Overview:
To lower your A1C to 5.3%, individuals should adopt a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, manage stress, and monitor their blood sugar levels. The article outlines practical strategies, such as prioritizing whole foods and incorporating exercise, while emphasizing the importance of regular consultations with healthcare professionals for personalized management and support.
Introduction
Understanding the A1C test is crucial for anyone navigating the complexities of diabetes management. This test serves as a vital indicator of blood sugar control, providing insights that can significantly impact health outcomes. As T2DSolutions emerges as a comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education, it is essential to grasp the implications of A1C levels, which range from normal to prediabetic and diabetic classifications.
With an emphasis on proactive management, this article delves into practical strategies for lowering A1C levels, the role of medications, and the importance of continuous monitoring and community support. By equipping individuals with the knowledge to make informed decisions, T2DSolutions aims to foster a supportive environment that empowers effective diabetes management.
Understanding A1C: What It Is and Why It Matters
As T2DSolutions launches as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 health education and community support, it's essential to understand the A1C test, a critical tool in assessing blood sugar control. This test measures the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached, known as glycated hemoglobin. An A1C measurement below 5.7% is considered normal, while readings between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes.
An A1C of 6.5% or higher indicates the existence of the condition. Maintaining an A1C measurement as low as 5.3% is crucial for minimizing the risk of diabetes-related complications, including cardiovascular disease and neuropathy. Consistent oversight of A1C readings is crucial for assessing the success of your condition control strategy and monitoring your progress over time.
Comprehending how different elements—like daily routines, food selections, and medication—impact your A1C values enables you to make significant lifestyle changes. For example, the standards outlining prediabetes emphasize that individuals with A1C readings of 5.7–6.4% are at a heightened risk for a metabolic disorder, highlighting the significance of proactive management. This continuous risk increases notably at higher glucose levels, making it imperative to monitor and manage A1C effectively.
Furthermore, T2DSolutions offers tailored educational resources and community support to help you navigate these challenges. It's also important to note that high-risk HLA-DR4 is present in 76% of individuals with immune checkpoint inhibitor-related cases of type 1, indicating a significant risk factor associated with the condition. As Roopa Naik states, 'Disclosure: Roopa Naik declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies,' which emphasizes the importance of unbiased information in understanding the condition and reinforces the commitment of T2DSolutions to provide reliable and impartial resources.
The case study titled 'Criteria Defining Prediabetes' further illustrates that prediabetes is defined by A1C levels of 5.7–6.4%, FPG between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL, and 2-h PG during OGTT between 140 mg/dL and 199 mg/dL, reinforcing the importance of monitoring A1C levels and proactive oversight.
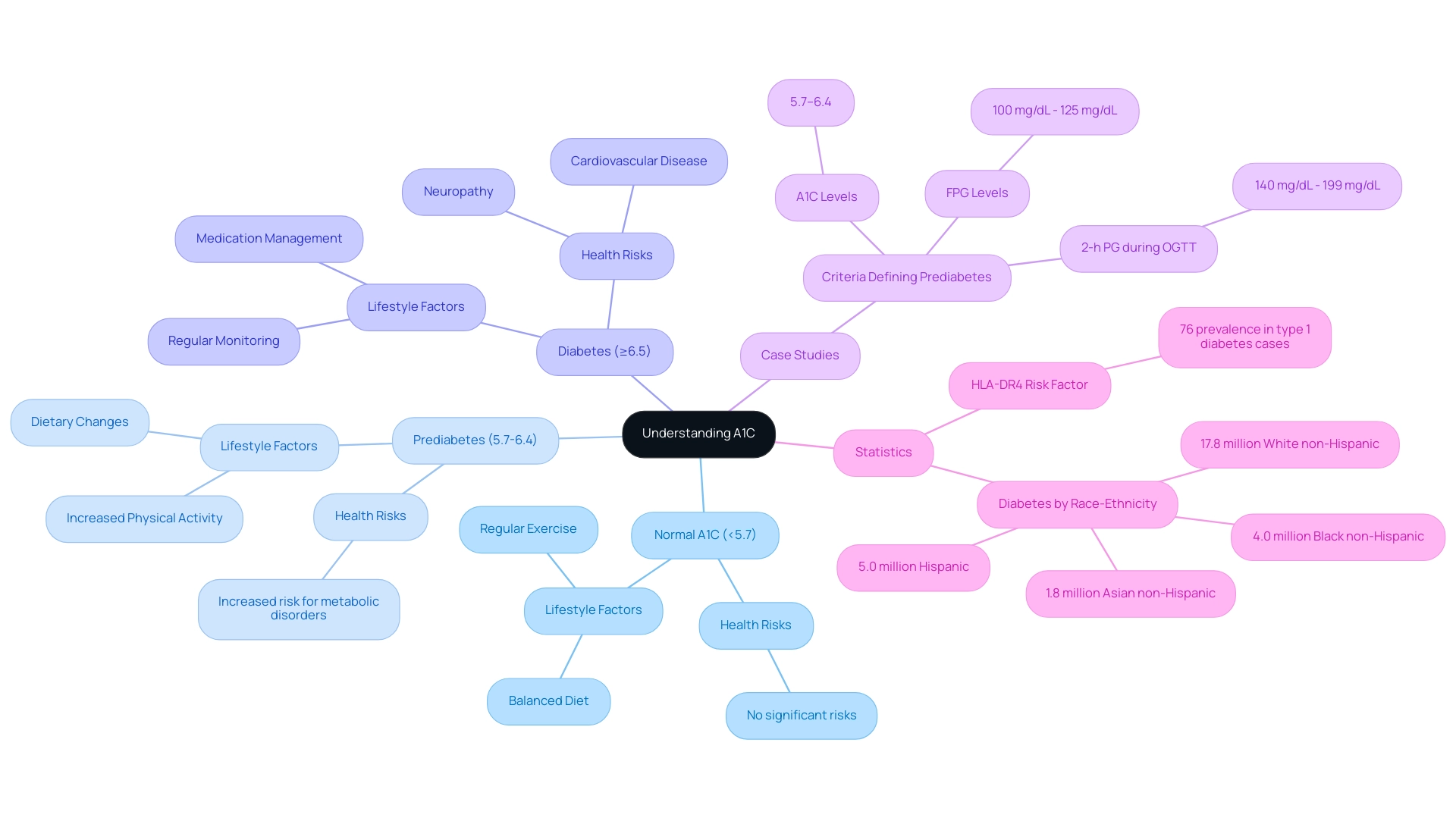
Practical Strategies to Lower Your A1C to 5.3%
As T2DSolutions prepares to launch as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 health education and community support, we recognize the importance of effective management strategies for newly diagnosed patients. While our platform is coming soon, we invite you to subscribe for updates and be the first to access valuable content and resources. To lower your A1C to a1c 5.3%, consider implementing the following strategies:
-
Adopt a Balanced Diet:
Prioritize whole foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is essential to limit the intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-carbohydrate snacks. Engaging a registered dietitian can be instrumental in crafting a personalized meal plan that aligns with your health goals.
As Andrew Reynolds points out, 'Diet and lifestyle recommendations are cornerstones of advice to prevent and manage diabetes; however, there are recognized barriers to heeding advice and implementing lifestyle change.' -
Monitor Carbohydrate Intake:
Being mindful of carbohydrate consumption is crucial. Utilize tools like carbohydrate counting and the glycemic index to select foods that have minimal effects on blood sugar.
Recent research underscores the significance of dietary choices in managing A1C values, highlighting that specific food types can significantly affect blood glucose response. For instance, a review of 29 RCTs indicated that while artificial sweeteners do not elevate blood glucose amounts, the overall content of the food or drink must be considered, especially for those with diabetes. -
Engage in Regular Physical Activity:
Strive for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week, incorporating activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
Additionally, integrating strength training exercises at least twice a week can enhance insulin sensitivity, a key factor in blood sugar management. -
Manage Stress:
Acknowledge that stress can negatively influence blood sugar readings. Implement relaxation techniques, including yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, to effectively manage stress and promote overall well-being. -
Stay Hydrated:
Adequate hydration is vital for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, as staying hydrated supports overall metabolic functions. -
Regularly Monitor Blood Sugar Levels:
Tracking blood glucose readings is essential for understanding how your body reacts to different foods and physical activities. This data enables informed adjustments to your diet and exercise regimen. -
Consult with Healthcare Professionals:
Regular consultations with your healthcare team, including a health educator, offer invaluable support tailored to your specific health needs. This ongoing dialogue is essential, as it may result in necessary adjustments in medication or insulin therapy based on your progress.
It's important to note that Hispanic individuals account for 5.0 million diagnosed cases of this condition and 1.9 million undiagnosed cases, highlighting the prevalence of this issue. By consistently implementing these strategies, you can work towards achieving your A1C target of a1c 5.3 while enhancing your overall health. T2DSolutions is here to support you on this journey, and we look forward to providing you with the resources you need.
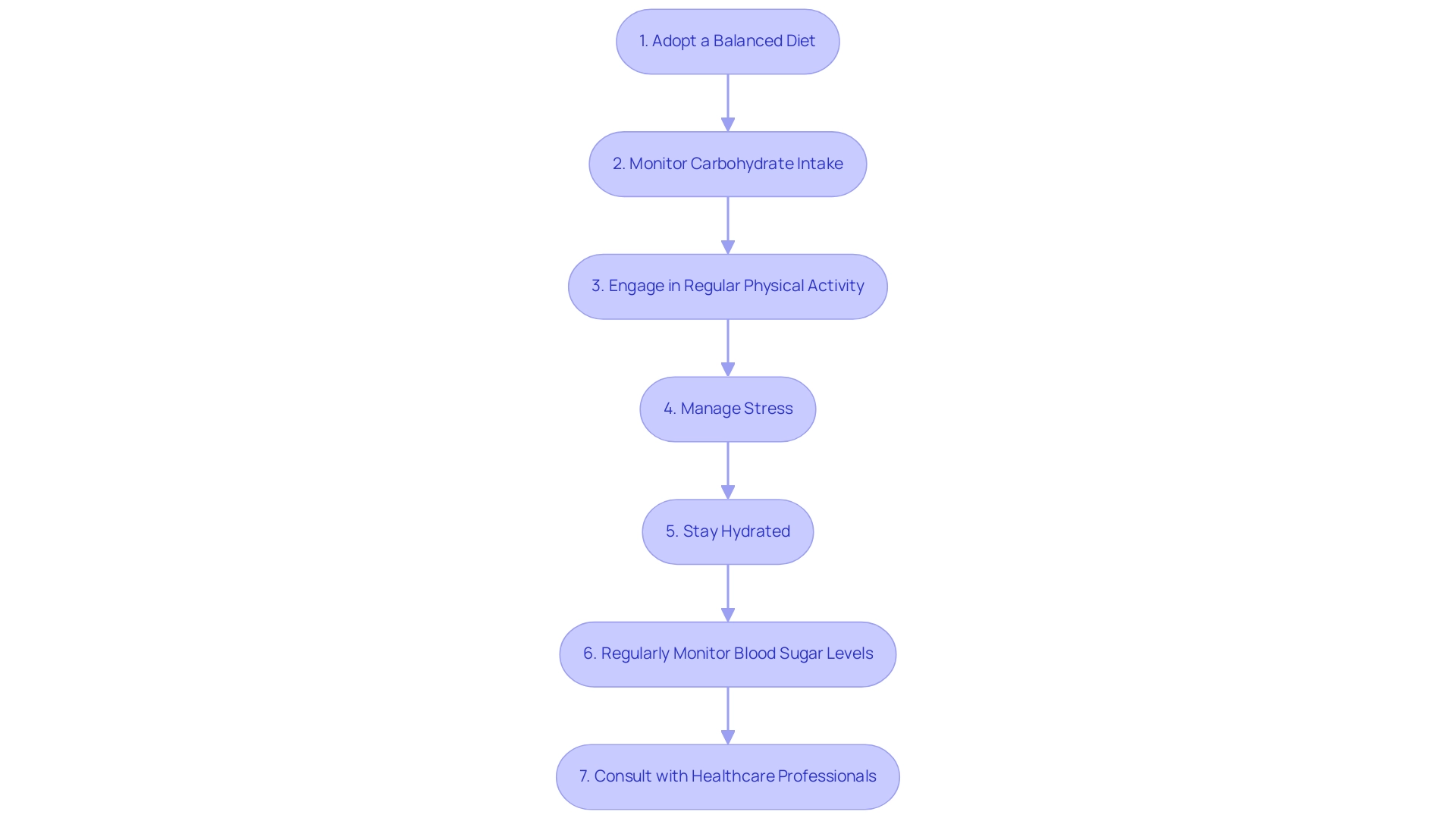
The Role of Medication in Managing A1C Levels
While lifestyle modifications are essential for managing blood sugar, they may not always suffice in achieving the desired A1C 5.3 levels for some individuals. In such instances, pharmacological interventions become pivotal. As Kenneth R. Feingold, Emeritus Professor of Medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, states, "Oral and Injectable (Non-Insulin) Pharmacological Agents for the Treatment of Type 2" play a crucial role in effective management of the condition.
The principal classes of diabetes medications include:
-
Metformin: Regarded as the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, Metformin primarily functions by decreasing hepatic glucose production and enhancing peripheral insulin sensitivity. Its widespread use is backed by numerous studies showing its efficacy in lowering A1C values to A1C 5.3. Notably, Empagliflozin/Metformin is available as Synjardy, providing patients with a combined option to manage their blood sugar effectively.
-
Sulfonylureas: This class of medications functions by encouraging the pancreas to release more insulin, thus assisting in the decrease of blood sugar amounts. However, careful monitoring is essential due to the potential risk of hypoglycemia associated with their use.
-
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These agents not only promote insulin secretion but also decelerate gastric emptying, resulting in improved glycemic control. Recent advancements in this class of drugs have shown promising results in clinical settings, making them a valuable addition to management strategies for blood sugar control.
-
Insulin Treatment: For individuals with type 1 conditions or those with advanced type 2 conditions, insulin treatment may be necessary to effectively regulate blood sugar concentrations. This approach ensures that patients receive the appropriate dosage tailored to their unique metabolic needs.
-
Meglitinides: This class of medications binds to a different site on SUR1 than sulfonylureas, leading to insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. A case study on the mechanism of action of meglitinides illustrates their effectiveness in lowering postprandial glucose concentrations with a reduced risk of hypoglycemia.
Collaborating closely with your healthcare provider is vital to establish a personalized medication regimen that aligns with your health status. Ongoing observation of A1C values, particularly aiming for an A1C 5.3 level, and transparent dialogue about treatment effectiveness are essential in adjusting your strategy for handling this condition.
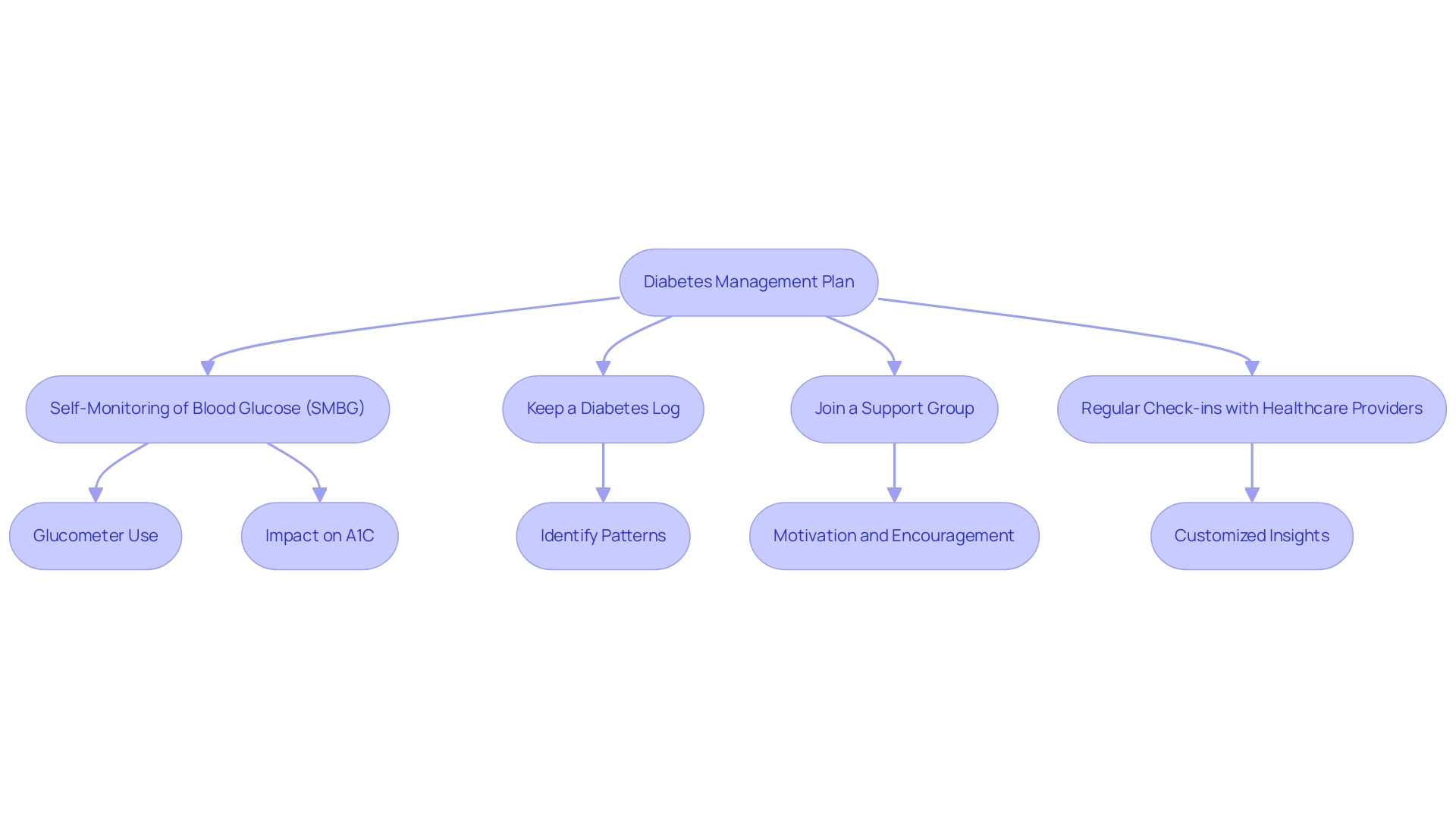
Incorporating Regular Monitoring and Support
To effectively lower and maintain your A1C values to a1c 5.3, it is crucial to incorporate regular monitoring and support into your diabetes management plan. T2D Solutions is here to assist you in this journey by providing valuable resources and community support. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): Regularly checking your blood glucose readings with a glucometer is vital. This practice enables you to gain insights into how your diet, physical activity, and medications affect your blood sugar readings. A meta-analysis of seven randomized controlled trials demonstrated that blood glucose self-monitoring significantly reduced glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) concentrations by 0.41%.
Significantly, adopting a regimen for blood sugar control based on self-monitoring results resulted in a greater decrease of 0.42% in HbA1c levels. Education on lifestyle changes is essential for SMBG to show positive effects on glycemic control.
-
Keep a Diabetes Log: Documenting your blood sugar readings, dietary intake, physical activity, and medications is essential. Keeping a health log enables you to identify patterns in your blood sugar fluctuations, helping you to make informed adjustments to your management plan. Expert opinions highlight the significance of health logs in enhancing self-management efficacy.
-
Join a Support Group: Engaging with a support group for those managing blood sugar issues, whether in-person or online, can be highly beneficial. T2D Solutions offers a platform for connecting with others facing similar challenges, providing motivation and encouragement, and fostering a sense of community. Recent findings indicate that support groups can significantly improve control outcomes, demonstrating their role in enhancing A1C levels to achieve a1c 5.3.
Schedule regular check-ins with your healthcare providers to discuss your progress and review your A1C 5.3 results. These experts can offer customized insights and assistance, ensuring that your strategy remains effective and aligned with your individual needs. Regular interaction with healthcare providers is essential in adjusting your approach as needed and enhancing your condition control.
Moreover, take into account the financial aspects of condition oversight; for example, diet-only therapy can cost Can$292,144, emphasizing the significance of efficient self-care strategies. As noted by Fontbonne et al., the baseline HbA values of studies varied from 12.4% in Allen et al. to 8.2% in Fontbonne et al., which might have influenced the results, emphasizing the need for personalized approaches in managing blood sugar conditions.
T2D Solutions aims to provide the necessary educational resources to help you navigate these challenges.
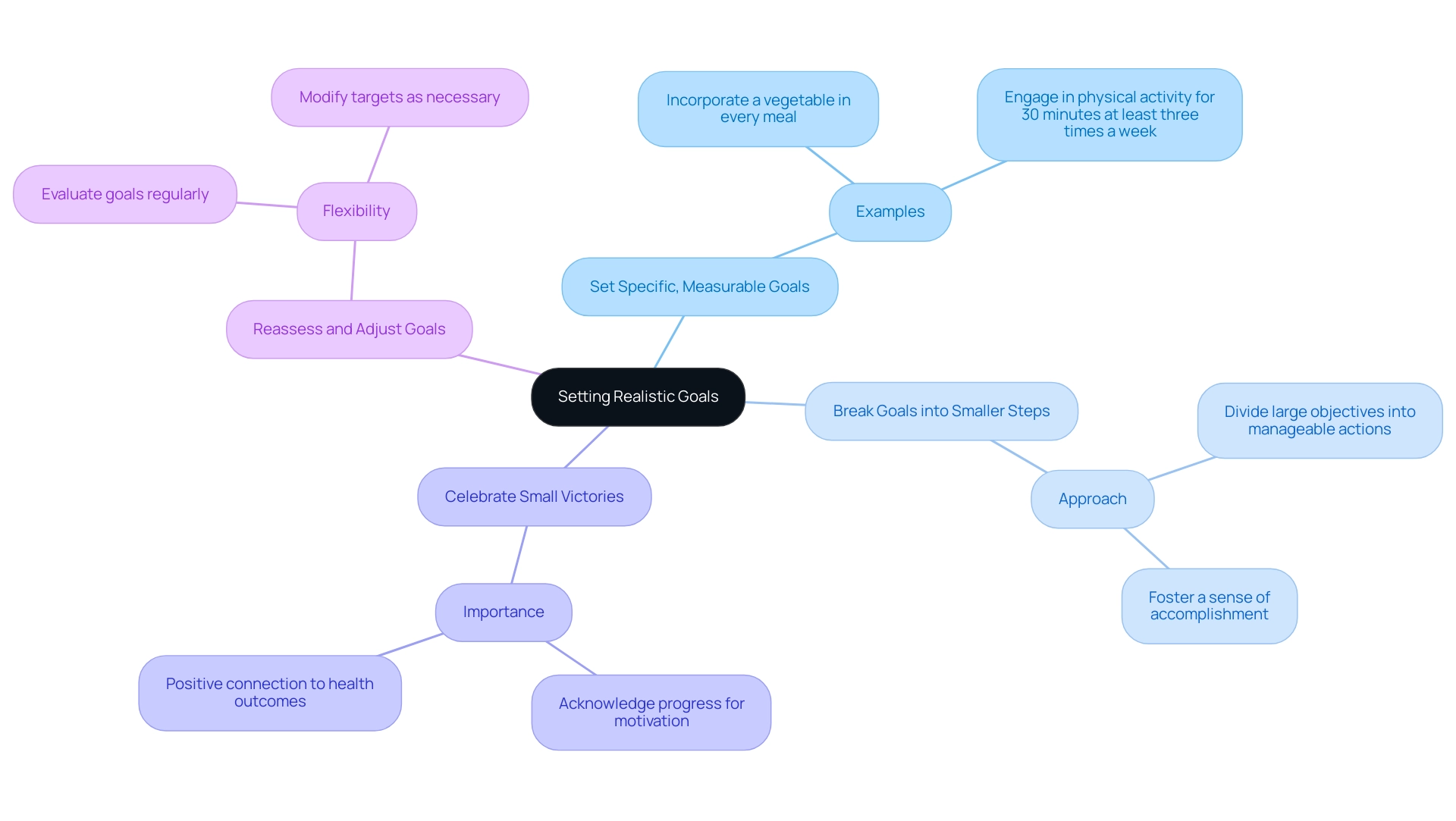
Setting Realistic Goals and Celebrating Progress
Setting realistic and attainable objectives is a cornerstone of effective health oversight. At T2DSolutions, a brand new resource hub for education and community support, we emphasize the significance of such goals as part of our commitment to empowering health oversight through education and community support. Research has indicated that the impact of self-efficacy related to blood sugar management on outcome results is significant (F (1,85) = 10.39, p = .002), highlighting the necessity of establishing achievable goals.
Here are several strategies to guide you:
-
Set Specific, Measurable Goals: Replace vague aspirations like 'eat healthier' with concrete objectives such as 'incorporate a vegetable in every meal' or 'engage in physical activity for 30 minutes at least three times a week.' Specificity enhances focus and accountability, paving the way for success.
-
Break Goals into Smaller Steps: Large objectives can be intimidating. Divide them into smaller, manageable actions that allow for gradual progress. This approach not only makes goals feel more attainable but also fosters a sense of accomplishment with each step forward.
-
Celebrate Small Victories: Recognizing and celebrating your progress, no matter how minor, is essential. Whether it's achieving consistent blood sugar readings for a week or experimenting with a new healthy recipe, acknowledging these achievements can significantly elevate your motivation. In fact, studies highlight the positive connection between acknowledging small achievements and better health outcomes.
-
Reassess and Adjust Goals: Regularly evaluate your goals and be prepared to modify them as necessary. As you advance in your journey, some targets may become less pertinent, while new challenges may emerge. Maintaining flexibility in your approach is crucial for staying motivated and focused on achieving an A1C of 5.3.
As noted in recent research, implementation studies are needed to identify alternative designs that facilitate wider dissemination of effective goal-setting strategies. Additionally, consider the insights from a case study on parental involvement in diabetes management, which highlights how support networks can facilitate goal achievement. Engaging with family members or friends can provide the encouragement needed to stay on track. By implementing these strategies—setting realistic goals, recognizing your progress, and celebrating small victories—you can sustain motivation and continue making meaningful advancements in managing your A1C levels, aiming for a target of A1C 5.3. At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to providing resources and support to help you every step of the way.
Subscribe now to stay updated on our latest resources and community support initiatives!
Conclusion
Understanding and managing A1C levels is fundamental for anyone dealing with diabetes, particularly those navigating Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes. This article has outlined the significance of the A1C test as a reliable measure of blood sugar control, emphasizing the importance of maintaining A1C levels below 5.7% to mitigate health risks. Strategies such as:
- Adopting a balanced diet
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Managing stress
play critical roles in achieving these targets. Additionally, the integration of medications when lifestyle changes are insufficient ensures a comprehensive approach to diabetes management.
Regular monitoring and community support are vital components of effective diabetes care. By leveraging resources like T2DSolutions, individuals can access tailored education and connect with others who share similar challenges. Setting realistic goals, celebrating progress, and maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals further empower individuals to take charge of their health.
Ultimately, the journey to lower A1C levels is a multifaceted process that requires commitment and informed decision-making. By implementing the discussed strategies and utilizing available resources, individuals can enhance their diabetes management and improve their overall health outcomes. Prioritizing proactive management not only fosters a better quality of life but also builds a supportive community dedicated to navigating the complexities of diabetes together.



