Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding the A1C test is essential for individuals navigating their health journey. This critical assessment not only measures average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months but also serves as a key indicator for diagnosing diabetes and monitoring treatment efficacy.
With the prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes being significant, the A1C test emerges as a vital tool for early detection and intervention. As healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of regular testing and understanding A1C results, individuals are better equipped to make informed decisions regarding their lifestyle and treatment options.
This article delves into the intricacies of the A1C test, its conversion to estimated average glucose, and the implications of maintaining optimal levels, providing readers with the knowledge needed to enhance their diabetes management effectively.
Understanding the A1C Test and Its Importance
At a2d Solutions, we acknowledge that the A1C test is an essential instrument in managing blood sugar, and we utilize the a1c to blood glucose converter to assess the average glucose amounts over the past 2 to 3 months. Expressed as a percentage, it reflects the proportion of glucose attached to hemoglobin in the blood, providing a comprehensive overview of an individual's glycemic control. This test is essential not only for diagnosing the condition but also for monitoring how effectively blood sugar levels are managed over time.
As noted by Dr. Lara J. Akinbami, understanding A1C results is paramount, as they guide informed decisions regarding health management and necessary lifestyle modifications. With the age-adjusted prevalence of undiagnosed conditions at:
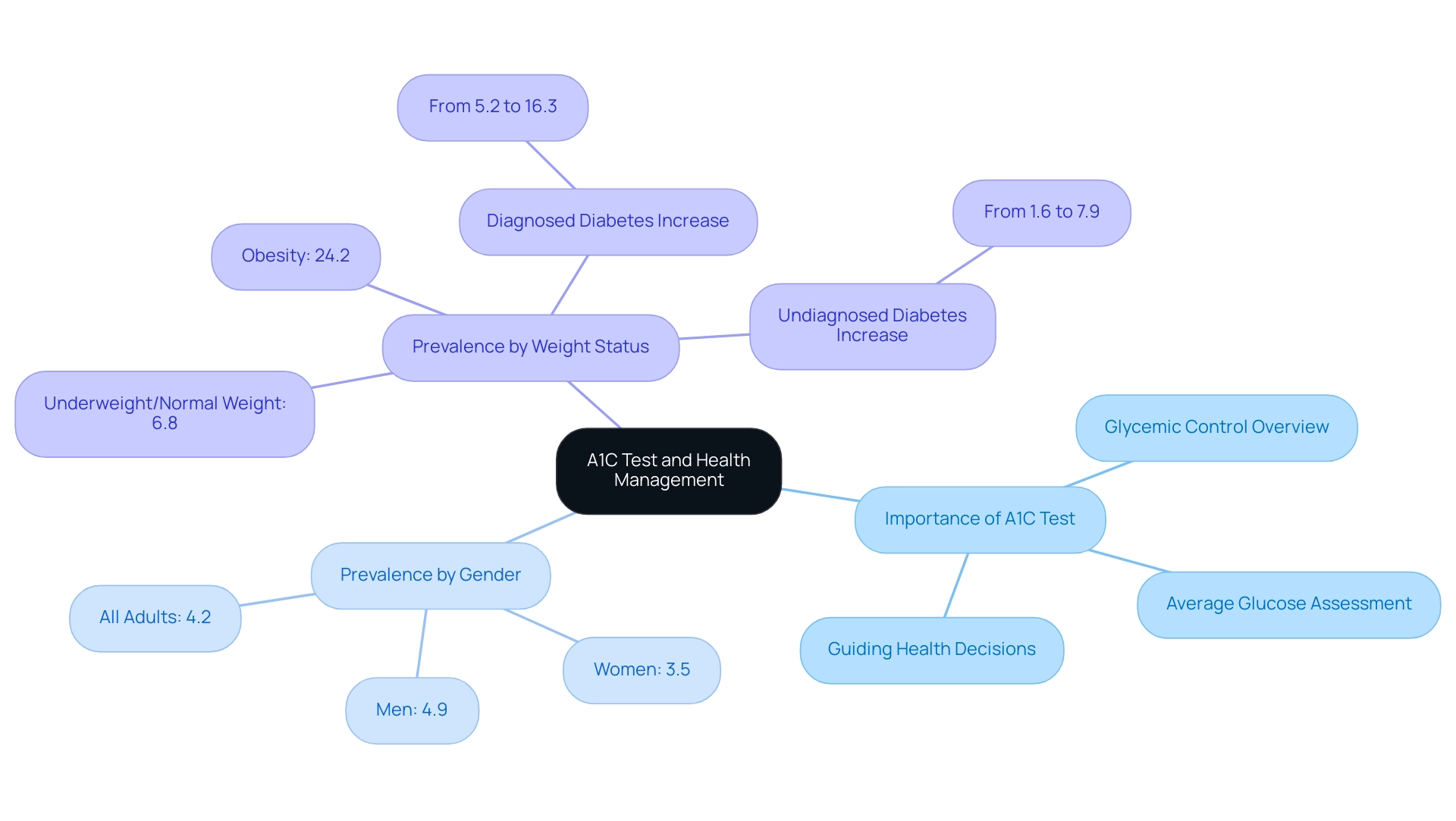
- 4.2% for all adults
- 4.9% for men
- 3.5% for women
the A1C test plays a pivotal role in identifying those at risk and facilitating timely interventions. Furthermore, a recent case study analyzed the prevalence of the condition by weight status, revealing that total prevalence rose significantly from:
- 6.8% in underweight/normal weight adults
- 24.2% in those with obesity
Thus, understanding one’s A1C levels is essential for enhancing glucose control and utilizing an a1c to blood glucose converter to improve overall health results. As T2DSolutions introduces itself as your all-encompassing source for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar education, we stress the significance of precise information in condition oversight. Our platform will offer educational resources, assistance services, and community involvement opportunities to guarantee our community comprehends the importance of dependable testing outcomes and has access to the tools they require for effective health oversight.
Step-by-Step Guide to Converting A1C to Blood Glucose
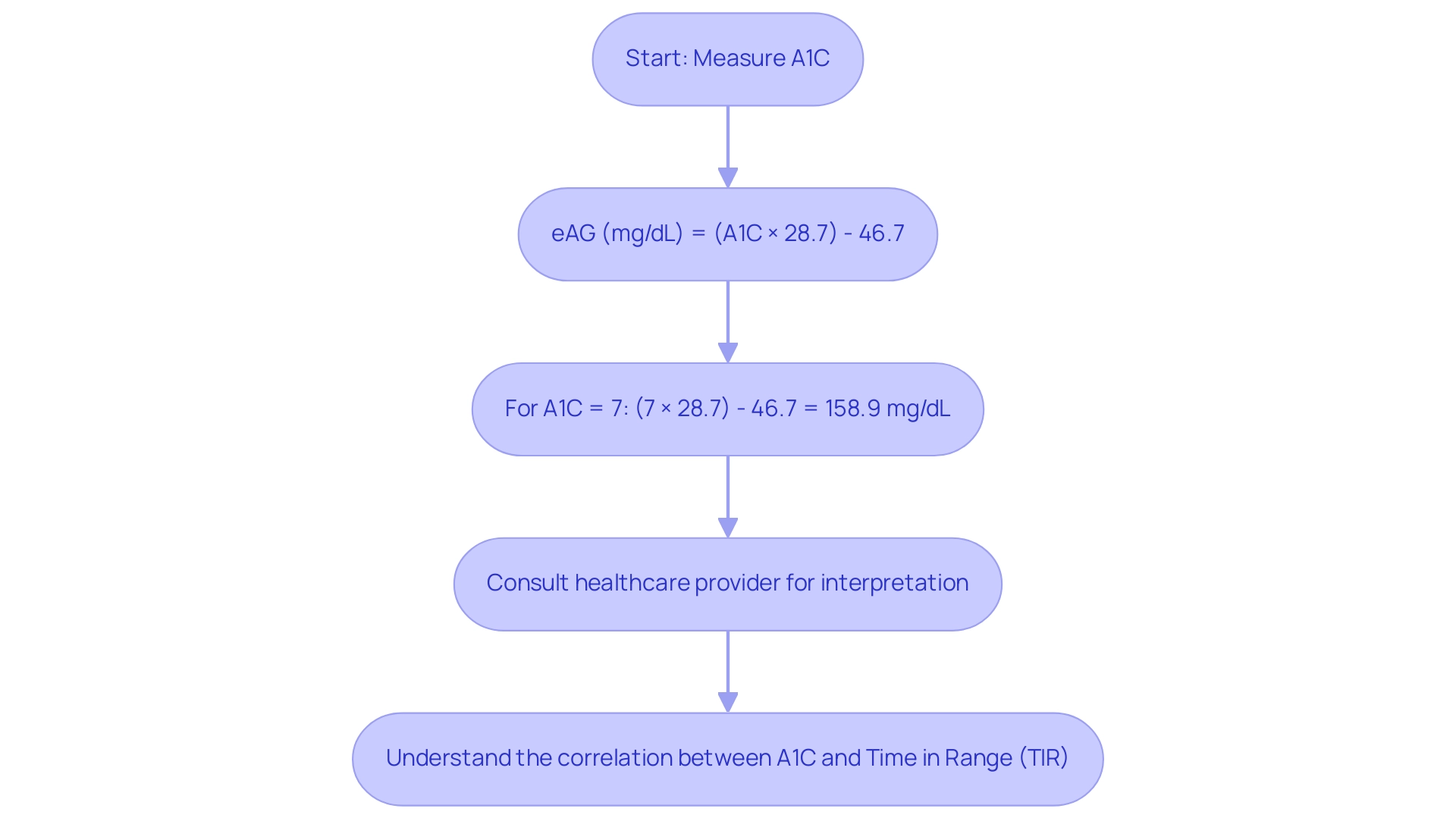
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your new resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 sugar illness education and community support. As we introduce this extensive platform, we intend to offer you essential information and resources needed for efficient control of blood sugar. To convert your A1C to estimated average glucose (eAG) using an a1c to blood glucose converter, the following formula is employed:
eAG (mg/dL) = (A1C × 28.7) - 46.7
For instance, if your A1C is 7%, the calculation would be:
(7 × 28.7) - 46.7 = 158.9 mg/dL
It is noteworthy that in a significant portion of patients (19.2%), the variance between HbA1c and GMI exceeds 1% (11 mmol/mol), highlighting the importance of accurate assessments. As C.E.P., editor of Diabetes Care, emphasizes, "Understanding the nuances of A1C and its conversion to eAG using an a1c to blood glucose converter is crucial for effective control of the condition."
Furthermore, a case study named 'Translating the A1C Assay Into Estimated Average Glucose Values' demonstrates the reliability of the A1C assay and the discrepancies that can occur, clarifying the connection between average glucose and A1C measurements. Numerous online calculators and conversion charts, such as an a1c to blood glucose converter, can provide immediate results to facilitate this process. However, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider to accurately interpret these values within the broader context of your diabetes care plan.
Recent studies emphasize the correlation between Time in Range (TIR) and A1C, suggesting that achieving a TIR of approximately 70% is associated with an A1C value of around 7%. This highlights the significance of comprehending how A1C levels connect to daily glucose control. Furthermore, the accuracy of continuous glucose monitoring systems during exercise has been evaluated, adding another layer of consideration for managing this condition effectively.
Stay tuned for more content as we continue to develop this resource, and consider subscribing to receive updates on new articles and tools to support your diabetes management journey.
The Relationship Between A1C and Average Blood Glucose
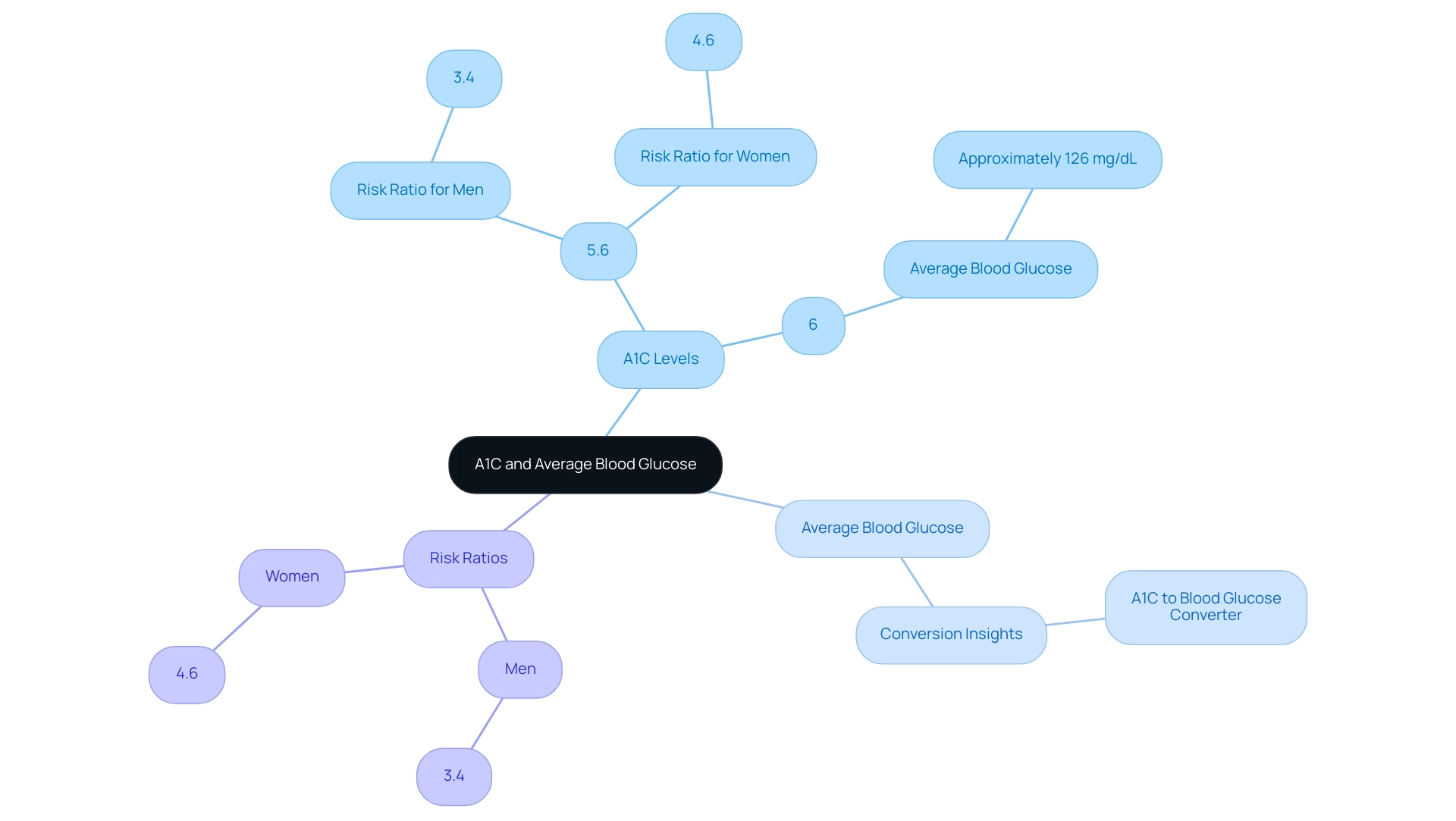
The A1C test serves as a vital indicator of your average blood glucose readings over an extended period, typically reflecting the past two to three months. An A1C of 6% corresponds to an average blood glucose concentration of approximately 126 mg/dL. For each percentage point increase in A1C, there is typically a corresponding rise of 30 to 40 mg/dL in average blood glucose values.
This relationship is critical, as monitoring A1C levels offers invaluable insights into long-term glucose control and the associated risk of diabetes-related complications. Recent research highlights that an A1C cutoff of 5.6% significantly predicts the onset of the condition, with a risk ratio of:
- 3.4 for men
- 4.6 for women
This indicates a substantial increase in risk. Additionally, logistic regression models have evaluated the predictive ability of HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and 2-hour glucose for abnormal continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) area under the curve (AUC), underscoring the importance of A1C in managing blood sugar levels.
A case study titled 'A1C Measurement and Prediction of New-Onset Conditions' evaluated the risk ratio of new-onset issues based on A1C readings, illustrating how an A1C threshold of 5.6% can effectively forecast incident health problems. Thus, understanding this conversion through the A1C to blood glucose converter is essential for managing blood sugar levels effectively and mitigating potential health issues.
At A2D Solutions, we offer resources and educational materials to assist you in comprehending your A1C values and their importance in overseeing health conditions.
As highlighted by Levente Kovacs, 'Comprehending these metrics is essential for effective control of blood sugar levels and patient education.
The Importance of Regular A1C Testing and Monitoring
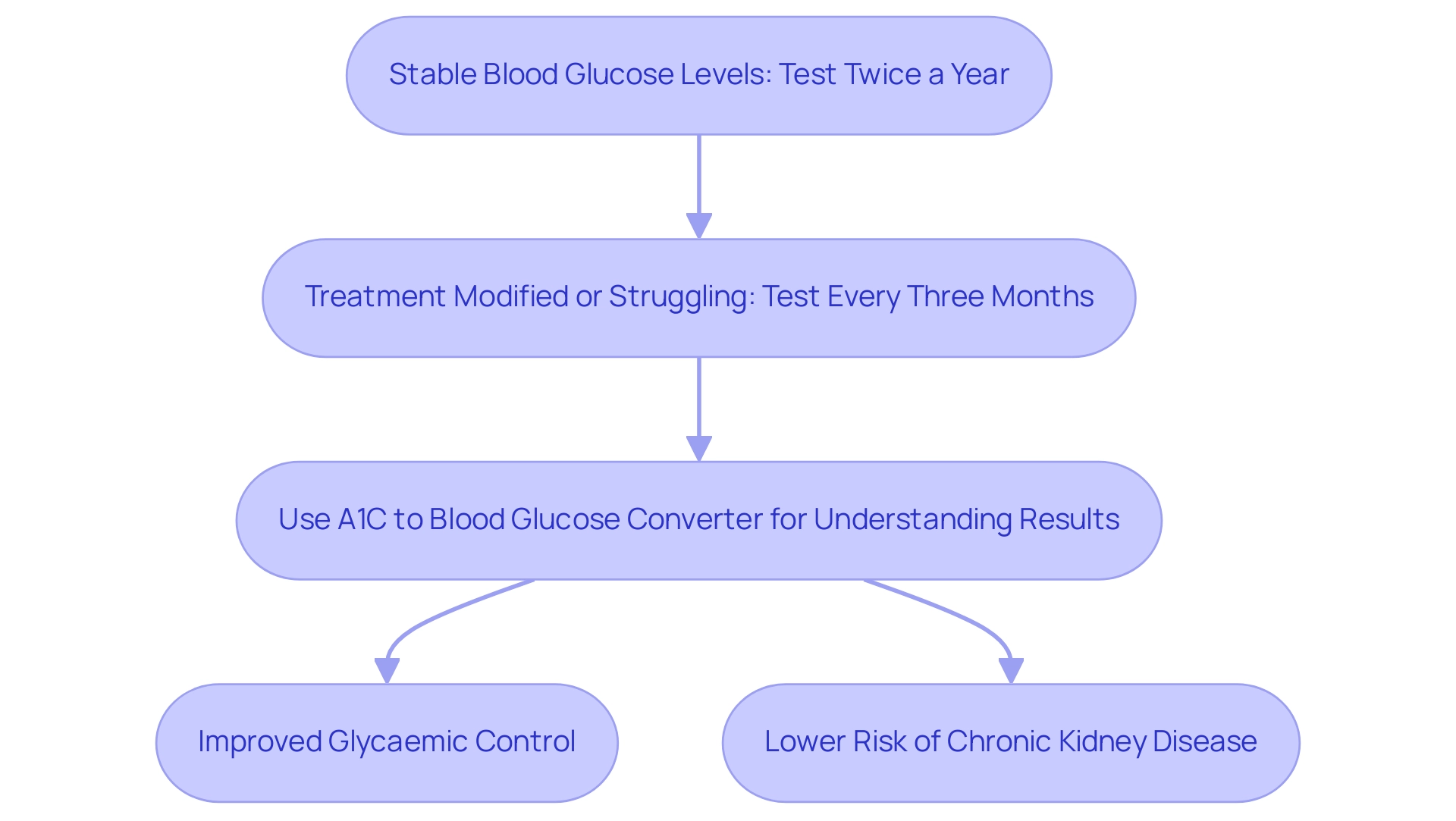
As part of the resources provided by Td Solutions, a new comprehensive center for Type 2 and Type 3 health education, individuals with stable blood glucose levels are encouraged to undergo A1C testing at least twice a year, as recommended by the American Diabetes Association. For those whose treatment has been modified or who are struggling to meet their targets, testing every three months is advised. T2DSolutions seeks to assist recently diagnosed individuals by offering educational materials and resources that enhance their understanding of A1C testing, the a1c to blood glucose converter, and its consequences for health care.
Regular A1C monitoring, when using an a1c to blood glucose converter, plays a crucial role in enabling healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of current treatment strategies, identify emerging complications early, and implement necessary adjustments to optimize patient health outcomes. As Roopa Naik states, 'Regular A1C testing is essential for effective control of blood sugar levels.' Research indicates that patients with better adherence to recommended A1C testing frequencies experience improved glycaemic control and a significantly lower risk of developing chronic kidney disease, with an odds ratio of 0.42 (95% CI 0.18 to 0.99).
Additionally, A1C results can also be reported as estimated average glucose (eAG), which helps patients comprehend their blood glucose measurements with the use of an a1c to blood glucose converter in a more relatable manner. A case study titled 'Impact of HbA1c Testing Frequency on Patient Outcomes' found that better adherence to guideline-recommended HbA1c testing frequency was associated with improved glycaemic control and a lower risk of chronic kidney disease. By staying informed about their A1C levels and utilizing an a1c to blood glucose converter, patients are enabled to participate actively in their health care, promoting a cooperative relationship with their medical teams.
T D Solutions is dedicated to being a valuable resource for patients, providing guidance and support throughout their health journey.
Benefits of Maintaining Optimal A1C Levels
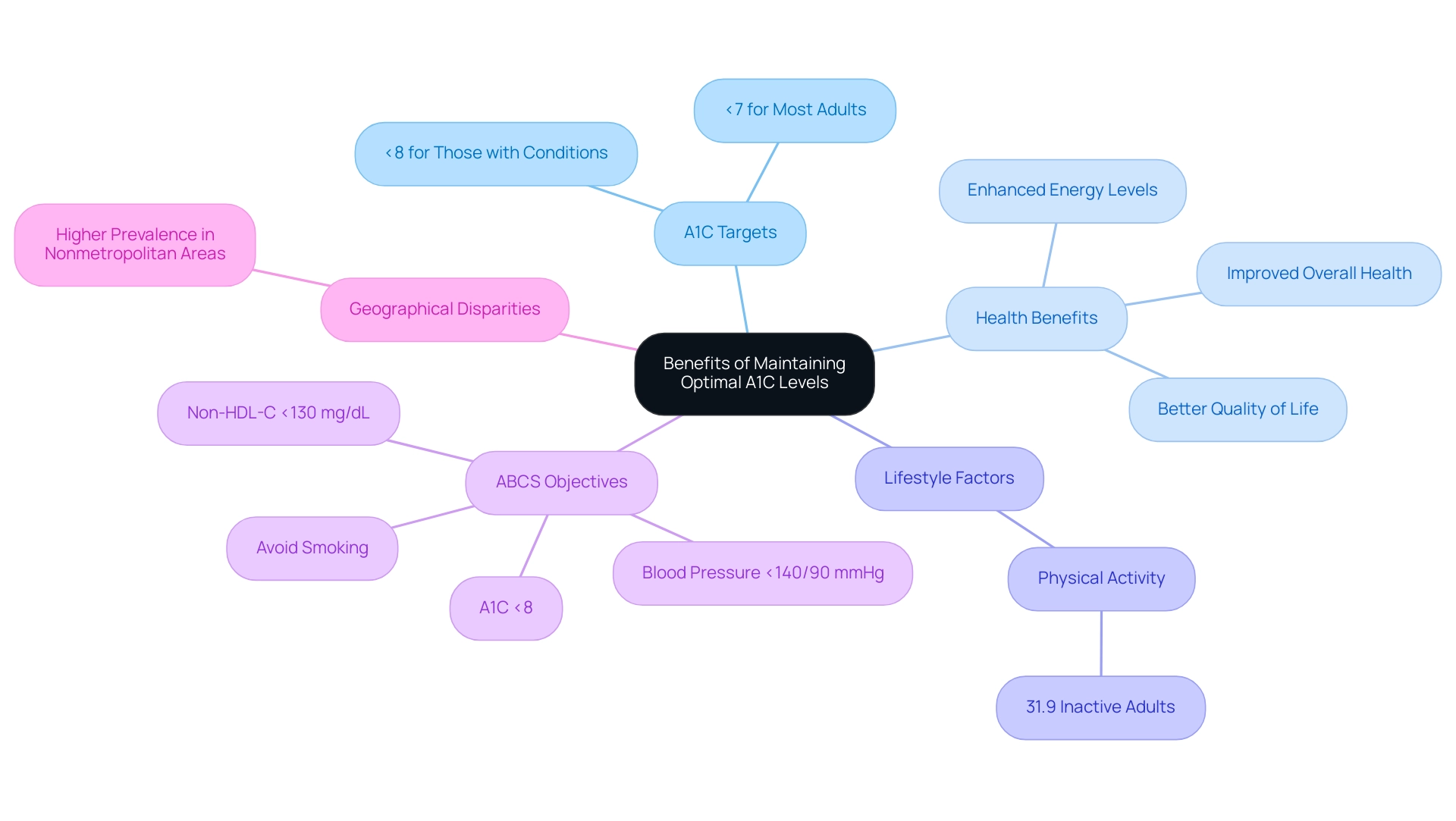
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your new resource hub for diabetes management! In this blog, we emphasize the importance of maintaining optimal A1C values, generally advised to be below 7% for most adults, which can be monitored using an A1C to blood glucose converter, as crucial in mitigating the risk of diabetes-related complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney failure. Evidence indicates that individuals who achieve these A1C targets experience improved overall health, enhanced energy levels, and a better quality of life.
In fact, a lack of physical activity can significantly hinder A1C control, as recent data revealed that 31.9% of U.S. adults diagnosed with the condition were physically inactive, engaging in less than 10 minutes of moderate or vigorous activity per week. As stated by Yu Chen, the corresponding author on research related to blood sugar regulation, 'The American Diabetes Association recommends using an A1C to blood glucose converter to set a goal of <7% for many nonpregnant adults, while a less stringent A1C goal of <8% is suggested for individuals with other medical conditions and limited life expectancy.' Additionally, it is crucial to take into account the ABCS objectives, which involve keeping an A1C <8%, blood pressure <140/90 mmHg, non-HDL-C <130 mg/dL, and refraining from smoking, as these factors collectively enhance better control of the condition, particularly when using an A1C to blood glucose converter.
Significantly, state-level estimates show that only 22.3% to 28.2% of adults achieve these combined goals, emphasizing the need for enhanced strategies. Furthermore, a case study discovered that the occurrence of diagnosed conditions is greater among adults residing in nonmetropolitan regions, indicating geographical disparities in care. T D Solutions is committed to empowering individuals with Type 2 and Type 3 Diabetes by providing comprehensive resources and community support, which includes an A1C to blood glucose converter to enable better A1C management and overall well-being.
Stay tuned for the latest updates and articles that will assist you in managing your condition effectively. By diligently managing A1C levels with an A1C to blood glucose converter and addressing these factors, individuals with diabetes can lead more active lifestyles, thereby minimizing the condition's impact on daily activities and improving their quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is crucial for effective diabetes management, as it provides essential insights into average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. This test not only aids in diagnosing diabetes but also plays a vital role in monitoring treatment effectiveness and facilitating timely interventions. With a significant percentage of individuals remaining undiagnosed, regular A1C testing is imperative for early detection and proactive management.
The relationship between A1C levels and average blood glucose underscores the importance of maintaining optimal A1C targets, generally recommended to be below 7% for most adults. Achieving these levels can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease and kidney failure. Moreover, understanding how to convert A1C to estimated average glucose (eAG) empowers patients to grasp their health metrics more intuitively, fostering better engagement in their diabetes care.
Regular monitoring and adherence to recommended testing frequencies are key components in achieving improved glycemic control and minimizing health risks. By leveraging the resources provided by platforms like T2DSolutions, individuals can better navigate their diabetes management journey, ensuring they are equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary for optimal health outcomes. Ultimately, proactive management of A1C levels is a cornerstone of effective diabetes care, leading to enhanced quality of life and overall well-being.



