Overview
Understanding Diabetes Mellitus is crucial, especially when distinguishing between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. It’s important to recognize that Type 1 is an autoimmune condition, often presenting with sudden onset symptoms. In contrast, Type 2 is related to insulin resistance and typically develops gradually. This distinction can feel overwhelming, but you’re not alone in this journey.
To help clarify your understanding, specific evaluations like the A1C test play a vital role in diagnosing the type of diabetes you may be facing. Additionally, lifestyle factors are significant in this process. It's completely normal to have questions and concerns, and seeking support can make a world of difference.
Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way. If you have any uncertainties or need guidance, please reach out for resources or community support. You deserve to feel informed and empowered in your health journey.
Introduction
Diabetes Mellitus is a complex condition that affects millions worldwide, and it's understandable that many remain unaware of its various forms and implications. Primarily categorized into Type 1 and Type 2, each type presents unique challenges and risk factors that can significantly impact your health.
- Type 1 diabetes, often diagnosed in childhood, arises from an autoimmune response that destroys insulin-producing cells.
- In contrast, Type 2 diabetes, which is increasingly prevalent among younger populations, is typically associated with lifestyle choices and insulin resistance.
As awareness of these distinctions grows, so does the importance of early detection and effective management strategies. This article delves into the intricacies of diabetes, highlighting symptoms, diagnostic steps, and lifestyle considerations crucial for those navigating this chronic condition.
You're not alone in this journey; understanding these elements not only empowers you but also fosters a supportive community for shared experiences and knowledge. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Understand Diabetes Mellitus: Types and Definitions
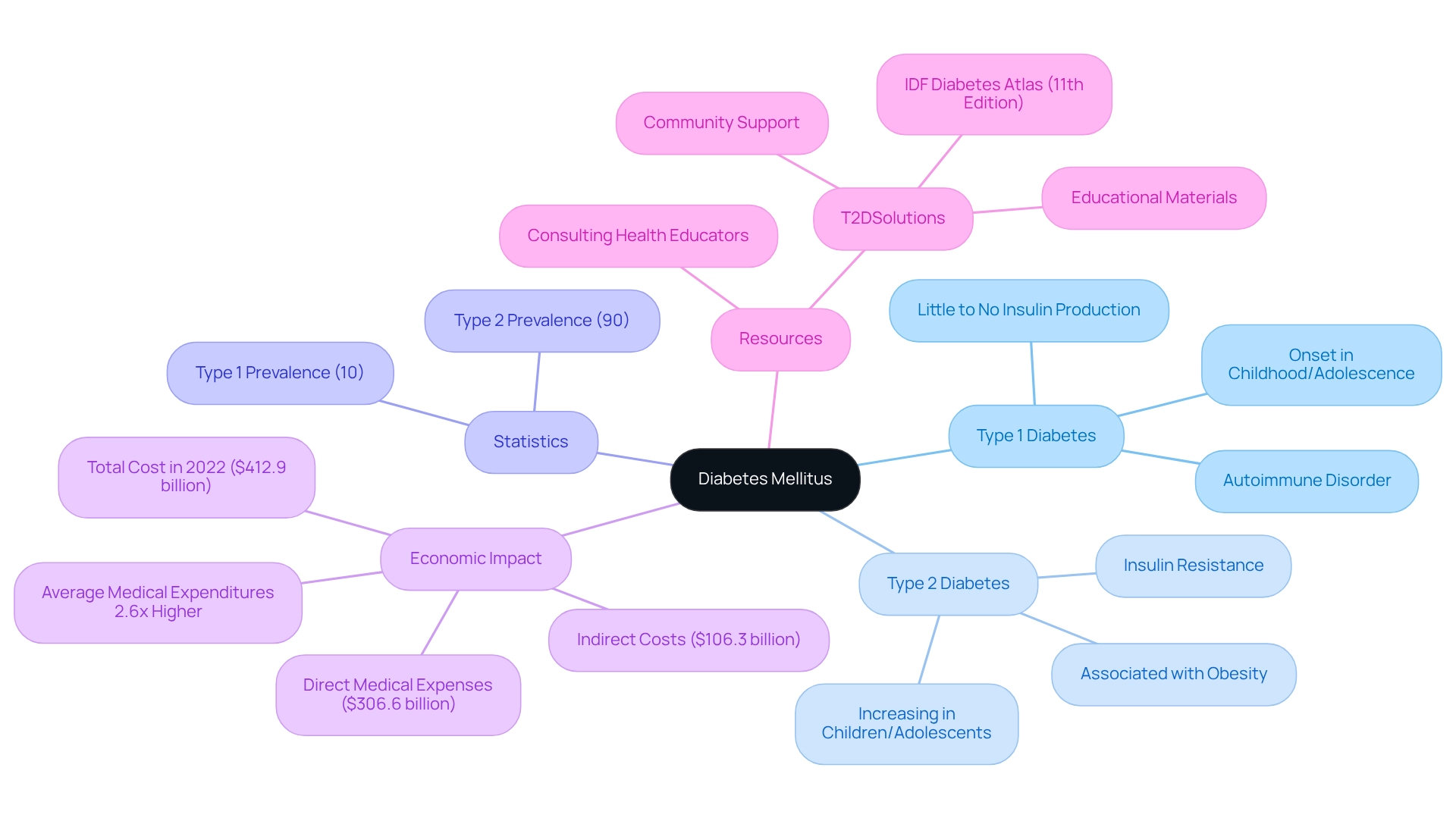
The primary categorization of diabetes is diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2. Type 1 is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, resulting in little to no insulin production. This type often appears during childhood or adolescence, but it can develop at any age. In contrast, Type 2 is characterized by insulin resistance, meaning the body does not use insulin effectively. This form is frequently associated with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle. While it traditionally occurs in adults, the rising rates of obesity have led to an increasing number of cases among children and adolescents.
Understanding these definitions is crucial for recognizing symptoms and determining whether it is diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2 for the right steps in diagnosis. Recent statistics reveal that globally, the prevalence of diabetes cases is diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2, with Type 1 accounting for about 10% and Type 2 representing approximately 90%. T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource for those recently diagnosed, offering educational materials and community support to help navigate this health journey. Consulting with a health educator can significantly aid those managing the condition over time.
Additionally, the 11th Edition of the IDF Diabetes Atlas is now available for download through T2DSolutions, providing essential resources for anyone seeking more information on blood sugar control.
The economic impact of diagnosed cases, which is diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2, is profound; in 2022, the total cost in the United States reached $412.9 billion, including $306.6 billion in direct medical expenses and $106.3 billion in indirect costs. This underscores the importance of effective management strategies to alleviate both health and financial burdens associated with diabetes. As our understanding of this condition evolves, it is vital to stay informed about the latest classifications and research developments for effective management. Remember, "Managing this condition can be challenging, but everything you do to enhance your health is worthwhile!" You're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way!
Identify Symptoms of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
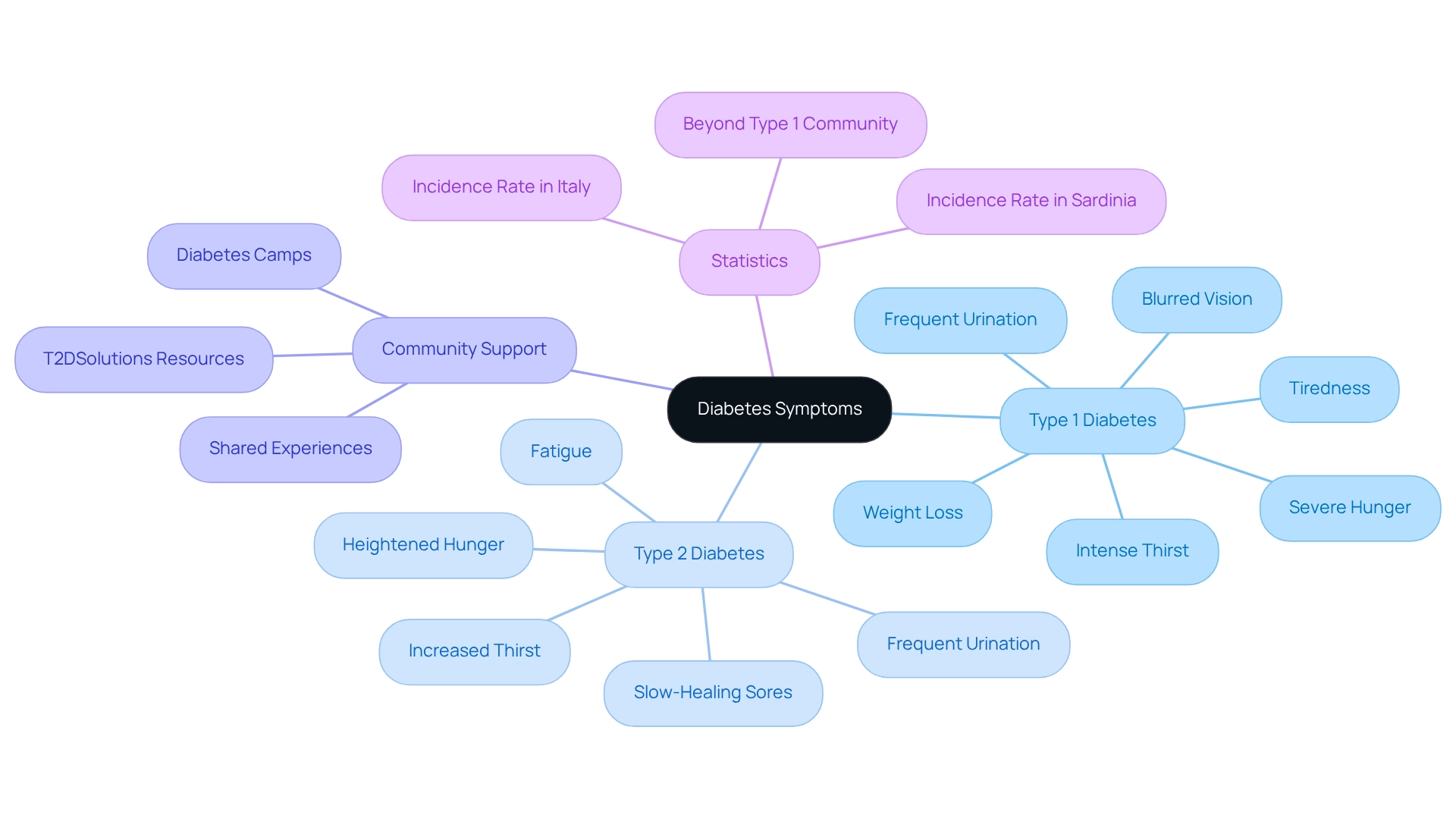
Signs of an insulin-dependent condition can appear suddenly, often accompanied by intense thirst, frequent urination, severe hunger, considerable weight loss, tiredness, and blurred vision. These symptoms may understandably prompt immediate medical attention, as they can indicate a serious condition requiring urgent care. In contrast, symptoms of the second form of this condition tend to develop gradually and may be less noticeable. Common indicators include increased thirst, frequent urination, heightened hunger, fatigue, and slow-healing sores. This gradual onset can lead to a delayed diagnosis, making awareness essential for effective management.
Recent statistics reveal a concerning trend: the incidence of Type 1 conditions is rising globally. In certain regions, such as Sardinia, rates are as high as 45 per 100,000 among children, while Italy reports an incidence rate of 12 per 100,000. This underscores the importance of recognizing symptoms early. Moreover, community support plays a crucial role in managing diabetes-related health. T2DSolutions emphasizes the value of shared experiences, which can enhance resilience and improve health outcomes for those affected. For instance, health camps offer children opportunities to learn about their condition and connect with peers, fostering a nurturing atmosphere. As Dr. Karen Gill observes, "These are an excellent method for children to understand what they can achieve and to connect with others who have the condition."
Both forms of the condition can lead to serious complications if not managed appropriately. Therefore, it’s vital for individuals to remain vigilant about their symptoms and seek medical advice if they notice any concerning changes. By understanding the differences in symptom presentation and the significance of community support, individuals can take proactive steps in their health management journey. Additionally, T2DSolutions serves as a comprehensive resource for newly diagnosed patients, offering valuable information and community connections. Organizations like Beyond Type 1, which boasts a community of over 1 million members, highlight the importance of shared experiences in addressing the challenges related to managing health conditions.
Follow Diagnostic Steps: Tests and Evaluations
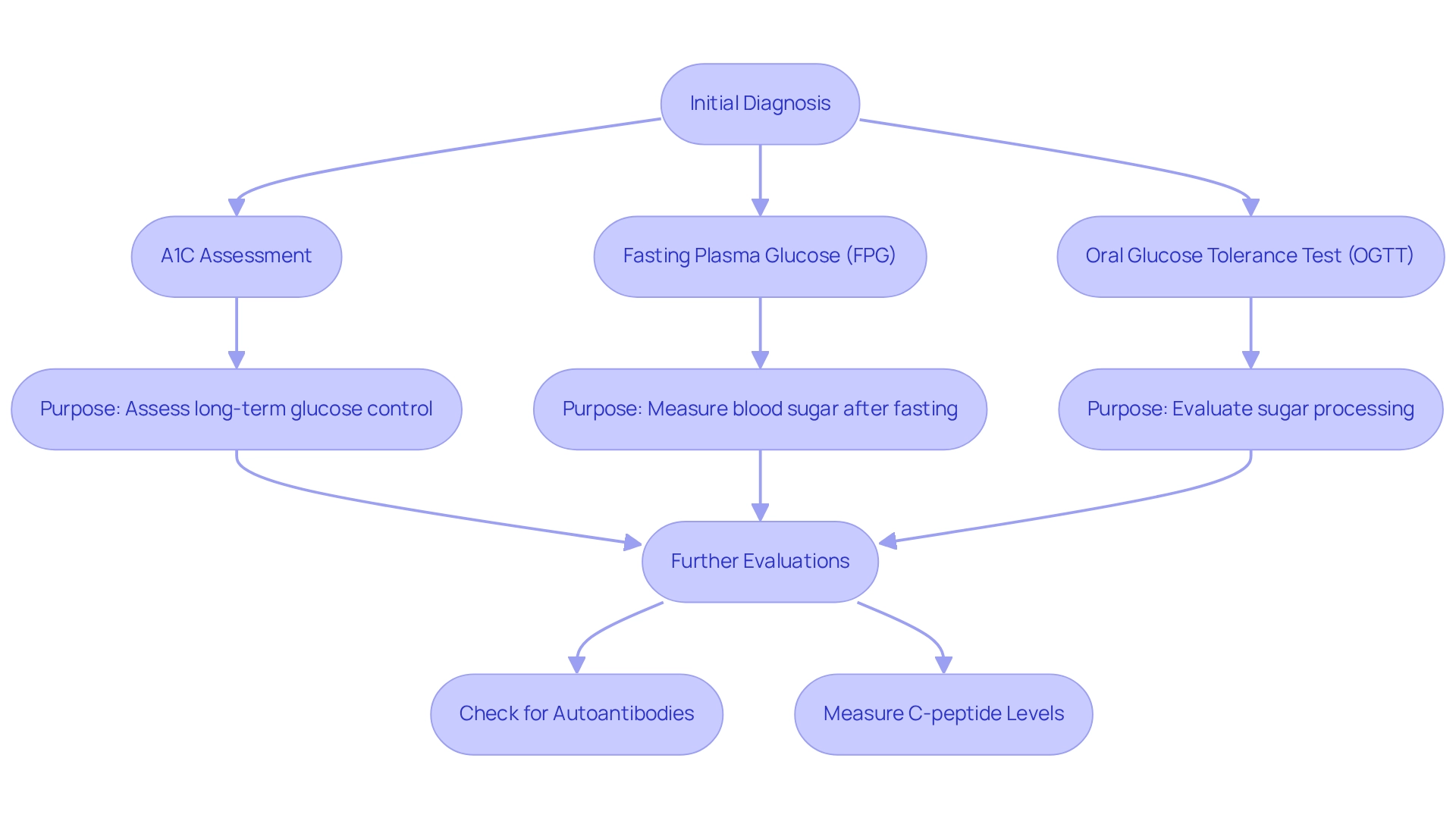
Identifying your illness involves a series of essential evaluations that healthcare professionals use to determine the type and intensity of your condition. One of the most common methods is the A1C assessment, which measures your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. An A1C level of 7% corresponds to an estimated average glucose (eAG) of 154 mg/dL, while a level of 9% indicates an eAG of 212 mg/dL. This evaluation is crucial for assessing long-term glucose control and is particularly helpful in distinguishing whether the condition is diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2.
In addition to the A1C assessment, the fasting plasma glucose (FPG) procedure is frequently utilized. This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast. Another valuable diagnostic tool is the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), which evaluates how effectively your body processes sugar by measuring blood glucose levels at intervals after consuming a glucose-rich beverage.
To further differentiate between conditions, healthcare providers may carry out additional evaluations to determine if it is diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2, such as:
- Checking for autoantibodies
- Measuring C-peptide levels
These tests clarify the underlying mechanisms of the disease, especially in cases where the diagnosis is uncertain.
Current statistics show that the age-standardized proportion of individuals with screen-detected conditions exhibiting elevated fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c levels ranges from 29% to 39% across various regions. This underscores the necessity for effective screening and early diagnosis to prevent complications.
As the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion advises, "Let your doctor know if any of these factors apply to you." It’s so important for you to engage in conversations with your healthcare providers to accurately interpret these results and understand their significance for your health maintenance. By staying informed about the latest diagnostic tests and updates, including advancements in A1C testing for 2025, you can take proactive steps in your health journey. Sharing uplifting personal experiences can also foster connection and encouragement, helping newly diagnosed individuals feel supported as they navigate their health journey. Following these diagnostic steps, you can better understand your condition and prepare for the next steps in managing your health.
Evaluate Risk Factors: Lifestyle and Family History
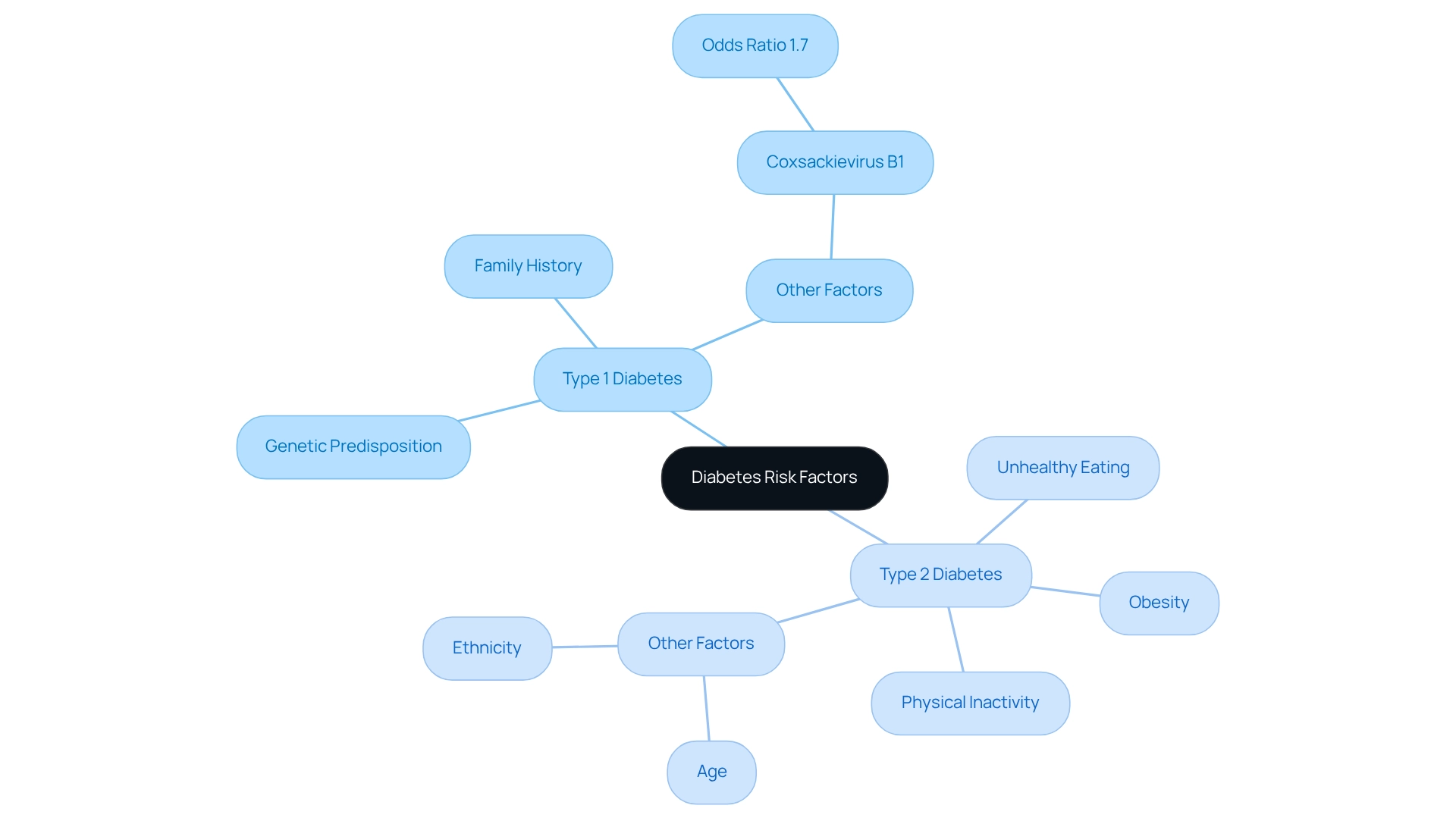
Understanding the risk factors for diabetes is crucial for both prevention and management. While the risk factors for type 1 diabetes are not as clearly defined, they include genetic predisposition and family history. Recent research has shown that lifestyle factors may also play a role. For instance, a study of Israeli recruits aged 16–19 found that a higher body mass index (BMI) was associated with an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes later in life, with a hazard ratio of 1.54 (95% CI 1.23–1.94). It’s important to approach these findings with caution, as a review highlighted the need for further research to confirm the connections between metabolic changes and diabetes risk.
On the other hand, type 2 diabetes is primarily linked to lifestyle choices. Key contributors include:
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Unhealthy eating habits
Other significant risk factors encompass age, ethnicity, and family history. Recent statistics emphasize that maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a balanced diet can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Nutritionists often recommend making lifestyle changes, such as increasing fruit and vegetable intake while reducing processed foods, as vital steps in preventing what is diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2. Additionally, T2DSolutions offers valuable resources for those newly diagnosed, providing information on available support and the benefits of joining support groups. This empowerment can help individuals make informed lifestyle choices.
Real-life examples illustrate how family history can impact diabetes risk; individuals with a parent or sibling diagnosed with diabetes face a higher risk themselves. By recognizing these connections, newly diagnosed individuals can take proactive steps toward healthier living, ultimately improving their chances of preventing or managing diabetes effectively. Furthermore, a study revealed that coxsackievirus B1 was more prevalent in diabetes cases than in controls, with a significant odds ratio of 1.7 (95% CI 1.06–2.74), highlighting the complex nature of type 1 diabetes risk factors.
Conclusion
Diabetes Mellitus is a significant global health issue, primarily divided into Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, each presenting distinct challenges. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder often diagnosed in childhood, while Type 2 is linked to lifestyle factors and increasingly affects younger populations. Recognizing these differences is essential for early diagnosis and effective management.
Awareness of symptoms is crucial. Type 1 diabetes symptoms manifest suddenly and can be severe, whereas Type 2 symptoms develop gradually. This highlights the need for education and understanding. Diagnostic tests, such as the A1C and fasting plasma glucose tests, are vital for confirming diabetes and determining treatment.
Lifestyle choices play a particularly important role in Type 2 diabetes, where obesity and inactivity increase risk. By understanding these risk factors and making healthier lifestyle choices, individuals can take proactive steps in managing their health. Community resources like T2DSolutions provide support and foster a sense of belonging among those living with diabetes.
In summary, understanding the types, symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and risk factors of diabetes empowers individuals to take control of their health. Emphasizing education, early detection, and lifestyle changes can lead to better management and improved well-being. Remember, each step taken toward better health is valuable. You’re not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the two primary types of diabetes?
The two primary types of diabetes are diabetes mellitus type 1 and type 2.
What is diabetes mellitus type 1?
Diabetes mellitus type 1 is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, resulting in little to no insulin production. It often appears during childhood or adolescence but can develop at any age.
How does diabetes mellitus type 2 differ from type 1?
Diabetes mellitus type 2 is characterized by insulin resistance, meaning the body does not use insulin effectively. It is frequently associated with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle and traditionally occurs in adults, though increasing rates of obesity have led to more cases among children and adolescents.
What percentage of diabetes cases are type 1 and type 2?
Type 1 diabetes accounts for about 10% of diabetes cases, while type 2 diabetes represents approximately 90%.
How can T2DSolutions assist those diagnosed with diabetes?
T2DSolutions provides educational materials and community support to help individuals navigate their health journey after a diabetes diagnosis.
What recent resource is available for information on blood sugar control?
The 11th Edition of the IDF Diabetes Atlas is available for download through T2DSolutions, offering essential resources for blood sugar control.
What was the economic impact of diabetes in the United States in 2022?
In 2022, the total cost of diagnosed diabetes in the United States reached $412.9 billion, which included $306.6 billion in direct medical expenses and $106.3 billion in indirect costs.
Why is it important to stay informed about diabetes?
Staying informed about the latest classifications and research developments is vital for effective management of diabetes and to alleviate both health and financial burdens associated with the condition.



