Overview
This article highlights effective daily management strategies for individuals navigating life with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. It underscores the significance of personalized management plans, which encompass essential elements such as:
- Blood sugar monitoring
- Nutrition management
- Physical activity
- Medication adherence
- Stress management
- The use of technology
These components are vital for maintaining optimal health and enhancing the quality of life for those living with diabetes.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed when managing diabetes, but remember, you're not alone in this journey. Personalized plans not only help in monitoring your health but also empower you to take control of your life. By integrating these strategies, you can make informed choices that positively impact your daily routine.
We encourage you to explore these management strategies further. Seek support from healthcare professionals, connect with others who share similar experiences, and utilize available resources. Together, we can navigate this journey toward better health and well-being.
Introduction
In the complex landscape of diabetes management, it’s essential to understand the nuances between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes for effective self-care. Each type presents unique challenges, and tailored strategies—from insulin therapy to lifestyle modifications—are necessary to navigate them. With diabetes affecting approximately 1 in 10 Americans and its prevalence rising globally, the importance of informed and proactive management cannot be overstated.
This article delves into essential daily management strategies, the role of technology, and the creation of personalized plans. Our goal is to empower you to take control of your health and improve your quality of life. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
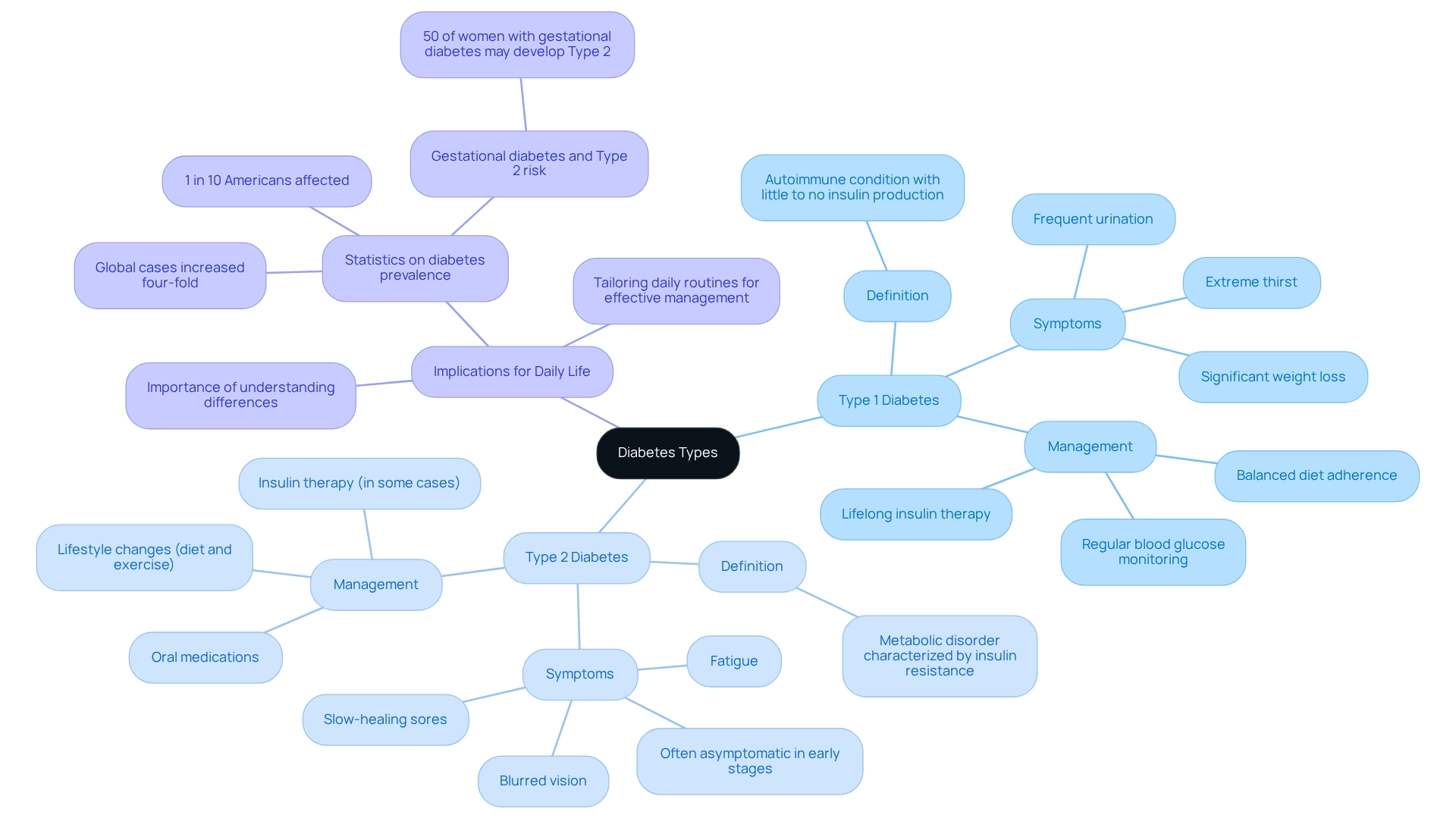
Understand Diabetes: Types and Their Implications
Diabetes is primarily categorized into two main types: Type 1 and Type 2, each with distinct characteristics and management strategies.
Type 1 Diabetes
- Definition: Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little to no insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include frequent urination, extreme thirst, and significant weight loss.
- Management: Lifelong insulin therapy is essential. Regular blood glucose monitoring and adherence to a balanced diet are vital for managing this condition.
Type 2 Diabetes
- Definition: Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance, where the body fails to use insulin effectively.
- Symptoms: Often, there are no symptoms in the early stages. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores.
- Management: Management typically involves lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, oral medications, and in some cases, insulin therapy.
Implications for Daily Life
Understanding these differences is crucial for effective self-management. The management of type 1 & 2 diabetes requires a strict regimen of insulin administration for Type 1, while Type 2 treatment often emphasizes lifestyle changes and medication adherence. Recognizing these distinctions allows individuals to tailor their daily routines, enhancing their ability to manage their condition effectively. It's important to note that recent statistics indicate approximately 1 in 10 Americans is affected by blood sugar disorders, which include type 1 & 2 diabetes. This statistic underscores the urgent need for effective management strategies. According to the IDF Diabetes Atlas, global cases of the condition have risen four-fold over the past decades, emphasizing its worldwide impact. Furthermore, case studies show that about 50% of women who experience gestational issues may later develop Type 2 diabetes. This highlights the significance of early intervention and education in controlling the condition. Comprehending these connections is essential for proactive oversight and awareness. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Implement Daily Management Strategies for Diabetes Control
Effective daily management of diabetes hinges on several essential strategies:
Blood Sugar Monitoring
- Action: Regularly check your blood glucose levels using a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor (CGM).
- Tip: Keep a log of your readings to identify patterns and discuss them with your healthcare provider. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but statistics indicate that consistent monitoring can significantly enhance blood sugar management. Many patients report better outcomes when they check their levels frequently. T2DSolutions offers resources to help you understand your readings and make informed decisions.
Nutrition Management
- Action: Adhere to a balanced diet tailored to your diabetes type.
- Tip: Utilize the Diabetes Plate method to ensure proper portion sizes and nutrient balance. Focus on whole foods, including vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Recent articles highlight that dietary adjustments can lead to improved blood sugar levels and overall health. T2DSolutions provides meal planning tools and nutritional guidance to support your dietary choices.
Physical Activity
- Action: Integrate regular exercise into your routine, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week.
- Tip: Choose activities you enjoy, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, to enhance your commitment. Engaging in physical activity not only aids in blood sugar control but also contributes to mental well-being. T2DSolutions encourages community events and group activities to keep you motivated.
Medication Adherence
- Action: Follow your healthcare provider's medication regimen diligently.
- Tip: Use pill organizers or set reminders on your phone to ensure you take your medications as prescribed. It's vital to manage your medication effectively, as research indicates that compliance can lower additional healthcare expenses linked to conditions related to type 1 & 2 diabetes, which increased from $8,417 to $9,601 per individual between 2012 and 2017. By adhering to your medication plan, you can help mitigate these costs and improve your overall health. T2DSolutions offers reminders and tracking tools to help you stay on top of your medications.
Stress Management
- Action: Employ stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises.
- Tip: Identify stressors in your life and develop coping strategies to manage them effectively. Managing stress is vital, as it can directly impact blood sugar levels and overall health. T2DSolutions provides resources and workshops focused on stress management techniques.
Community Support
- Action: Engage with community resources and support groups for diabetes management.
- Tip: Share your experiences and connect with others facing similar challenges. This community-centered approach, as highlighted by T2DSolutions, boosts user involvement and offers emotional support, which is essential for effectively handling health conditions.
By applying these tactics and utilizing the resources available through T2DSolutions, you can take proactive charge of your well-being, resulting in enhanced health outcomes and an improved quality of life. Remember, community support can further enhance these efforts, offering emotional assistance and shared experiences that are vital for effective health oversight.

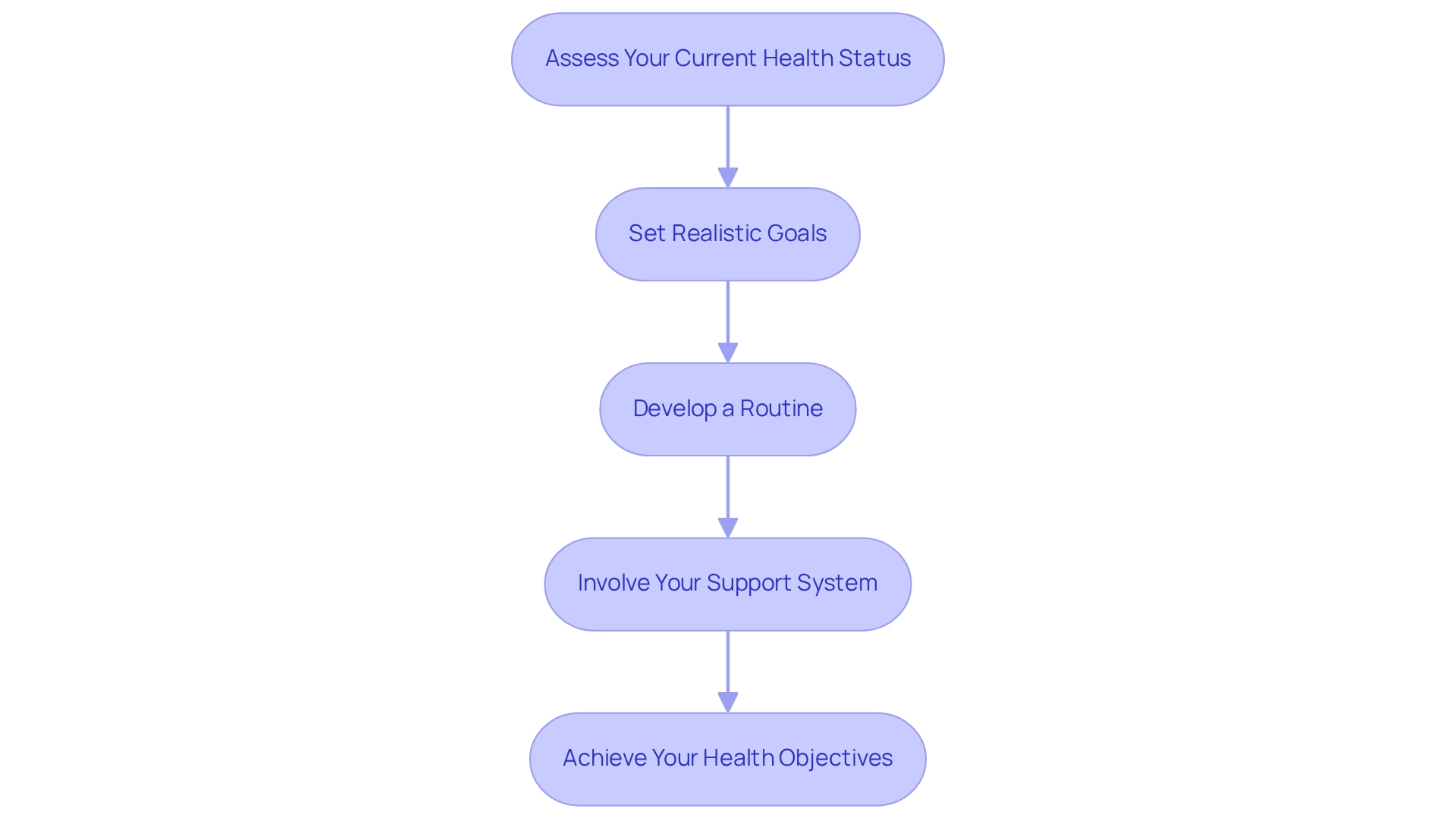
Create a Personalized Diabetes Management Plan
Creating a personalized diabetes management plan involves several essential steps:
Assess Your Current Health Status
- Action: It's important to consult with your healthcare provider to evaluate your current health, including blood sugar levels, weight, and any complications.
- Tip: Sharing your medical history and any medications you are currently taking can help ensure a comprehensive understanding of your health. Remember, monitoring blood glucose levels is crucial; studies show a mean score of 28.7 for the quality of analysis and discussion of these values among patients.
Set Realistic Goals
- Action: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for your diabetes management.
- Tip: Your goals may include weight loss, improved blood sugar control, or increased physical activity. Research suggests that tailored care planning greatly improves diabetes control results, aligning with recent discoveries. Many patients are now focusing on both immediate health risks and long-term outcomes when setting their goals.
Develop a Routine
- Action: Create a daily routine that includes meal planning, exercise, medication schedules, and monitoring.
- Tip: Consider using planners or apps to help track your routine and make adjustments as needed. This consistency can support your organizational efforts. Remote health data monitoring and real-time communication with patients can enhance self-care, leading to short-term improvements in health metrics.
Involve Your Support System
- Action: Engage family members, friends, or support groups in your management plan.
- Tip: Sharing your goals and progress with them can foster accountability and encouragement. Case studies indicate that patients who engage their support systems in their care plans report higher satisfaction and improved health outcomes. Understanding patient preferences, as emphasized in research on patient preference categories, can assist in customizing your care strategy to better fit your needs.
By adhering to these steps, you can develop a thorough care plan that aligns with your personal health objectives and lifestyle. This approach enhances your ability to manage blood sugar levels effectively while considering the distinctions and commonalities between type 1 & 2 diabetes. You're not alone in this journey; for additional resources and support, visit T2DSolutions, your center for education and community support.
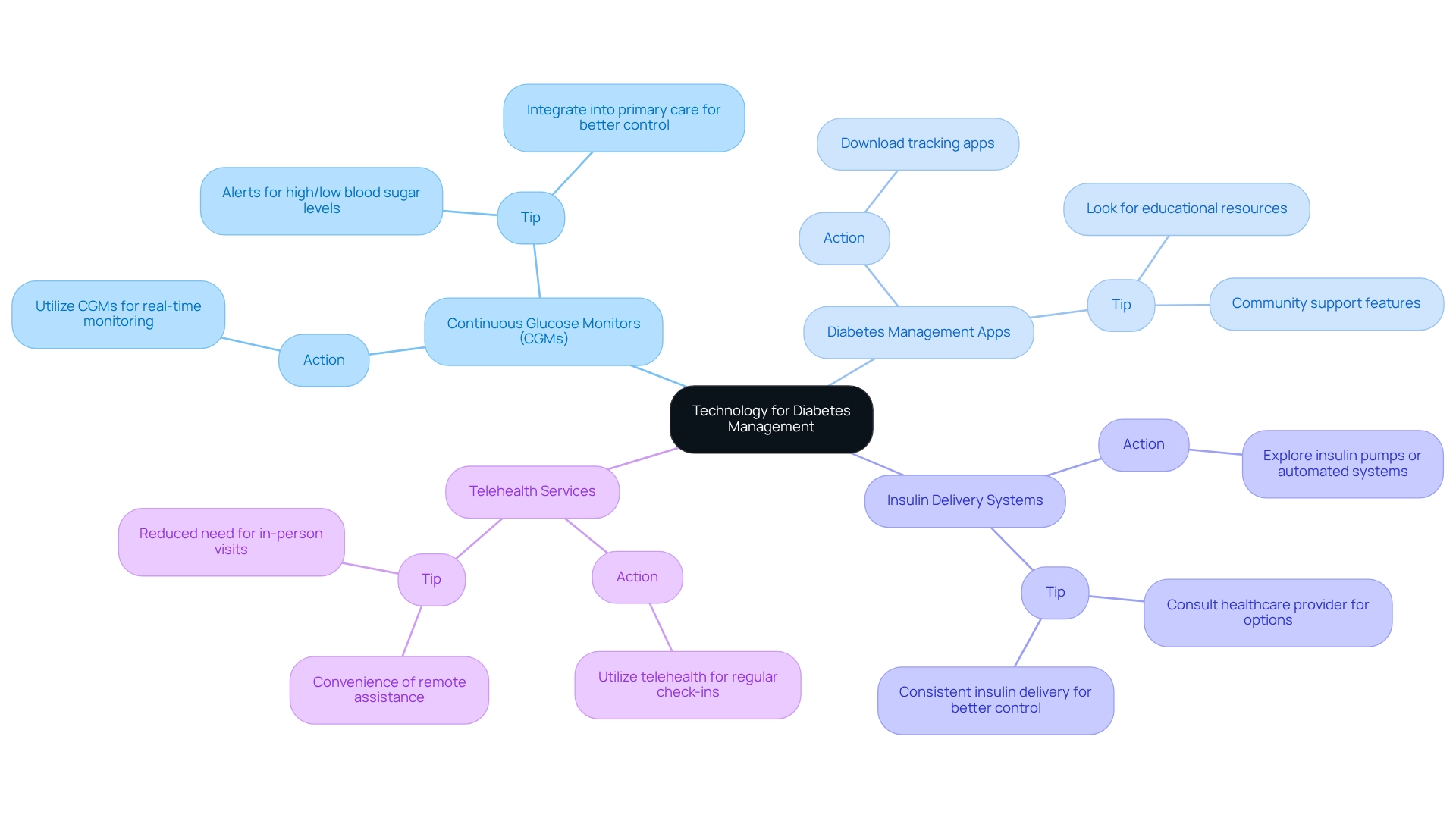
Utilize Technology for Diabetes Management
Technology plays a vital role in helping you manage your blood sugar levels effectively, providing innovative tools that empower you to take charge of your health. Here are some essential resources to consider:
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
- Action: Consider utilizing CGMs to monitor your blood sugar levels in real-time.
- Tip: These devices can alert you to high or low blood sugar levels, allowing for timely interventions. Recent studies, including one by Durham, J., show that integrating CGMs into primary care can significantly enhance diabetes control, particularly for patients with type 1 & 2 diabetes who are using noninsulin or basal insulin therapies.
Diabetes Management Apps
- Action: Download apps designed to help you track your food intake, exercise, and blood sugar levels.
- Tip: Look for apps that offer educational resources and community support features. Current trends indicate a growing reliance on these apps, which not only help you maintain awareness of your health metrics but also foster a sense of community.
Insulin Delivery Systems
- Action: Explore insulin pumps or automated insulin delivery systems for precise insulin management.
- Tip: It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider to find the best options tailored to your condition and lifestyle. These systems can provide more consistent insulin delivery, improving your overall glycemic control.
Telehealth Services
- Action: Take advantage of telehealth services for regular check-ins with your healthcare team.
- Tip: This method offers convenience and ensures you receive continuous assistance without the need for frequent in-person appointments, making it easier to manage your condition.
By embracing these technologies, you can enhance your health management, making it more efficient and responsive to your unique needs. For instance, the effectiveness of CGMs is highlighted in the case study titled 'Effectiveness of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Older Adults,' which evaluated CGM effectiveness in older adults with type 1 & 2 diabetes treated with basal insulin. Furthermore, the data provided by continuous glucose monitors can help you learn how to manage your metabolism without making major lifestyle changes. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest developments will empower you further on your health journey. For more resources and support related to these technologies, be sure to explore T2DSolutions, your comprehensive hub for diabetes management.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes is crucial for effective management and improved health outcomes. Each type presents unique challenges that require tailored strategies, from insulin therapy to lifestyle modifications. It’s essential to recognize that by implementing daily management practices—such as regular blood sugar monitoring, balanced nutrition, and consistent physical activity—you can take proactive steps toward controlling your diabetes. Moreover, integrating technology, including continuous glucose monitors and diabetes management apps, enhances your ability to track progress and make informed decisions.
Creating a personalized diabetes management plan can empower you to set realistic goals and develop routines that align with your lifestyle. Engaging support systems, whether through family, friends, or community groups, fosters accountability and provides the emotional backing essential for navigating the complexities of diabetes management. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; many others share similar experiences and challenges.
Ultimately, proactive and informed diabetes management is not just about controlling blood sugar levels; it’s about enhancing your overall quality of life. By embracing a comprehensive approach that combines education, technology, and community support, you can take charge of your health journey. Together, we can pave the way for a brighter and healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of diabetes?
Diabetes is primarily categorized into two main types: Type 1 and Type 2, each with distinct characteristics and management strategies.
What is Type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little to no insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
What are the common symptoms of Type 1 diabetes?
Common symptoms of Type 1 diabetes include frequent urination, extreme thirst, and significant weight loss.
How is Type 1 diabetes managed?
Management of Type 1 diabetes requires lifelong insulin therapy, regular blood glucose monitoring, and adherence to a balanced diet.
What is Type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance, where the body fails to use insulin effectively.
What symptoms may indicate Type 2 diabetes?
In the early stages of Type 2 diabetes, there are often no symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores.
How is Type 2 diabetes managed?
Management of Type 2 diabetes typically involves lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, oral medications, and in some cases, insulin therapy.
Why is it important to understand the differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
Understanding the differences is crucial for effective self-management, as Type 1 requires a strict regimen of insulin administration, while Type 2 emphasizes lifestyle changes and medication adherence.
What is the prevalence of diabetes in the United States?
Approximately 1 in 10 Americans is affected by blood sugar disorders, including Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
How has the global prevalence of diabetes changed over the years?
According to the IDF Diabetes Atlas, global cases of diabetes have risen four-fold over the past decades, indicating its worldwide impact.
What is the significance of gestational issues related to Type 2 diabetes?
About 50% of women who experience gestational issues may later develop Type 2 diabetes, highlighting the importance of early intervention and education in controlling the condition.



