Overview:
The article provides a step-by-step guide on how to effectively use a glucose to A1C calculator, which is essential for managing diabetes by transforming average blood glucose levels into an estimated A1C percentage. This guide is supported by the importance of A1C testing in monitoring blood sugar control and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications, emphasizing that accurate calculations can significantly influence treatment plans and lifestyle adjustments.
Introduction
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, understanding the critical role of A1C testing in effective management becomes increasingly essential. A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, serves as a key indicator of average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, guiding treatment decisions and lifestyle adjustments for those living with diabetes.
With recommendations suggesting that individuals maintain A1C levels below 7% to mitigate the risk of complications, the importance of regular monitoring cannot be overstated. This article delves into the significance of A1C testing, the practical steps for utilizing glucose to A1C calculators, and the benefits of proactive self-monitoring.
By equipping individuals with the necessary tools and knowledge, T2DSolutions aims to empower those newly diagnosed with diabetes to navigate their health journey with confidence.
Understanding A1C: The Key to Diabetes Management
A1C, referred to as glycated hemoglobin, is an essential blood test that offers insights into average blood glucose readings over the prior two to three months. This measurement, expressed as a percentage, indicates the quality of blood sugar regulation; a higher percentage signifies poorer control. For individuals diagnosed with this condition, maintaining an A1C level below 7% is generally recommended, as this threshold is associated with a substantially lower risk of complications related to the illness, such as neuropathy and cardiovascular disease.
The importance of A1C testing cannot be overstated, as a glucose to A1C calculator helps guide treatment choices and lifestyle changes essential for effective health control. With the alarming rise in the prevalence of this condition in the U.S.—from 9.7% in 1999-2000 to 14.3% by August 2023, as highlighted in 'Trends in Diabetes Prevalence Over Time'—there is an urgent need for resources and strategies to empower individuals managing it. T2DSolutions, as a new resource hub, is committed to supporting newly diagnosed patients by providing educational resources, including a glucose to A1C calculator, community support, and innovative insights into Type 2 and Type 3 Diabetes.
Furthermore, the creation of the worldwide registry CoviDIAB seeks to improve our comprehension of the condition, particularly regarding COVID-19, illustrating ongoing studies into the intricacies of handling the illness. The National Center for Health Statistics highlights that undiagnosed conditions are frequently recognized through A1C readings of 6.5% or higher, emphasizing the test’s essential function in early identification and proactive management. Individuals testing positive for autoantibodies should also receive counseling about diabetes risk and symptoms, reinforcing the need for comprehensive support.
Comprehending and routinely tracking A1C values with a glucose to A1C calculator is crucial for managing the difficulties of this chronic condition. Stay tuned to our blog for the latest updates and resources, as T2 Solutions is here to provide the necessary guidance and community support.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Glucose to A1C Calculator
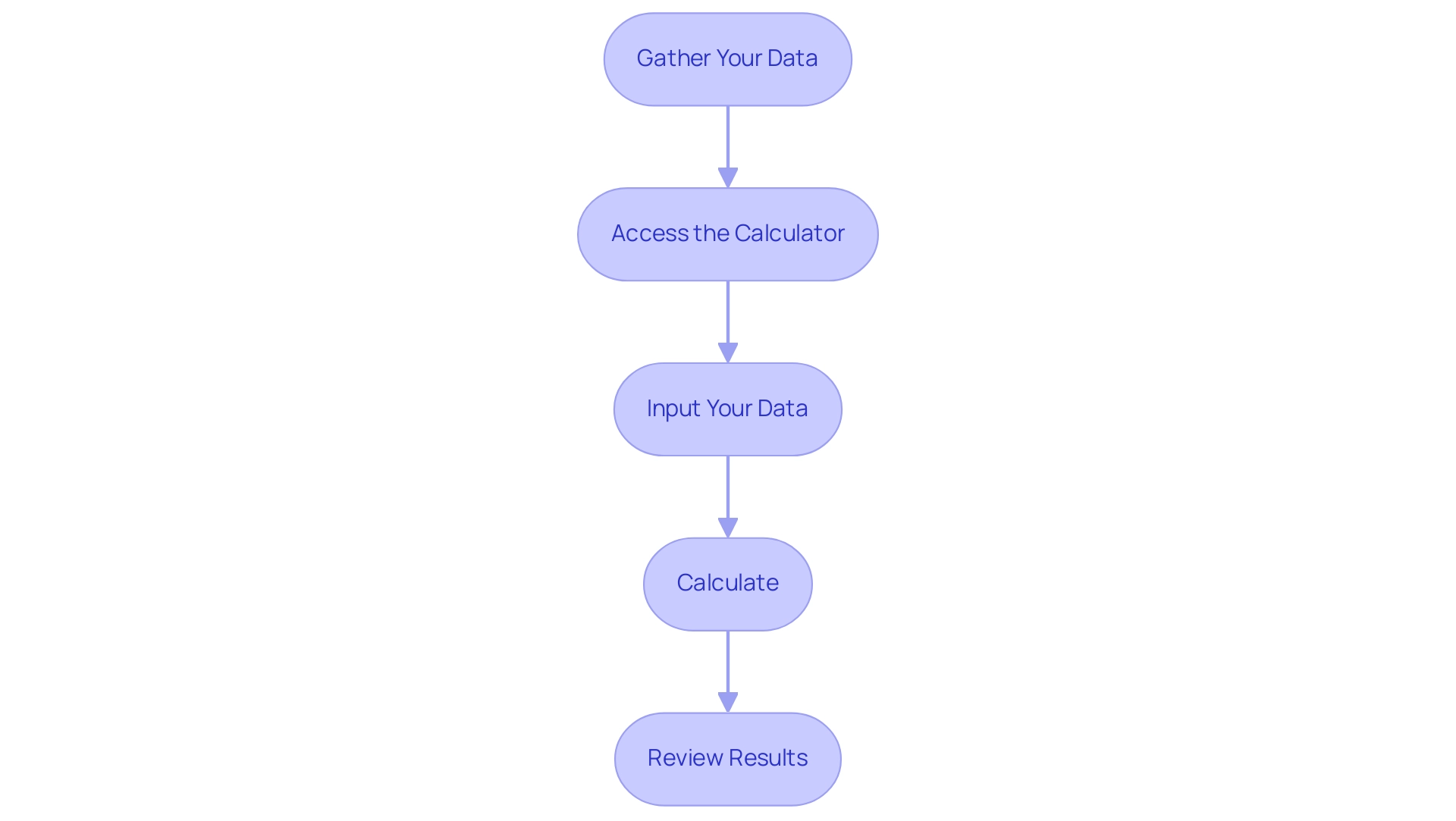
To effectively utilize the glucose to A1C calculator, please follow these steps:
-
Gather Your Data: Obtain your average blood glucose levels from your monitoring device or recent laboratory tests to ensure accuracy. It's important to note that 65 patients (35.7%) were prescribed Basal insulin +/- OAD/GLP-1, highlighting the significance of accurate A1C calculations in managing treatment plans.
-
Access the glucose to A1C calculator by navigating to a reputable diabetes control website or utilizing a dedicated app.
-
Input Your Data: Enter your average glucose level into the specified field. Ensure that you select the correct unit of measurement, either mg/dL or mmol/L, to avoid calculation errors.
-
Calculate: Click the 'Calculate' button to generate your estimated A1C percentage, which provides insight into your blood sugar control over the past few months.
-
Review Results: Carefully analyze the output of your calculation and consider discussing the findings with your healthcare provider, who can offer further insights and customized approaches based on your results. As Jennifer Sargent, Primary Handling Editor, emphasizes, utilizing reliable tools like the glucose to A1C calculator is crucial for effective blood sugar control.
Additionally, consider how continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) can impact A1C levels; for instance, a study titled 'Impact of CGM on A1c Reduction' found that the use of CGM was associated with a 0.62% greater reduction in A1c levels, demonstrating the practical implications of combining these tools for improved blood sugar management. For more extensive resources and assistance in your condition control journey, visit t2d solutions, your new center for Type 2 and Type 3 health education and community support.
The Importance of Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose and A1C
T2DSolutions is dedicated to supporting individuals recently diagnosed with the condition through comprehensive resources and community support. Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and A1C readings are vital elements of efficient management of the condition, and T2 Solutions aims to provide users with a glucose to A1C calculator along with the resources and insights required for this proactive method. Regularly checking blood glucose levels helps individuals identify patterns that can inform decisions regarding diet, exercise, and medication.
Recent findings demonstrate that patients utilizing insulin injections exhibit a significant association with higher adherence to monitoring practices (χ = 51.18, p < 0.001). A1C testing complements this by providing a comprehensive view of glucose control over time, which can be analyzed with a glucose to A1C calculator. This dual strategy not only assists individuals in managing their condition more effectively but also plays a pivotal role in reducing the risk of complications and enhancing overall quality of life.
Hiroshi Arima's study, 'Effects of Digitization of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose Records Using a Mobile App and the Cloud System on Outpatient Management of Diabetes: Single-Armed Prospective Study,' highlights the transformative potential of technology in the management of blood sugar levels, further supported by funding from ARKRAY Inc, Kyoto, Japan. Additionally, scenario analyses indicate that continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) remains cost-effective and beneficial compared to standard SMBG, leading to increased quality-adjusted life years (QALY) and cost savings over time. By combining these methods and using the resources available at T2 Solutions, individuals can take proactive steps toward better management of their condition and improved health outcomes.
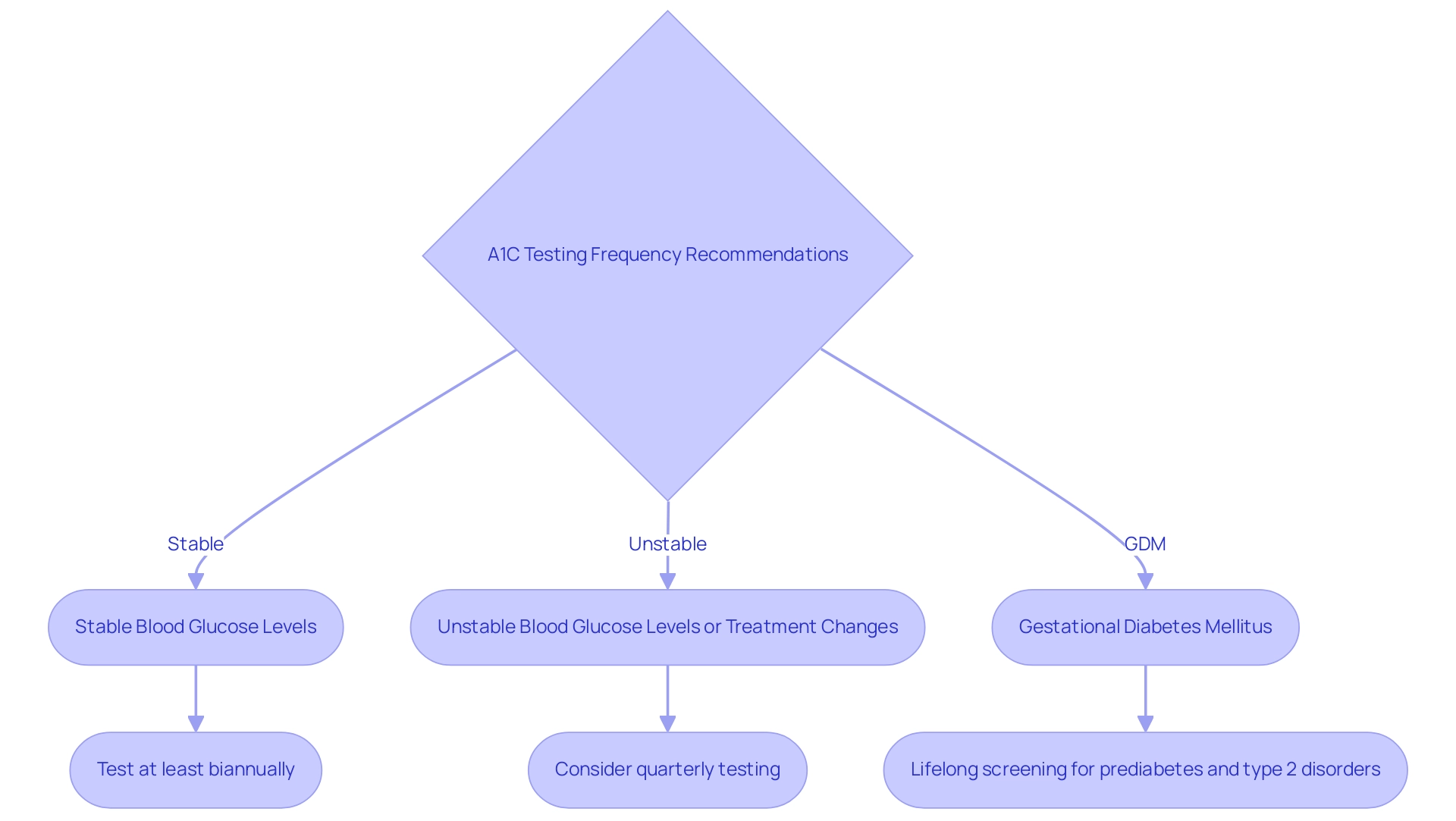
How Often Should You Get an A1C Test?
As T2DSolutions prepares to launch as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar education and community support, it is essential to understand the recommended frequency of A1C testing for individuals managing their condition. This frequency is not one-size-fits-all; it is influenced by individual health conditions and treatment plans. As a general guideline, individuals with stable and well-controlled blood glucose levels should have their A1C levels tested at least biannually.
Conversely, those who have experienced changes in their treatment regimen or who are struggling to meet their glucose targets should consider quarterly testing. This testing is particularly significant given that the prevalence of the condition has reached 14.3% from August 2021 to August 2023, underscoring the growing need for vigilant monitoring. Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H., emphasizes the importance of regular screenings, noting that the age-adjusted prevalence of this condition has increased over the years.
Furthermore, individuals diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) should receive lifelong screening for prediabetes and type 2 disorders, highlighting the ongoing need for monitoring in specific populations. The clinical significance of HbA1c is illustrated in case studies, which show that it serves as a crucial indicator of overall glycemic control, and can be evaluated using a glucose to A1C calculator to reflect average blood sugar levels over the preceding three months. Personalized discussions with healthcare providers are critical to establishing an appropriate testing schedule that aligns with individual health needs and goals.
As guidelines change, T2DSolutions will offer the most recent suggestions for A1C testing frequency, ensuring effective control of the condition is available to everyone. Don't forget to subscribe to remain informed about our forthcoming content and resources from the T2D Solutions Content Team, committed to enhancing your health journey.
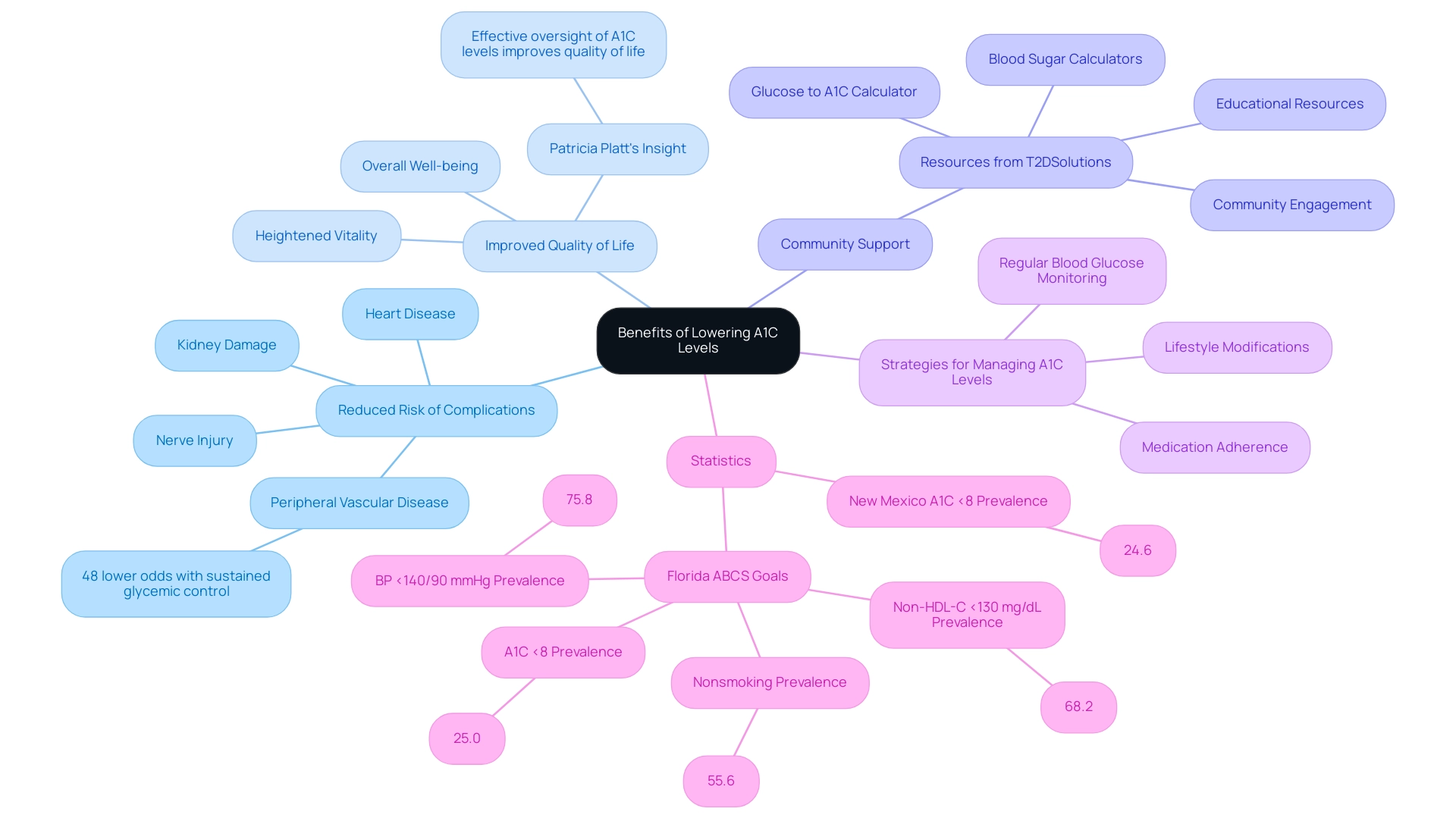
Benefits of Lowering Your A1C Levels
We are excited to introduce T2DSolutions, your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management, designed specifically for newly diagnosed patients. T2DSolutions will provide a range of tools, including:
- A glucose to A1C calculator
- Blood sugar calculators
- Educational resources
- Community support
to assist you in managing your health journey. Reducing A1C values is essential in decreasing the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve injury.
Research indicates that individuals who achieve sustained glycemic control experience significantly lower odds—by up to 48%—of developing peripheral vascular disease. In New Mexico, for example, the prevalence of individuals maintaining an A1C measurement below 8% is 24.6%, emphasizing the significance of effective diabetes management in the region. This highlights the need to maintain an A1C measurement below 7%, which is linked to better long-term health outcomes and improved quality of life.
Additionally, a case study named 'Florida ABCS Goals' reported prevalence rates of 25.0% for A1C <8%, showcasing real-world success in managing A1C values. People controlling their condition frequently indicate heightened vitality and improved overall well-being when their A1C remains consistently within target ranges. As Patricia Platt, an independent contractor for Health Metrics, notes, 'Effective oversight of A1C levels not only prevents complications but also significantly improves patients' quality of life.'
To achieve these vital health objectives, it is essential to implement lifestyle modifications, adhere to prescribed medication regimens, and engage in regular blood glucose monitoring with a glucose to A1C calculator. These strategies collectively contribute to better management of this condition and foster a sense of security and peace of mind for those navigating it, all supported by the resources and community available at T2 Solutions. Be sure to subscribe to stay updated on new content and resources that can assist you in managing your diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of A1C testing is paramount for individuals managing diabetes. This essential test not only reflects average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months but also serves as a critical tool in guiding treatment decisions and lifestyle changes. Regular monitoring of A1C levels, with a target of below 7%, is vital to reducing the risk of serious complications, as evidenced by increasing diabetes prevalence statistics.
Utilizing resources such as glucose to A1C calculators and engaging in self-monitoring practices empower individuals to take control of their health. By identifying patterns in blood glucose levels and adjusting treatment plans accordingly, patients can significantly improve their quality of life. The integration of technology, such as continuous glucose monitoring, further enhances these efforts, demonstrating the importance of proactive management strategies.
As the landscape of diabetes management continues to evolve, individuals are encouraged to maintain regular A1C testing schedules tailored to their specific health needs. Collaborating with healthcare providers and utilizing educational resources from platforms like T2DSolutions can lead to meaningful improvements in diabetes control. Through informed, proactive measures, individuals can navigate their diabetes journey with confidence, ultimately fostering better health outcomes and a higher quality of life.



