Introduction
The A1C test plays a crucial role in diabetes management by offering insights into average blood glucose levels over a period of two to three months. For individuals living with diabetes, understanding A1C results is essential, as elevated levels can signal inadequate blood sugar control and a heightened risk of serious health complications.
This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, how to interpret its results, and practical steps for monitoring and managing A1C levels effectively. By exploring the relationship between A1C and average blood glucose, as well as addressing common questions surrounding testing and management, readers will gain valuable knowledge to enhance their diabetes care strategies.
With a focus on empowering individuals through education and resources, this comprehensive guide aims to support better health outcomes for those navigating the complexities of diabetes management.
Understanding the A1C Test: Importance for Diabetics
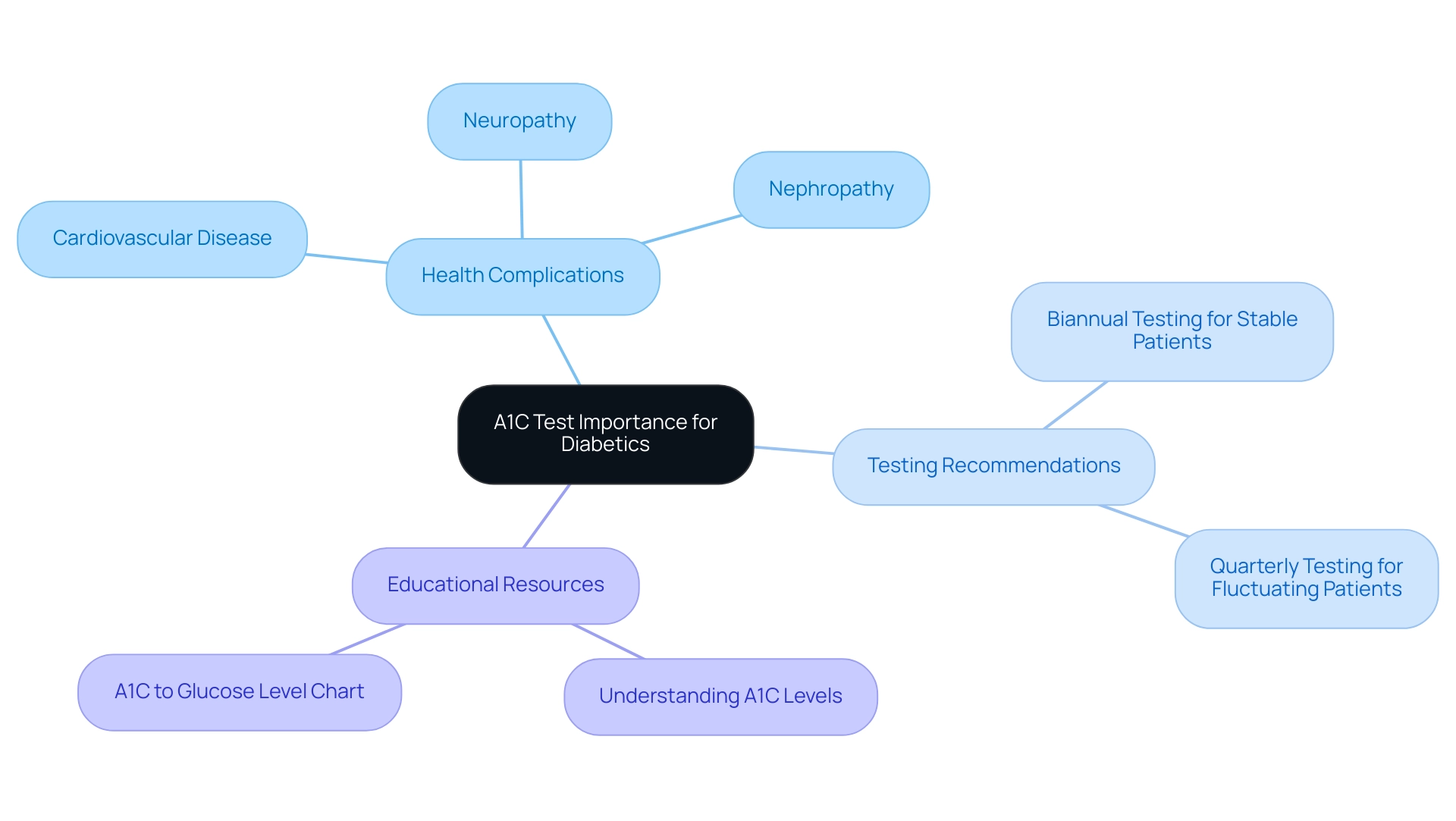
The A1C test is an essential diagnostic instrument that measures the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has been glycosylated, indicating average blood sugar concentrations over a period of two to three months. For individuals with this condition, this measurement is essential, as a higher A1C percentage signifies inadequate blood sugar control, which can precipitate serious health complications, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Neuropathy
- Nephropathy
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines, it is recommended that A1C measurements be assessed biannually for stable patients and at least four times annually for those experiencing glucose fluctuations.
This regular monitoring allows patients and healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of blood sugar management strategies and to make necessary adjustments. As healthcare expert Jaakko Tuomilehto highlights, while understanding A1C levels is crucial for effective management of blood sugar conditions, it is important to consider both the advantages and limitations of this test. For example, the Hemoglobin Glycation Index (HGI) case study shows that A1C indicates average sugar exposure but may not sufficiently represent sugar variations, which are essential for comprehending risk.
Recent studies reinforce that the A1C test remains a key indicator of long-term sugar control, emphasizing its importance in preventing diabetes-related complications. At T2DSolutions, we aim to provide educational resources that help patients understand their A1C results using the A1C to glucose level chart and how to use this information to improve their diabetes management and overall health.
How to Read and Use the A1C to Glucose Conversion Chart
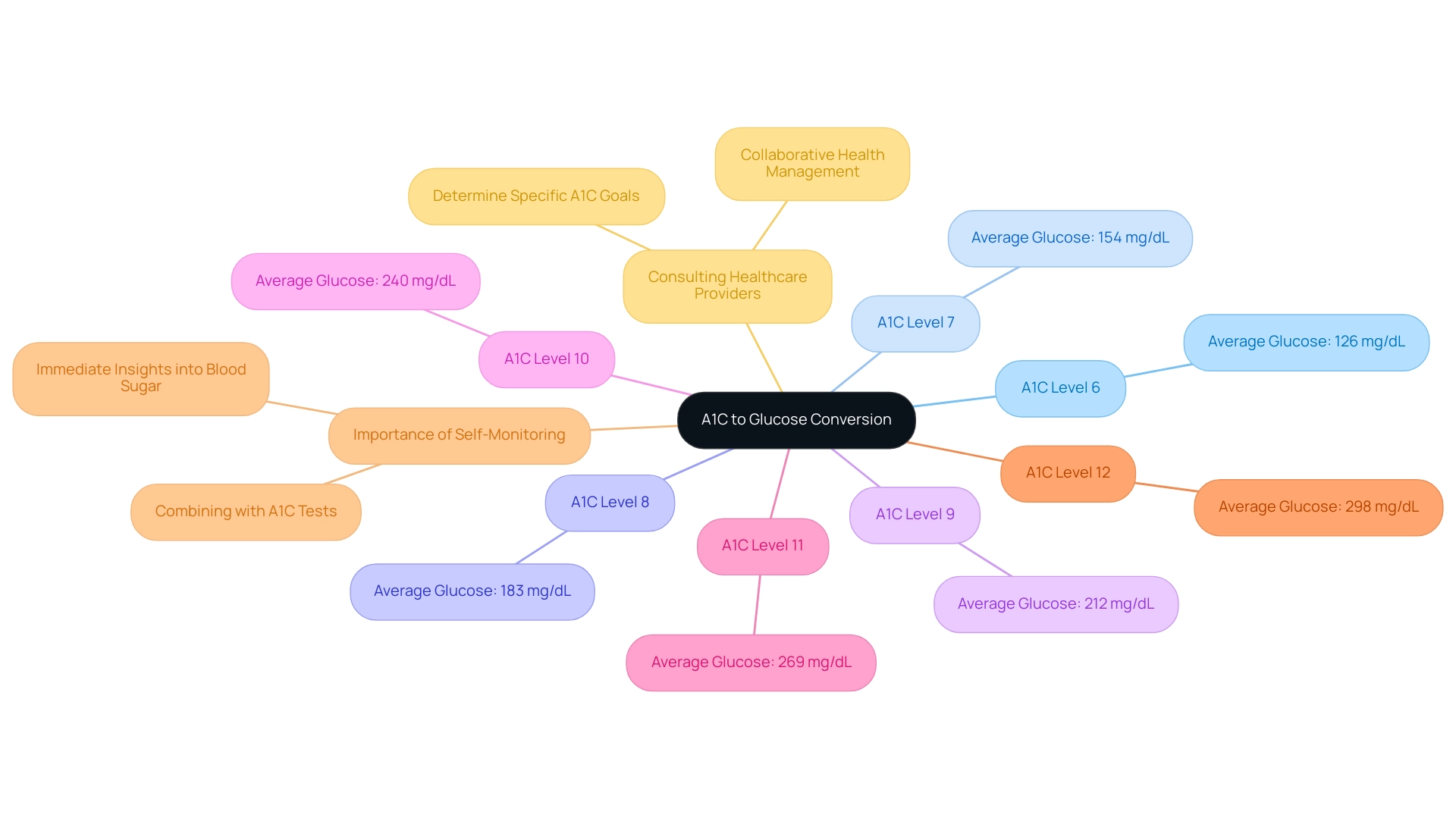
To effectively utilize the a1c to glucose level chart, start by identifying your A1C percentage along the left side of the chart. Next to this, you will find the corresponding average blood sugar concentration as indicated by the a1c to glucose level chart. For example, an A1C value of 7% corresponds with an estimated average sugar concentration of roughly 154 mg/dL.
Furthermore, an A1C value of 12% relates to an estimated average blood sugar of 298 mg/dL, offering a wider array of information for comprehending your blood sugar measurements. This information is crucial for monitoring your blood sugar readings and facilitating discussions with your healthcare provider about any necessary adjustments to your management plan. Regularly consulting the a1c to glucose level chart not only helps in understanding how your daily habits influence your A1C levels but also highlights the importance of frequent self-monitoring of blood glucose.
According to a case study titled 'Importance of Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose,' while A1C is vital for assessing long-term blood sugar control, it should be complemented by consistent self-checks for immediate insights into your blood sugar fluctuations. Therefore, combining day-to-day monitoring with periodic A1C tests and collaboration with healthcare teams is essential for comprehensive blood sugar management. It is also important to consult with your doctor to determine your specific A1C goal, as personalized targets can significantly impact your health management.
As D.M.N. states, 'Comprehending your A1C results is essential for effectively managing your condition and making informed choices about your health.' As T2DSolutions launches, it will function as a comprehensive resource hub, offering educational materials and community support to help you better understand A1C monitoring and its implications for your health management.
The Relationship Between A1C Levels and Average Blood Glucose
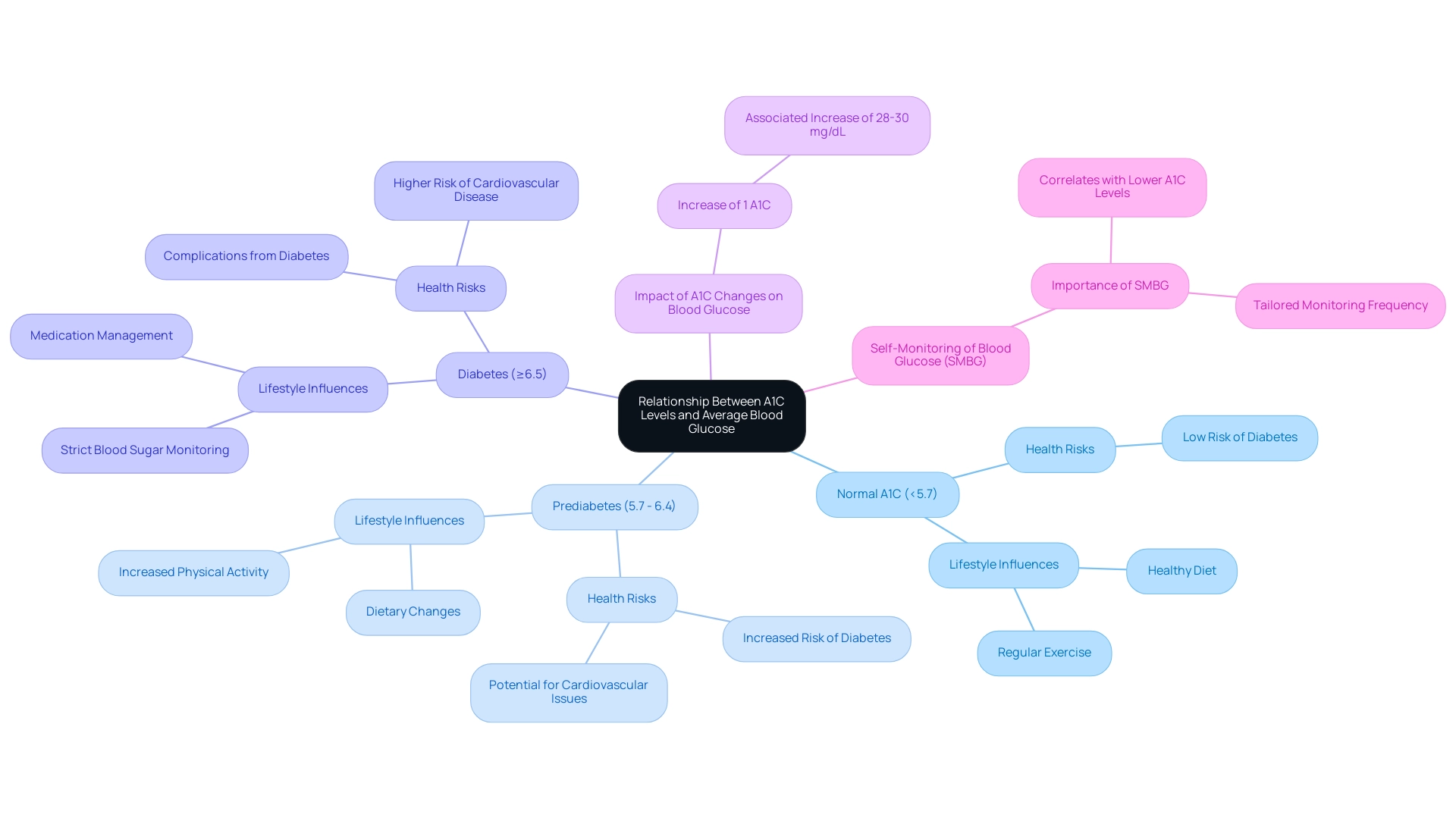
The A1C test functions as an essential marker of your average blood sugar concentrations over an extended duration, usually representing the previous two to three months. However, it is important to note that this test does not capture daily blood sugar fluctuations. Generally, A1C readings can be understood through the a1c to glucose level chart, where:
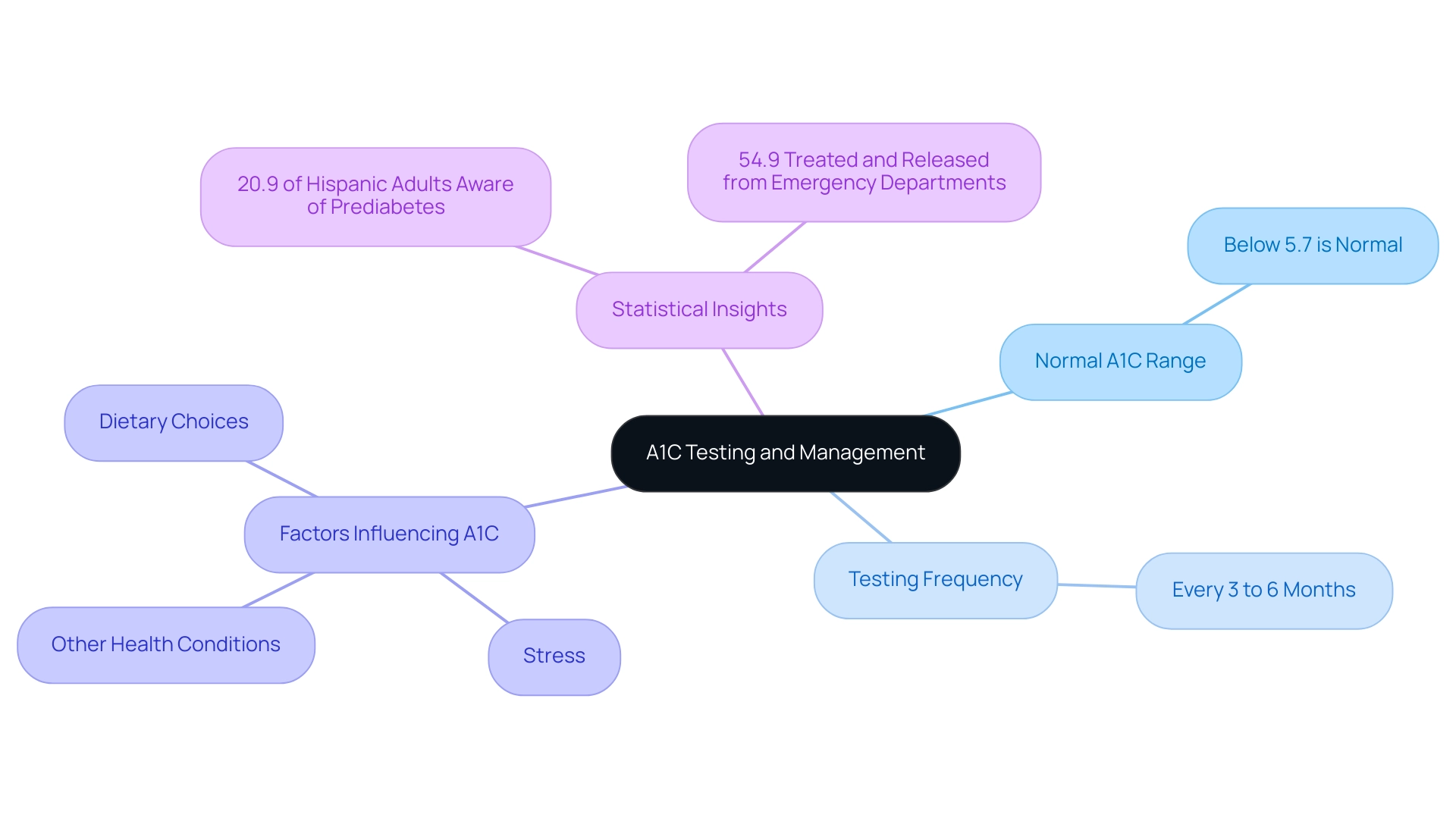
- A measurement below 5.7% is considered normal
- Numbers ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes
- An A1C of 6.5% or higher signifies diabetes
Significantly, studies suggest that every 1% rise in A1C, as shown in the a1c to glucose level chart, is associated with an estimated increase of 28-30 mg/dL in average blood sugar concentrations. This significant relationship underscores the necessity of understanding how lifestyle choices—such as dietary habits and physical activity—can directly influence your overall blood sugar management.
Furthermore, a recent study involving 6,180 invited individuals highlighted demographic differences in sugar tolerance statuses, revealing that participation rates were 45.4%, with time constraints being the most common reason for non-participation.
This highlights the significance of participating in consistent self-monitoring of blood sugar (SMBG), as increased SMBG frequency associates with reduced A1C values. Esther van 't Riet, a prominent researcher in this field, highlights the significance of this connection by stating, 'Therefore, our aim was to investigate the relationship between glucose and A1C in the general population and to assess the use of A1C for the screening and diagnosis of this condition.'
By understanding how your daily choices affect the a1c to glucose level chart, you can take proactive actions towards better management of your condition.
T2DSolutions is dedicated to enhancing your management journey by offering extensive resources, including tools for self-monitoring and educational materials, along with community support, ensuring you have the knowledge and tools necessary for effective health education and care.
Practical Steps for Monitoring Your A1C Levels
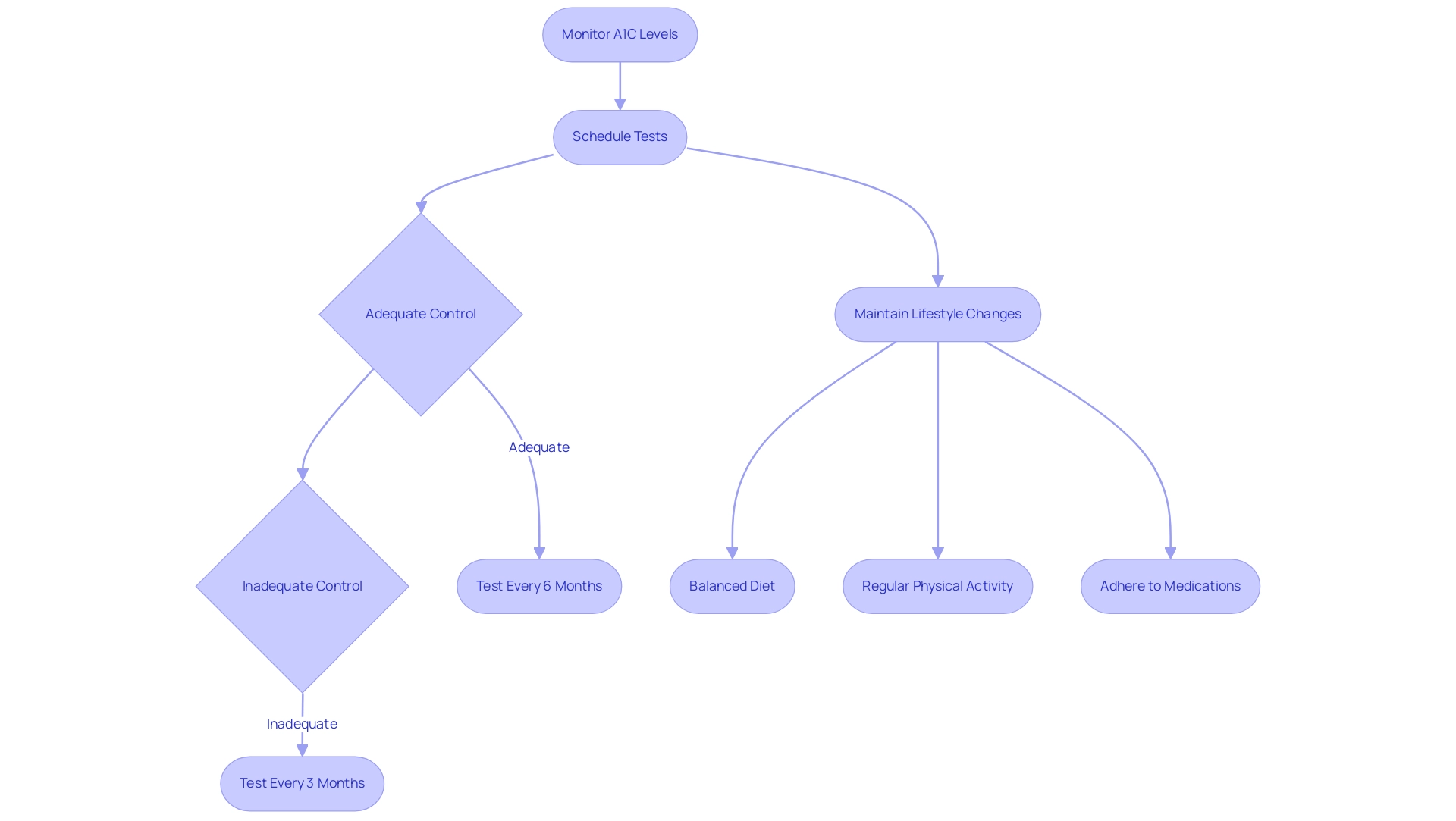
To effectively monitor your A1C readings, it is essential to schedule regular tests with your healthcare provider, typically every three to six months, based on your individual treatment plan. Recent guidelines recommend that patients with adequate glycaemic control undergo testing every six months, while those with inadequate control should be tested every three months. Notably, patients were required to have at least two HbA1c tests during the study period to ensure accurate monitoring.
Maintaining a comprehensive log of your A1C results, as well as using an a1c to glucose level chart, enables you to monitor trends over time, which is essential for managing your condition effectively. Adopting a healthy lifestyle plays a pivotal role in A1C management. This includes:
- Following a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Strictly adhering to prescribed medications
As Andrew Georgiou emphasizes, making these lifestyle changes can significantly improve A1C control. Moreover, utilizing continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) or blood glucose meters can provide valuable insights into daily fluctuations in your blood glucose levels, which can help you understand the a1c to glucose level chart and complement your A1C readings. A case study titled 'Impact of HbA1c Testing Frequency on Patient Outcomes' highlighted that better adherence to recommended testing frequencies correlates with improved glycaemic control and a reduced risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
By being proactive in your monitoring and lifestyle choices, you can significantly enhance your health management and overall well-being. As T2D Solutions gets ready to launch, stay tuned for additional resources that will further assist your journey in managing and educating about the condition.
Common Questions About A1C Testing and Management
Common queries surrounding A1C testing are crucial for effective diabetes management, and Td Solutions is here to support you as a newly diagnosed patient. Understanding the normal A1C range is a foundational aspect, particularly when referring to the a1c to glucose level chart; typically, a normal A1C measurement is considered to be below 5.7%. Patients are generally advised to have their A1C values checked every three to six months, depending on individual healthcare provider recommendations.
Fluctuations in A1C measurements are also a common concern; it is important to note that the a1c to glucose level chart can show variations due to factors such as dietary choices, stress, and other health conditions. As emphasized by Elizabeth Selvin, PHD, MPH, 'A1C levels would be linked with risk factors for type 2 and its complications even in the absence of elevated glucose levels.' If an A1C reading is elevated, it is imperative to consult with a healthcare provider to reassess and potentially modify the current management plan.
Additionally, with 20.9% of Hispanic adults being aware of their prediabetes status from 2017 to 2020, it underscores the importance of regular A1C testing in specific populations. Furthermore, data from emergency department visits in 2020 shows that 54.9% of patients with blood sugar issues were treated and released, indicating effective initial management in emergency settings. T2DSolutions aims to address these questions and alleviate concerns, enhancing your ability to manage this condition effectively.
Our platform will provide educational materials, access to support groups, and tools for monitoring your A1C levels, ensuring you have the resources needed for successful diabetes management.
Conclusion
Regular monitoring of A1C levels is indispensable for effective diabetes management. The A1C test not only reflects average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months but also serves as a critical indicator of long-term health risks associated with diabetes. Understanding how to interpret A1C results and their relationship with average blood glucose empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
By utilizing tools such as A1C to glucose conversion charts and engaging in consistent self-monitoring, patients can better understand how their daily choices impact their A1C levels. This proactive approach, combined with regular consultations with healthcare providers, supports the development of personalized management plans that can significantly enhance diabetes control.
Ultimately, the information and resources available through platforms like T2DSolutions are designed to empower individuals with diabetes to take charge of their health. By prioritizing education, regular testing, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can work towards improved A1C levels, minimizing the risk of complications and promoting overall well-being. Embracing these strategies is key to navigating the complexities of diabetes management effectively.



