Overview
The top five A1C cutoff points essential for diabetes management are as follows: under 5.7% indicates normal glucose levels, 5.7% to 6.4% signifies prediabetes, and 6.5% or higher confirms diabetes, necessitating immediate intervention. The article emphasizes the importance of these cutoff points for early detection and management of diabetes, highlighting how understanding these thresholds can empower patients to make informed lifestyle changes and seek appropriate medical care to mitigate complications.
Introduction
The A1C test serves as a cornerstone in the management of diabetes, providing vital insights into an individual's average blood glucose levels over a two to three-month period. This percentage-based measurement not only reflects the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies but also highlights the risk of complications associated with poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
With the rising prevalence of diabetes, particularly among younger populations, understanding the significance of A1C testing becomes essential for timely intervention and effective treatment. As healthcare providers and patients alike navigate the complexities of diabetes management, this article delves into the critical aspects of the A1C test, including:
- Its diagnostic criteria
- The importance of regular testing
- Lifestyle changes to improve outcomes
- The role of medications in achieving optimal A1C levels
By equipping individuals with this knowledge, a proactive approach to diabetes management can be fostered, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
Understanding the A1C Test: A Key Tool in Diabetes Management
The A1C test, often known as glycated hemoglobin, is an essential diagnostic tool that assesses the average glucose levels over a period of two to three months. Expressed as a percentage, the A1C result reflects the proportion of hemoglobin molecules bound with glucose. Significantly, higher A1C percentages indicate poorer blood glucose control, which is associated with an increased risk of diabetes-related complications.
For instance, data indicates that during 2017–2018, there were 5,293 newly diagnosed cases of type 2 illness among children and adolescents aged 10 to 19. This statistic highlights the importance of early intervention through regular monitoring of A1C figures, as timely management in relation to the A1C cutoff can significantly change health outcomes. Understanding the A1C test empowers patients to engage meaningfully with healthcare providers regarding treatment options and necessary lifestyle adjustments.
As noted by T.H.K., a Statistical Analyst, A1C level was effective and convenient for screening. This convenience is particularly vital for newly diagnosed patients, as it enables more efficient management of their condition and the initiation of appropriate care strategies. T2DSolutions acts as a comprehensive resource center for Type 2 and Type 3 metabolic disorder education and community support, providing valuable insights into A1C goals tailored for various age groups.
For example, the American Diabetes Association recommends an A1C cutoff of less than 7% for most adults, while specific targets may vary for children and older adults based on individual health circumstances. For additional information on blood sugar statistics and management, readers can access the full report online at the CDC's website. Furthermore, a case study titled 'Implications of A1C Variability' highlights the stability of A1C measurements compared to glucose, emphasizing that A1C's lower variability suggests a single measurement is often sufficient for diagnostic classification, reducing the need for multiple glucose tests in clinical practice.
Key A1C Cutoff Points for Diagnosing Diabetes
A1C test results are classified into separate ranges that play a crucial role in diagnosing conditions related to high blood sugar. The widely accepted cutoff points are as follows:
- Normal: An A1C measurement under 5.7% signifies typical glucose concentrations, suggesting no major risk for high blood sugar.
- Prediabetes: An A1C measurement between 5.7% and 6.4% signifies prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar amounts are increased but not high enough to necessitate a diagnosis of this illness.
- Diabetes: An A1C level of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of this condition, signaling the need for immediate management and intervention.
Understanding these A1C cutoff points is essential for early detection and proactive management of this condition. This knowledge empowers newly diagnosed patients to implement necessary lifestyle modifications or seek medical treatment, thereby mitigating the risk of progression to more severe forms of the condition.
As T2DSolutions launches as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 conditions education, it aims to support individuals in understanding these critical guidelines. The platform will offer resources, articles, and tools specifically created to assist patients in tracking their A1C readings and managing their condition effectively. Given that type 2 conditions account for 90–95% of all cases, awareness of these levels is particularly significant for at-risk populations.
A pertinent case study titled "Risk-Based Screening for Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents" suggests that screening for type 2 conditions in overweight or obese youth with additional risk factors can lead to early identification and timely intervention, ultimately preventing the onset of the disease.
As Richard Wender, MD, remarks, "The American Diabetes Association appreciates the following volunteer members of the writing group for the updated sections on diagnosis and categories of increased risk," highlighting the significance of understanding A1C cutoff points in the context of this health condition.
The Importance of Regular A1C Testing
Routine A1C assessments are fundamental to efficient management of the condition, particularly when considering the a1c cutoff, allowing individuals to track their glucose measurements over time. This practice is vital for identifying trends that inform treatment decisions. At T 2 Solutions, we recognize the importance of this practice, especially for newly diagnosed patients seeking comprehensive resources.
The American Diabetes Association recommends that most people with diabetes should have their A1C measurements assessed at least twice annually, especially if they are above the a1c cutoff and their sugar readings remain stable. For those who have experienced changes in their treatment or have not been meeting their blood sugar targets, it is recommended to conduct more frequent testing—typically every three months—to assess their status in relation to the a1c cutoff. By remaining attuned to their A1C levels and considering the a1c cutoff, individuals can engage in proactive discussions with their healthcare providers, adjusting management strategies as necessary.
Furthermore, as noted by Roopa Naik, the latest proposed methods, including estimated average glucose and glucose time in range, serve to enhance the understanding of A1C results, thereby supporting better management. This ongoing commitment to monitoring is not just beneficial for individual health outcomes but also crucial given the substantial economic burden of the condition, which was estimated at $413 billion in the U.S. in 2022, as detailed in the case study titled 'Economic Impact of Diabetes.' Regular A1C testing thus plays a pivotal role in both personal health management and broader public health strategies, especially as T2DSolutions aims to provide a new resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support, particularly in light of the recent updates in care, which now refer to automated insulin delivery systems instead of hybrid closed-loop technology, with the A1C cutoff being an important focus.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve A1C Levels
As T2DSolutions debuts as a comprehensive resource center for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, it's essential to implement targeted lifestyle changes that can lead to significant improvements in A1C readings, ultimately helping individuals reach their a1c cutoff for better overall diabetes management. Consider the following key strategies:
- Healthy Eating: Embracing a balanced diet that includes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins is essential for regulating glucose concentrations. Close monitoring of carbohydrate intake is also crucial. Nutritionists emphasize that dietary improvements can lead to measurable reductions in A1C, particularly when integrated with other lifestyle changes that consider the A1C cutoff. A meta-analysis involving 17 studies demonstrates that greater weight loss and improvements in A1C and fasting glucose were achieved with meal replacements compared to conventional diets.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in consistent physical activity is vital for enhancing insulin sensitivity and lowering sugar concentrations. The suggestion is to strive for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly, which is backed by recent research showing significant enhancements in A1C values, especially in relation to the a1c cutoff, through physical activity.
- Weight Management: Obtaining and sustaining a healthy weight greatly influences sugar regulation. Studies show that even a slight reduction in weight of 5-10% can positively affect A1C readings, underscoring the significance of maintaining an a1c cutoff in managing blood sugar.
- Stress Management: Increased stress can negatively impact sugar regulation. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Additionally, it's important to consider the glycemic response from fat in meals, which has been studied in children and adolescents with type 1 conditions, highlighting the need for age-specific dietary considerations.
By actively adopting these lifestyle changes, individuals can take substantial steps toward enhancing their A1C levels to meet the A1C cutoff and improve their overall health. As Robert A. Gabbay notes in the Standards of Care in Diabetes–2024, these preventive measures are crucial for effective management of this condition. Furthermore, the rising medical costs related to this condition, which increased from $10,179 to $12,022 per individual from 2012 to 2022, underscore the urgency of implementing these strategies to mitigate financial strain and improve health outcomes.
T2DSolutions is here to support you on this journey with valuable resources, community engagement, and a commitment to keeping you informed. Subscribe now to receive updates and be the first to know when new content is published!
Understanding the Role of Medications in A1C Management
For numerous individuals controlling their condition, lifestyle changes alone may prove insufficient in reaching the desired A1C cutoff targets. In such cases, medications become essential in facilitating effective glucose control, especially for those with elevated A1C levels that exceed the A1C cutoff. T2DSolutions is proud to be your new resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 health education and community support, offering comprehensive guidance on medication management and ongoing updates to assist you on your journey.
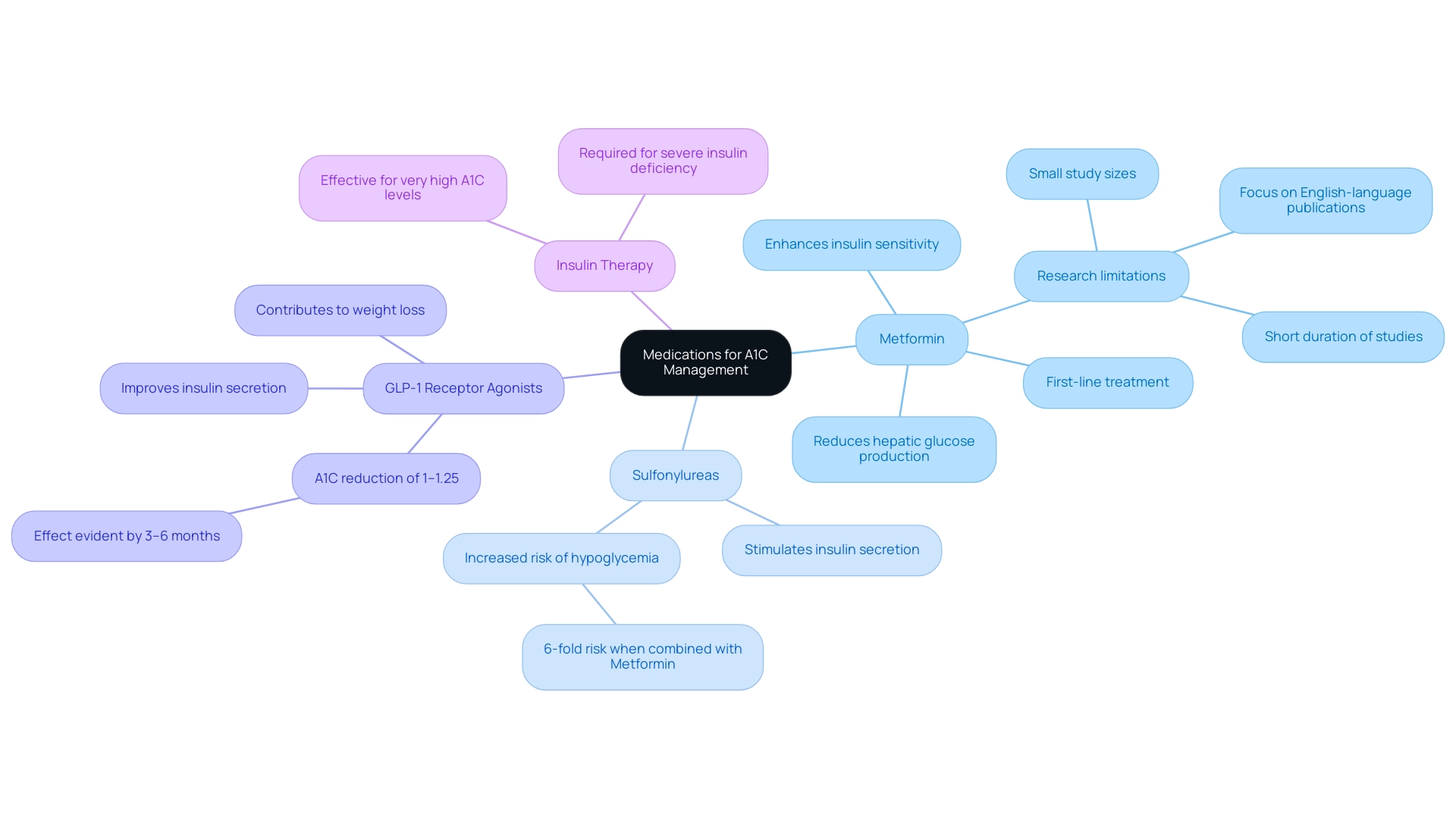
The landscape of glucose management medications includes several key classes, each serving a distinct purpose:
-
Metformin: Recognized as the first-line treatment for type 2 glucose intolerance, Metformin operates by reducing hepatic glucose production and enhancing insulin sensitivity. Recent reviews confirm that Metformin boasts the highest benefit-risk profile among medications for blood sugar management, although ongoing research is necessary to fully understand its long-term outcomes in higher-risk populations. It is important to note that the review faced limitations, including the exclusive focus on English-language publications and the small size of many studies, which suggests caution in interpreting the findings.
-
Sulfonylureas: This class of medications functions by stimulating the pancreas to secrete additional insulin, thus aiding in reducing sugar concentrations. However, it’s critical to highlight that studies indicate a six-fold increased risk of hypoglycemia when combining sulfonylureas with Metformin compared to other treatments, such as thiazolidinediones. This risk must be carefully considered when developing a treatment plan.
-
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These agents improve insulin secretion in response to meals and contribute to weight loss, making them a valuable option for many patients. Diana Sherifali, a leading expert in managing blood sugar levels, notes that the initiation of an oral antidiabetic (OAD) alongside existing therapy can yield an A1C reduction of approximately 1–1.25%, which can help patients meet the A1C cutoff within 3 to 6 months of treatment initiation. Moreover, the findings from the review highlight the need for further research on the long-term outcomes of Metformin, especially in higher-risk populations.
-
Insulin Therapy: For some individuals, particularly those with severe insulin deficiency or very high A1C levels, insulin injections may be required to effectively manage blood glucose levels.
In summary, understanding the function and role of these medication classes is critical for individuals managing their condition, as they can significantly aid in achieving and sustaining target A1C levels, which is vital for meeting the A1C cutoff. T2DSolutions is dedicated to providing you with the latest information and support for your diabetes management journey, ensuring that you remain informed about potential limitations and benefits to maintain a balanced approach. We encourage you to explore our resources and stay connected for ongoing support and updates.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is essential for effective diabetes management. This diagnostic tool not only provides insight into average blood glucose levels over a two to three-month period but also serves as a critical benchmark for identifying diabetes and prediabetes. By recognizing the importance of regular A1C testing, individuals can monitor their health proactively, enabling timely interventions that can lead to better long-term outcomes.
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in improving A1C levels. Healthy eating, regular physical activity, weight management, and stress reduction are all strategies that can lead to substantial improvements. By adopting these changes, individuals empower themselves to take control of their health and mitigate the risk of diabetes-related complications.
For many, lifestyle changes alone may not suffice in achieving target A1C levels, making medication management a key component of diabetes care. Understanding the various classes of diabetes medications, such as Metformin and GLP-1 receptor agonists, equips individuals with the knowledge necessary to engage in informed discussions with their healthcare providers about their treatment options.
In summary, the A1C test is a vital tool in the management of diabetes, guiding both diagnostic decisions and treatment strategies. By prioritizing regular testing, making informed lifestyle choices, and considering medication when necessary, individuals can significantly improve their health outcomes and lead healthier lives. Engaging with resources like T2DSolutions can further enhance this journey, providing valuable support and information to those navigating the complexities of diabetes management.



