Overview
This article explores the vital role of insulin in managing Type 2 diabetes, shedding light on various techniques that can help individuals navigate this condition. It's important to recognize that insulin resistance, which occurs when the body becomes less responsive to insulin, can lead to elevated blood sugar levels. This can understandably feel overwhelming.
To improve insulin sensitivity and overall health outcomes, lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise are essential. Alongside medical treatments, these adjustments can make a significant difference in managing your health. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Many have found success through small, manageable changes.
We encourage you to seek support and resources that resonate with you. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide comfort and guidance. You're taking a courageous step by seeking information, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
Type 2 diabetes is a growing global health concern that many are facing today. It is characterized by the body's inability to effectively utilize insulin, which can lead to dangerously high blood sugar levels. With millions affected worldwide, it’s understandable to feel overwhelmed. However, understanding the mechanisms behind insulin resistance and the critical management strategies available is essential for anyone navigating this complex condition.
What if the key to better health lies not just in medication, but in lifestyle changes that can significantly alter the course of diabetes? This thought can be both hopeful and daunting. This article delves into the intricacies of type 2 diabetes, exploring the vital role of insulin while offering actionable techniques to manage and potentially reverse the effects of this prevalent disease. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
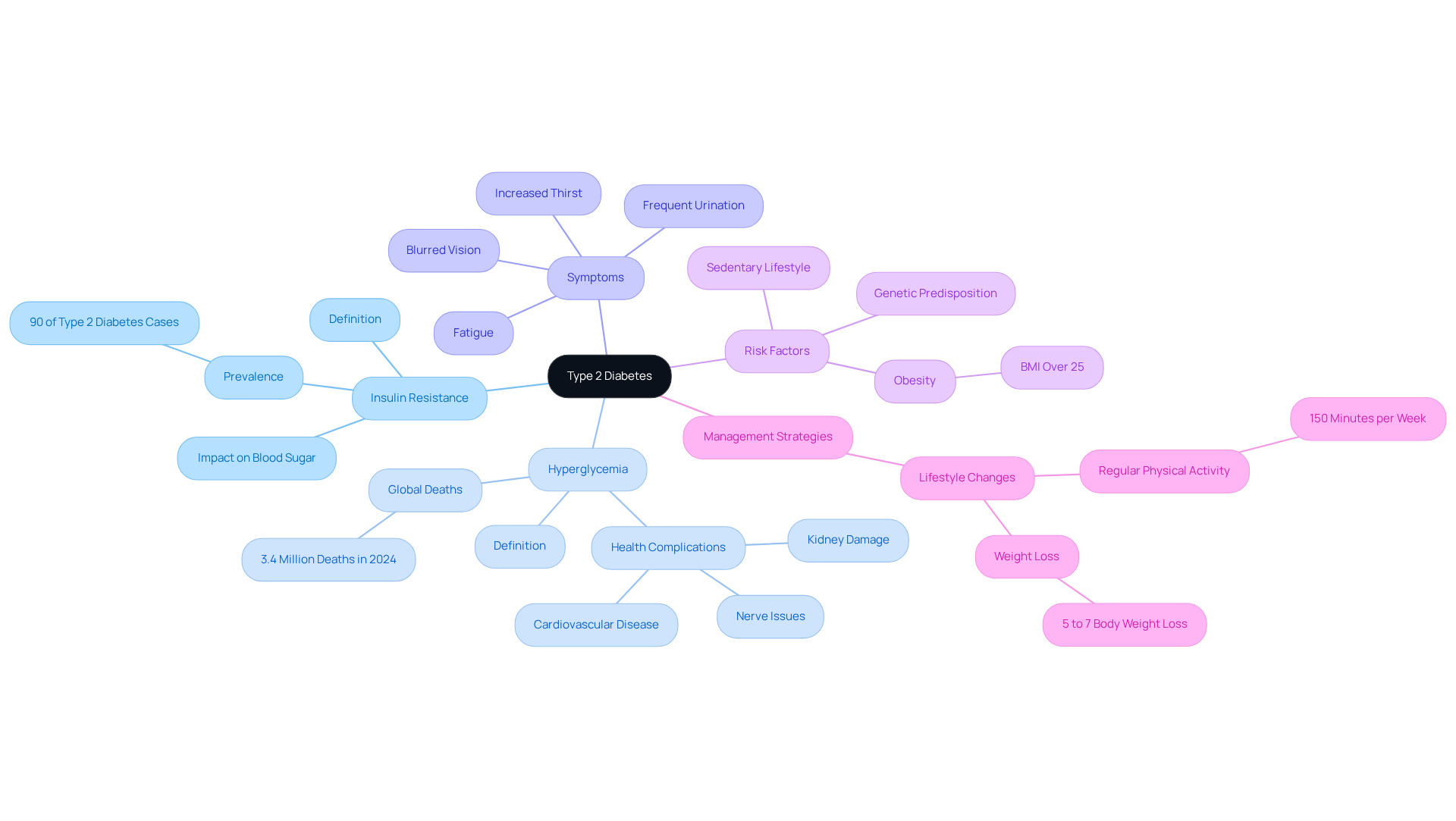
Define Type 2 Diabetes: Key Characteristics and Implications
Type 2 diabetes: insulin is a long-term issue characterized by hormone resistance, where the body does not utilize insulin effectively, leading to increased blood glucose levels. Understanding this condition is vital, as it can feel overwhelming.
-
Insulin Resistance: In this situation, your body's cells may not respond well to insulin. This means that your body has to produce even more insulin to keep blood sugar levels in check. It's important to note that about 90% of people with type 2 diabetes: insulin experience this type, and resistance to sugar regulation plays a significant role in its progression.
-
Hyperglycemia: When blood sugar levels remain high for too long, it can lead to serious health complications, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve issues. Effective management is crucial; after all, diabetes was responsible for 3.4 million deaths globally in 2024. You're not alone in facing this challenge.
-
Symptoms: Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Recognizing these signs early can help you seek timely intervention and management, which is so important.
-
Risk Factors: Factors like obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetic predisposition can significantly elevate your risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes. For instance, individuals with a body mass index (BMI) over 25 face a higher risk, as obesity is a major contributor to glucose resistance.
By understanding these characteristics, you can recognize type 2 diabetes: insulin early and implement effective management strategies. Recent research emphasizes the importance of lifestyle changes, such as engaging in regular physical activity—aiming for at least 150 minutes per week can greatly enhance insulin sensitivity and overall health outcomes. Real-world examples show that losing just 5% to 7% of body weight can lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, which translates to a loss of 10 to 14 pounds for someone weighing 200 pounds. Remember, by addressing these factors, you can take proactive steps toward managing your condition effectively. You're not alone in this journey, and support is available to help you every step of the way.
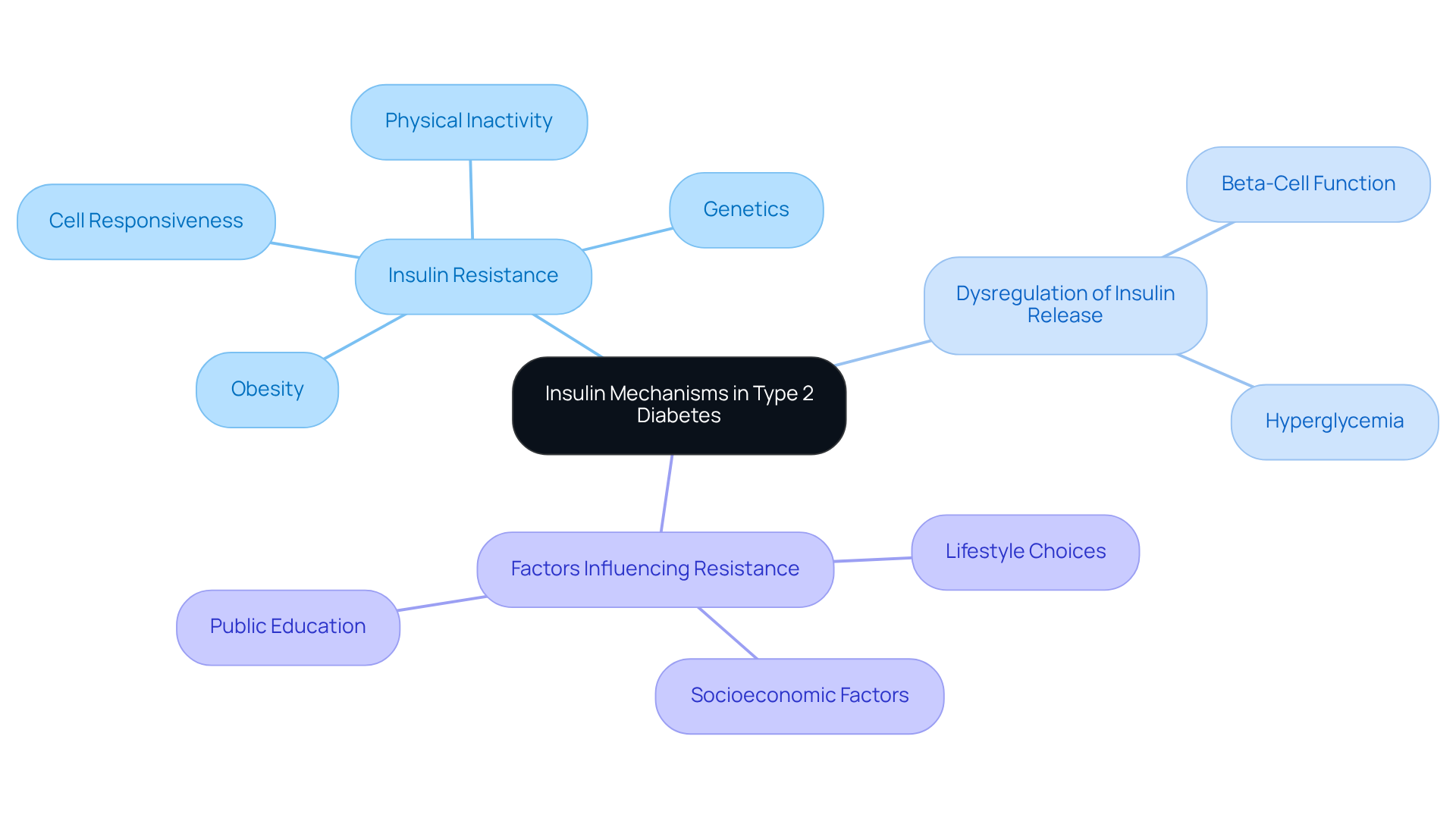
Explain Insulin Mechanisms: Resistance and Regulation in Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels, especially in the context of type 2 diabetes: insulin, where several key mechanisms are involved. At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive resources to help you understand these mechanisms and manage your diabetes effectively.
Insulin Resistance: In Type 2 Diabetes, it's common for cells in the muscles, fat, and liver to show decreased responsiveness to insulin. This condition often develops gradually and can be influenced by factors like obesity, physical inactivity, and genetic predispositions. As resistance to type 2 diabetes: insulin builds, your body requires more insulin to achieve the same glucose-reducing effect, which can lead to heightened blood sugar levels. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by this process, but know that you're not alone.
In response to insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes: insulin, your pancreas works hard to produce additional insulin to maintain normal blood glucose levels. While this mechanism can initially help manage blood sugar, it may lead to pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction over time. Studies indicate that nonobese individuals with type 2 diabetes often face challenges with this compensatory response, highlighting the importance of personalized treatment strategies. Remember, seeking tailored support can make a significant difference in your management journey.
Dysregulation of Insulin Release: As your condition progresses, the pancreas may struggle to produce enough insulin, worsening hyperglycemia. This dysregulation is often linked to reduced beta-cell function, which can result from prolonged exposure to elevated insulin levels and glucose toxicity. Understanding these dynamics is essential for creating effective interventions and management strategies for type 2 diabetes: insulin. We are here to support you in navigating these complexities.
Understanding these mechanisms not only helps you comprehend type 2 diabetes: insulin better but also guides the creation of targeted treatments and lifestyle changes aimed at improving insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health. At T2DSolutions, we are committed to supporting you on your journey to better health through education and community resources. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we are here to help you every step of the way.
Implement Management Techniques: Lifestyle Changes and Treatment Options
Effectively managing type 2 diabetes: insulin requires a multifaceted approach that integrates lifestyle changes with medical treatments. It’s important to remember that you’re not alone in this journey; support is available every step of the way.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a colorful array of fruits and vegetables. Reducing processed foods and sugars is vital, as research shows that dietary patterns significantly impact diabetes risk. For instance, embracing a Mediterranean diet has been associated with a lower incidence of type 2 diabetes.
- Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week, such as brisk walking or cycling. Regular physical activity can enhance insulin sensitivity and may cut the risk of developing type 2 diabetes: insulin by nearly 50%. It’s understandable to feel overwhelmed, but starting small can make a big difference.
- Weight Management: Losing just 5% to 7% of your body weight can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar control and overall health. In fact, a weight-management trial revealed an 86% remission rate in individuals with type 2 diabetes: insulin, who lost 15 kg or more. Every little bit counts, and your efforts matter.
Treatment Options:
- Medications: Metformin is often the first medication prescribed to help lower blood sugar levels effectively. Depending on individual needs and responses, other oral and injectable medications may also be considered. Remember, it’s important to communicate openly with your healthcare provider about what works best for you.
- Type 2 diabetes: insulin therapy is essential for some individuals to maintain optimal blood sugar levels, especially when other medications are not sufficient. This is a common step, and many find it beneficial in managing their condition.
By implementing these management techniques, individuals with type 2 diabetes: insulin can achieve improved health outcomes and enhance their quality of life. Remember, seeking support and resources can make this journey easier, and you are not alone in facing these challenges.

Conclusion
Understanding type 2 diabetes is crucial for effectively managing this complex condition. This disease is primarily characterized by insulin resistance, which leads to elevated blood glucose levels and a host of potential health complications. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but recognizing the symptoms early and understanding the risk factors can empower you to take proactive steps towards better health.
Key insights emphasize the importance of lifestyle changes. Adopting a balanced diet, increasing physical activity, and achieving weight management are essential strategies. These changes not only improve insulin sensitivity but also significantly reduce the risk of developing severe complications associated with type 2 diabetes. Additionally, medication options, including metformin and insulin therapy, play a critical role in managing blood sugar levels, underscoring the need for personalized treatment plans.
Ultimately, the journey towards managing type 2 diabetes requires support and commitment. By embracing lifestyle modifications and collaborating with healthcare providers, you can take charge of your health and potentially reverse the effects of this condition. Remember, every small step counts. With the right resources and community support, a healthier life is within reach. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a long-term condition characterized by insulin resistance, where the body does not utilize insulin effectively, leading to increased blood glucose levels.
What is insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance occurs when the body's cells do not respond well to insulin, requiring the body to produce more insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. This type of resistance is experienced by about 90% of people with type 2 diabetes.
What are the health risks associated with hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar levels, can lead to serious health complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve issues.
What are the common symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes?
Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Recognizing these signs early can help with timely intervention and management.
What are the risk factors for developing Type 2 Diabetes?
Risk factors include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetic predisposition. Individuals with a body mass index (BMI) over 25 are at a higher risk, as obesity significantly contributes to glucose resistance.
How can lifestyle changes impact Type 2 Diabetes management?
Engaging in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes per week, can greatly enhance insulin sensitivity and overall health outcomes.
How much weight loss can lower the risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes?
Losing just 5% to 7% of body weight can lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, which translates to a loss of 10 to 14 pounds for someone weighing 200 pounds.
What support is available for managing Type 2 Diabetes?
There are various support systems available to help individuals manage their condition effectively, including healthcare professionals, support groups, and lifestyle change programs.



