Introduction
Understanding the A1C test is crucial for effective diabetes management, as it provides insights into average blood sugar levels over a two to three-month period. This important metric serves as a more comprehensive measure than daily blood sugar readings, enabling healthcare providers to assess treatment efficacy and make necessary adjustments.
With a significant portion of the population facing prediabetes and diabetes, the A1C test's role in early diagnosis and intervention cannot be overstated. As organizations like T2DSolutions strive to educate and empower individuals managing these conditions, it becomes essential to grasp the significance of A1C testing and its implications for long-term health outcomes.
This article delves into the functionality of the A1C test, effective strategies for managing levels, and the importance of self-monitoring in the journey towards optimal diabetes care.
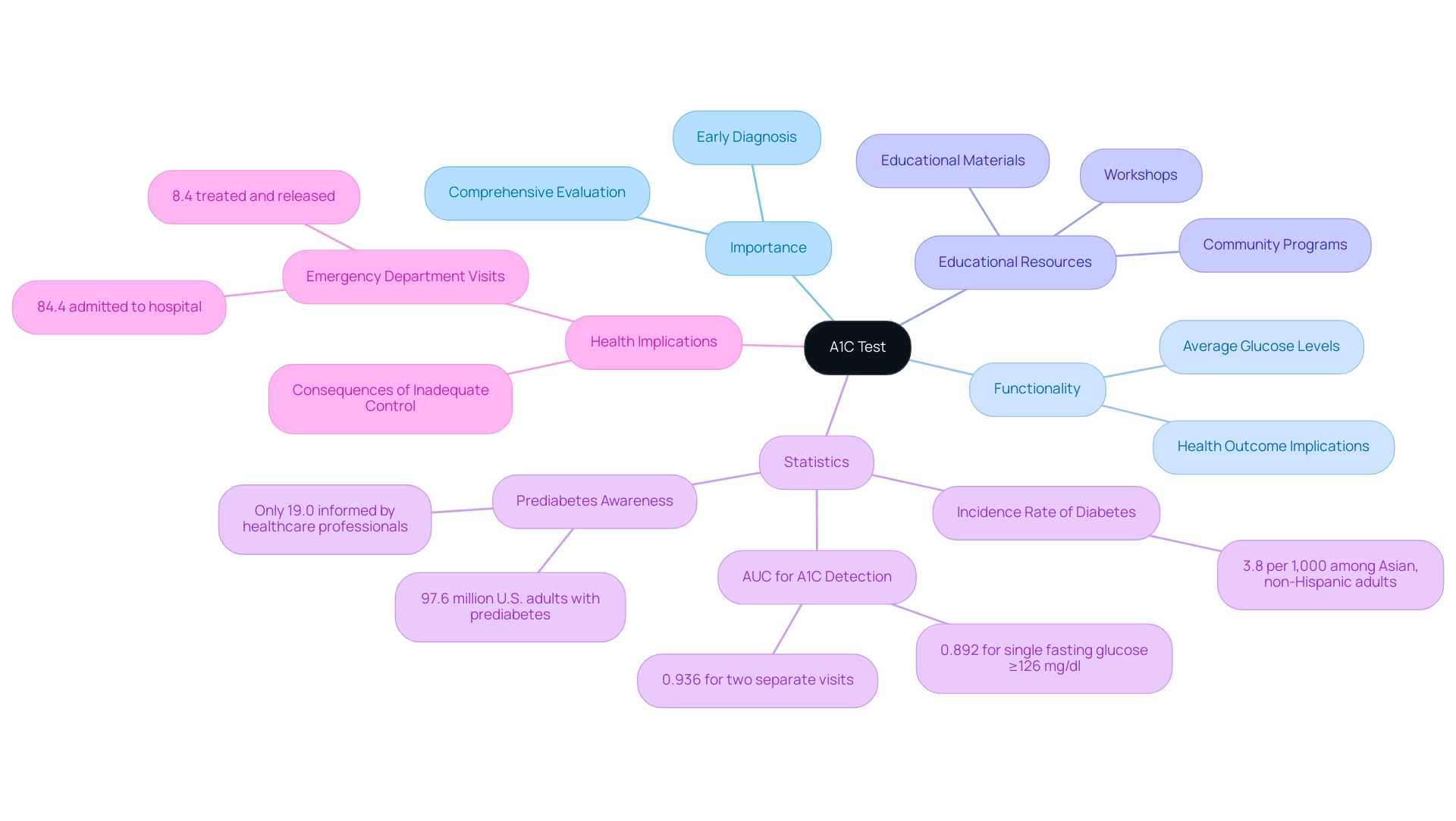
Understanding the A1C Test: Importance and Functionality
The A1C test, often known as hemoglobin A1C or glycosylated hemoglobin, acts as an essential instrument in the care of individuals with blood sugar issues by assessing the average glucose levels over the past two to three months. This metric is expressed as a percentage; higher percentages indicate poorer blood sugar control, which can have significant implications for health outcomes. For individuals with high blood sugar, a thorough understanding of the A1C test is crucial, as it provides a more comprehensive evaluation of glucose control compared to the values in the a1c to blood sugar table.
Regular A1C testing is essential for healthcare providers to evaluate treatment efficacy and make informed adjustments to improve patient outcomes. T2DSolutions is dedicated to enhancing management of the condition through education and community support, offering resources such as:
- Educational materials
- Workshops
- Community programs
These resources assist newly diagnosed patients in understanding the significance of A1C testing and how to interpret their results. Notably, the AUC for A1C detection of the condition was 0.892 for a single fasting glucose ≥126 mg/dl and 0.936 for two separate visits in the ARIC study, underscoring the test's effectiveness.
Among adult populations, the incidence rate of diagnosed conditions related to blood sugar stands at 3.8 per 1,000 among Asian, non-Hispanic adults, highlighting the critical need for effective monitoring strategies. According to Dr. Frederick L Brancati, "Its performance would be best when judged against stronger, most clinically relevant gold standards," reinforcing the A1C test's vital role in managing blood sugar conditions. Furthermore, a concerning statistic reveals that in 2021, an estimated 97.6 million U.S. adults aged 18 years or older had prediabetes, yet only 19.0% of these individuals reported being informed by healthcare professionals about their condition.
This gap in awareness emphasizes the importance of A1C testing for early diagnosis and intervention, which is illustrated in the a1c to blood sugar table featured in T2DSolutions’ educational resources. Furthermore, among emergency department visits related to hyperglycemic crises in 2020, 8.4% were treated and released, while 84.4% were admitted to the hospital, emphasizing the serious consequences of inadequate control and the importance of A1C testing in preventing such situations, along with the supportive network provided by T2DSolutions. T2DSolutions intends to further enhance its offerings with new features and content aimed at improving education and oversight of blood sugar conditions.
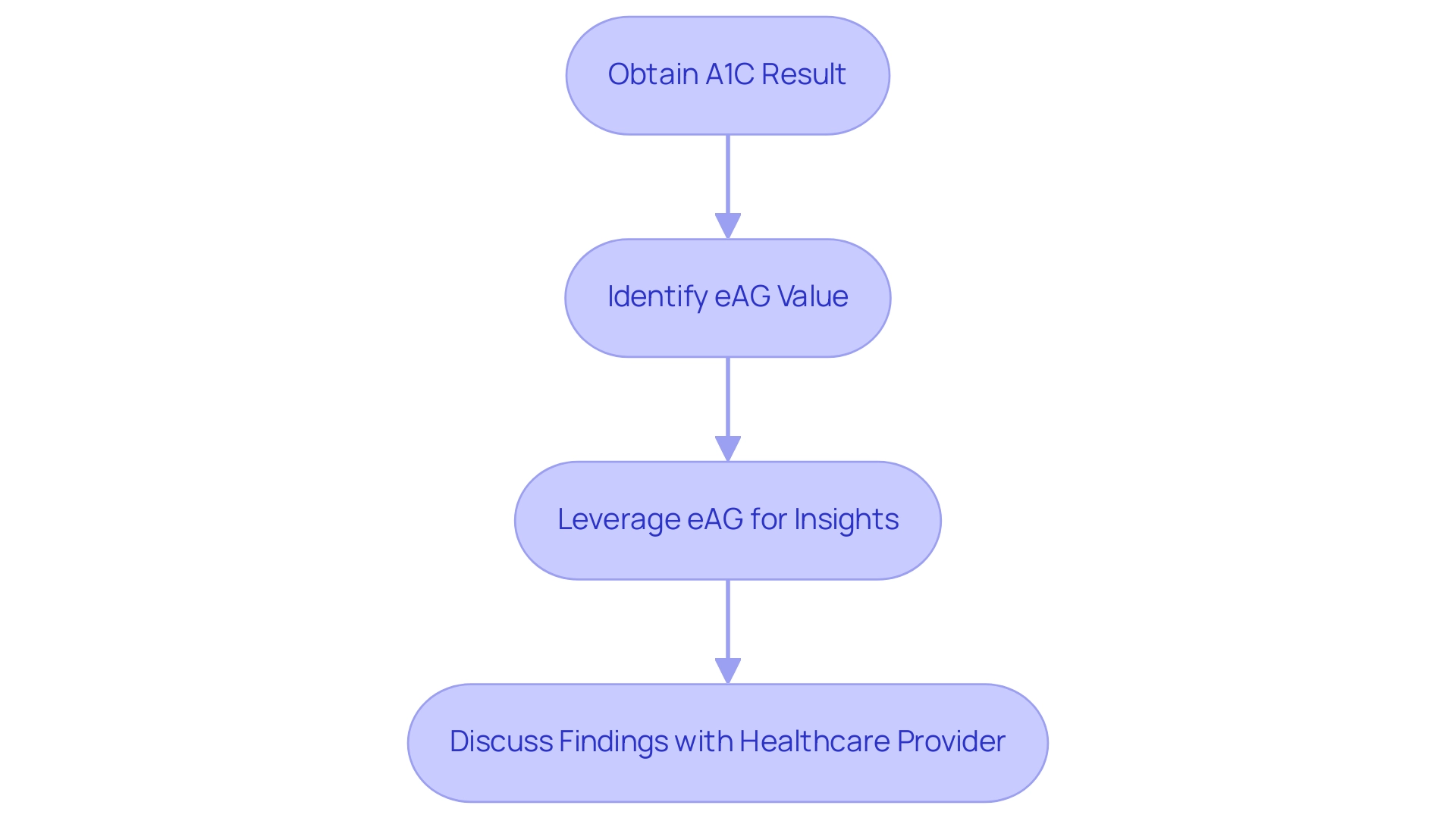
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the A1C to Blood Sugar Table
To effectively utilize the a1c to blood sugar table, adhere to the following steps:
- Obtain your most recent A1C result from your healthcare provider, which will be expressed as a percentage.
- Identify the corresponding estimated average glucose (eAG) value in the a1c to blood sugar table. For instance, an A1C of 7% equates to an eAG of approximately 154 mg/dL.
- Leverage the eAG value to gain insight into your average blood glucose levels over the preceding months. This understanding can aid in identifying patterns that are essential for informed health care choices.
- Engage in a discussion with your healthcare provider regarding your findings. This dialogue is crucial for making any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan, ensuring that your approach aligns with your current health status.
As T2DSolutions launches as your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar control, expert opinions highlight the importance of interpreting A1C results.
Dr. Baum, an Endocrinology Fellow, highlights the importance of comprehending these figures, stating that 'A1C readings offer crucial insights into overall health control.' Furthermore, research shows a significant link between A1C and other diagnostic standards, with randomized controlled trials affirming that keeping A1C <7% (53 mmol/mol) during continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) studies is essential for effective metabolic health. A recent investigation into prediabetic individuals revealed that despite higher glucose levels, A1C alone may not be sufficient to diagnose prediabetes effectively.
This is illustrated in the case study titled 'Associations Between Prediabetes and Categorical Variables,' which highlights the limitations of A1C compared to other diagnostic methods like the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT). Stay tuned for more resources and support from T2DSolutions, including educational articles, webinars, and community forums, to aid in your health management journey. Don’t forget to subscribe for updates on our latest content and resources!
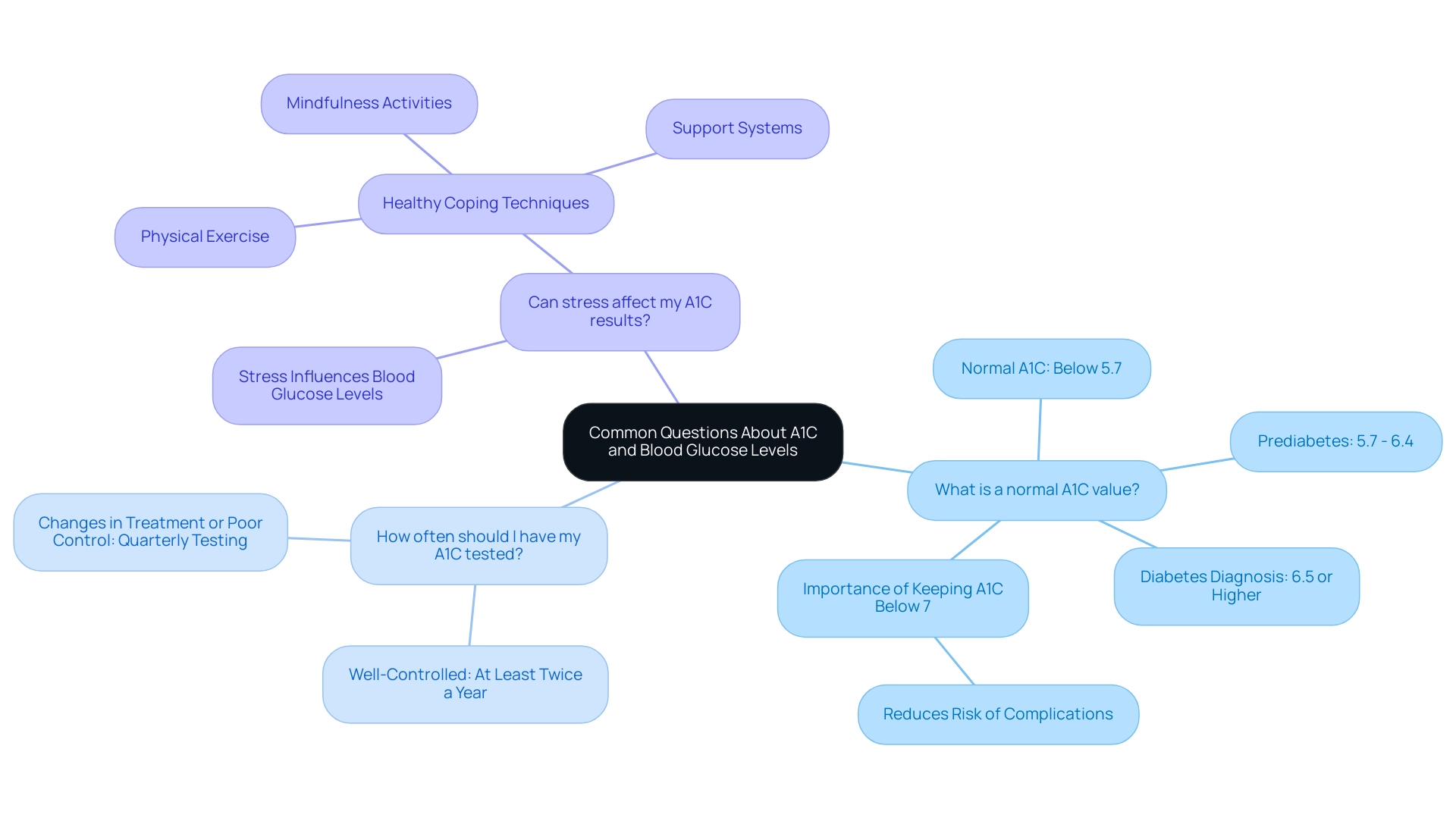
Common Questions About A1C and Blood Glucose Levels
Welcome to T2DSolutions, a new resource hub dedicated to supporting individuals managing Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes. As you navigate your journey, understanding key health metrics such as the A1C to blood sugar table is essential.
- What is a normal A1C value?
A normal A1C measurement is generally regarded as being below 5.7%. A range between 5.7% and 6.4% suggests prediabetes, indicating an increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes, while according to the A1C to blood sugar table, a measurement of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of diabetes.
Research has indicated that keeping A1C measurements below 7 percent, according to the A1C to blood sugar table, can greatly lower the risk of diabetes-related complications, emphasizing the significance of regular monitoring. As Heather Grey stated, 'Keeping A1C levels in check is essential for long-term health and preventing complications.'
- How often should I have my A1C tested?
The frequency of A1C testing is essential for effective control of blood sugar levels. For individuals whose condition is well-controlled, it is generally recommended to have the A1C test performed at least twice a year.
However, if there have been changes in treatment or if blood sugar levels are not well-regulated, testing should occur quarterly to ensure optimal oversight and timely adjustments to care plans.
Can stress affect my A1C results?
Yes, stress can significantly influence blood glucose measurements, leading to fluctuations that may affect A1C test results.
Stress control is consequently a crucial part of blood sugar care. Adopting healthy coping techniques, like consistent physical exercise, mindfulness activities, and support systems, can assist in stabilizing blood sugar and improving overall health control. Stay tuned for more valuable information and resources as we work to empower your health management journey.
Don't forget to subscribe to receive updates and be the first to know when new content is published! This is brought to you by the T2D Solutions Content Team, dedicated to providing you with the best support and resources.
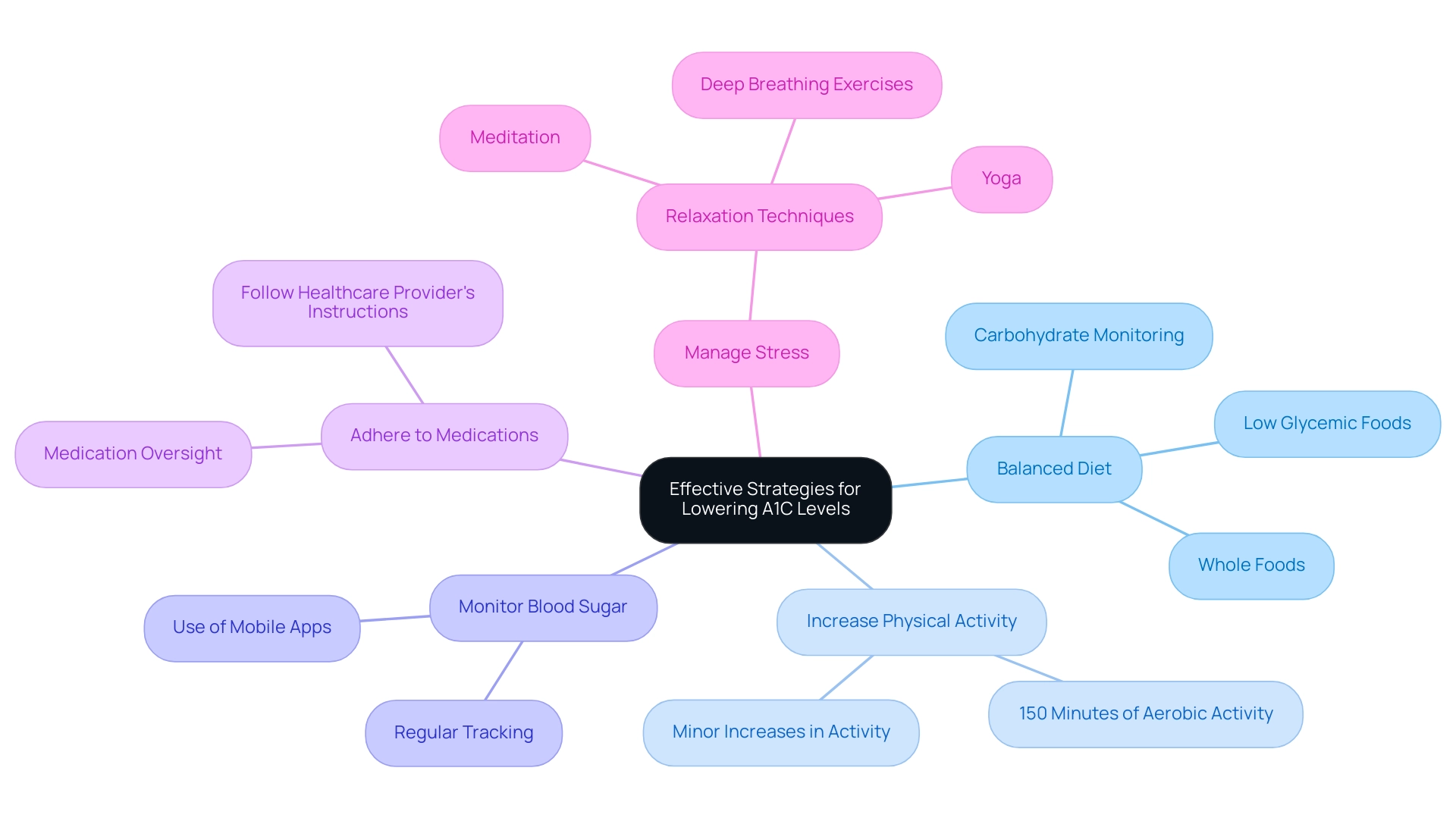
Effective Strategies for Lowering Your A1C Levels
To effectively lower your A1C levels, implementing the following strategies is crucial, especially with the support of T2DSolutions, your new resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support:
-
Adopt a balanced diet: Emphasize whole foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. A recent study noted that participants consuming an average of 0.38 servings of sugar-sweetened beverages daily had a notable impact on their HbA1c concentrations. Therefore, monitoring carbohydrate intake and prioritizing low glycemic index foods can be particularly beneficial. A case study concluded that a low-carbohydrate diet intervention resulted in larger reductions in HbA1c compared to a usual diet among adults with elevated untreated HbA concentrations, suggesting this dietary approach may be beneficial for those at high risk of type 2 diabetes.
-
Increase physical activity: Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week. Regular exercise not only helps in reducing blood sugar amounts but also has a positive effect that can be reflected in the a1c to blood sugar table, improving insulin sensitivity. According to fitness specialists, even minor increases in physical activity can result in substantial enhancements in overall health and A1C values.
-
Monitor blood sugar regularly: Consistently tracking your blood sugar readings enables you to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to your diet and medication regimen. This proactive approach is essential for effective diabetes control, and T2DSolutions will provide tools such as mobile apps, tracking logs, and an a1c to blood sugar table to assist you with this.
-
Adhere to prescribed medications: Following your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding medications is essential for maintaining optimal blood glucose. Proper medication oversight can significantly affect your measurements in the A1C to blood sugar table over time.
-
Manage stress: Participating in relaxation methods like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises is crucial for stress control, which can directly affect blood glucose values. As noted by Dr. Kirsten S. Dorans, "We thank all study participants and research study staff for contributing to the study," underscoring the importance of comprehensive support during dietary interventions.
Integrating these evidence-based approaches, along with educational resources, community support groups, and testimonials from successful users provided by T2DSolutions, can lead to significant improvements in the A1C to blood sugar table and overall health oversight.
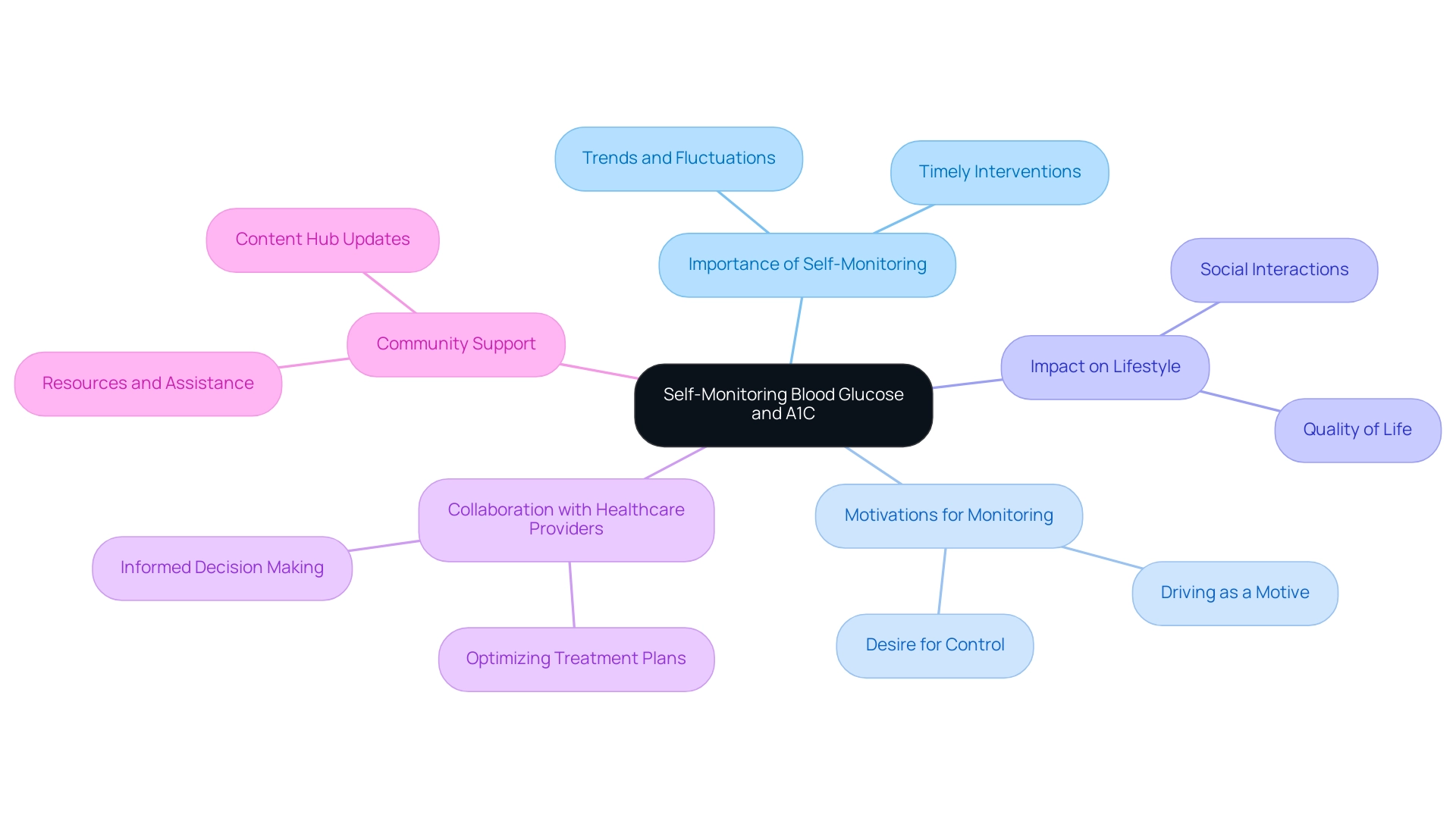
The Importance of Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose and A1C
Self-monitoring blood glucose and referring to the A1C to blood sugar table is essential for effective management of the condition, and T2DSolutions aims to support this practice by providing valuable resources and community assistance tailored for those newly diagnosed with the illness. This practice enables individuals to detect trends and fluctuations in their blood sugar readings, facilitating timely interventions. Notably, a recent study found that seven of the ten participants with high blood sugar indicated that driving was a strong motive for self-monitoring blood glucose, reinforcing the idea that practical considerations can enhance adherence to monitoring routines.
Regular self-monitoring empowers individuals to understand how their lifestyle choices, medication regimens, and stress levels affect their condition, as reflected in the A1C to blood sugar table. By remaining informed, individuals can engage in a more collaborative relationship with their healthcare providers, ultimately optimizing treatment plans and improving health outcomes. As one speaker noted, 'I like the connection.
One less step you have to do,' highlighting how simplifying the monitoring process can encourage adherence. The case study titled 'Desire for Control' underscores this perspective, revealing that participants aimed to manage their condition without allowing it to dominate their daily lives. They recognized that while their choices might lead to suboptimal self-management at times, prioritizing quality of life and social interactions remained paramount.
This balance illustrates the complex dynamics of self-management, emphasizing the importance of self-monitoring in achieving a sense of normalcy. T2D Solutions is here to facilitate this journey by providing essential knowledge and support, including the use of an A1C to blood sugar table to enhance the effectiveness of self-monitoring strategies. Additionally, the T2DSolutions Content Team is dedicated to creating a comprehensive resource hub, and we invite you to subscribe for updates to stay informed about new content and features that will benefit your diabetes management journey.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is vital for anyone managing diabetes, as it offers a deeper insight into average blood sugar levels over a two to three-month period. Regular testing not only helps in assessing the effectiveness of treatment plans but also serves as an early warning system for those at risk of developing diabetes. With alarming statistics highlighting the prevalence of prediabetes and undiagnosed diabetes, the importance of A1C testing becomes even more pronounced.
Effective diabetes management requires a multifaceted approach that includes:
- Adopting a balanced diet
- Increasing physical activity
- Practicing self-monitoring of blood glucose levels
These strategies, supported by educational resources from organizations like T2DSolutions, empower individuals to take control of their health. The ability to interpret A1C results and engage in meaningful discussions with healthcare providers is crucial for making informed decisions about treatment adjustments.
In conclusion, prioritizing A1C testing and understanding its implications can significantly enhance diabetes care and improve long-term health outcomes. By combining knowledge with proactive management strategies, individuals can navigate their diabetes journey with confidence and clarity, ultimately leading to better health and quality of life. Embracing these practices today can pave the way for a healthier tomorrow.



