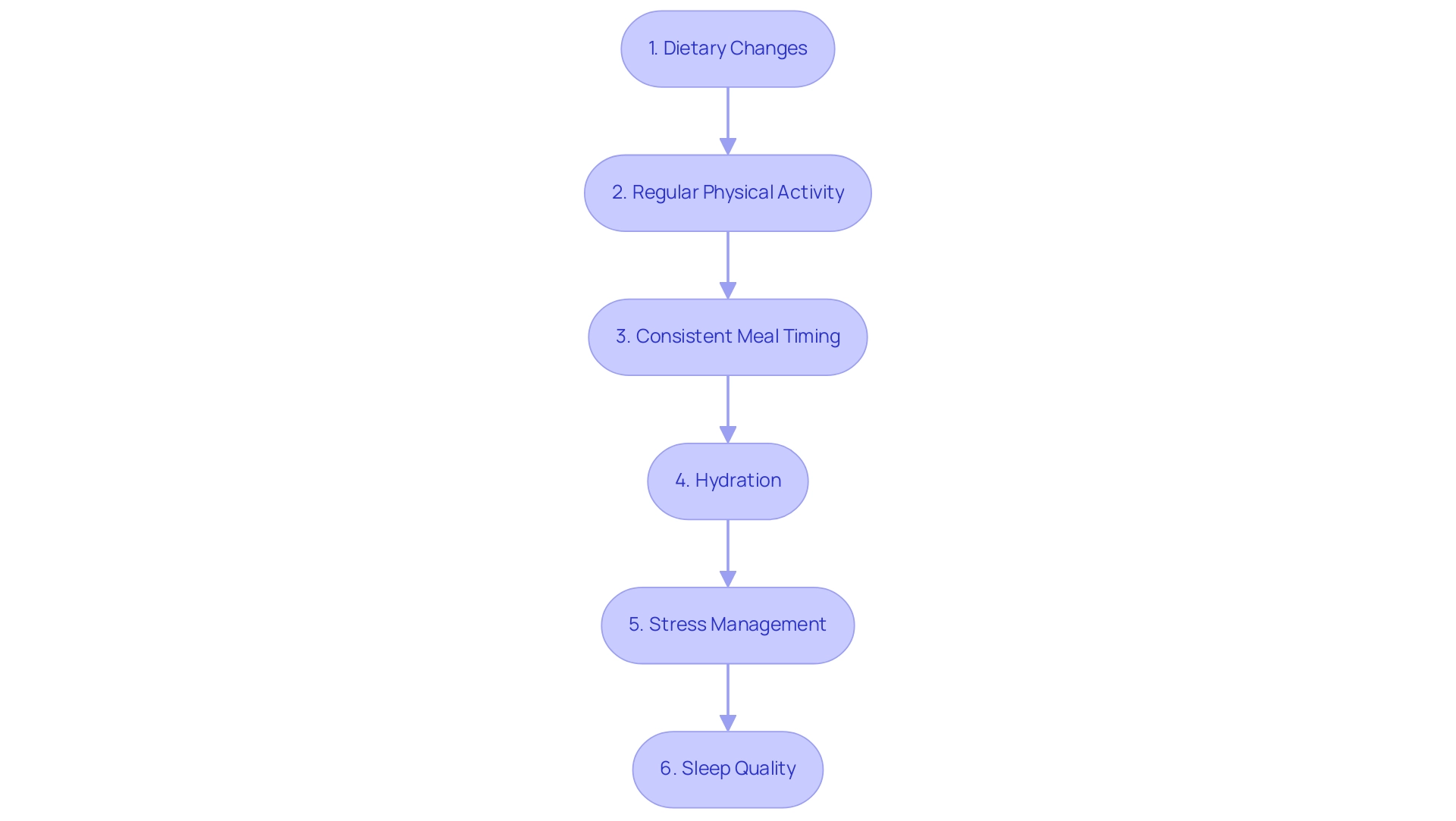
Effective Strategies to Lower Your A1C: A Step-by-Step Approach
-
Dietary changes: Embracing a balanced diet is crucial for effectively managing A1C 6.7. Focus on incorporating whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables into your meals. It is advisable to limit the intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-carbohydrate meals. Collaborating with a registered dietitian can help you develop a personalized meal plan tailored to your specific needs. Recent research indicates that dietary modifications can lead to significant reductions in A1C values; for instance, a clinical trial demonstrated that participants on a low-carbohydrate diet showed a decrease in A1C 6.7 by 0.23% compared to those on a standard diet. Furthermore, a change in RAPA score was linked to a change in the healthy food score among men at the third year of follow-up, further highlighting the significance of dietary changes in regulating sugar levels. Furthermore, the reduction in sulfonylurea dose by 1.6 ± 3.6 mg across both arms of the study highlights the effectiveness of dietary changes and physical activity in achieving an A1C 6.7. As noted by Kirsten S. Dorans, ScD, from the Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, "These findings were presented in part as an abstract at the American Diabetes Association 82nd Scientific Sessions; June 5, 2022; New Orleans, Louisiana," underscoring the significance of these dietary strategies.
-
Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining A1C 6.7. The current recommendation is to accumulate at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, which can include activities such as brisk walking, swimming, and cycling. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises at least twice a week has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity, further supporting glucose control.
-
Consistent Meal Timing: Maintaining a regular eating schedule can assist in glucose regulation. It is important to avoid skipping meals, as this can lead to fluctuations in glucose concentrations. Instead, consider smaller, more frequent meals to promote stable glucose concentrations throughout the day.
-
Hydration: Sufficient hydration is essential for overall well-being and can help in regulating sugar concentrations. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps the kidneys flush out excess sugar through urine, thereby supporting metabolic processes.
-
Stress Management: Incorporating stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can be beneficial. Stress has a negative effect on blood sugar amounts, making stress management a vital aspect of diabetes control.
-
Sleep Quality: Prioritize obtaining 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night, as inadequate sleep can adversely affect insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. By addressing these lifestyle factors, individuals can significantly enhance their health outcomes and aim to achieve an A1C of A1C 6.7.
The Impact of Weight Loss on A1C Levels
Research demonstrates that even a modest weight loss of 5-10% of total body weight can lead to a significant decrease in A1C 6.7 levels. This improvement is primarily attributed to enhanced insulin sensitivity and a reduction in hepatic glucose production. The SURPASS studies emphasize this relationship, showing that participants with a mean baseline A1C ranging from 7.9% to 8.6% and a mean duration of type 2 condition from 4.7 to 13.3 years benefited from weight management interventions.
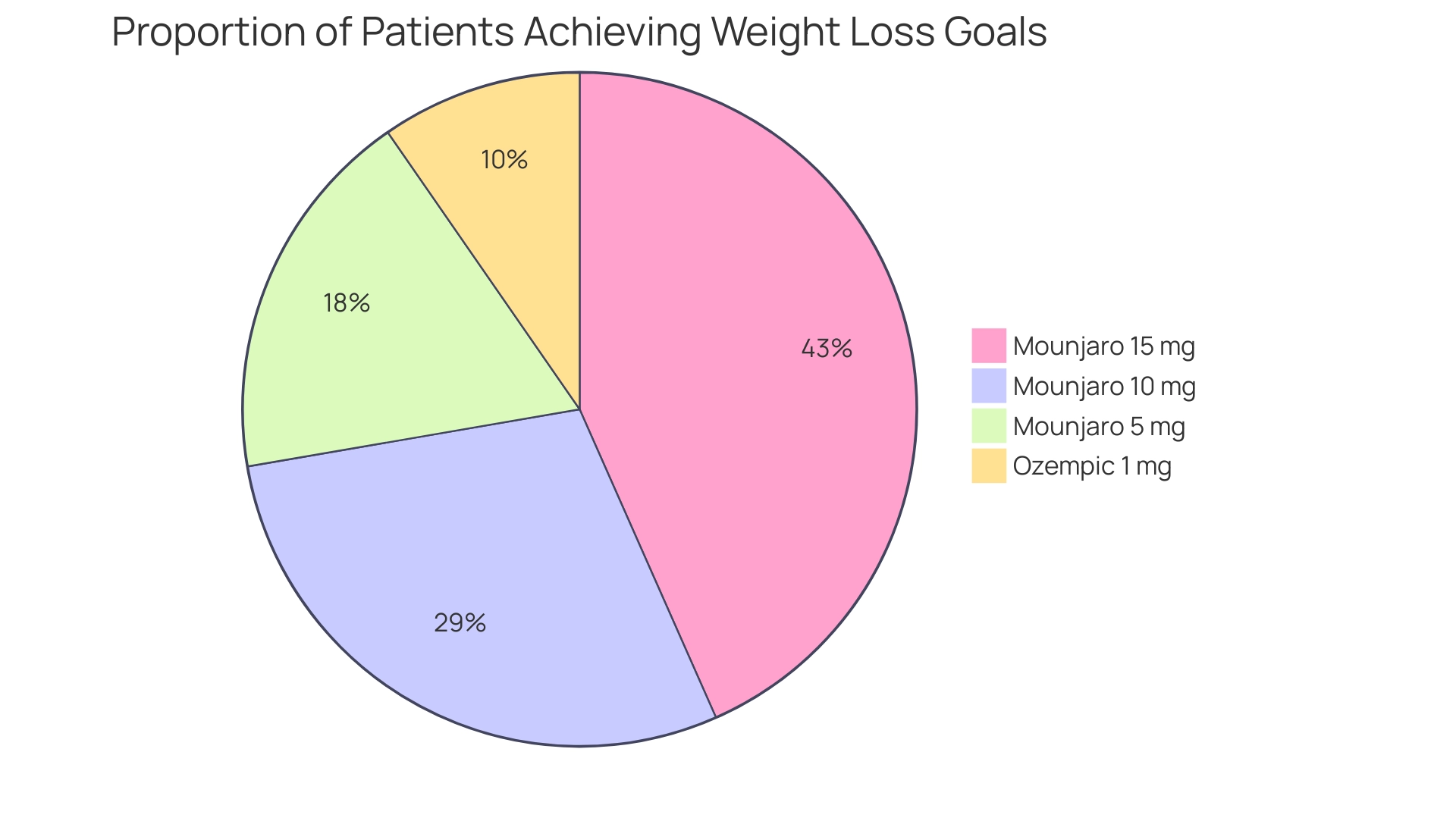
For instance, the SURPASS-2 study assessed the proportion of patients achieving a weight reduction of ≥15% after 40 weeks of treatment, showing that:
- 15% of patients on Mounjaro 5 mg
- 24% on Mounjaro 10 mg
- 36% on Mounjaro 15 mg
- 8% on Ozempic 1 mg
achieved this target. Effective strategies for achieving weight loss include a comprehensive approach that encompasses:
- Dietary modifications
- Increased physical activity
- Behavioral changes
Setting realistic weight loss goals and diligently tracking progress can serve as powerful motivators in this journey.
As T2DSolutions prepares to launch, we aim to provide resources that support these weight management strategies, helping newly diagnosed patients understand their role in managing their condition. Notably, Williamson et al. reported that individuals with diabetes who engage in intentional weight loss may experience substantial long-term health benefits, including a 25% reduction in total mortality and a 28% reduction in cardiovascular disease-plus-diabetes mortality.
Hence, pursuing weight loss not only aids in lowering A1C 6.7 levels but also contributes positively to overall health outcomes.
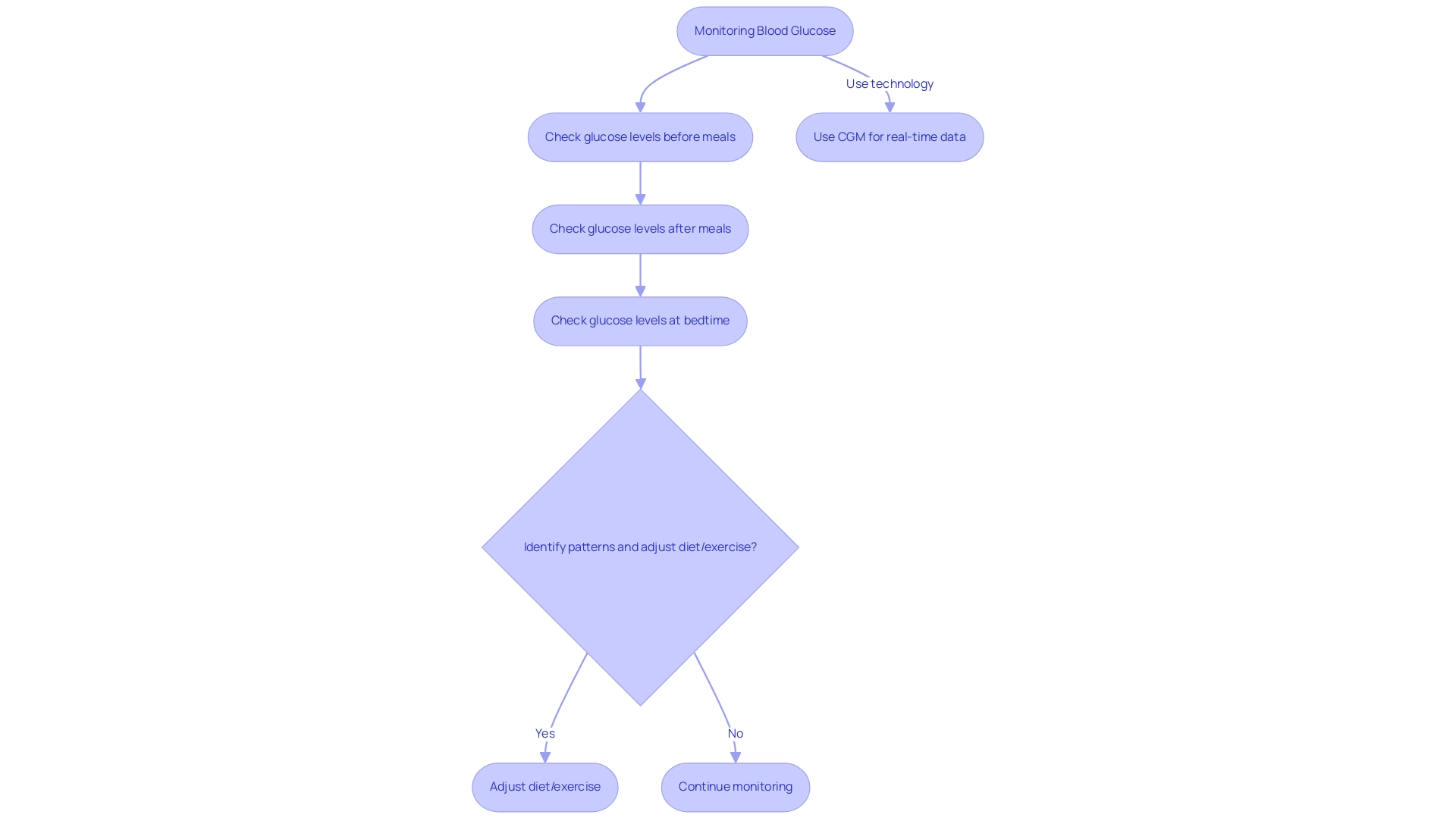
Monitoring Blood Glucose: Key to Managing Your A1C
Consistent monitoring of glucose levels is vital for comprehending how your body reacts to dietary choices, physical activity, and medications. It is recommended to check your glucose levels at multiple points throughout the day, particularly before and after meals, as well as at bedtime. By maintaining a detailed log of these readings, you can identify patterns that may necessitate adjustments to your diet and exercise routines.
Healthcare providers, like Lee GS, emphasize the importance of this practice, noting,
Continuous monitoring is key in managing this condition effectively.
It is crucial to discuss your glucose monitoring schedule with your healthcare provider to ensure it is in line with your treatment objectives. Current technology, including continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, offers real-time data that can further enhance your management strategy.
In fact, the recent study on medication use trends in managing blood sugar shows that as patients increasingly adopt CGM, there is a notable shift towards newer therapies such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors. Considering that in 2020, there were 202,000 emergency department visits due to hypoglycemia among adults with high sugar levels, equating to 8.6 visits per 1,000 adults, proactive glucose monitoring becomes even more essential in preventing such incidents. Furthermore, it’s worth noting that 63.2% of patients continued using p-CGM during the 6-month follow-up, highlighting the growing trend of technology adoption in managing blood sugar.
Comprehending and incorporating blood glucose monitoring into your daily routine is a fundamental aspect of managing the condition that T2 Solutions aims to support through its educational resources and community initiatives.
When Lifestyle Changes Aren't Enough: Medication Options for A1C Management
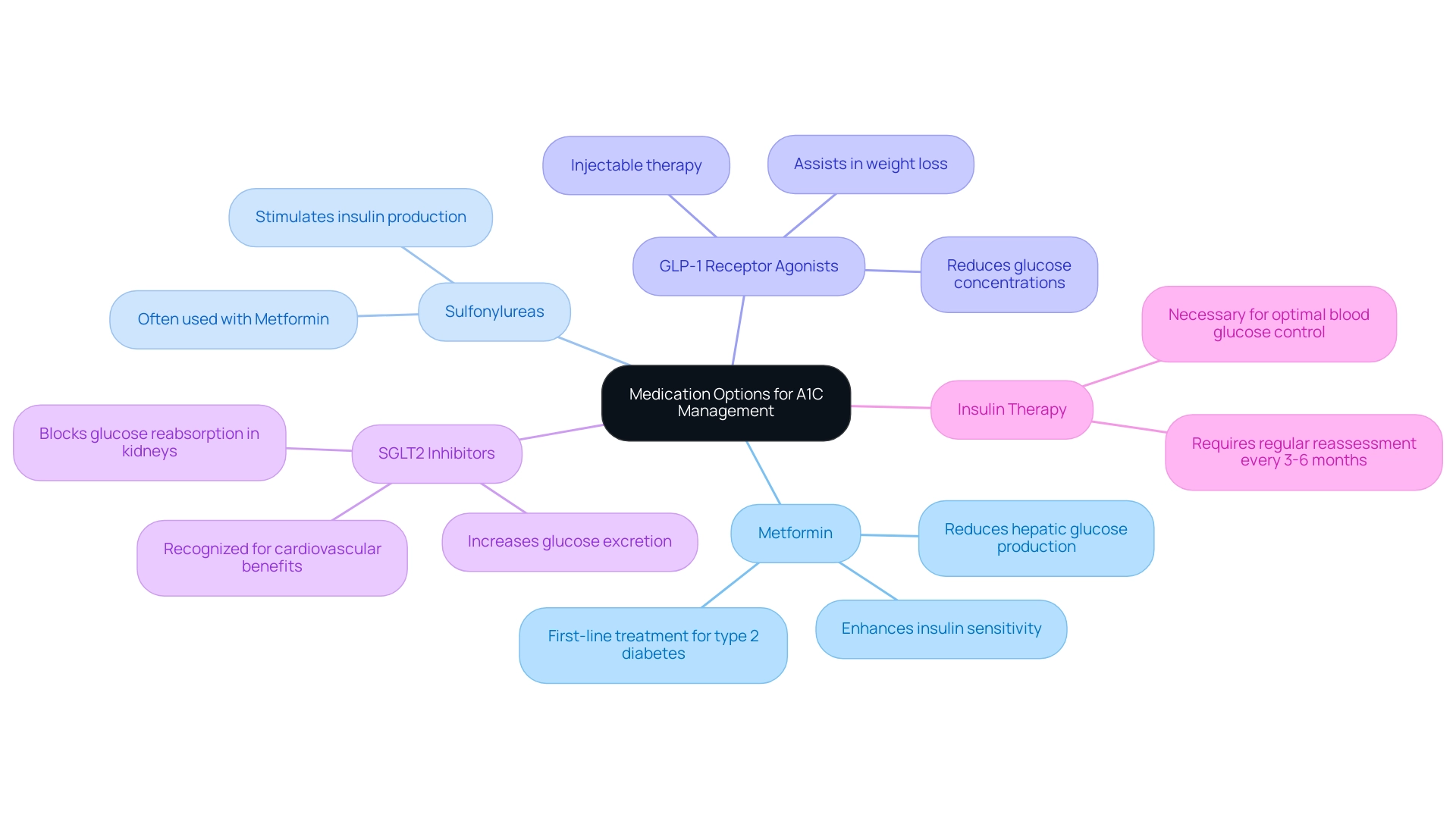
When lifestyle modifications alone do not yield satisfactory reductions in A1C levels, achieving an A1C of 6.7 may require the introduction of medications. The most commonly prescribed classes of diabetes medications are as follows:
-
Metformin: Recognized as the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, Metformin effectively reduces hepatic glucose production while enhancing insulin sensitivity, making it a cornerstone in diabetes management. Recent studies endorse its effectiveness, emphasizing a significant decrease in A1C values, with many users achieving an A1C of 6.7.
-
Sulfonylureas: These medications operate by stimulating the pancreas to increase insulin production. They are often prescribed alongside Metformin to achieve better glycemic control.
-
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: As injectable therapies, GLP-1 receptor agonists not only reduce glucose concentrations but can also assist in weight loss, a helpful aspect for many patients. Their effectiveness has been demonstrated in clinical settings, including recent studies involving over 1,800 adults with type 2 diabetes, where an average baseline A1C of 6.7 was reported.
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors: These medications function by blocking glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, leading to increased glucose excretion and reduced sugar concentrations. They are increasingly being recognized for their cardiovascular benefits in addition to glycemic control.
-
Insulin Therapy: In particular cases, insulin may be necessary to achieve optimal blood glucose control. It is vital to regularly reassess insulin treatment plans and behaviors every 3 to 6 months to ensure that individualized glycemic targets are consistently met.
The recent Mounjaro Clinical Data Review emphasizes how healthcare providers can improve their comprehension of medications for managing blood sugar, including Mounjaro, specifically for effectively managing A1C 6.7 values. Consulting with your healthcare provider is crucial to determine the most suitable medication tailored to your specific health needs and treatment objectives. According to Michael S. Smith, a noted expert in the field, "understanding the durability of oral diabetic medications is essential for effective diabetes management," especially for achieving target levels like A1C 6.7, as highlighted in recent clinical discussions surrounding options like Metformin.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing A1C levels is crucial for preventing the progression of prediabetes to type 2 diabetes. An A1C reading of 6.7% serves as a wake-up call, emphasizing the need for proactive measures to mitigate health risks. The article outlined effective strategies for managing A1C levels, including:
- Dietary changes
- Regular physical activity
- Consistent meal timing
- Hydration
- Stress management
- Quality sleep
Each of these lifestyle modifications plays a significant role in improving insulin sensitivity and overall health.
Weight management emerged as a pivotal factor in lowering A1C levels, with even modest weight loss leading to substantial health benefits. The evidence presented underscores the interconnectedness of weight control and diabetes management, reinforcing the importance of comprehensive strategies that encompass dietary adjustments and increased physical activity.
Furthermore, monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for understanding personal responses to lifestyle choices and medications. Technology, such as continuous glucose monitoring systems, enhances this process, allowing for data-driven decisions in diabetes management. When lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, exploring medication options becomes necessary, with various treatments available to help achieve targeted A1C levels.
In summary, effective diabetes management hinges on a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle adjustments, weight management, vigilant monitoring, and, when necessary, medication. By adopting these strategies and utilizing available resources, individuals can take meaningful steps towards better health outcomes and a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications.



