Overview
The article provides a comprehensive guide on how to effectively use a lancing device and lancets for blood glucose monitoring, essential for diabetes management. It outlines a step-by-step process for using these tools, emphasizing the importance of proper technique and maintenance to ensure accurate readings and minimize discomfort, supported by statistics highlighting the health risks associated with poor monitoring practices.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, lancing devices serve as critical tools that empower individuals to monitor their blood sugar levels effectively. These instruments, designed to puncture the skin and collect blood samples for glucose testing, play a vital role in making informed health decisions.
With diabetes-related complications affecting millions, understanding the functionality and proper use of lancing devices is essential. As T2DSolutions emerges as a comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education, this article delves into the purpose, types, and best practices of lancing devices, offering valuable insights and guidance for those navigating their diabetes management journey.
From troubleshooting common issues to maintaining optimal performance, readers will discover how to enhance their experience and improve their health outcomes through effective blood sugar monitoring.
Understanding Lancing Devices: Purpose and Functionality
A lancing device and lancets are vital instruments for people controlling their condition, created specifically to pierce the skin and acquire a small sample for glucose testing. The lancing device and lancets play an essential role in facilitating precise blood sugar level monitoring, which is crucial for efficient management of the condition. In 2021, there were 399,401 death certificates with a metabolic disorder listed as the underlying or contributing cause of death, highlighting the importance of effective monitoring tools.
As T2DSolutions launches, we intend to be your all-encompassing resource center for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, offering insights into the best puncture tools available. Usually, lancing devices and lancets include adjustable depth settings, enabling users to reduce discomfort while guaranteeing a sufficient sample is obtained. Regular blood sugar testing is not just a routine; it serves as a key component in making informed health decisions regarding diet, exercise, and medication.
The occurrence of type 2 conditions has notably risen among all racial and ethnic groups from 2002 to 2018, highlighting the necessity of utilizing a lancing device and lancets for monitoring. Recent advancements in lancing technology have further improved the effectiveness of lancing devices and lancets, making them more user-friendly and less painful. The Centers for Disease Control emphasizes the significance of lancing devices and lancets, noting that around 8.6 million individuals are unaware they have undiagnosed blood sugar issues.
Moreover, diabetes is the leading cause of new cases of blindness among adults aged 18–64 years, with 10.1% of diagnosed diabetics reporting severe vision difficulty or blindness in 2021. This case study emphasizes the importance of regular blood sugar monitoring through a lancing device and lancets. By utilizing tools such as a lancing device and lancets, diabetics can gain valuable insights into their health, enabling proactive management of their condition.
T2DSolutions will offer guides and product comparisons to assist you in selecting the appropriate puncture tool, along with user testimonials to share experiences and advice. Stay tuned with T2D Solutions as we offer you the latest information and assistance for your health management journey.
Exploring Different Types of Lancing Devices
At T2DSolutions, we acknowledge that puncturing instruments are essential tools for effective diabetes management, particularly for those recently diagnosed. Available in both automatic and manual styles, these tools cater to different user preferences. For example, automatic puncturing tools such as the Accu-Chek FastClix employ a spring-loaded mechanism, providing a quick and steady puncture with minimal effort, making them especially attractive for individuals who prioritize simplicity.
Conversely, manual instruments like the BD Lancet require users to engage a button to initiate the puncture, which may be less convenient for some. A significant benefit of various puncturing tools is their adjustable depth setting feature, allowing customization based on individual skin thickness. This adaptability is vital as it can significantly reduce discomfort during sampling—a factor linked to enhanced patient compliance with self-monitoring of glucose levels.
Medical professionals should prescribe lancing instruments perceived as virtually pain-free to enhance patient quality of life. For example, testimonials from users of the Accu-Chek FastClix highlight its comfort and ease of use, leading to more consistent blood glucose monitoring. As we introduce T2DSolutions as your all-encompassing resource for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, we stress the significance of choosing user-friendly tools that promote regular monitoring and ultimately improve the overall quality of life for diabetes patients.
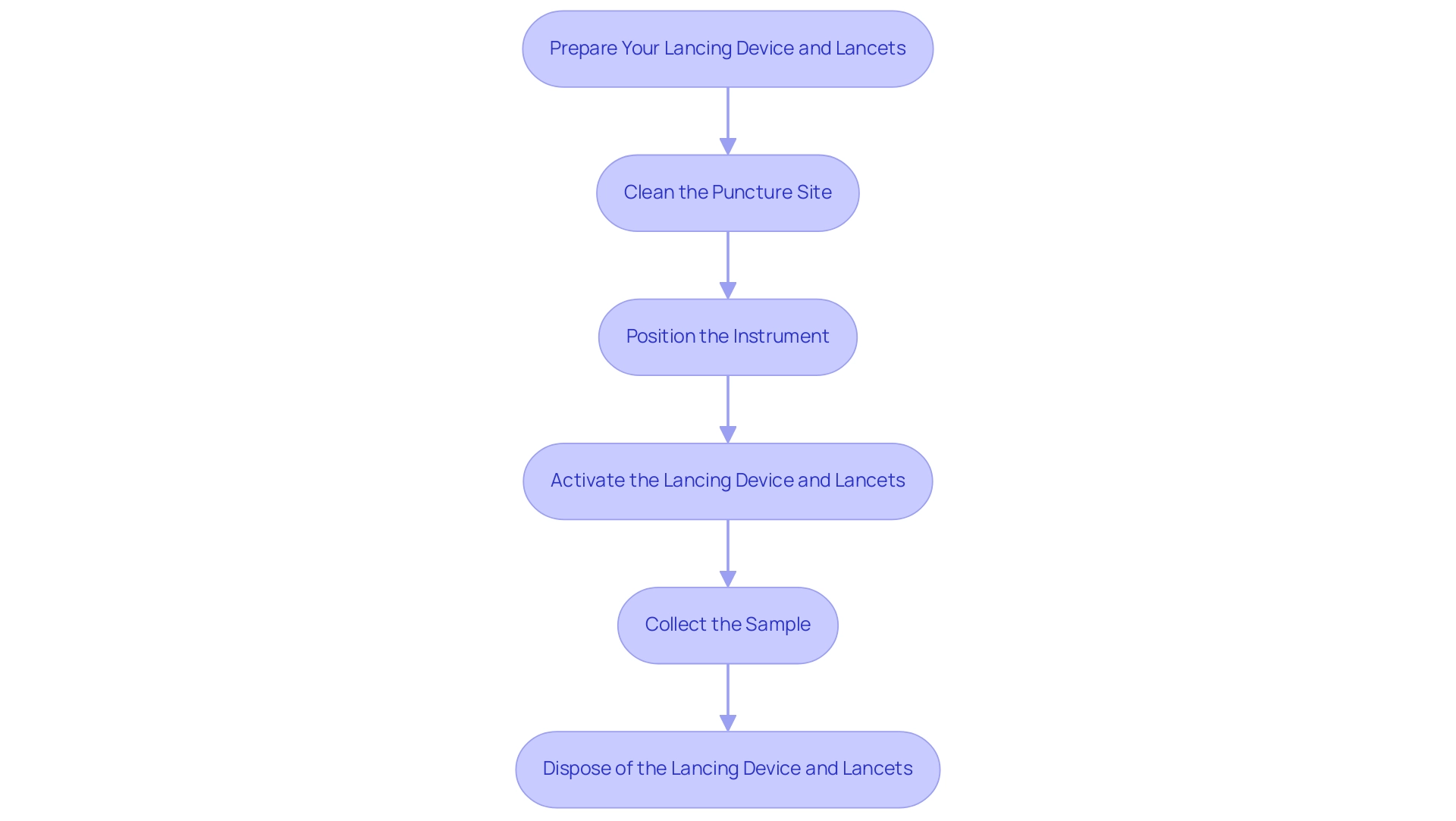
Step-by-Step Instructions for Using a Lancing Device
- Prepare Your Lancing Device and Lancets: Begin by inserting a new lancet into the lancing device and lancets as per the manufacturer's instructions. This ensures the apparatus functions effectively. Significantly, tools such as the Accu-Chek Mobile system can reduce handling steps by approximately 73%, enhancing efficiency. Adjust the depth setting to your comfort level to minimize discomfort during the puncture.
- Clean the Puncture Site: Prior to use, clean the fingertip area where you’ll puncture the skin with an alcohol wipe. Allow the site to dry completely to prevent irritation and ensure accurate results.
- Position the Instrument: Hold the lancing instrument firmly against your fingertip, positioning it perpendicular to the skin. This alignment is crucial for a clean and efficient puncture. Some contemporary gadgets include a lancet storage compartment that moves with the door, offering easy access to lancets for a smoother experience.
- Activate the Lancing Device and Lancets: Once positioned, press the button or trigger to activate the lancing device and lancets. It should quickly puncture the skin, allowing for an efficient sample collection.
- Collect the Sample: After the puncture, gently squeeze your fingertip to form a droplet. This drop is essential for use with your glucose meter, allowing for an accurate reading of your blood glucose levels.
- Dispose of the Lancing Device and Lancets: After testing, immediately dispose of the used lancing device and lancets in a sharps container. This practice not only avoids possible harm but also upholds cleanliness and safety in your blood sugar management routine.
Conclusion: Recognizing the significance of utilizing easy-to-handle pricking tools is essential, particularly considering the difficulties within the diabetic pricking tool market, such as patient compliance with treatment protocols. At&T Solutions, we are dedicated to offering recently diagnosed individuals extensive resources and assistance for managing their condition, including insights on how to effectively utilize lancing tools. For instance, we will offer detailed guides, video tutorials, and community forums where patients can share experiences and tips.
Proper usage of these devices can significantly influence your health management journey, and we will continue to offer guidance and community support for every step of the way.
Best Practices for Using Lancets Safely and Effectively
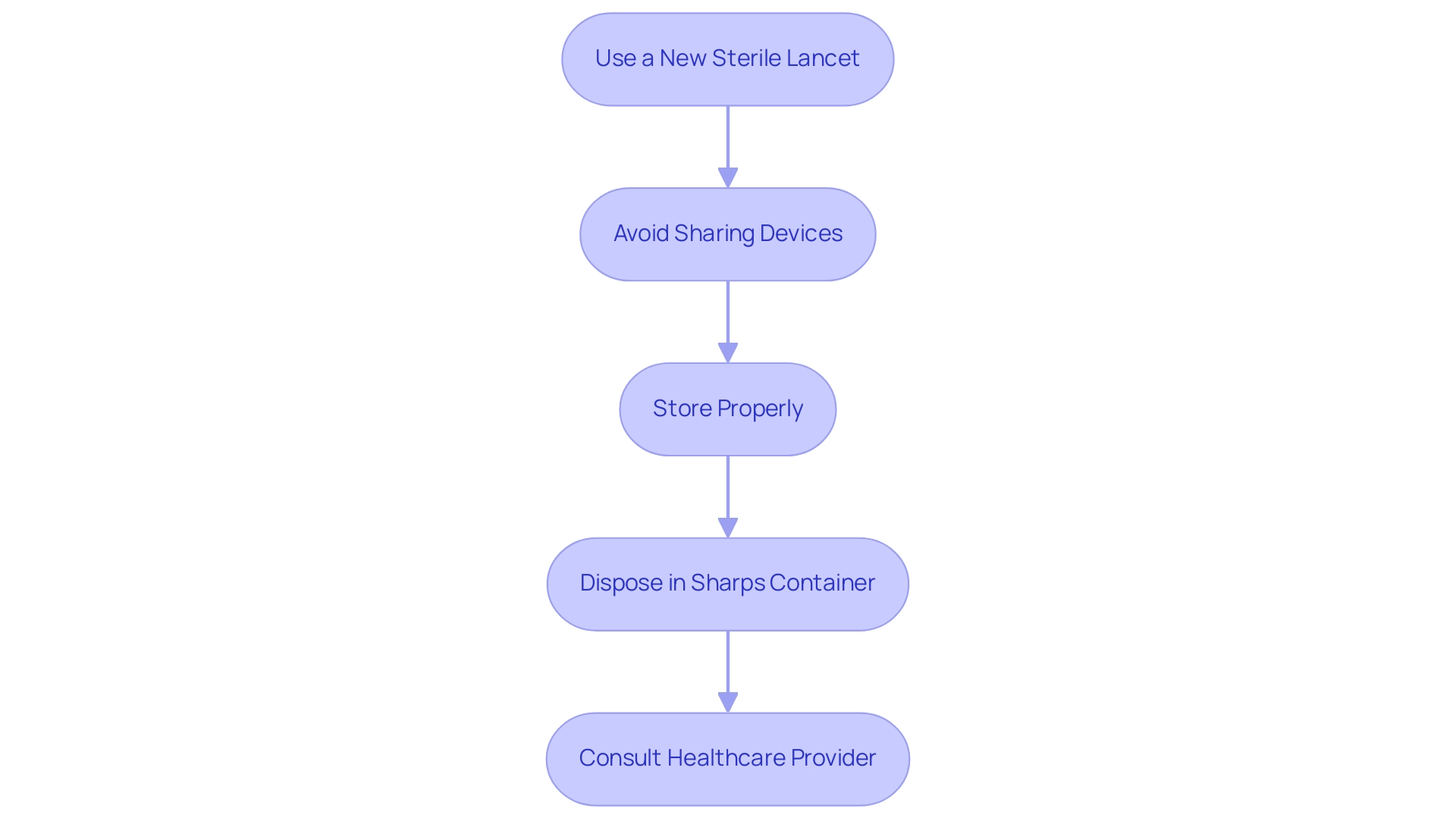
To ensure safety and effectiveness in diabetes management, it is crucial to adhere to best practices when using a lancing device and lancets. Here are essential guidelines to follow:
- Always use a new, sterile lancet for each blood sample: This reduces the risk of infections, which can arise from reusing lancets. In fact, statistics indicate that improper lancet usage can lead to significant infection rates, emphasizing the need for vigilance. The Global Burden of Disease Study reported 1,610,000 deaths from inadequate WASH in 2017, underscoring the critical importance of proper infection prevention practices.
- Avoid sharing lancing devices and lancets with others: Sharing can lead to cross-contamination, which is a common factor in the spread of infections. J.L. Walson emphasizes the importance of individual device use, stating that "shared equipment can compromise safety and health," highlighting the risks associated with sharing a lancing device and lancets.
- Store the lancing device and lancets in a cool, dry place: Proper storage helps maintain the sterility of the lancing device and lancets, ensuring that each lancet remains safe for use.
- Dispose of used lancets and the lancing device immediately in a designated sharps container: This practice prevents accidental needle sticks and potential injuries, which can occur when used lancets and the lancing device are left unsecured. Strategies for combating AMR, including infection prevention, point to the necessity of maintaining strict disposal protocols to safeguard health.
- Consult your healthcare provider if you experience pain or excessive bleeding: Any unusual symptoms could indicate a problem that needs professional attention.
By following these practices, individuals can significantly lower the risk of infection and improve their overall management experience using a lancing device and lancets. For more resources and support on managing your condition, T2D Solutions is here to assist you in navigating your journey.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Lancing Devices
Common problems with the lancing device and lancets can significantly affect the effectiveness of blood glucose monitoring, but understanding these challenges is essential for newly diagnosed patients. As part of T2DSolutions, your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes management, we aim to provide valuable insights and support. Here are some typical problems and expert troubleshooting tips to resolve them:
-
Device Not Puncturing: Verify that the lancing device and lancets are correctly inserted and that the depth setting is suitable for your skin type.
If the lancing device and lancets still fail to puncture, consider trying a new lancet to rule out any defects.
-
Excessive Pain: Many users report discomfort during testing with the lancing device and lancets, often due to depth settings that are too deep. Adjusting the depth to a shallower setting can alleviate this pain. If discomfort continues, it’s advisable to discuss the use of a lancing device and lancets as alternative options with your healthcare provider. Mitchel Pineau noted,
The purpose of this study was to determine the volume of fluid expressed when these patients perform routine fingersticks using their own lancing device and lancets and to evaluate the relationship between fluid volume and pain,
highlighting the importance of minimizing discomfort in the sampling process. Addressing these pain issues is crucial, especially considering barriers such as cost and convenience that may prevent patients from switching to less painful devices.
To ensure a sufficient sample for testing with a lancing device and lancets, keep the puncture site clean and gently squeeze the fingertip to promote flow. If you’re still having trouble, switching fingers while using a lancing device and lancets might provide better results. Patients generally prefer larger drop sizes for testing, as it eases sampling and reduces waste.
-
Lancet Jammed: If the lancet becomes jammed, carefully remove the stuck lancet and replace it with a new one using a lancing device and lancets. It’s also important to check for any debris or blockages within the lancing device and lancets that could be causing the jam.
Understanding these common issues can enhance your experience with lancing devices and lancets, thereby improving compliance with self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG). As you navigate your health management journey, remember that T2D Solutions is here to support you with resources and community insights that can significantly influence your satisfaction and discomfort levels with equipment choices. For example, in a study comparing different puncture tools, Accu-Chek products were described as 'virtually pain-free' by 61.5% to 72.9% of participants, significantly surpassing rivals.
This indicates that choosing the appropriate instrument is vital for effective management of blood sugar levels, as it not only influences pain levels but also overall adherence to SMBG.
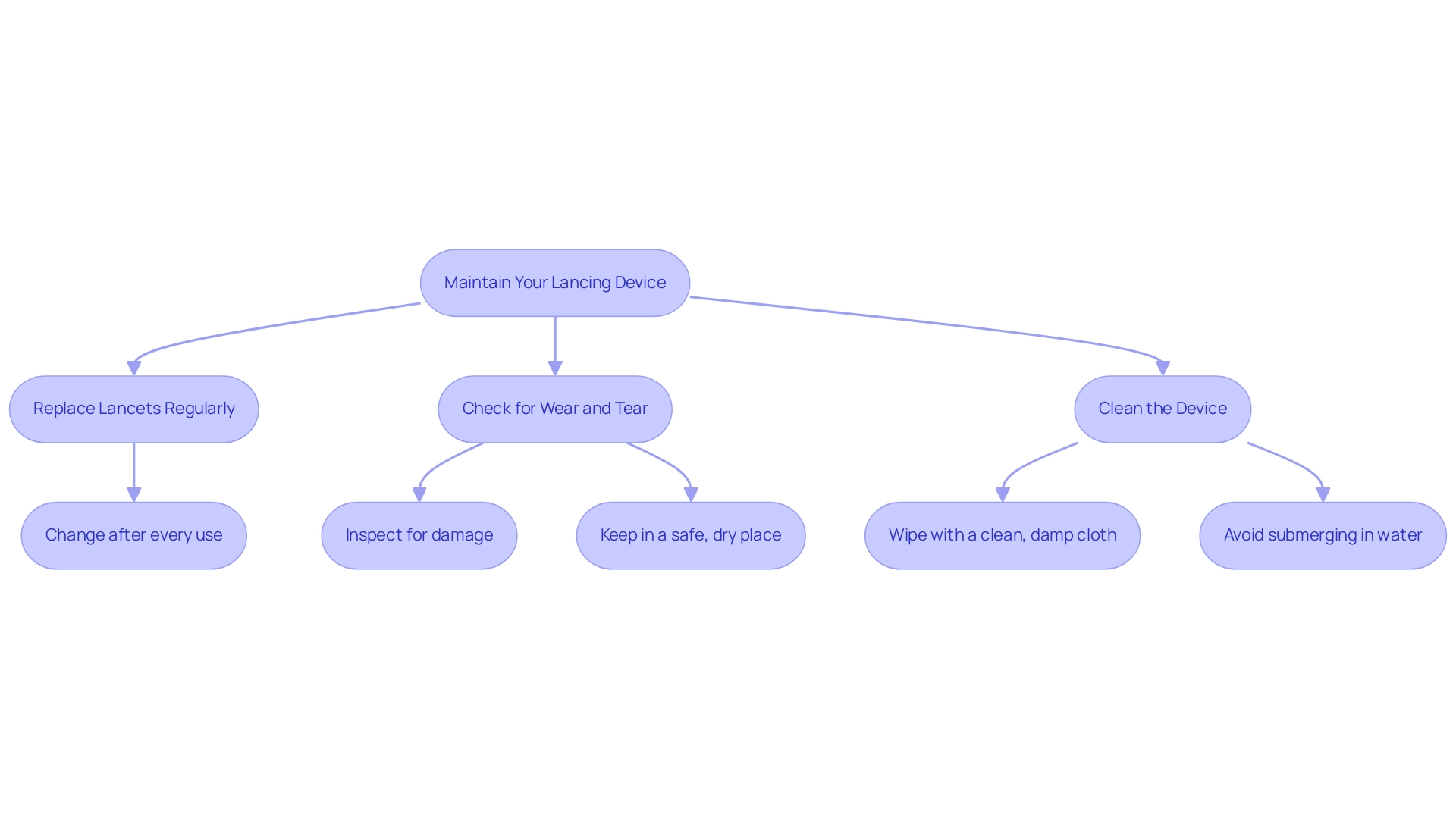
Maintaining Your Lancing Device: When and How to Replace Lancets
To uphold your pricking instrument and ensure optimal performance in blood sugar management, consider the following essential practices:
-
Replace Lancets Regularly: It is crucial to change your lancet after every use or at least every few days. This habit prevents dulling, which can compromise the quality of the puncture and lead to discomfort. Recent studies emphasize that the overall MARD for the Dexcom G7 was 13.6%, considerably greater than the FreeStyle Libre 3's MARD of 8.9%, highlighting the significance of effective diabetes management tools.
Regularly clean the lancing device and lancets by wiping the exterior of your pricking tool with a clean, damp cloth to remove any blood or debris. Avoid submerging the equipment in water to maintain its integrity and functionality.
-
Check for Wear and Tear: Conduct routine inspections of your equipment for any signs of damage or wear. If you identify any issues, consult the manufacturer for guidance or replace the item as necessary to ensure continued effectiveness.
Always keep your lancing device and lancets in a safe, dry place. Proper storage helps prevent damage and ensures that the device is readily available when needed.
As T2DSolutions launches as a comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 conditions, these maintenance tips will be part of the valuable insights shared with newly diagnosed patients. T2DSolutions aims to provide a range of educational resources, including maintenance practices, to support effective management of blood sugar. Recent insights have shown that improved comfort is reported in newer piercing systems compared to traditional ones, enhancing the overall user experience.
Furthermore, studies highlight the significance of regular replacement of the lancing device and lancets, with patient reports indicating a direct correlation between maintenance practices and comfort levels during use. As noted by Basu et al., medication use is crucial, with 84.2% of patients reporting adherence to prescribed treatments. Following these maintenance suggestions not only extends the lifespan of your lancing device and lancets but also contributes to more efficient blood sugar management.
A case study analysis indicated that continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) was 100% likely to be dominant over self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG), demonstrating the cost-effectiveness of maintaining such devices for optimal diabetes management outcomes.
Conclusion
Effective diabetes management hinges on the proper use of lancing devices, which are indispensable tools for monitoring blood sugar levels. This article has explored the purpose and functionality of these devices, emphasizing their role in providing accurate glucose readings that are crucial for informed health decisions. The different types of lancing devices available cater to varying user preferences, with features like adjustable depth settings enhancing comfort and compliance among users.
Best practices for using lancets safely, troubleshooting common issues, and maintaining lancing devices have been highlighted as vital steps in ensuring a smooth diabetes management journey. By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can minimize discomfort, prevent infections, and maximize the effectiveness of their monitoring routine.
As T2DSolutions continues to provide educational resources and community support, it is evident that understanding and effectively utilizing lancing devices can significantly impact health outcomes for those managing diabetes. Taking proactive steps in monitoring blood glucose levels not only contributes to better day-to-day management but also plays a crucial role in preventing complications associated with diabetes. Empowering individuals with the right knowledge and tools is essential for navigating the challenges of diabetes management successfully.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are lancing devices and lancets used for?
Lancing devices and lancets are essential tools for individuals managing diabetes, specifically designed to pierce the skin and obtain small blood samples for glucose testing.
Why is regular blood sugar monitoring important?
Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for making informed health decisions regarding diet, exercise, and medication, which helps in the effective management of diabetes.
What features do modern lancing devices typically have?
Modern lancing devices often include adjustable depth settings, allowing users to customize the puncture depth to reduce discomfort while ensuring a sufficient blood sample is obtained.
How has the prevalence of type 2 diabetes changed in recent years?
The occurrence of type 2 diabetes has significantly increased among all racial and ethnic groups from 2002 to 2018, highlighting the need for effective monitoring tools like lancing devices and lancets.
What advancements have been made in lancing technology?
Recent advancements in lancing technology have improved the effectiveness and user-friendliness of lancing devices and lancets, making them less painful for users.
What are the consequences of undiagnosed blood sugar issues?
Approximately 8.6 million individuals are unaware they have undiagnosed blood sugar issues, which underscores the importance of regular monitoring with lancing devices and lancets.
What is the relationship between diabetes and vision problems?
Diabetes is the leading cause of new cases of blindness among adults aged 18–64, with 10.1% of diagnosed diabetics reporting severe vision difficulty or blindness in 2021.
How does T2DSolutions support individuals with diabetes?
T2DSolutions offers guides, product comparisons, and user testimonials to assist individuals in selecting the appropriate lancing tools, along with providing the latest information and resources for health management.
What types of lancing instruments are available?
Lancing instruments are available in both automatic and manual styles, catering to different user preferences, with automatic tools offering quick and easy punctures, while manual tools require user engagement to initiate the puncture.
How do adjustable depth settings benefit users of lancing devices?
Adjustable depth settings allow users to customize the puncture based on their skin thickness, significantly reducing discomfort during blood sampling, which can enhance compliance with glucose monitoring.



