Overview:
To lower your A1C from 7.5, it is recommended to implement dietary changes, engage in regular exercise, manage weight, and adhere to prescribed medications. The article supports this by highlighting that these strategies collectively improve blood sugar management and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, emphasizing the importance of a balanced approach to lifestyle modifications and medical oversight.
Introduction
Understanding A1C levels is essential for effective diabetes management and prevention of complications. A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, reflects average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, serving as a critical indicator of an individual's diabetes control.
With a target A1C level often set below 7%, maintaining this benchmark can significantly reduce the risk of serious health issues, including:
- cardiovascular diseases
- neuropathy
This article delves into the importance of A1C testing, effective strategies to lower elevated levels, and the role of lifestyle modifications and medication management in achieving optimal health outcomes. By providing insights and practical advice, this resource aims to empower individuals in their journey toward better diabetes management.
Understanding A1C: What It Means and Why It Matters
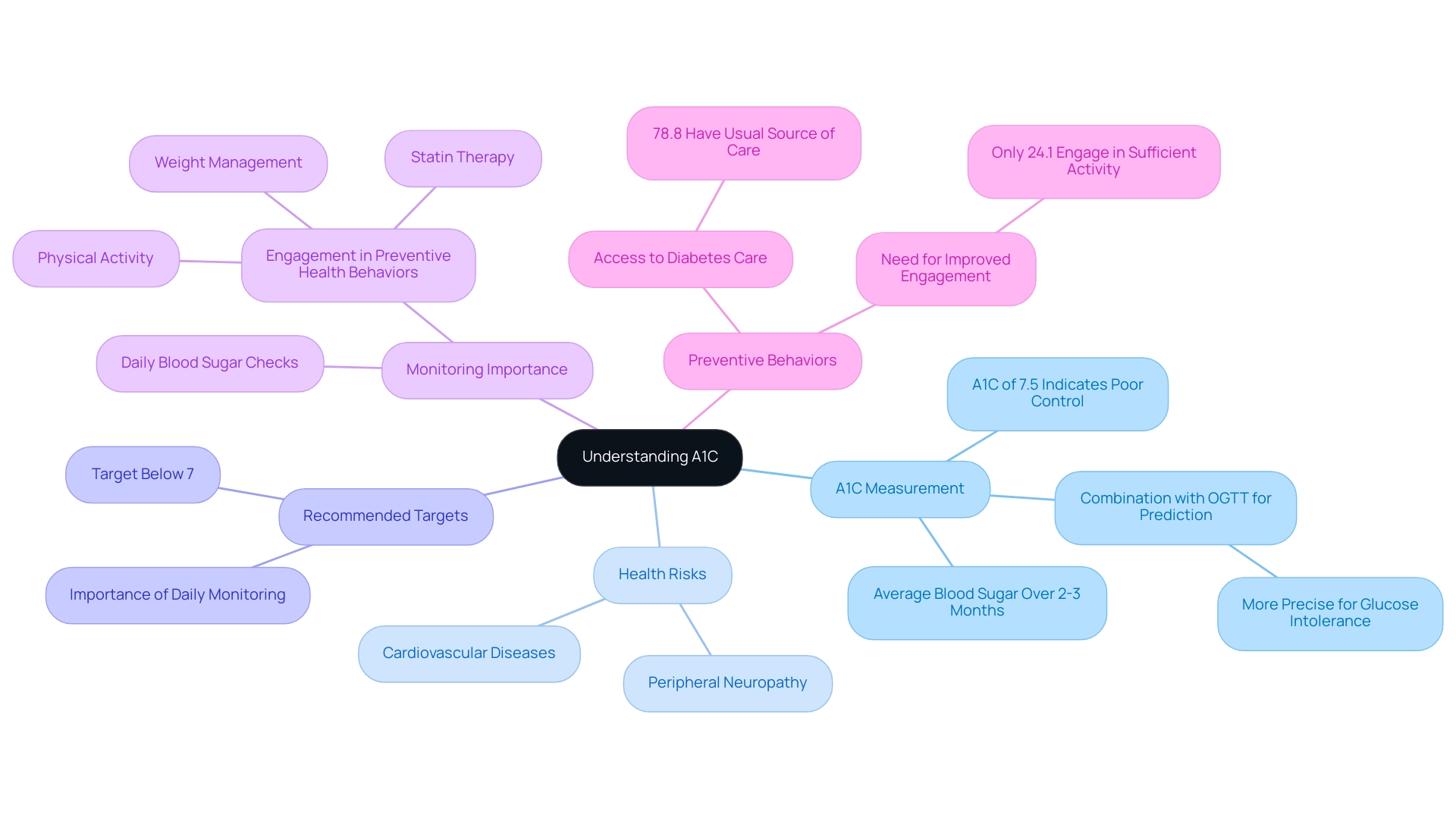
A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, acts as an essential blood test that shows your average blood sugar readings over the past two to three months. An A1C measurement of 7.5% indicates that blood sugar readings have consistently surpassed the recommended targets for effective management of the condition. This reading is critical as it correlates with an increased risk of diabetes-related complications, including cardiovascular diseases and peripheral neuropathy.
As a general guideline, aiming for an A1C target below 7% is often advised for individuals managing their condition, as this reduction can significantly lessen the risks associated with these complications and improve overall health outcomes. Moreover, the average baseline fasting plasma glucose (FPG) across studies was determined to be 5.4 mmol/l, offering a reference point for comprehending blood sugar amounts in relation to A1C. Recent insights emphasize that the combination of A1C and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) can lead to a more precise prediction of the condition's progression, particularly in those experiencing glucose intolerance, as noted by expert Yoshinaga.
Furthermore, raising the percentage of adults with insulin-dependent conditions who check their blood sugar daily is essential for effective control of A1C values. A case study titled 'Preventive Factors for Diabetes Care' highlights that while 78.8% of individuals had at least one usual source of care for their condition, only 24.1% engaged in sufficient physical activity, underscoring the need for improved preventive health behaviors. Monitoring A1C readings, especially when aiming for 7.5%, is thus not merely a standard examination; it is a crucial element of effective care and prevention strategies.
T2D Solutions aims to provide resources and support for newly diagnosed patients in managing A1C levels effectively. Subscribe to stay informed about the latest management resources and support provided by T2D Solutions.
Effective Strategies to Lower Your A1C from 7.5
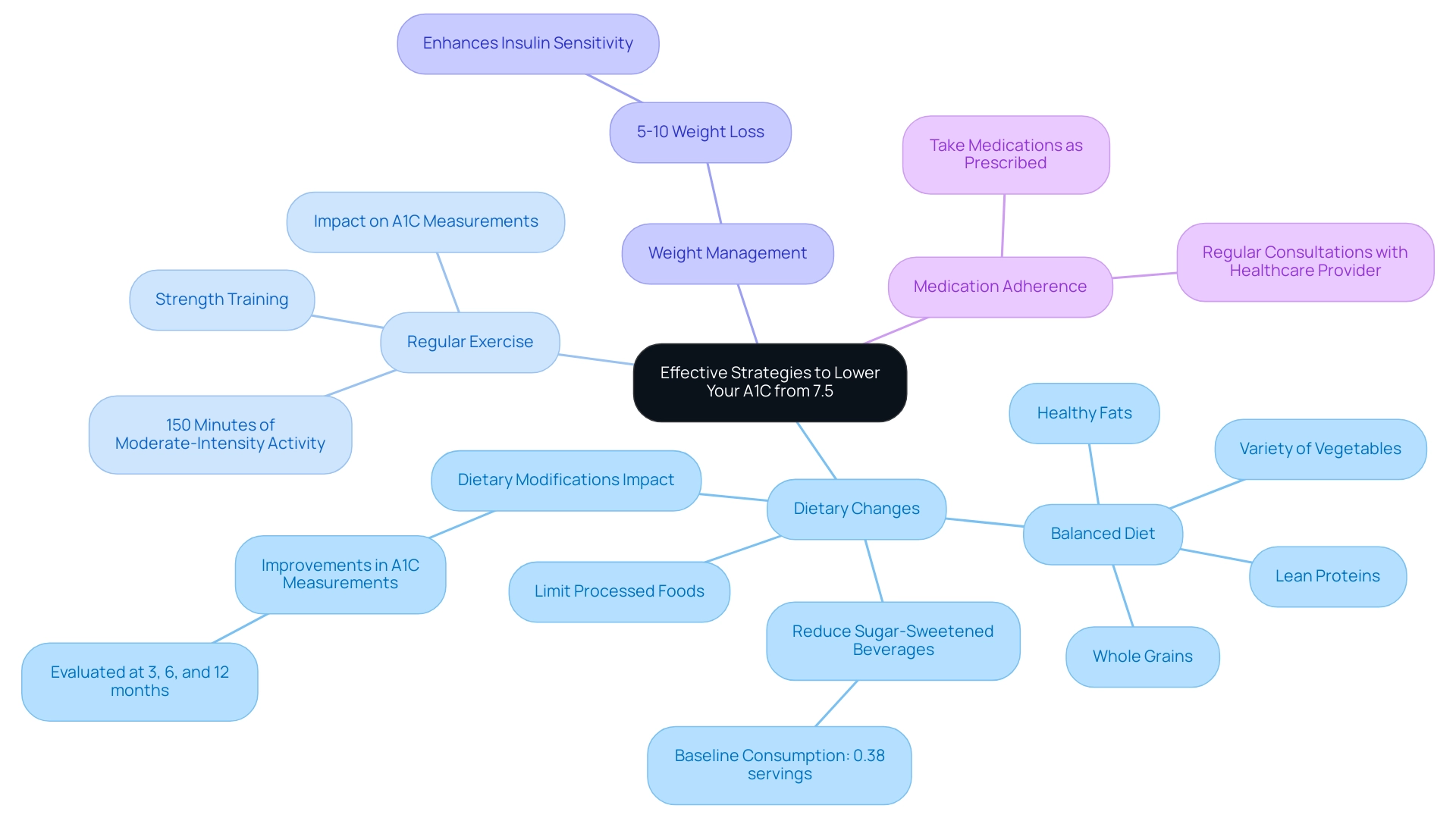
To effectively lower your A1C 7.5, consider implementing the following strategies, with support from T2D Solutions, your new resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education that is just getting started:
- Dietary Changes:
Emphasize a balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of vegetables. It is crucial to limit the intake of processed foods, sugary beverages—averaging 0.38 servings at baseline among typical dietary groups—and high-carbohydrate snacks.
Reducing sugar-sweetened beverage intake is essential, as these contribute significantly to overall sugar consumption. Recent studies indicate that dietary modifications play a significant role in managing A1C values, as highlighted by Robert H. Shmerling, MD, who stated,
However, the dose response does suggest that diet is playing a significant role.
In our study, participants who made dietary changes during individual study visits demonstrated enhancements in their A1C measurements over time, with outcomes evaluated at 3, 6, and 12 months after randomization.
-
Regular Exercise:
Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, complemented by strength training exercises. Physical activity has been demonstrated to greatly affect A1C measurements, providing an effective method for managing A1C 7.5. -
Weight Management:
Achieving a modest weight loss, even as little as 5-10% of your body weight, can enhance insulin sensitivity and contribute to lowering your A1C 7.5 levels. -
Medication Adherence:
It is vital to take your blood sugar medications as prescribed. Regular consultations with your healthcare provider can help ensure that your treatment plan is effectively tailored to your needs.
By following these strategies, you can actively engage in managing your condition and enhancing your overall health, with T2D Solutions as your guide.
Don't forget to subscribe for updates and explore the resources available on T2D Solutions as we continue to develop this platform for your support.
Monitoring Your Progress: How Often Should You Check Your A1C?
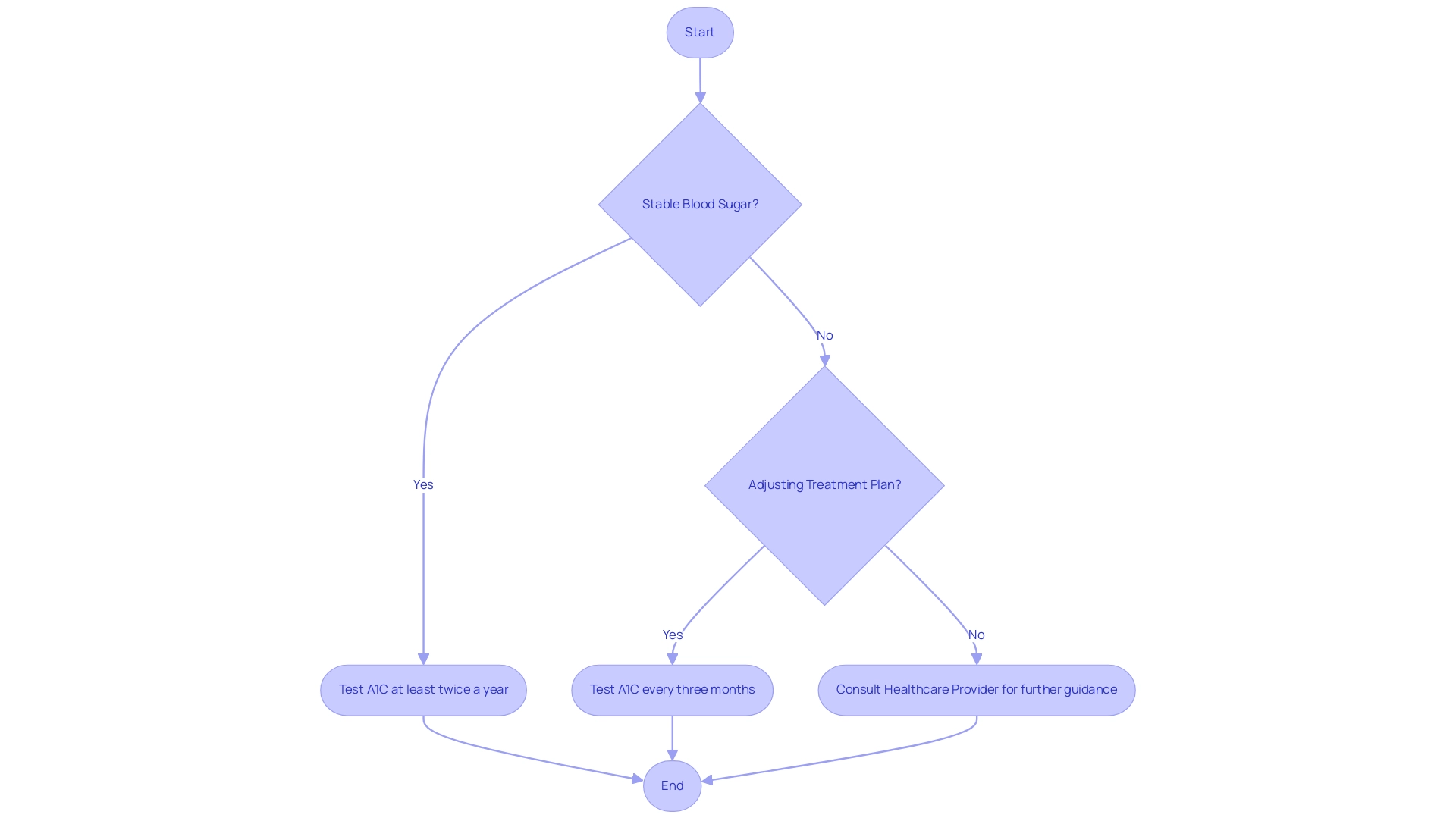
Introducing T 2 Solutions: your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management. At T 2 Solutions, we recognize that the frequency of A1C 7.5 testing is influenced by personal treatment plans and overall blood sugar management. According to the American Diabetes Association's updated guidelines published in January 2019, individuals with stable blood sugar readings, particularly those with an A1C of 7.5, are advised to undergo A1C testing at least twice a year.
For individuals undergoing adjustments in their blood sugar control strategy or inadequately regulated glucose readings, it is advised to test for an A1C 7.5 more frequently, usually every three months. This approach is essential for effectively tracking progress and making necessary adjustments. Monitoring A1C values helps provide insight into the effectiveness of management approaches and is particularly important when aiming for an A1C 7.5, as it also assists healthcare providers in assessing the risk of complications related to the condition.
As mentioned by Roopa Naik, 'Regular monitoring of A1C 7.5 values is crucial for adapting treatment plans to meet the individual needs of patients.' With T 2 Solutions, newly diagnosed patients can access valuable resources, including educational materials, community support, and subscription options for updates to understand their A1C values and manage their condition effectively. Our platform also features testimonials from users who have benefited from our services, enhancing the credibility of our offerings.
Both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes involve a progressive loss of beta-cell function, which can lead to hyperglycemia and an increased risk of chronic complications. The case study titled 'Progressive Loss of Beta-Cell Function' highlights that future classification schemes will likely focus on the underlying pathophysiology of beta-cell dysfunction to optimize personalized treatment approaches. Regular testing of A1C 7.5 is a critical component in managing these risks and achieving better health outcomes.
Lifestyle Modifications: Nutrition and Exercise for Better A1C Control
To effectively manage your A1C through lifestyle modifications, it is crucial to concentrate on the following areas:
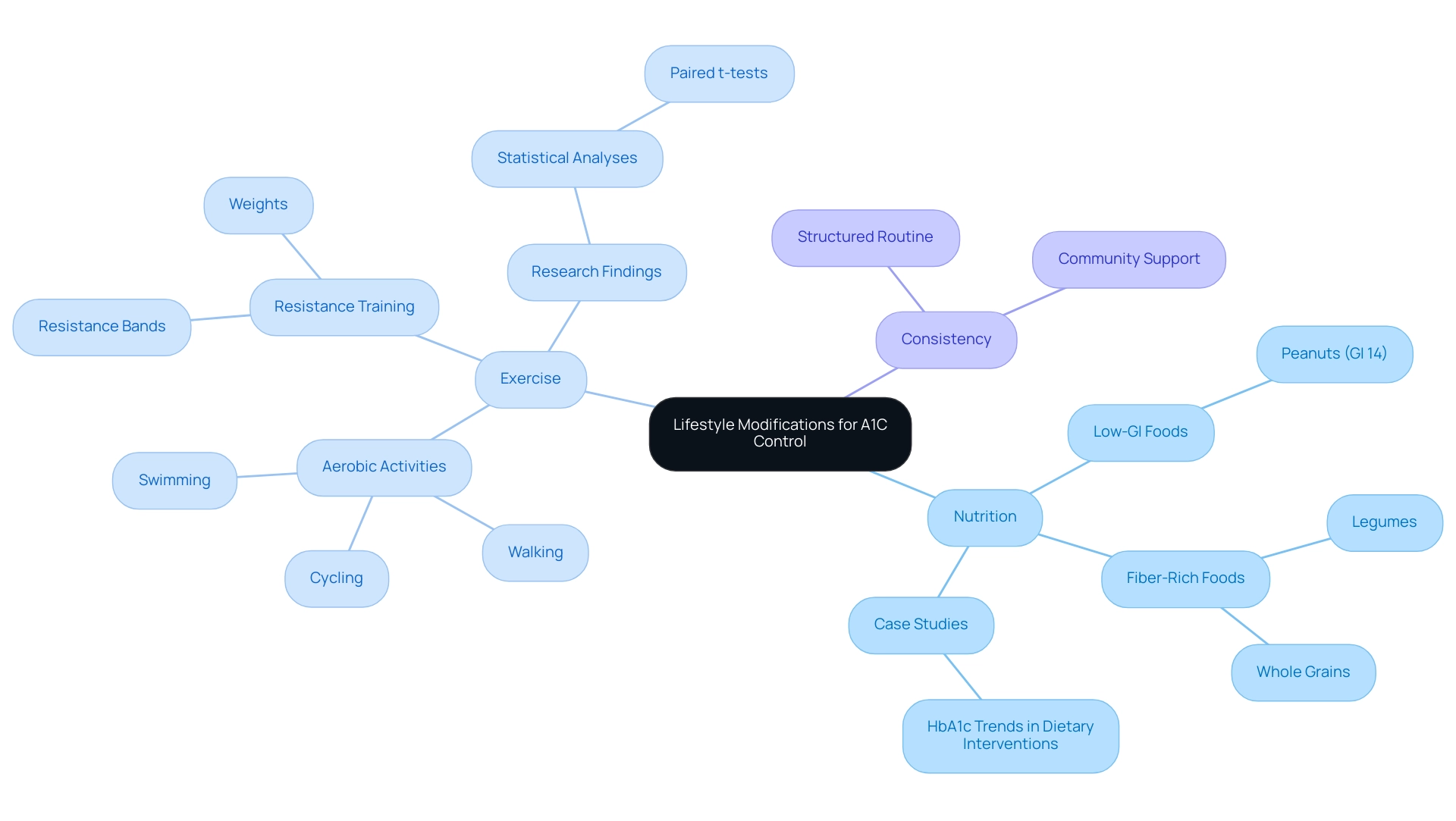
- Nutrition: Implement a dietary plan that prioritizes low-glycemic index (GI) foods, as they play a vital role in regulating blood sugar. For instance, peanuts, which have a GI value of 14, are an excellent choice due to their low impact on glucose.
Additionally, integrating fiber-rich foods, such as legumes and whole grains, can enhance satiety and support digestive health. As noted by Simin Liu, M.D., maintaining a balanced diet is essential for effective diabetes management. Moreover, case studies, like 'HbA1c Trends in Dietary Interventions,' have indicated trends demonstrating the effect of dietary interventions on A1C 7.5 measurements compared to controls, implying that dietary choices greatly influence A1C results.
- Exercise: Incorporate a balanced routine that consists of both aerobic activities—such as walking, cycling, or swimming—and resistance training using weights or resistance bands. Aim to engage in at least 30 minutes of physical activity on most days of the week.
Research has indicated that various forms of exercise can result in significant enhancements in A1C 7.5 measurements. Statistical analyses, including paired t-tests, have demonstrated differences in blood glucose concentrations and macronutrient intake between usual diets and low GI diets, reinforcing the effectiveness of such dietary modifications.
- Consistency: Establishing a structured routine that includes regular meal times and consistent physical activity is essential, as maintaining this consistency is key to sustaining stable blood sugar levels. Recent studies have highlighted the importance of lifestyle modifications, including dietary adjustments and exercise, in achieving better A1C control with a target of A1C 7.5. Furthermore, as T2DSolutions seeks to assist individuals with Type 2 and Type 3 conditions, connecting with community resources and support groups can offer valuable encouragement and shared experiences that improve your journey toward better health.
When to Consider Medication Changes for A1C Management
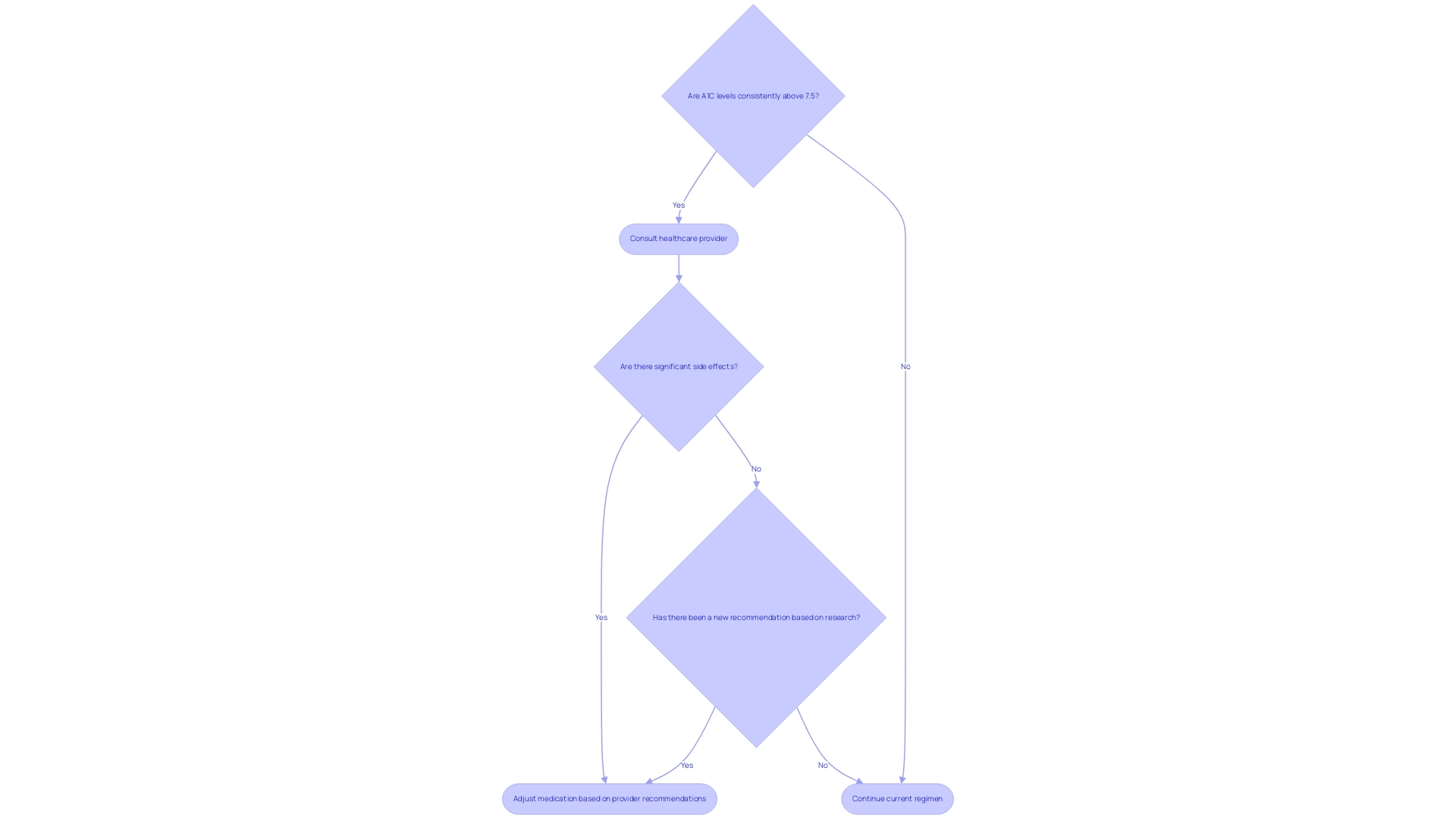
As you navigate your health condition journey, consulting with your healthcare provider regarding potential medication changes is essential under several circumstances. If your A1C levels are consistently above A1C 7.5 despite your commitment to lifestyle modifications and adherence to your current medication regimen, it may indicate a need for reevaluation. The presence of significant side effects from your current medications that negatively impact your quality of life also warrants discussion about alternatives.
Moreover, should your healthcare provider suggest a different medication or combination based on the latest research or adjustments in your health status, it's vital to consider those recommendations. Regular consultations with your healthcare team are essential for optimizing your health plan and achieving your A1C 7.5 targets. Supporting this need for vigilance, data from 2020 revealed 202,000 emergency department visits due to hypoglycemia, translating to 8.6 visits per 1,000 adults with blood sugar issues, underscoring the importance of effective medication oversight.
Furthermore, a systematic review highlighted that initiating an oral antidiabetic drug (OAD) alongside existing therapy could lead to an additional A1C reduction of approximately 1–1.25%, with sulfonylureas and TZDs showing the most significant effects. As Dr. David Price remarked, 'Effective medication management is crucial for individuals with this condition to maintain optimal A1C 7.5 levels.' By engaging in these discussions and utilizing T2 Solutions as your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, you will be empowered to make informed decisions about your treatment plan.
T2DSolutions offers tools and resources to help you understand your A1C levels better, focusing on achieving A1C 7.5 and tracking your progress, along with information on the most frequently prescribed medication classes, such as biguanides, sulfonylureas, and GLP-1 receptor agonists, which can further guide your treatment options.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing A1C levels is critical for effective diabetes control and the prevention of serious complications. The article emphasizes that maintaining an A1C level below 7% can significantly reduce risks associated with cardiovascular diseases and neuropathy. It highlights the importance of regular A1C testing as a means to monitor blood sugar levels and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Practical strategies for lowering A1C levels include:
- Dietary changes
- Regular exercise
- Weight management
- Adherence to prescribed medications
These lifestyle modifications, supported by community resources such as T2DSolutions, empower individuals to take charge of their diabetes management. Moreover, the article underscores the need for ongoing communication with healthcare providers to evaluate and adjust medication regimens as necessary, ensuring optimal outcomes.
In conclusion, proactive management of A1C levels through a combination of lifestyle changes and medical oversight is essential for individuals living with diabetes. By prioritizing these strategies, individuals can enhance their health, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life. Utilizing available resources and support networks further strengthens this journey towards better diabetes management.



