Introduction
Understanding A1C levels is essential for anyone navigating the complexities of diabetes management. This crucial blood test provides a window into average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, offering valuable insights that can inform treatment strategies and lifestyle adjustments.
With diabetes affecting a significant portion of the population, the importance of regular monitoring cannot be overstated. A1C results, expressed as a percentage, serve as a key indicator of blood sugar control, guiding patients in their discussions with healthcare providers.
As the landscape of diabetes management continues to evolve, grasping the nuances of A1C testing and its implications for overall health is critical for individuals seeking to optimize their well-being.
Understanding A1C: The Key to Blood Sugar Management
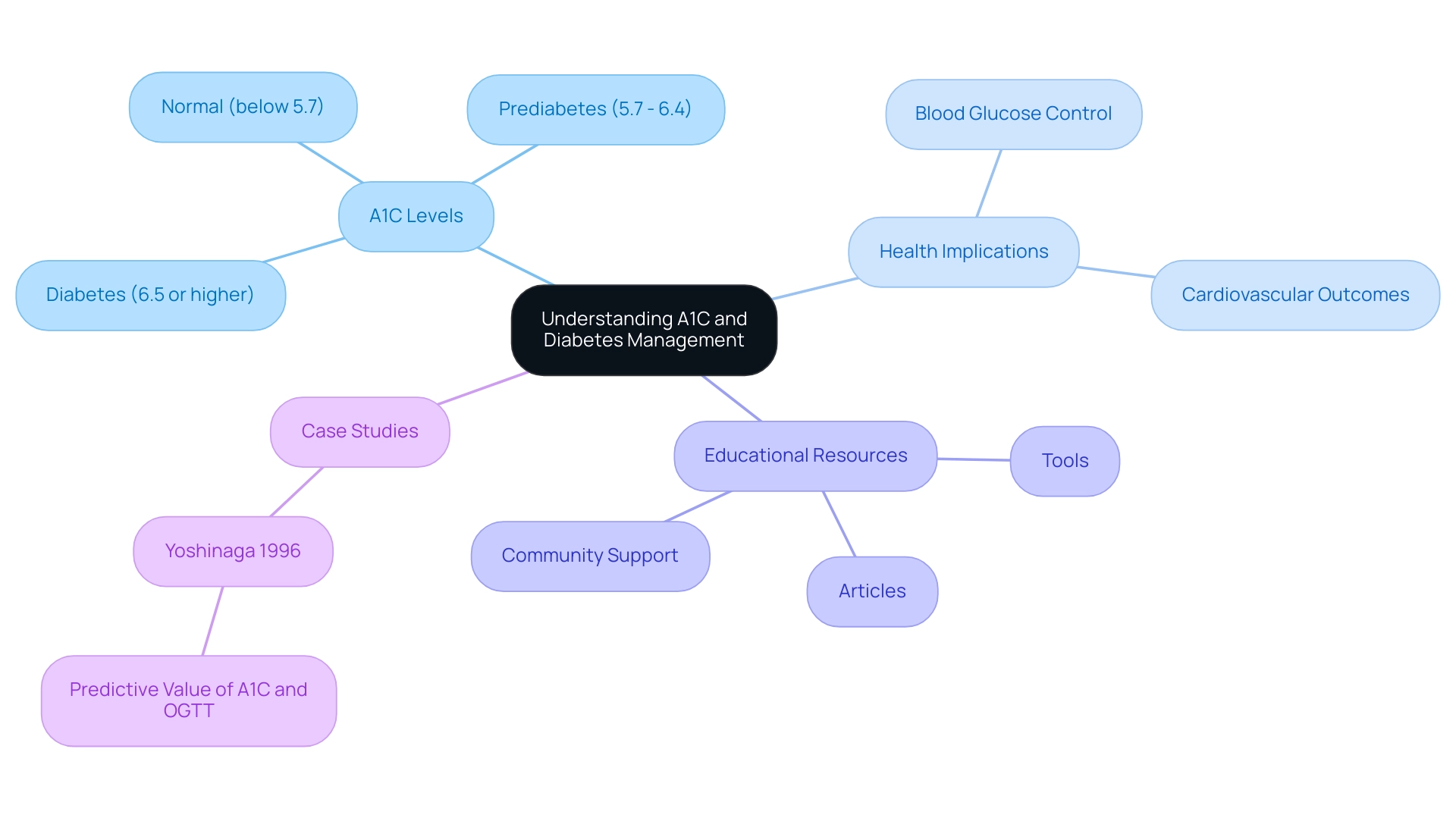
A1C, commonly referred to as glycated hemoglobin, is an essential blood test that evaluates your average blood glucose readings over the past two to three months. This measurement is essential for effective management of the condition, as it provides insight into how well blood sugar levels have been controlled during that timeframe. According to recent statistics, the prevalence of this illness stands at 14.3% in the population, underscoring the importance of monitoring this condition.
A1C results are expressed as percentages: a lower percentage indicates better blood glucose control. For individuals without the condition, an A1C level below 5.7% is regarded as normal. A range between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of the condition.
Recognizing your A1C number is crucial for utilizing an A1C to blood sugar converter, which can guide discussions with your healthcare provider regarding treatment strategies and lifestyle modifications necessary for optimal diabetes management. Recent studies have shown that maintaining target A1C values can significantly influence cardiovascular outcomes, emphasizing the metric's importance in overall health. T2DSolutions will provide a variety of educational resources to help you understand your A1C levels better and utilize the A1C to blood sugar converter to manage them effectively.
This includes:
- Tools
- Articles
- Community support
to ensure you have the knowledge needed for proactive management of the condition. Additionally, a case study titled 'Yoshinaga 1996' examined the predictive value of A1C and OGTT for the progression of the condition, demonstrating that the combination of these tests provides a more precise prediction of the disease's advancement.
How to Use A1C to Blood Sugar Conversion Tools
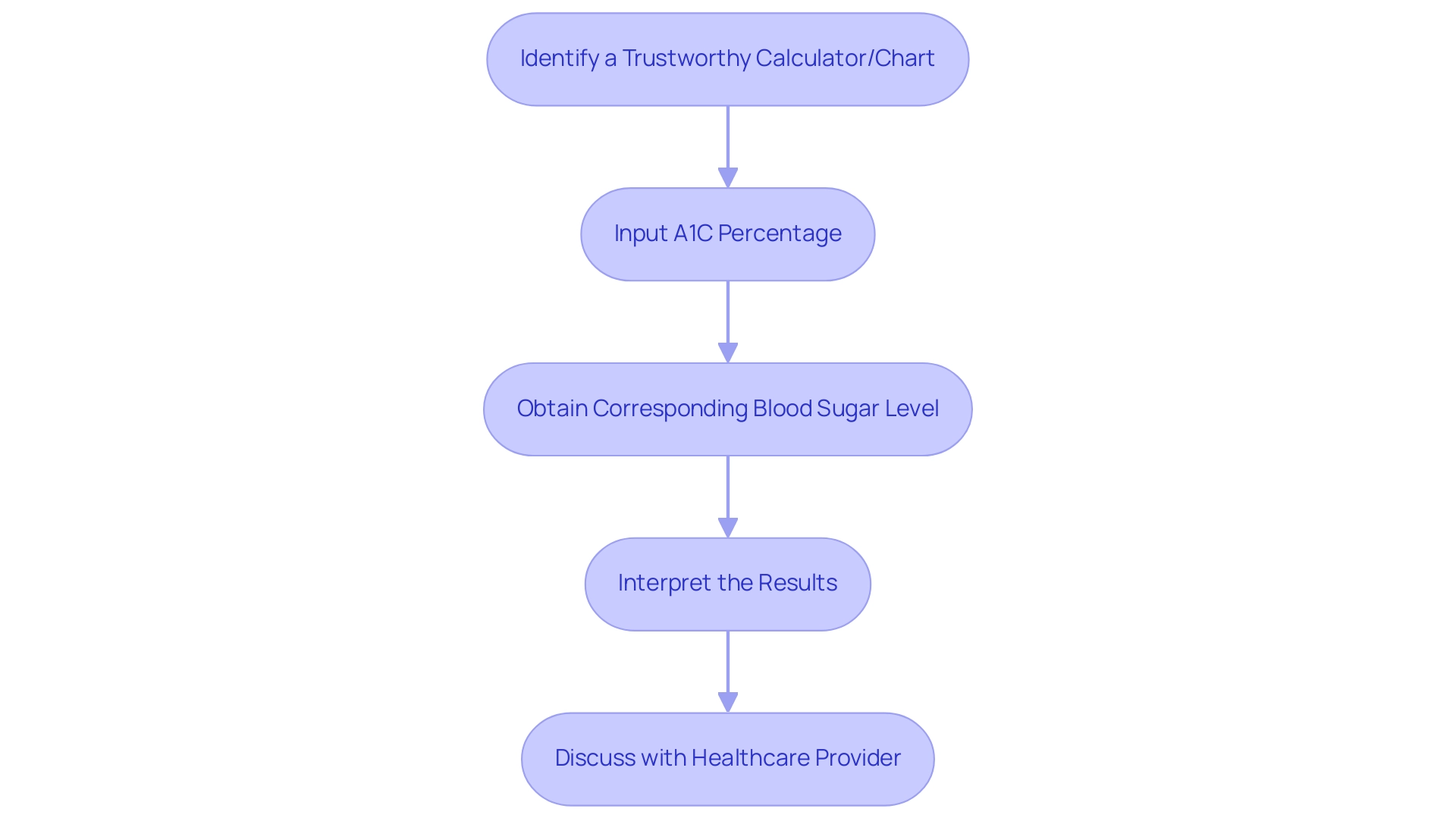
As T2DSolutions launches as your comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 health education, it is essential to effectively utilize a1c to blood sugar converter. Begin by identifying a trustworthy online calculator or an accurate conversion chart. The American Diabetes Association supports the use of A1C for diabetes diagnosis, emphasizing its convenience in reflecting chronic blood sugar values over traditional testing.
Input your A1C percentage into the designated field; for example, an A1C reading of 7% corresponds with an average blood sugar concentration of roughly 154 mg/dL. According to the American Diabetes Association, an A1C of 7 percent for nonpregnant adults is a recommended target, emphasizing the importance of personalized glycemic goals. Many of these conversion tools will act as an a1c to blood sugar converter, presenting a range of corresponding blood sugar readings based on your A1C result and providing valuable context for your measurements.
Additionally, the A1C-Derived Average Glucose (ADAG) Study established a clear relationship between A1C and average glucose levels, aiding in managing the condition and minimizing confusion for patients and healthcare providers. It is crucial to understand that these tools provide estimates and should be used as guidelines rather than definitive measures. Consistently using these conversion tools can help in monitoring your blood sugar trends over time, which is essential for encouraging informed discussions with your healthcare provider about your management plan.
e2 Solutions will also be providing a variety of educational resources, including articles and tools to assist your health management journey, so be sure to subscribe for updates on new content as it becomes available.
The Relationship Between A1C Levels and Average Blood Glucose
T2DSolutions is excited to announce our upcoming launch, designed as a comprehensive resource hub for individuals managing Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes. This new site is just getting started, and we invite you to subscribe to stay updated and receive emails when new content is published. As part of this initiative, we will provide essential information on the relationship between A1C values and average blood sugar, which can be understood through an a1c to blood sugar converter that quantifies the percentage of glycated hemoglobin.
For example, an A1C measurement of 6% usually corresponds to an average blood sugar concentration of roughly 126 mg/dL. Comprehending this relationship is essential for newly diagnosed patients, as it enables them to interpret their A1C results with the help of an a1c to blood sugar converter in the context of daily blood sugar management. This understanding can assist in keeping blood sugar rates within advised targets, thus reducing the risk of issues associated with poorly managed blood sugar conditions.
Recent evaluations have also underscored the importance of tracking A1C levels across various demographics, including children with type 1 conditions. Moreover, data indicate that the slope of the HbA1c versus non fasting sugar measurements is 33, reinforcing the link between these two metrics. Nathan, a specialist in blood sugar research, observes that their regression equation (average sugar CGM = 31.5 × HbA1c - 68.6) slightly varies from those obtained from glucometers, possibly indicating the incorporation of lower overnight sugar readings in CGM data.
Additionally, a comprehensive case study titled 'Hemoglobin A1c Versus Fasting Venous Plasma Glucose' analyzed 33,563 samples and found that fasting samples showed lower average glucose levels compared to nonfasting ones. This insight highlights the importance of utilizing accurate measurement methods and understanding their implications for effective management of the condition. Stay tuned for more valuable resources and support from T2 Solutions as we strive to empower individuals in their health journey.

The Importance of Regular A1C Testing
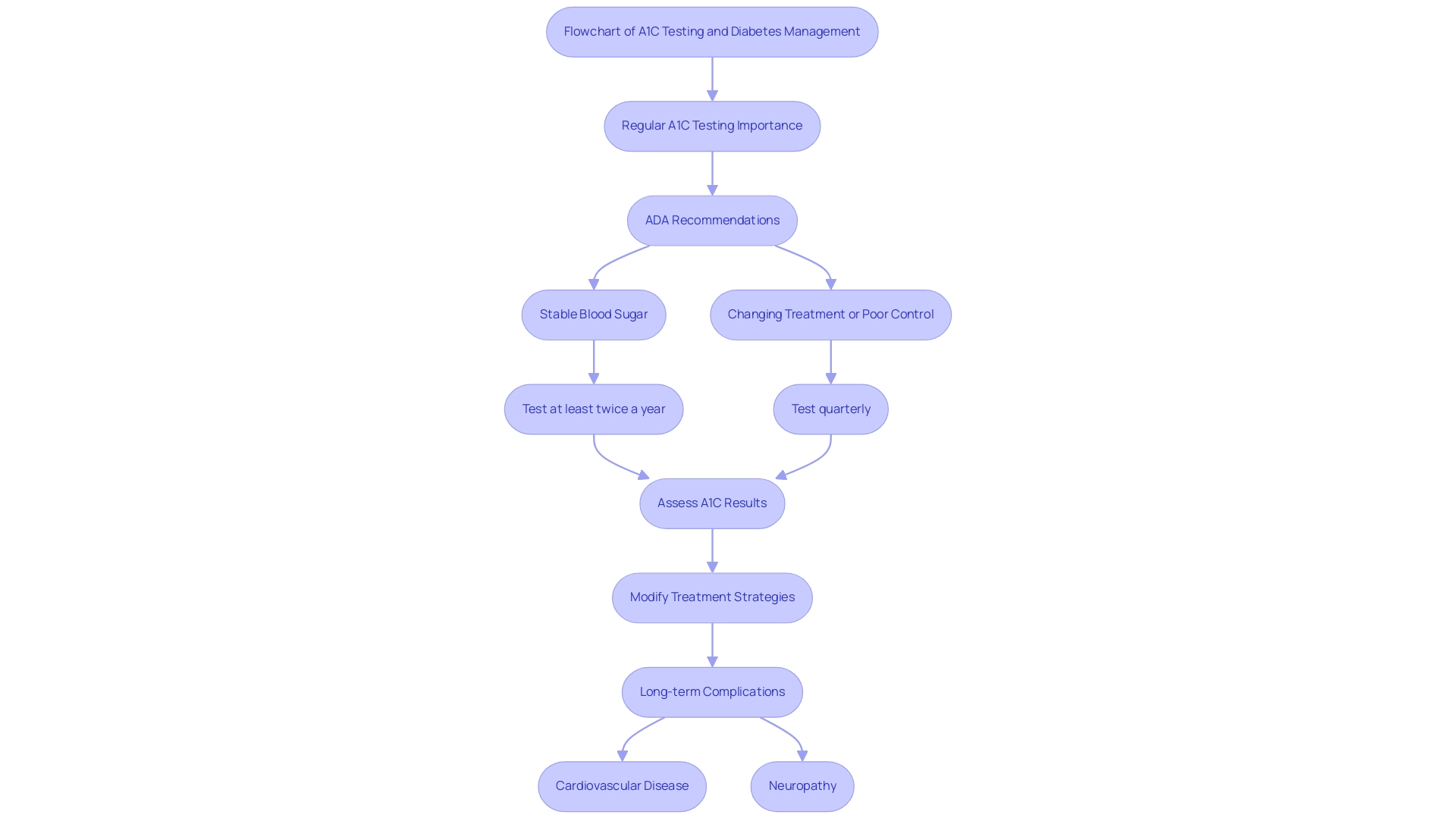
At T2DSolutions, we acknowledge that regular A1C testing is crucial for effective diabetes management, as it serves as a1c to blood sugar converter, providing a comprehensive perspective on blood sugar control over time. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends that individuals with stable blood sugar readings undergo A1C testing at least twice a year, while those whose treatment has changed or who are struggling to meet their blood sugar goals should test quarterly. These assessments are crucial for identifying trends in blood glucose levels, enabling timely modifications to treatment strategies.
Moreover, consistent A1C monitoring plays a significant role in preventing long-term complications associated with blood sugar disorders, including cardiovascular disease and neuropathy. Notably, in 2015, the ADA revised its preprandial glycemic target from 70–130 mg/dL to 80–130 mg/dL to limit overtreatment, reflecting an evolving understanding of diabetes management. According to findings from the A1C-Derived Average Sugar Study Group, which concentrated on using an a1c to blood sugar converter to estimate average sugar values from A1C assay results, the correlation between A1C and average sugar amounts is remarkably strong at 0.92, underscoring the test's reliability.
This case study offers a structure for clinicians to better interpret A1C results with the help of an a1c to blood sugar converter in the context of average glucose readings. As of 2024, ongoing discussions among specialists in blood sugar regulation highlight the necessity of regular A1C testing, reinforcing its status as a cornerstone in management protocols. At T2DSolutions, we are committed to supporting newly diagnosed patients through resources such as educational articles, community forums, and tools for tracking A1C levels.
Our platform improves comprehension and management of the condition, ultimately aiding in reducing the escalating medical expenses linked to it, which rose from $10,179 to $12,022 per person from 2012 to 2022.
Benefits of Lowering Your A1C Levels
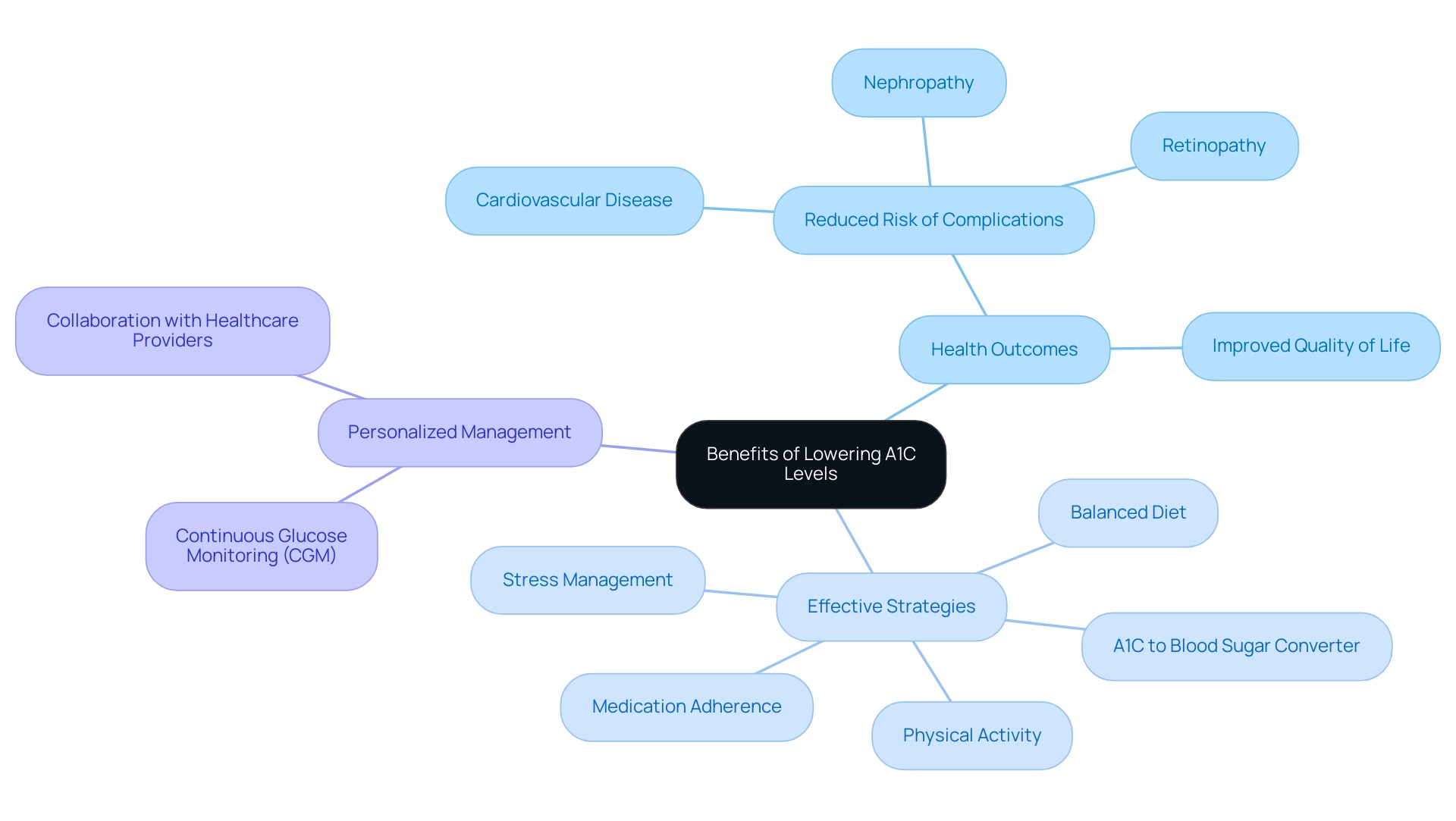
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support. As a new site, we are excited to offer you valuable insights and tools to help you manage your condition effectively. Using an A1C to blood sugar converter is essential for reducing A1C values and decreasing the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
For most adults with diabetes, maintaining an A1C below 7% is advisable, and an A1C to blood sugar converter can help individuals achieve this target, as studies indicate it correlates with improved health outcomes. However, it is important to note that glycemic targets for older patients can vary significantly, with recommendations ranging from A1C <6.5% to <8.0%, as highlighted in recent case studies on glycemic control recommendations for older diabetic patients. Specifically, a recent analysis found that for individuals aged 70 to 79, the risk of complications or mortality at an A1C measurement below 6.0 is relatively low, at 0.98 (0.91–1.06).
Effective strategies to achieve reduced A1C values include:
- Utilizing an A1C to blood sugar converter
- Adopting a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Managing stress effectively
- Adhering to prescribed medication regimens
Collaborating with healthcare providers can further personalize management plans, enhancing the likelihood of achieving individual targets. Adam Brown observes that the inclusion of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in clinical guidelines by the European Medicines Agency highlights its significance for developing medications for this condition.
This tool can provide real-time feedback and assist patients in making informed decisions about their daily management. Moreover, case studies reveal that patients who implement these strategies often experience significant reductions in A1C levels, which can be monitored with an A1C to blood sugar converter, leading to improved health and quality of life. In light of recent findings showing that the total indirect costs associated with diagnosed conditions rose from $89 billion to $106 billion from 2012 to 2022, it becomes even more critical to adopt effective management strategies to mitigate these costs and improve both individual and societal health.
Subscribe now to stay updated on our latest content and resources as we continue to grow and support your diabetes management journey!
Conclusion
Understanding A1C levels is paramount for effective diabetes management, offering insights that directly influence treatment strategies and lifestyle choices. Regular A1C testing not only helps in tracking average blood glucose levels over time but also plays a vital role in preventing complications associated with poorly managed diabetes. The correlation between A1C percentages and average blood glucose levels serves as a critical tool in guiding both patients and healthcare providers in their diabetes management discussions.
The importance of maintaining A1C levels below recommended thresholds cannot be overstated. Achieving and sustaining target A1C levels significantly reduces the risk of serious complications, such as cardiovascular disease and neuropathy. Effective management strategies, including:
- Dietary adjustments
- Regular physical activity
- Adherence to prescribed medications
are essential in this pursuit. The recent emphasis on personalized care, particularly for older patients, highlights the need for individualized management plans that consider unique health profiles and goals.
As diabetes continues to affect a large segment of the population, the role of resources like T2DSolutions becomes increasingly important. By providing educational tools, community support, and practical resources, individuals can better understand and manage their A1C levels. Staying informed and proactive in diabetes management not only enhances individual health outcomes but also contributes to reducing the broader economic impact associated with diabetes care. Embracing these practices is a crucial step towards a healthier future for those living with diabetes.



