Introduction
Navigating the complexities of diabetes management requires a solid understanding of key indicators, with the A1C test standing out as a critical tool for individuals managing their condition. This test measures the average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, providing essential insights into long-term glucose control.
For newly diagnosed patients, familiarizing themselves with A1C results is not just beneficial; it is imperative for making informed decisions regarding treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
As diabetes continues to affect millions, the importance of regular A1C testing cannot be overstated, especially given its role in preventing serious health complications.
This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, effective monitoring strategies, and actionable steps to help individuals lower their A1C levels, ultimately empowering them to take charge of their health.
Understanding the A1C Test: A Key to Diabetes Management
As T2DSolutions launches as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 conditions education and community support, understanding key concepts such as the A1C equivalent chart becomes essential for newly diagnosed patients. The A1C test, commonly referred to as glycated hemoglobin, quantifies the percentage of glucose that is attached to hemoglobin in the bloodstream. This test is fundamental for managing blood sugar, as it provides an average of levels over the preceding two to three months.
A higher A1C percentage, as shown in an A1C equivalent chart, indicates suboptimal blood sugar control, which can lead to various complications associated with the condition. Understanding the A1C equivalent chart is essential as it enables you and your healthcare team to make informed choices about your treatment plan and required lifestyle changes. According to Dr. Frederick L Brancati, MD, MHS, 'A1C and fasting glucose can be compared head-to-head against the subsequent development of clinically diagnosed condition as the gold standard.'
This highlights the A1C test's vital role not only in monitoring existing conditions but also in guiding preventative strategies for at-risk individuals, as illustrated by an A1C equivalent chart. Recent studies, including findings by Herman et al., have shown distinct variations in A1C levels across different racial and ethnic groups, further emphasizing the need for personalized management approaches. Furthermore, with total direct and indirect estimated costs of diagnosed conditions in the United States reaching $413 billion in 2022, effective management strategies are more crucial than ever.
A study on cardiovascular illness and type 1 metabolic disorder revealed that participants undergoing intensive glycemic management exhibited a notable 57% decrease in the risk of nonfatal myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality compared to those receiving standard care. As of 2024, the average A1C levels for diabetic patients are being closely monitored with the help of an A1C equivalent chart, as healthcare professionals recognize its direct impact on treatment efficacy and overall health outcomes. T2DSolutions is here to assist you in navigating these critical aspects of managing your condition.
Visit T2DSolutions to access resources, subscribe for updates, and join our community for ongoing support in your diabetes journey.
How to Utilize the A1C Equivalent Chart for Effective Monitoring
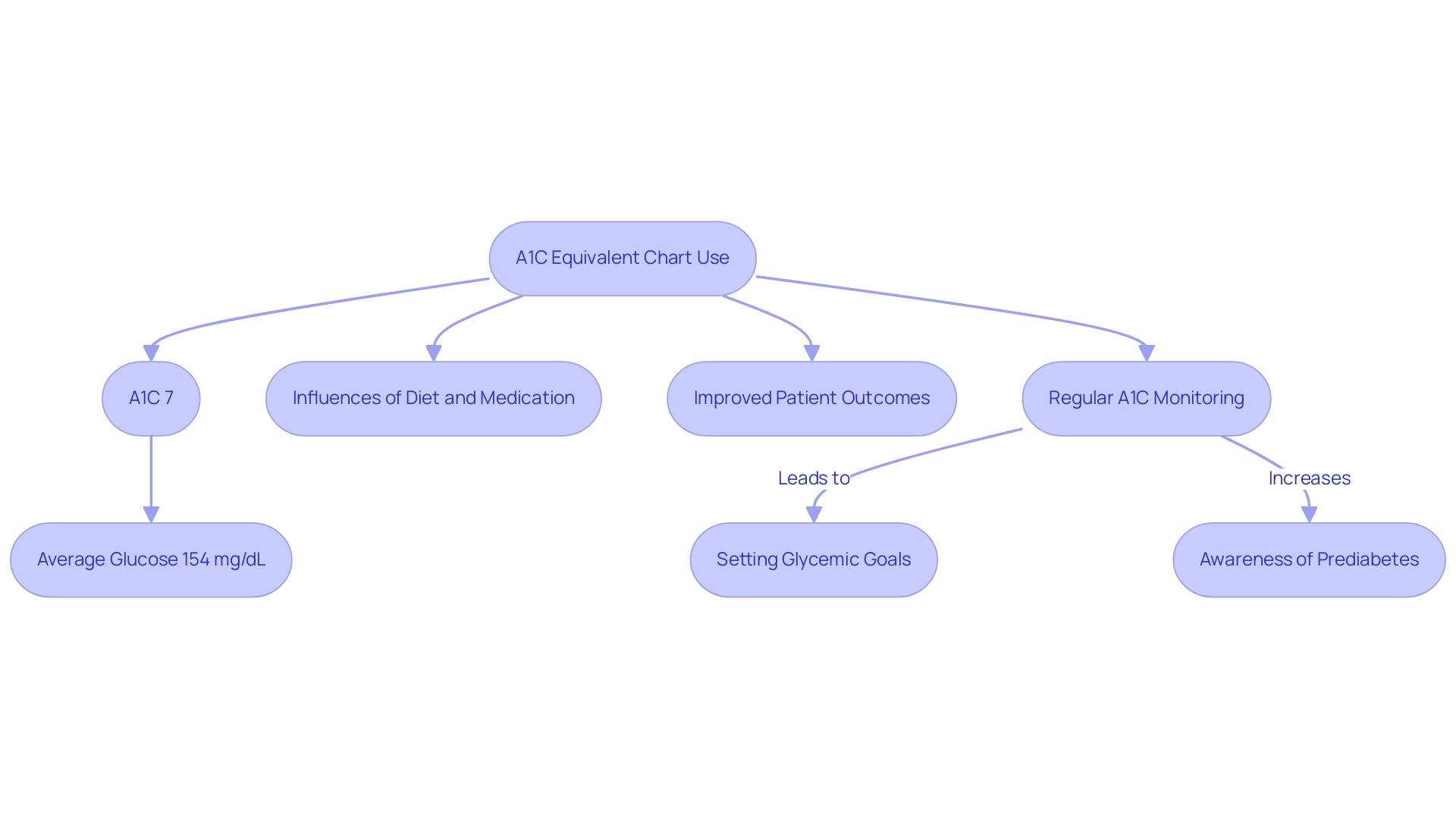
To effectively utilize the a1c equivalent chart, start by identifying your A1C percentage. The chart acts as an a1c equivalent chart by presenting A1C values alongside their corresponding average blood glucose readings, measured in mg/dL. For instance, an A1C of 7% is associated with an average blood glucose measurement of about 154 mg/dL.
Regularly monitoring your A1C using an a1c equivalent chart allows for an insightful overview of your blood glucose control over time, facilitating necessary adjustments in your management strategies. This tool is particularly beneficial for recognizing how your dietary choices and adherence to prescribed medications, along with the a1c equivalent chart, can influence your overall glucose. As highlighted by recent findings, setting a glycemic goal during consultations is likely to improve patient outcomes, further emphasizing the critical role of A1C monitoring in effective management of the condition.
With a prevalence of this condition at 14.3%, understanding your A1C levels is crucial for managing your health. Additionally, a case study reveals that in 2021, an estimated 97.6 million U.S. adults had prediabetes, underscoring the importance of awareness and preventive measures. T2DSolutions will soon provide extensive materials, including a comprehensive A1C equivalent chart, along with detailed blood glucose charts, educational content, and tools aimed at empowering newly diagnosed patients in their health management journey.
To remain updated on these materials and news, think about subscribing to T2DSolutions. Furthermore, the international consensus by Danne et al. on continuous glucose monitoring highlights its relevance in conjunction with A1C monitoring strategies.
The Importance of Regular A1C Testing in Diabetes Care
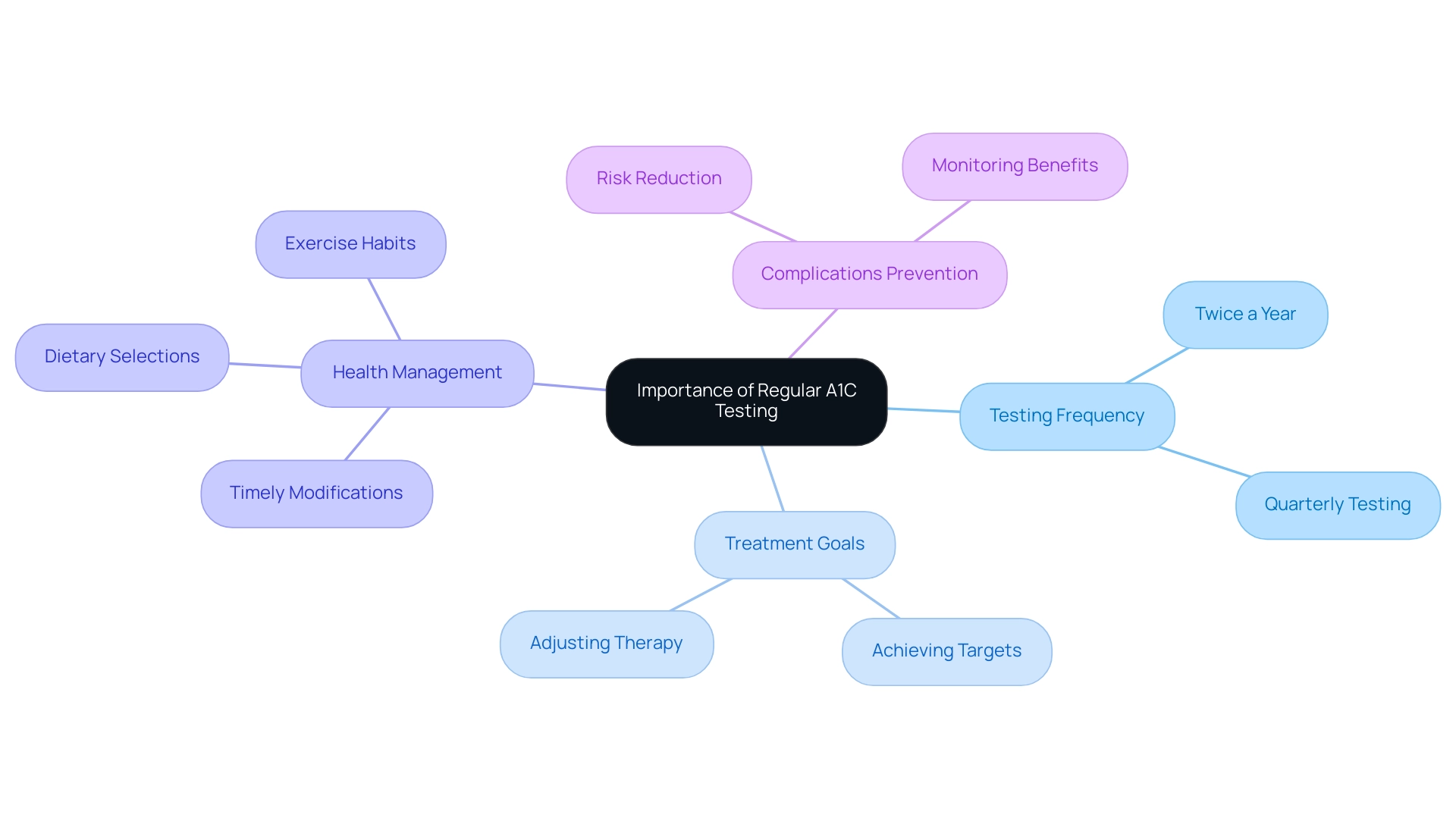
T2DSolutions is excited to announce the launch of a new resource hub dedicated to supporting individuals with Type 2 and Type 3 conditions. As part of our commitment to providing comprehensive education and community support, we emphasize the importance of regular A1C testing in managing blood sugar levels, which can be referenced using an A1C equivalent chart. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends that individuals with the condition undergo A1C testing at least twice a year if treatment goals are being met.
For those whose therapy has changed or who are not achieving their targets, quarterly testing is advised. Regular A1C evaluations are crucial for prompt modifications to medication, dietary selections, and exercise habits, which are vital in preventing complications from poorly managed blood sugar levels, as illustrated in the A1C equivalent chart. According to the ADA, 'A1C testing is fundamental to understanding long-term glucose control and making informed care decisions, as referenced in the A1C equivalent chart.'
Additionally, with the revised Medicare reimbursement rules, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is now accessible for adults with type 2 conditions on insulin, further underscoring the significance of regular monitoring. At&T Solutions, we are dedicated to providing you with the tools and resources necessary for effective management of blood sugar. By diligently monitoring A1C levels with the A1C equivalent chart, patients can actively engage in their health management, leading to better outcomes.
Our hub aims to enhance management strategies for the condition, as consistent A1C monitoring, illustrated in the A1C equivalent chart, has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of complications, emphasizing the vital role these tests play in effective care. To stay updated with our latest resources and support options, we invite you to subscribe to our newsletter and be part of our growing community.
Interpreting A1C Results: What They Mean for Your Health
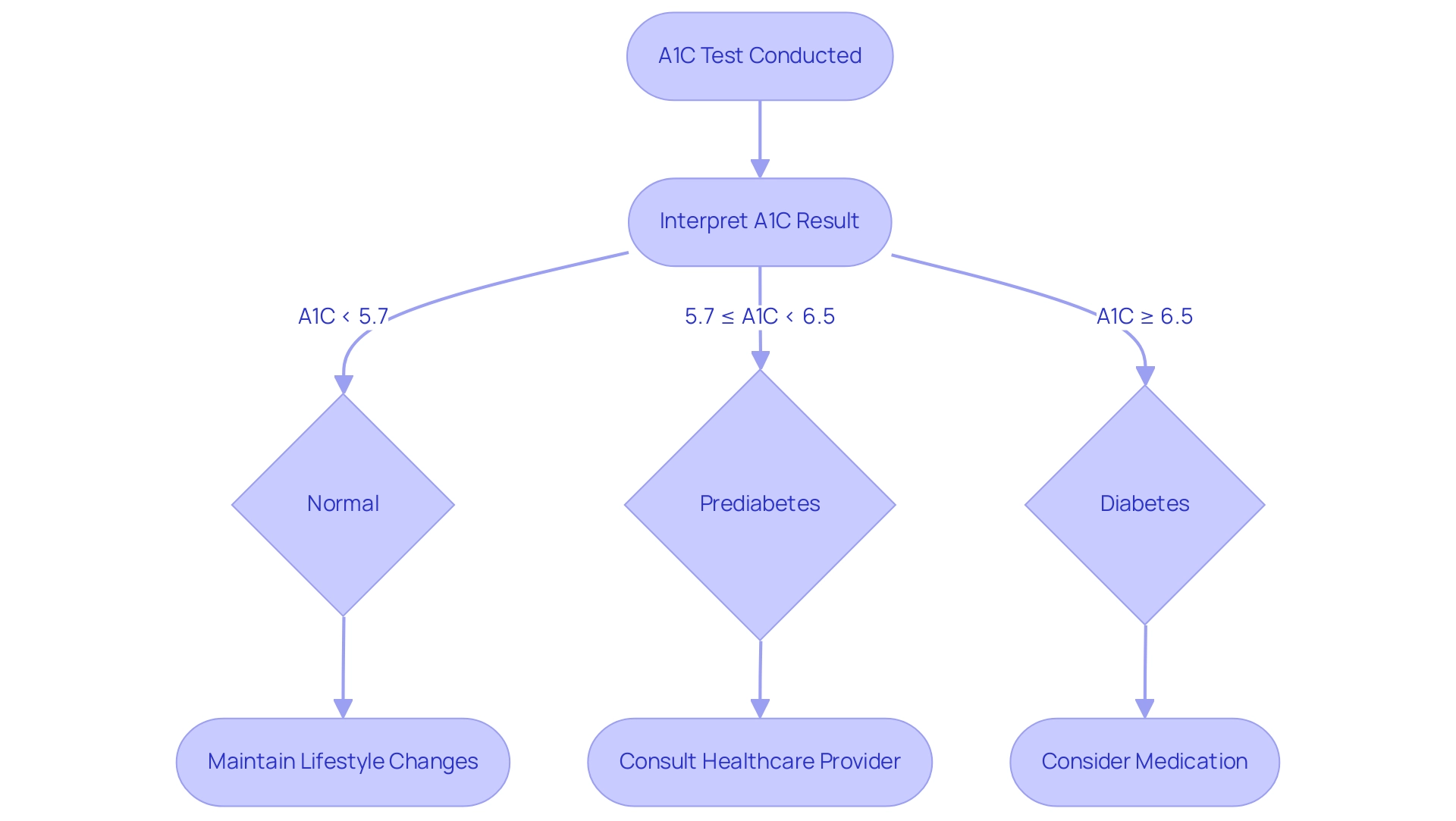
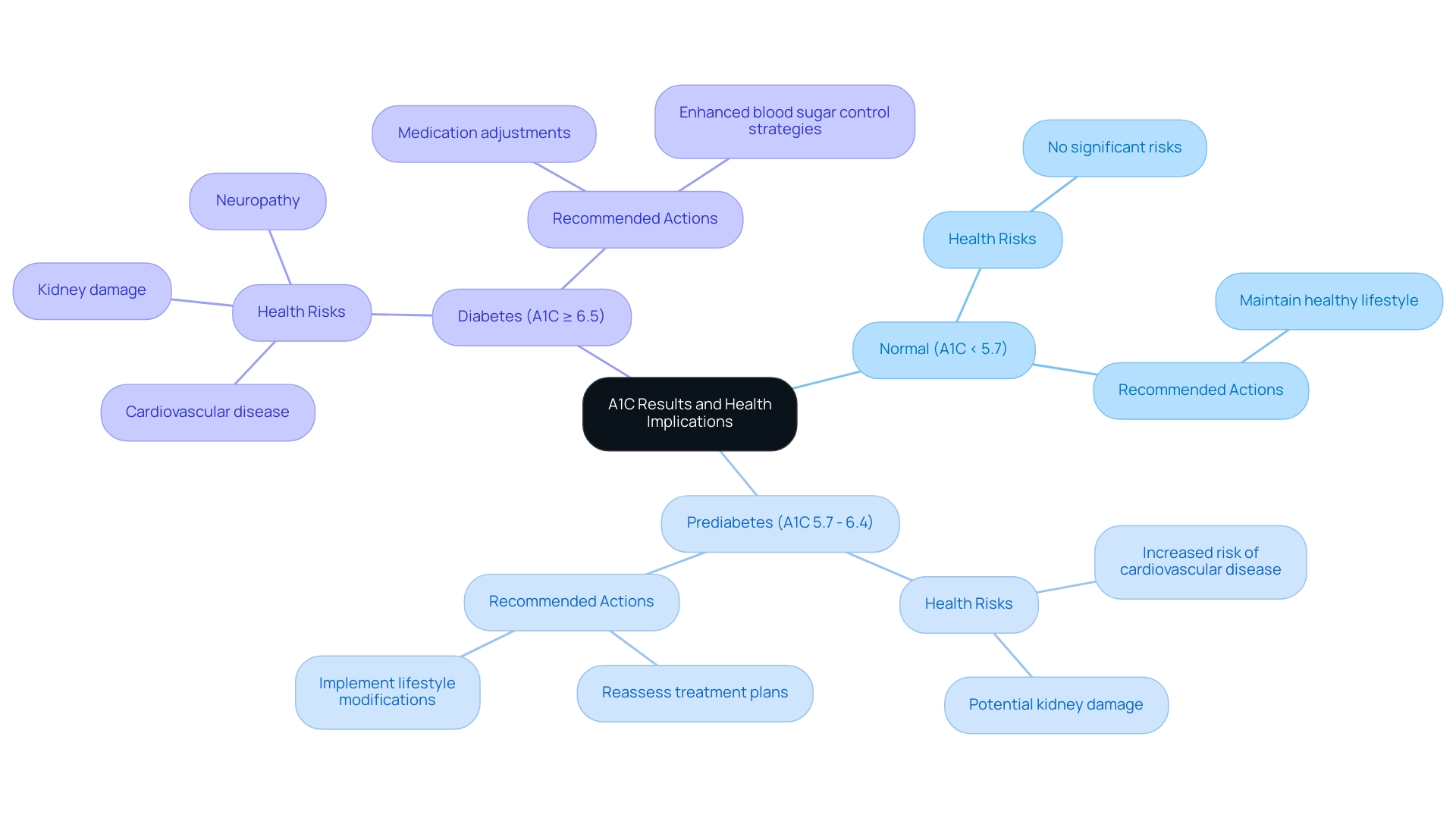
A1C results are categorized into separate groups that offer essential insights into a person's condition. An A1C measurement below 5.7% is regarded as normal, whereas readings between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes. A reading of 6.5% or above verifies a diagnosis of the condition.
Understanding where your A1C falls within these ranges is crucial, as it directly correlates with the risk of developing complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and neuropathy, which can be assessed with an A1C equivalent chart. For instance, individuals with A1C readings above the target range may need to reassess their treatment plans, which could involve medication adjustments or lifestyle modifications aimed at enhancing blood sugar control. Recent statistics indicate that, from August 2021 to August 2023, the prevalence of the disease was noted at 14.3% among a sample size of 2,938 individuals.
This highlights the urgency of monitoring A1C values not only for personal health but also for broader public health initiatives. Furthermore, case studies such as the 2017-2020 analysis of prediabetes awareness by race-ethnicity reveal disparities in recognition of these health markers, suggesting a need for culturally tailored health education to improve awareness across diverse communities. As Roopa Naik states, 'Disclosure: Roopa Naik declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies,' highlighting the importance of unbiased information in managing blood sugar.
Recently diagnosed individuals can gain from T2DSolutions, a thorough information center focused on Type 2 and Type 3 conditions education and community assistance, which will provide crucial insights and tools, including an A1C equivalent chart, for managing A1C values effectively. T2DSolutions aims to provide educational articles, community support forums, and tools for tracking A1C levels, including the A1C equivalent chart, ensuring that patients have access to vital information as they navigate their health management journey. Furthermore, materials for managing CFRD, as detailed in the Clinical Care Guidelines and the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes guidelines, can offer valuable guidance for newly diagnosed patients.
To remain informed about these materials and more, subscribing to T2DSolutions is strongly recommended, as it will offer timely information that can greatly assist in managing the condition effectively. Such insights emphasize the vital role of understanding A1C results in managing diabetes effectively, particularly with the use of an A1C equivalent chart.
Strategies for Lowering Your A1C Levels Effectively
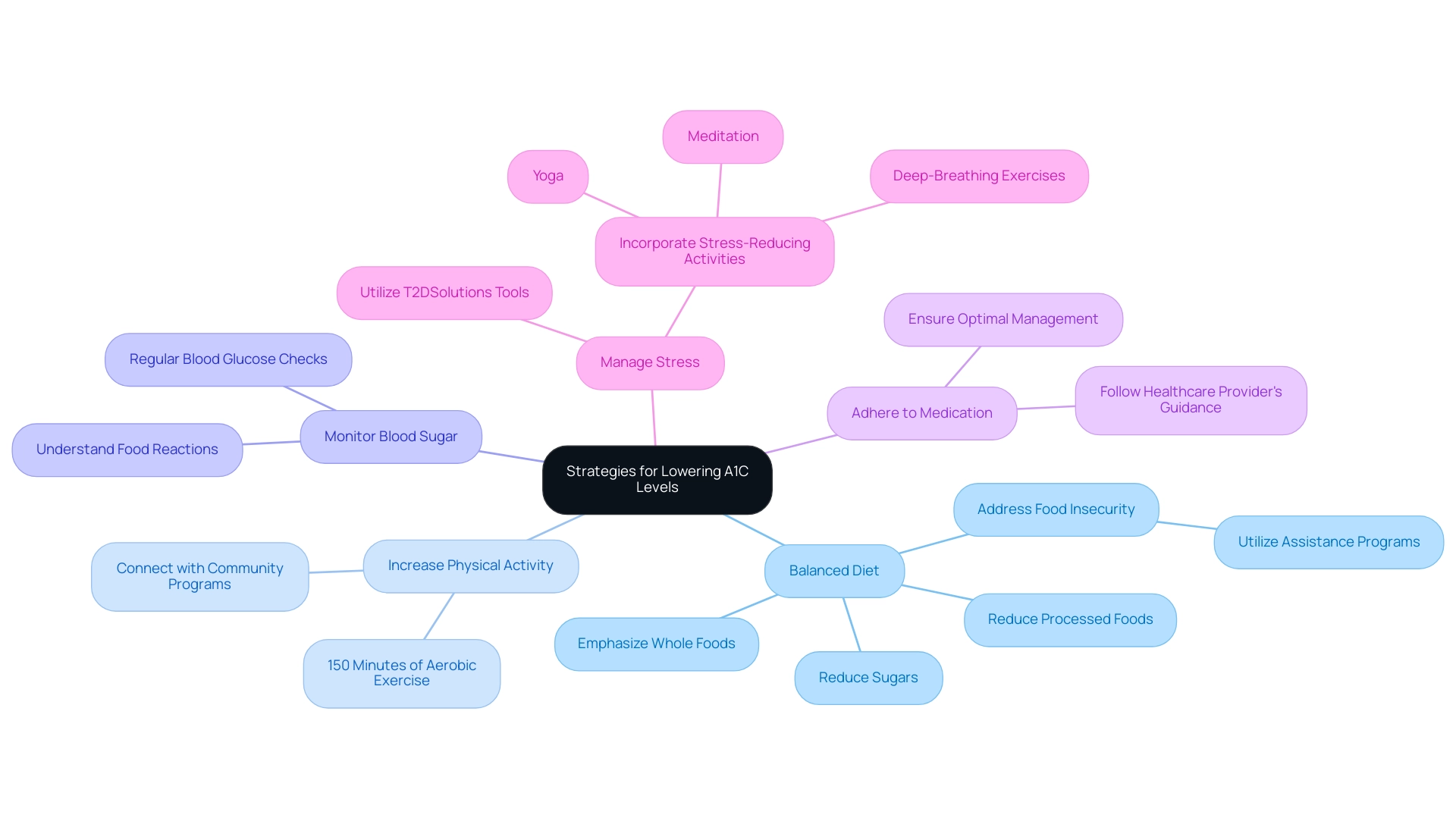
To effectively reduce your A1C values, consider applying the following strategies, which can be supported by the A1C equivalent chart and materials available at T2DSolutions:
- Adopt a balanced diet: Emphasize whole foods such as vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while significantly reducing processed foods and sugars. Savoca and Miller highlight that patients’ food selection and dietary behaviors can be profoundly influenced by a strong understanding of diabetic diet recommendations.
Notably, 70.9% of adults with a BMI ≥30 experience food insecurity and low diet quality, which underscores the need for supportive dietary practices. T2DSolutions offers guidance and resources to help you make informed dietary choices.
-
Increase physical activity: Strive for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week, as this amount of activity has been shown to markedly enhance insulin sensitivity. T2DSolutions can connect you with local community programs to help you stay active.
-
Monitor blood sugar readings: Regularly checking your blood glucose is crucial for understanding how your body reacts to different foods and physical activities, which can inform better management practices.
-
Adhere to medication: It is essential to follow your healthcare provider's guidance regarding diabetes medications and insulin therapy to ensure optimal management of your condition.
-
Manage stress: Incorporate stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises into your routine, as stress can adversely affect blood sugar levels. T2DSolutions offers tools and support to help you manage stress effectively.
Tackling food insecurity by utilizing assistance may further enhance diabetes management, as indicated by recent studies suggesting that referrals to support services can improve health outcomes. The study also noted several limitations, including baseline weight differences between diet groups and potential biases in dietary recall methods, which should be considered when applying these recommendations.
By diligently applying these strategies and utilizing the resources available at T2DSolutions, you can achieve significant improvements in your A1C levels, as indicated by the A1C equivalent chart, and enhance your overall well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing A1C levels is paramount for individuals living with diabetes. The A1C test serves as a vital indicator of long-term blood glucose control, allowing patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Regular monitoring of A1C levels, as highlighted in the American Diabetes Association guidelines, is essential for timely interventions that can prevent serious complications associated with poorly managed diabetes.
By familiarizing oneself with A1C results and utilizing tools such as the A1C equivalent chart, patients can gain crucial insights into their glucose control and adapt their management strategies accordingly. Strategies for lowering A1C levels—including:
- Maintaining a balanced diet
- Increasing physical activity
- Adhering to prescribed medications
can significantly enhance health outcomes. Moreover, addressing factors such as stress and food insecurity can further contribute to effective diabetes management.
The importance of personalized approaches in diabetes care cannot be overstated, as variations in A1C levels across different populations highlight the need for tailored strategies. With resources like T2DSolutions, individuals can access valuable educational materials and community support to navigate their diabetes journey more effectively. Taking proactive steps towards understanding and managing A1C levels empowers individuals to take control of their health and improve their quality of life.



