Overview:
The top A1C guidelines for effective diabetes management emphasize maintaining an A1C level below 7% for most adults, while also recognizing the need for individualized targets based on personal health factors. The article supports this by highlighting the significant reduction in complications associated with lower A1C levels and advocating for a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and personalized medical strategies.
Introduction
The A1C test stands as a critical component in the management of diabetes, providing essential insights into average blood glucose levels over a period of two to three months. This measurement, expressed as a percentage, serves as an indicator of blood sugar control, with higher values suggesting an increased risk of serious health complications. As healthcare providers strive to tailor treatment plans for individuals with diabetes, understanding the nuances of A1C results becomes paramount.
This article delves into the significance of the A1C test:
- The latest guidelines for optimal levels
- The health implications of varying A1C results
- Ongoing debates within the medical community regarding target settings
- Effective strategies for achieving and maintaining optimal A1C levels
By exploring these facets, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how to navigate their diabetes management journey effectively.
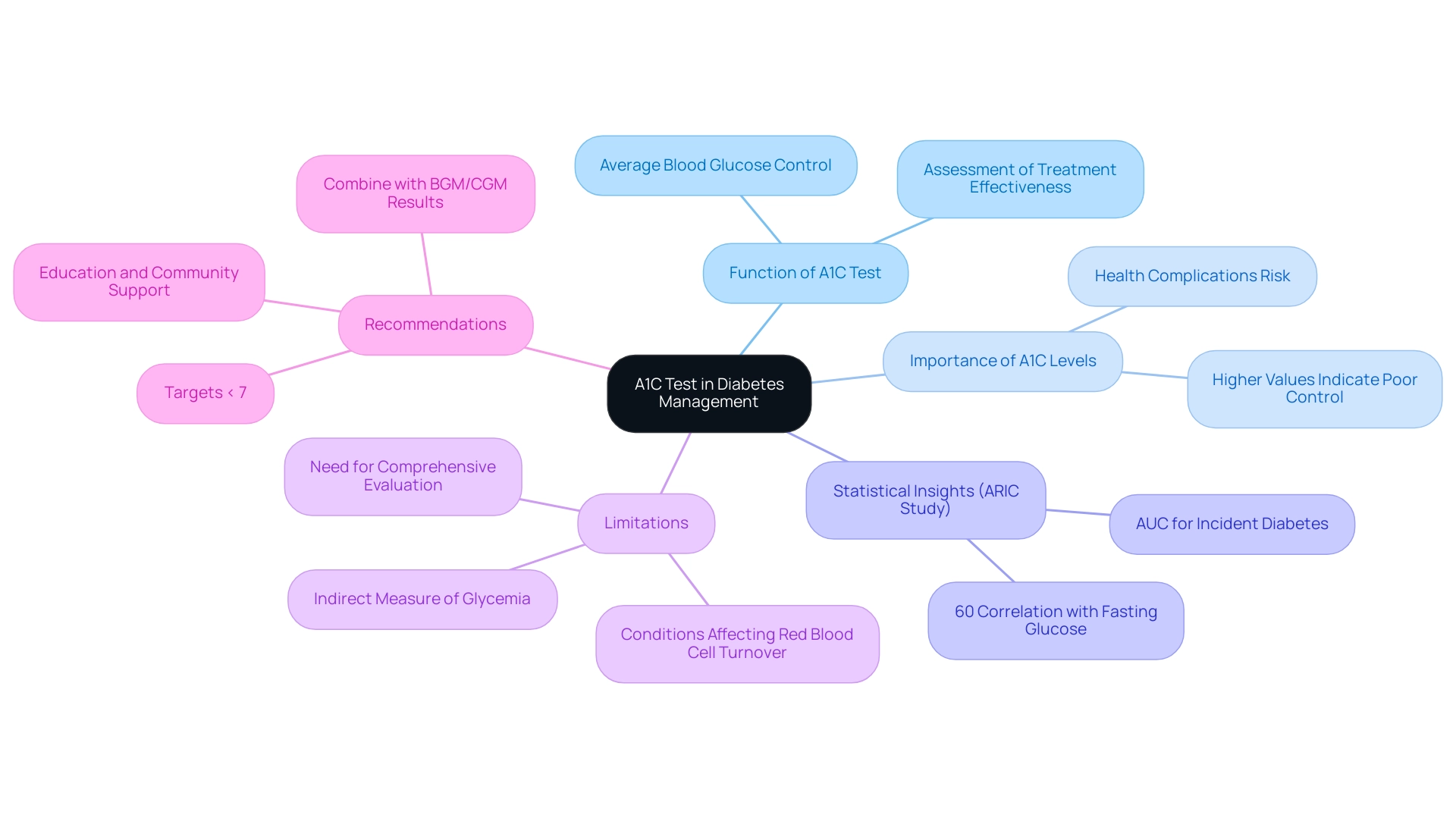
Understanding the A1C Test: A Cornerstone of Diabetes Management
The A1C test, or glycated hemoglobin test, functions as a crucial instrument in managing blood sugar by assessing average blood glucose readings over the prior two to three months. Expressed as a percentage, higher A1C values signify poorer blood sugar control, which can lead to serious health complications. This test is essential for healthcare providers in assessing the effectiveness of treatment strategies for blood sugar management.
Recent statistics highlight its relevance; for instance, in the ARIC study:
- 60% of participants with fasting glucose ≥126 mg/dl at baseline also had fasting glucose ≥126 mg/dl at the 3-year follow-up visit, demonstrating a significant correlation between fasting glucose levels and A1C results.
However, it is important to recognize the limitations of the A1C test, which is an indirect measure of average glycemia. Conditions affecting red blood cell turnover can lead to discrepancies in results, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive evaluation that includes results from blood glucose monitoring (BGM) and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM).
As researcher E.G. states, 'The A1C test is crucial, but it should not be the sole measure for assessing glycemic control.' At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to empowering individuals through education, community support, and innovative insights regarding health management.
Our resources include A1C guidelines recommending targets of below 7% for most adults with this condition, which can help in reducing the risk of complications. By comprehensively understanding A1C results and utilizing our educational materials and community forums, individuals are empowered to make informed decisions regarding lifestyle modifications and medication adjustments, ultimately aiming for improved health outcomes.
Latest A1C Guidelines: What You Need to Know
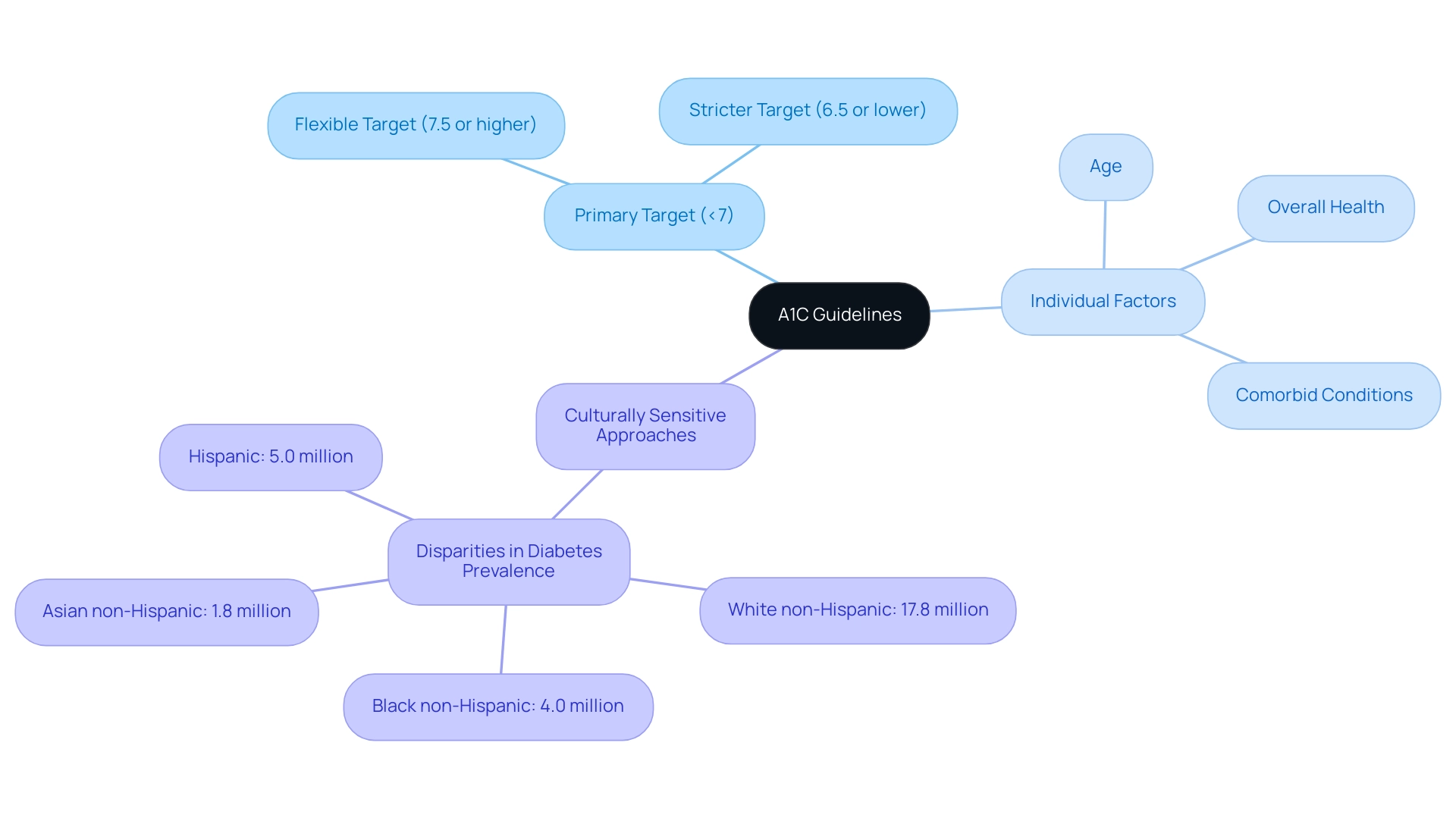
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your new comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support. As we introduce this platform, we acknowledge the significance of individualized blood sugar control. In accordance with the American Diabetes Association's 2024 A1C guidelines, the primary target for most adults living with the condition is established at less than 7%.
However, it is essential to customize these targets based on individual factors such as:
- Age
- Overall health
- Comorbid conditions
For some, a more flexible A1C target of 7.5% or higher might be appropriate, while others may benefit from more stringent goals of 6.5% or lower. Participating in conversations with healthcare experts regarding these particular goals is essential for creating a customized health strategy.
This method not only helps in effective blood sugar control but also improves overall well-being, reflecting the recent emphasis on personalized care in chronic condition treatment. Furthermore, statistics show significant disparities in diabetes prevalence among racial and ethnic groups, highlighting the need for culturally sensitive approaches. T2DSolutions aims to facilitate such discussions and provide support for achieving individualized A1C goals while adhering to A1C guidelines, ultimately improving health outcomes for all.
We invite you to subscribe to our platform for updates and to learn more about the resources and community support we will provide as we grow together in this journey.
Health Implications of A1C Levels: Risks and Complications
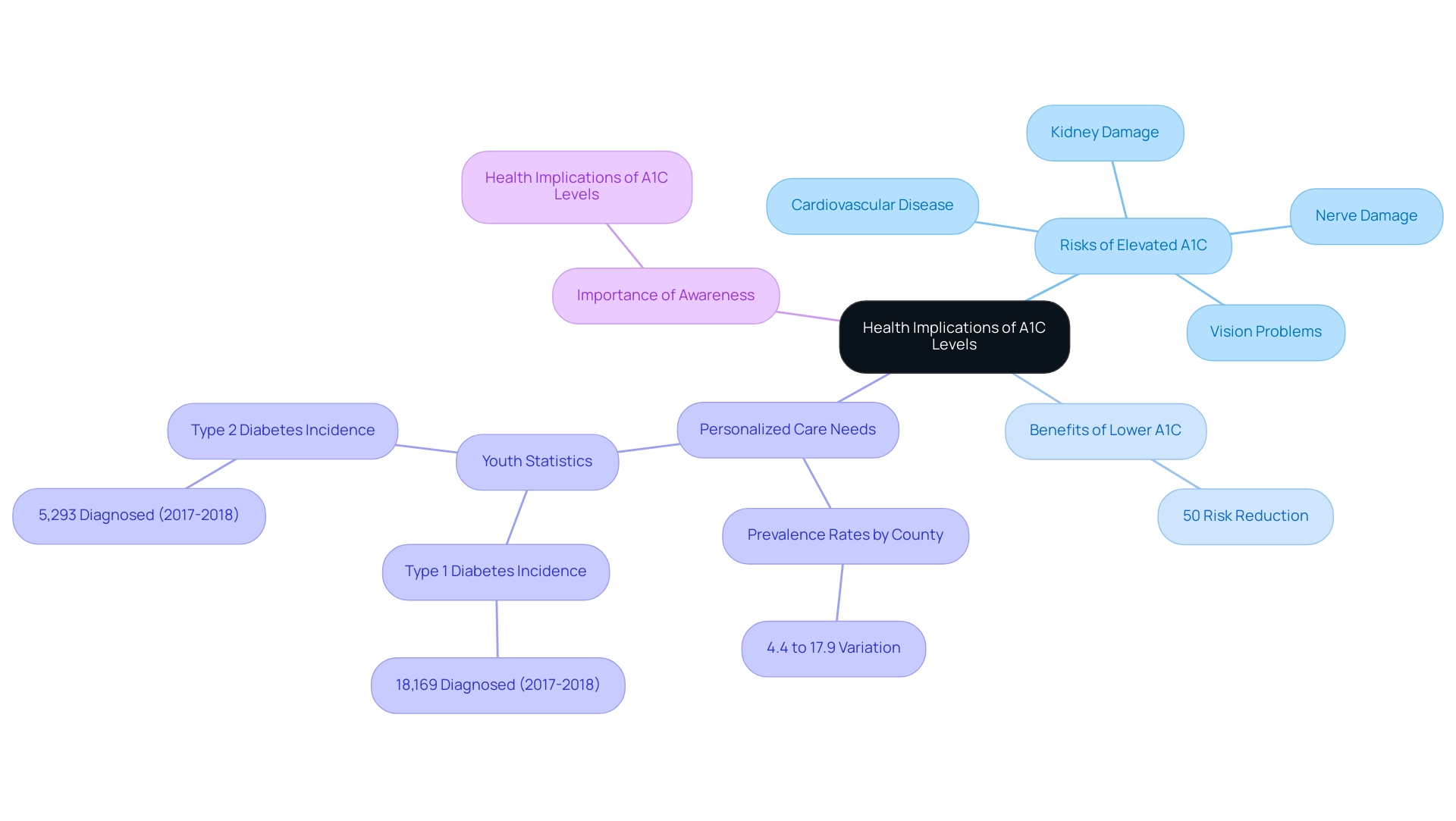
The management of A1C values in accordance with a1c guidelines is crucial to overall health, as elevated amounts are closely linked to a spectrum of serious complications. Notably, individuals with an A1C value exceeding 8% should follow the A1C guidelines, as they face a significantly heightened risk of developing conditions such as:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Kidney damage
- Nerve damage
- Vision problems
Recent analyses indicate that maintaining an A1C measurement below 7% in accordance with a1c guidelines can reduce the risk of these complications by as much as 50%.
This reduction highlights the essential importance of effective strategies for controlling blood sugar levels. T2DSolutions aims to be a comprehensive resource center for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education, providing essential information on managing A1C values effectively according to a1c guidelines. Moreover, diagnosed prevalence of blood sugar conditions among U.S. adults aged 20 years or older differs by county, ranging from 4.4% to 17.9%, emphasizing the necessity for personalized care in handling these conditions.
As indicated in a study with 29,629 participants, awareness of the health implications associated with A1C levels and the a1c guidelines is crucial for encouraging individuals to actively participate in their health care. The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study also highlights that data are model-adjusted incidence estimates, pointing to the increasing incidence rates of both type 1 and type 2 conditions among youth, with an estimated 18,169 children and adolescents diagnosed with type 1 condition in 2017-2018. Such findings serve as a reminder of the urgent need for vigilance in monitoring A1C according to a1c guidelines to avert potential complications.
Stay tuned for more resources on T2D Solutions as we launch our platform dedicated to assisting you on your health journey.
Controversies in A1C Guidelines: Understanding the Debate
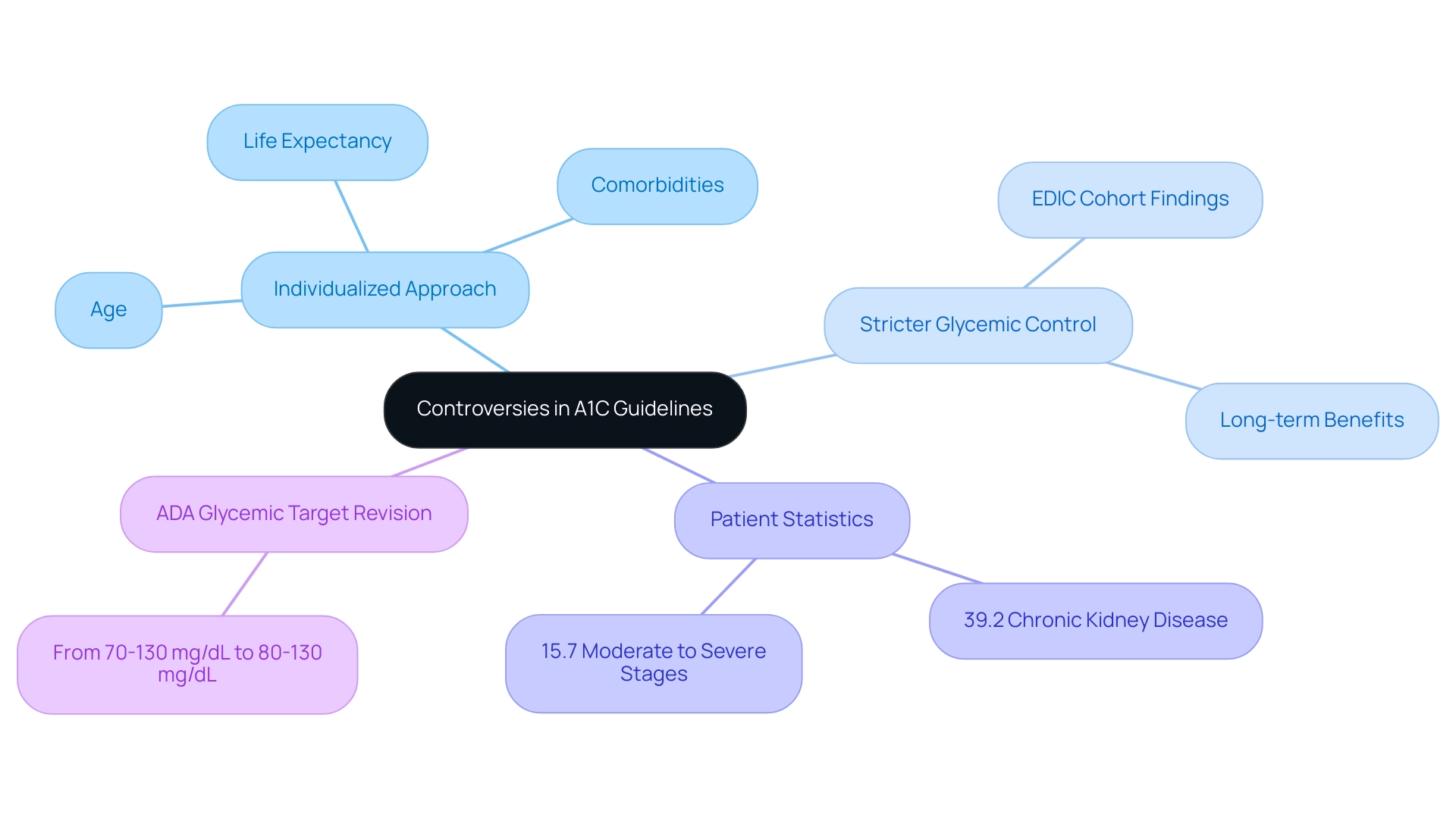
The discourse surrounding optimal A1C targets according to A1C guidelines for various populations remains a contentious issue among healthcare professionals. Many advocate for a more individualized approach to target setting, emphasizing that factors such as age, comorbidities, and life expectancy should inform these decisions. For instance, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) revised its preprandial glycemic target in 2015 from 70–130 mg/dL to 80–130 mg/dL to mitigate the risks associated with overtreatment.
This adjustment underscores the importance of customizing management strategies for the unique circumstances of each patient. Additionally, a small study found a highly statistically significant correlation between A1C and mean blood glucose in children with type 1 conditions, with a correlation coefficient of 0.7, highlighting the necessity of personalized A1C targets. Conversely, there are advocates who argue for stricter glycemic control to mitigate the long-term complications of the condition, as evidenced by findings from the EDIC cohort, which show that the benefits of intensive glycemic control persist for several decades and are associated with a modest reduction in all-cause mortality.
This debate emphasizes the necessity for personalized health plans that prioritize individual patient needs over a generic approach. As Elsayed NA expresses in the Standards of Care in Diabetes–2023, the significance of personalized oversight according to A1C guidelines cannot be overstated. Moreover, among U.S. adults aged 18 years or older diagnosed with this condition, 39.2% had chronic kidney disease, with 15.7% facing moderate to severe stages, highlighting the significant health risks linked to the illness and the need for continuous monitoring and care.
Ultimately, fostering an environment for ongoing dialogue among healthcare professionals is crucial to refine A1C targets and enhance patient outcomes. As T2DSolutions prepares to launch, it aims to serve as a vital resource hub for individuals managing Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes. T2DSolutions will offer a variety of educational resources, including guides on A1C guidelines, webinars featuring healthcare professionals, and community support forums where newly diagnosed patients can exchange experiences and strategies.
This comprehensive approach will empower patients to navigate their health journeys effectively and address the challenges associated with managing A1C values.
Strategies for Achieving Optimal A1C Levels
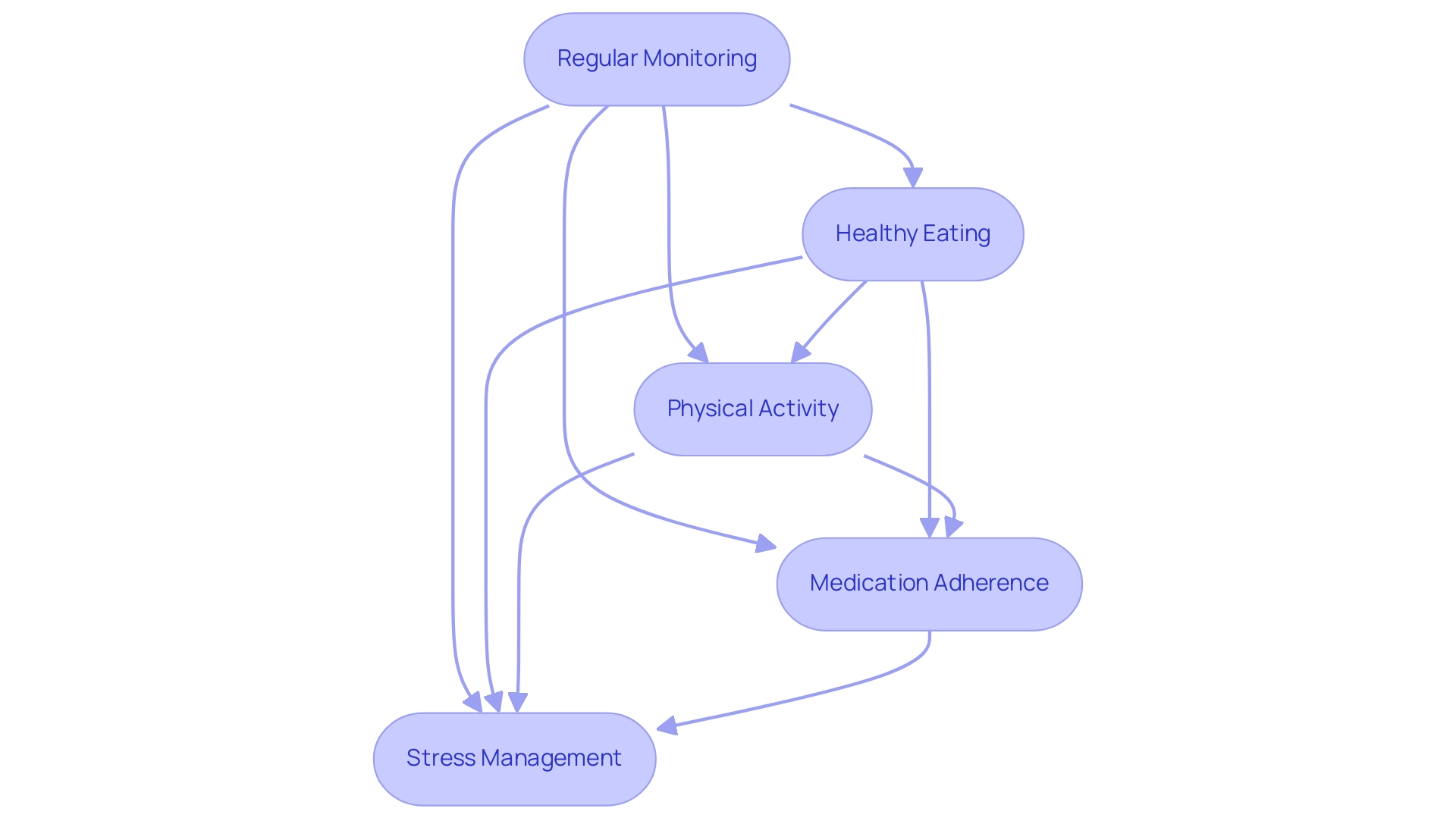
At T2DSolutions, we acknowledge that attaining optimal A1C values requires a multifaceted approach that follows a1c guidelines and includes both lifestyle changes and effective medical management. As a new resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 health education and community support, we aim to provide comprehensive guidance for newly diagnosed patients. Key strategies include:
-
Regular Monitoring: Frequent observation of blood glucose readings is essential. Understanding how various factors—such as food intake, physical activity, and medications—impact these readings empowers patients to make informed decisions about their diabetes management. T2DSolutions provides tools and resources to assist patients in monitoring their glucose amounts effectively.
-
Healthy Eating: Adopting a well-balanced diet that incorporates whole grains, a variety of fruits and vegetables, and lean proteins is crucial. It is equally important to restrict the consumption of processed foods and sugars, which can lead to spikes in blood glucose. Nutritionists emphasize that dietary choices play a vital role in maintaining glycemic control. T2DSolutions provides educational materials and meal planning resources to assist patients in making healthier food choices.
-
Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly is recommended to enhance insulin sensitivity and promote overall health. Recent studies indicate that structured exercise training can lead to an average weight loss of 3.7 kg, further benefiting glycemic control. T2DSolutions connects patients with community exercise programs and resources to support their physical activity goals.
-
Medication Adherence: Following prescribed medications as instructed is essential for effective control of the condition. Patients should openly communicate any concerns with their healthcare providers to ensure optimal treatment plans are in place. T2DSolutions encourages regular check-ins and provides resources to help patients stay on track with their medications.
-
Stress Management: Implementing stress-reduction techniques—such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep breathing exercises—can significantly influence blood sugar levels. Stress is recognized to worsen psychological insulin resistance, making stress control a vital aspect of glucose regulation. T2DSolutions offers workshops and resources to help patients learn effective stress management techniques, enabling individuals to make substantial progress towards achieving and maintaining their A1C goals as outlined in the a1c guidelines.
At T2DSolutions, we emphasize that intensive lifestyle interventions are often more effective than standard care in maintaining glycemic control, which aligns with the a1c guidelines that underscore the importance of these lifestyle modifications. Furthermore, a case study focusing on the impact of structured exercise on patients with type 2 conditions revealed significant improvements in lipid levels and body composition, indicating that exercise can enhance glycemic control without necessarily affecting body weight.
Overall, these strategies and insights, coupled with the support from T2 Solutions, provide crucial guidance for individuals striving to manage their diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is essential for effective diabetes management, as it provides vital insights into long-term blood glucose control. The recent guidelines emphasize maintaining A1C levels below 7% for most adults, tailored to individual health circumstances. Elevated A1C levels pose significant health risks, underscoring the importance of proactive management strategies to mitigate complications.
The ongoing debates among healthcare professionals regarding A1C targets highlight the necessity of personalized care. Factors such as age, comorbidities, and individual health conditions should guide treatment plans, ensuring that each patient receives the best possible care tailored to their unique needs. The strategies outlined—ranging from regular monitoring and healthy eating to physical activity and medication adherence—are crucial in achieving optimal A1C levels.
In conclusion, effectively managing A1C levels is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a combination of education, support, and individualized strategies. By leveraging resources like T2DSolutions, individuals can navigate their diabetes management journeys with confidence, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life. Prioritizing A1C management is not just about numbers; it’s about empowering individuals to take control of their health and well-being.



