Overview:
The article addresses how alcohol consumption can impact A1C levels and overall diabetes management for individuals with diabetes. It highlights that moderate alcohol intake may have beneficial effects on A1C levels, while excessive consumption poses risks such as hypoglycemia, emphasizing the importance of informed choices and monitoring blood glucose levels to maintain optimal health.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of diabetes management requires a comprehensive understanding of various factors, including the critical role of A1C levels. A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, serves as a vital indicator of average blood sugar control over the preceding months, directly influencing treatment decisions and health outcomes.
With diabetes on the rise, particularly Type 2 diabetes, the importance of monitoring A1C levels cannot be overstated.
This article delves into the relationship between A1C levels and alcohol consumption, offering insights into how individuals with diabetes can make informed choices while enjoying social occasions.
By exploring the impact of different types of alcoholic beverages and providing practical management tips, this piece aims to empower readers with the knowledge needed to maintain stable blood sugar levels and enhance their overall diabetes care.
Understanding A1C: What It Measures and Its Importance for Diabetics
A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, is an essential biomarker that assesses average blood glucose concentrations over the prior two to three months. Expressed as a percentage, elevated A1C readings indicate suboptimal blood sugar control, which can lead to serious health complications. For individuals diagnosed with this condition, a common target is to maintain an A1C level below 7%.
This benchmark is essential not only for assessing the effectiveness of various management strategies—such as dietary adjustments, physical activity, and adherence to prescribed medication—but also for guiding future treatment decisions. In light of the increasing prevalence of this condition, T2D Solutions is launching as a comprehensive resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 education and community support. Our platform will provide newly diagnosed patients with essential information on A1C monitoring, empowering them to make informed decisions that enhance their overall health management.
Recent findings indicate a concerning rise in the age-adjusted prevalence of both total and diagnosed conditions related to blood sugar from 1999–2000 to August 2021–August 2023, based on a sample size of 2,938, underscoring the necessity of diligent A1C monitoring. Additionally, the case study titled 'Lifelong Screening for Diabetes Post-GDM' highlights that individuals diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) should undergo lifelong screening for prediabetes and type 2 disorders, emphasizing the role of A1C monitoring in early intervention and treatment. Comprehending how lifestyle factors, including A1C alcohol consumption, influence A1C readings is essential, and T2D Solutions is dedicated to offering resources that assist patients in this journey.
As emphasized by Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H., 'The age-adjusted prevalence of total and diagnosed diabetes increased between 1999–2000 and August 2021–August 2023,' which highlights the critical need for continuous education and proactive management strategies to combat the growing diabetes epidemic.
The Impact of Alcohol on A1C Levels and Diabetes Control
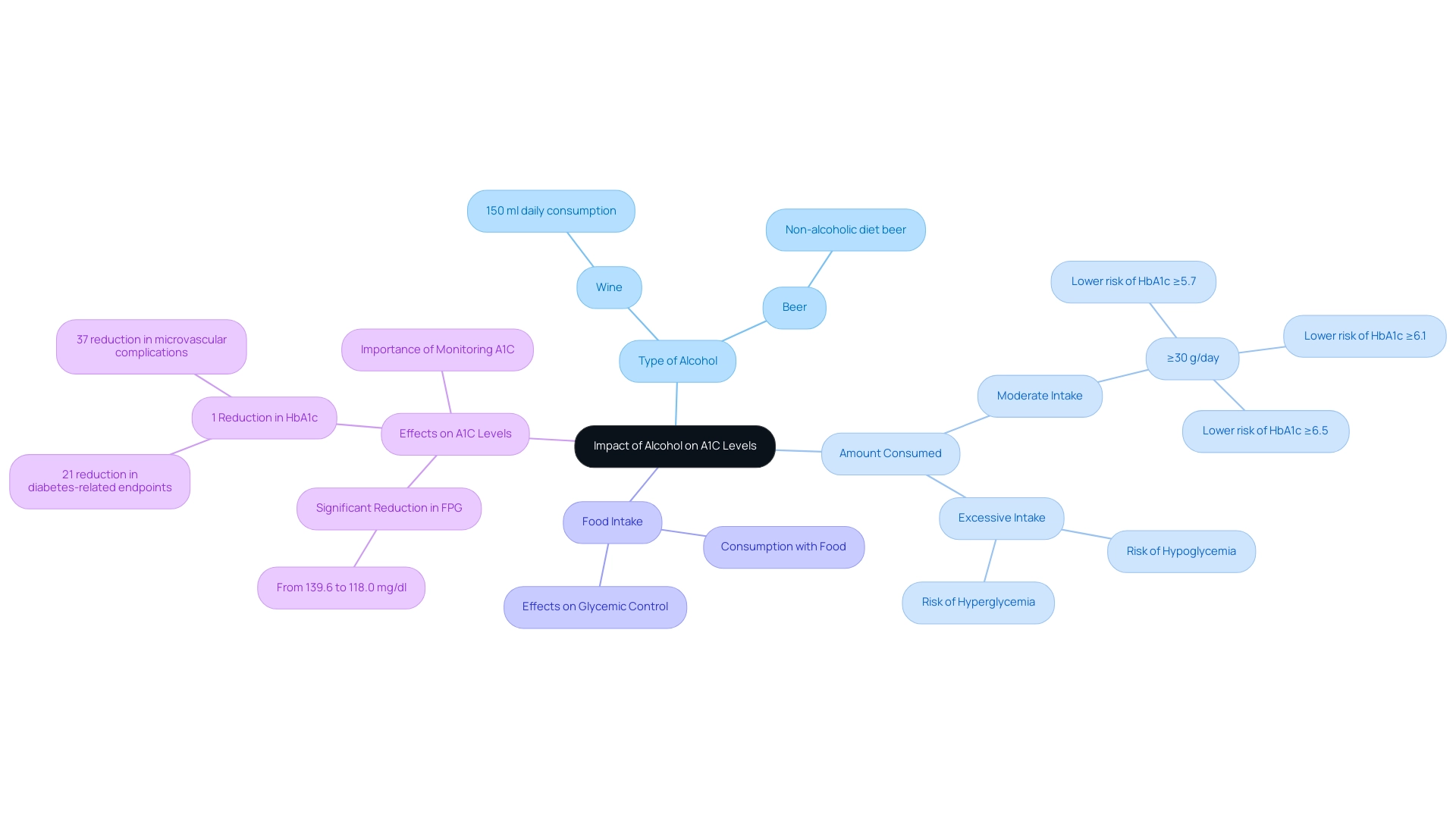
Alcohol affects blood glucose concentrations in various manners, particularly a1c alcohol, mainly influenced by the kind of drink, the amount taken, and whether it is consumed with food. Research suggests that moderate beverage consumption can have a nuanced effect on A1C levels, with a study indicating that 13.8% of subjects had a drink intake of ≥30 g/day, which was associated with a lower risk of having HbA1c levels at thresholds of ≥5.7%, ≥6.1%, and ≥6.5% compared to abstainers, particularly in relation to a1c alcohol. However, excessive intake of beverages with a1c alcohol may lead to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), thus introducing variability in managing blood sugar levels.
For example, a multicenter randomized trial assessed the glycemic effects of moderate beverage consumption among individuals with type 2 blood sugar issues, revealing that those who consumed 150 ml of wine daily experienced a significant reduction in fasting plasma glucose levels related to a1c alcohol—from 139.6 to 118.0 mg/dl—while the control group showed no notable change. Moreover, patients with higher baseline A1C values demonstrated more pronounced improvements regarding a1c alcohol. Furthermore, it is important to note that a 1% reduction in HbA1c is associated with a 21% reduction in the risk of any diabetes-related endpoint and a 37% reduction in the risk of microvascular complications.
In general, it is crucial for diabetics to consistently check their A1C readings and collaborate with healthcare providers to create a tailored management strategy that considers the impact of a1c alcohol on their overall condition. As T2DSolutions launches as a new resource hub for education on diabetes-related issues, it will offer valuable insights and support regarding a1c alcohol effects on blood glucose management, helping patients navigate their health journey effectively.
Choosing the Right Alcohol: Options for Diabetics
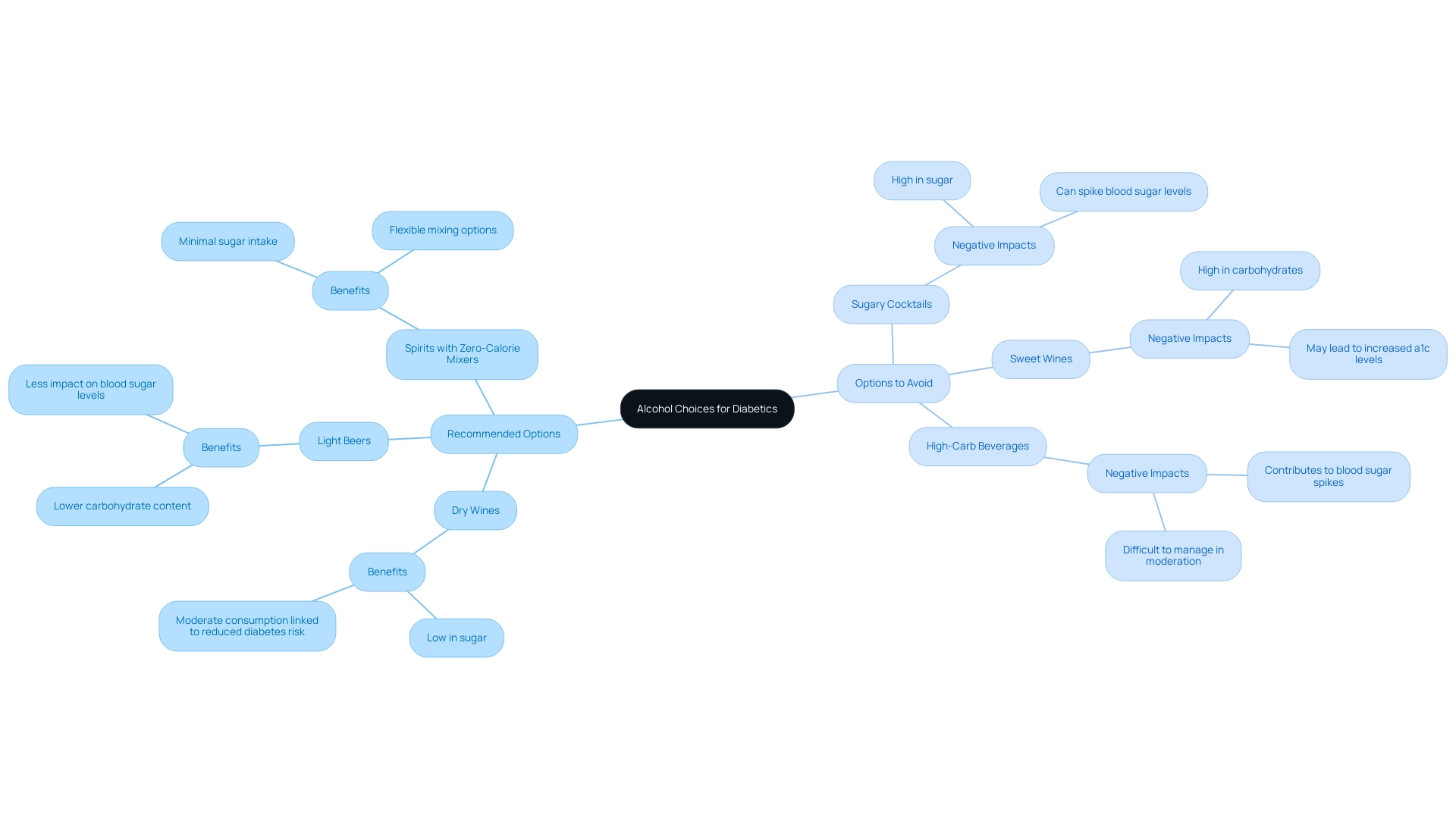
For individuals handling diabetes, choosing the appropriate alcoholic drinks, particularly regarding a1c alcohol, is essential for keeping blood glucose stable. It is advisable to choose options that are lower in sweeteners and carbohydrates to help maintain healthy a1c alcohol levels. Dry wines, light beers, and spirits mixed with zero-calorie mixers are generally considered the best choices when considering a1c alcohol levels.
Conversely, sugary cocktails, sweet wines, and beverages high in carbohydrates should be avoided, as they can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels, negatively impacting a1c alcohol. A comprehensive meta-analysis titled 'Meta-Analysis of Alcohol Consumption and Type 2 Diabetes Risk' aimed to investigate the relationship between alcohol consumption and the risk of developing type 2 sugar intolerance. The analysis indicated that moderate consumption—especially of wine—was associated with a significant reduction in the risk of diabetes-related issues, with men experiencing a 30% reduction (RR 0.72) and women a 32% reduction (RR 0.68).
This highlights the potential benefits of certain alcoholic beverages, especially concerning a1c alcohol, when consumed mindfully. As Joe Leech, MS, states, 'Choosing low-sugar options can be an effective strategy for managing blood sugar levels while enjoying social occasions.' Additionally, reading labels for sugar content and being mindful of portion sizes can further assist in managing beverage consumption effectively.
For additional advice and resources on handling blood sugar issues, including beverage consumption strategies, visit T2DSolutions, your all-encompassing source for Type 2 and Type 3 glucose management education and community assistance. Making informed choices is foundational to managing blood sugar conditions, and T2 Solutions is here to help you navigate these decisions.
Risks of Alcohol Consumption for Diabetics: What You Need to Know
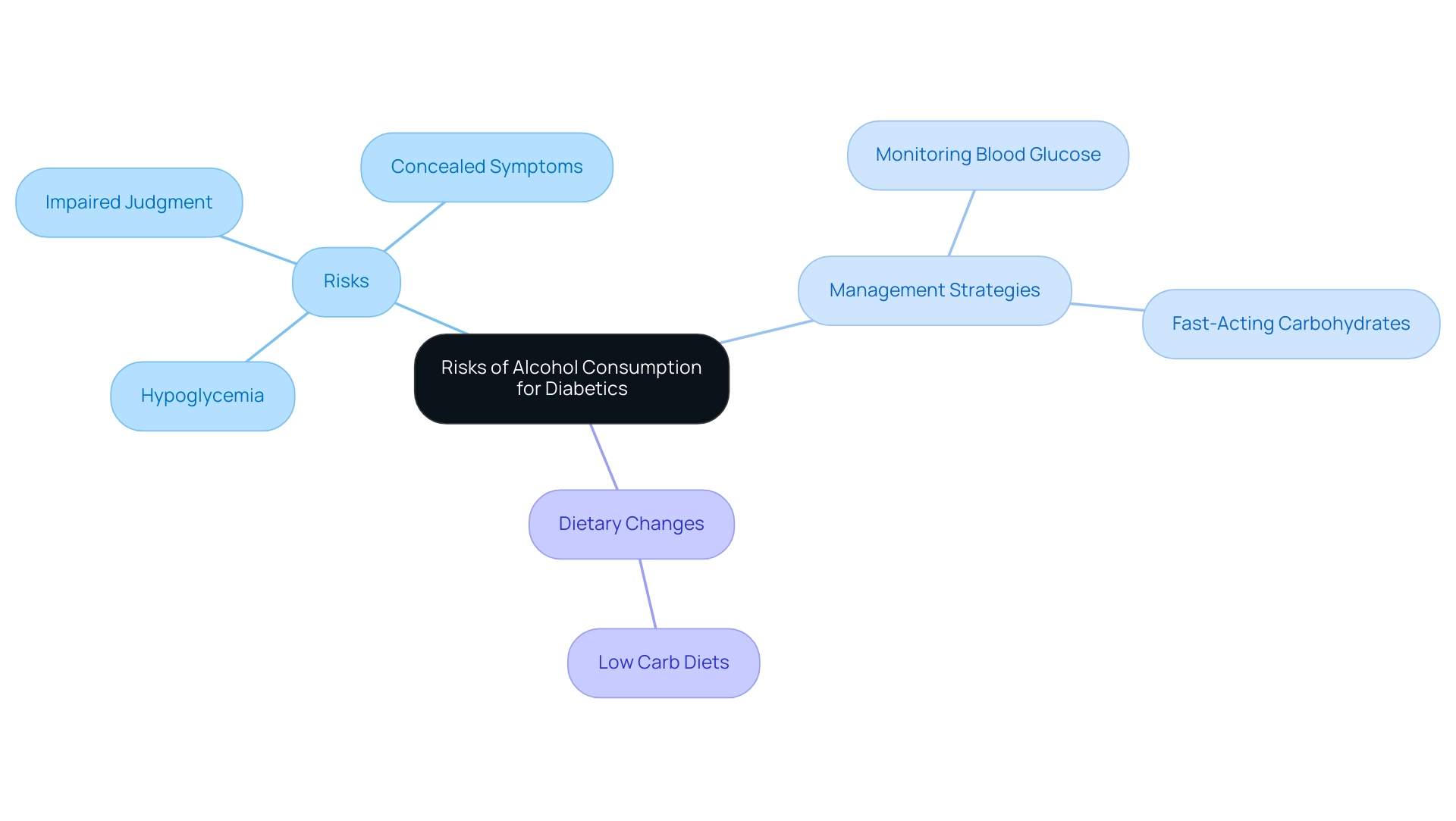
As part of T2D Solutions, a new resource hub dedicated to diabetes education and community support, it is important to understand the distinct risks associated with beverage consumption for individuals with diabetes. Alcohol can impair judgment and significantly decrease blood glucose levels, which can affect a1c alcohol levels, leading to hypoglycemia. A significant issue is that beverages may conceal the signs of low blood levels, making it difficult to identify when prompt action is needed.
Recent studies, categorized based on 13 studies from Asian populations and 25 studies from non-Asian populations, emphasize the concerning frequency of hypoglycemia incidents linked to beverage consumption among diabetics. Authorities such as Mary Ann Emanuele, M.D., highlight the significance of attentiveness, asserting, 'People with this condition need to be highly conscious of how a1c alcohol can influence their blood glucose, as the hazards of hypoglycemia can be serious.' Consequently, it is essential for diabetics to keep track of their blood glucose amounts carefully when consuming beverages.
Additionally, having a source of fast-acting carbohydrates on hand can counteract potential hypoglycemia. This proactive strategy can assist in reducing the risks linked to beverage consumption and aid in overall management of blood sugar levels. Moreover, dietary changes, like those recommended in the case study on low carb diets, may also contribute to managing the effects of spirits on blood sugar readings, highlighting the significance of a holistic approach to health management.
For more insights and resources on managing diabetes-related issues, we encourage you to subscribe to T2D Solutions to stay updated on new content.
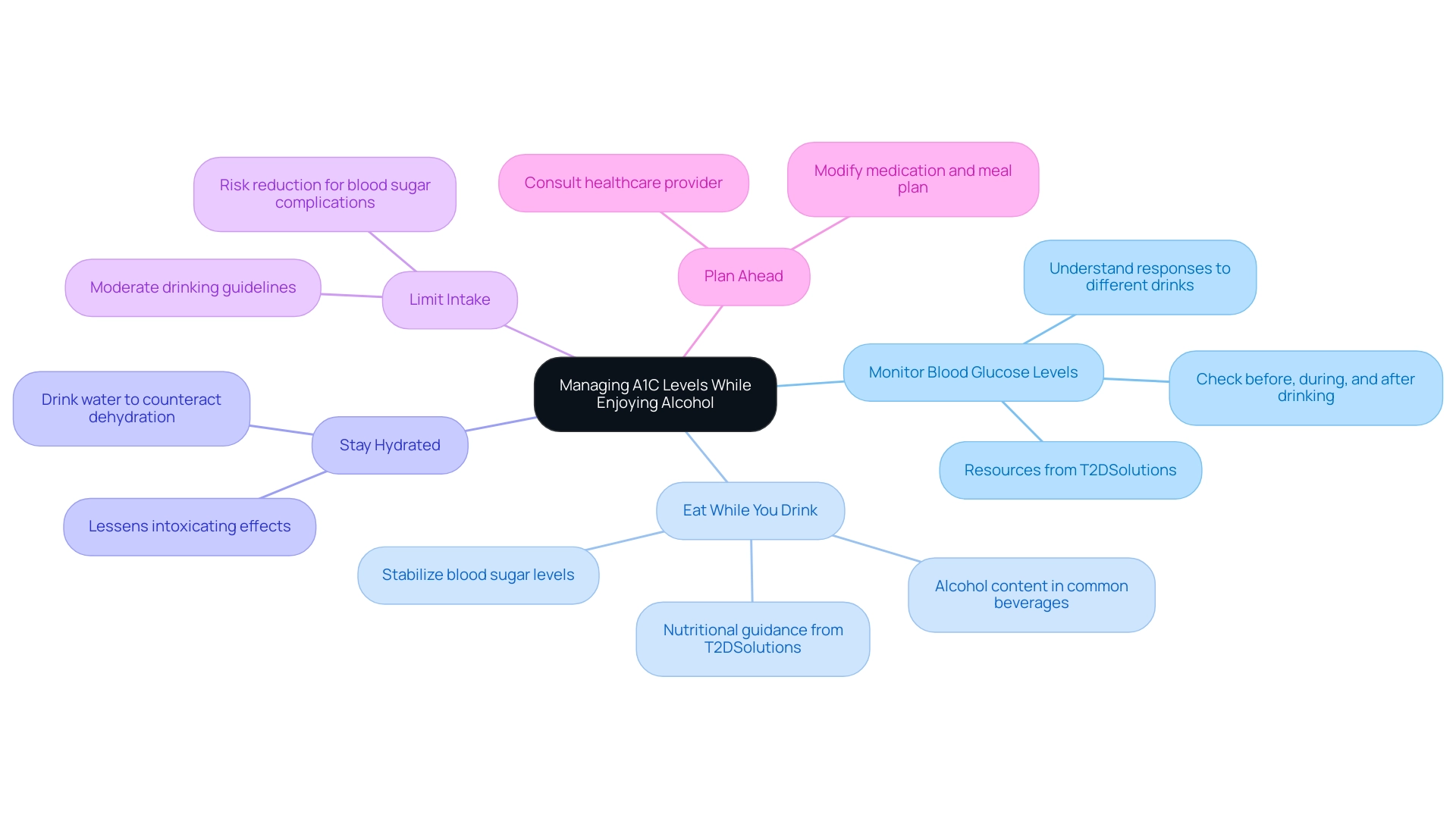
Tips for Managing A1C Levels While Enjoying Alcohol
To effectively manage A1C levels and A1C alcohol consumption while enjoying beverages, it is essential to implement the following strategies, supported by resources from T2DSolutions, your comprehensive hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education:
-
Monitor Blood Glucose Levels:
Regularly check your blood glucose before, during, and after drinking. This practice will help you understand your body's responses to various alcoholic beverages, as the impact of A1C alcohol levels can vary between different drinks.
T2DSolutions will offer insights into the ethanol levels in typical drinks and the impact of A1C alcohol through comprehensive articles and guides, directing your decisions to assist you in tracking your blood glucose effectively. -
Eat While You Drink:
Consuming food alongside beverages can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
T2DSolutions will offer nutritional guidance, including meal planning resources that emphasize the importance of carbohydrates and proteins in your meals. -
Stay Hydrated:
Adequate hydration is crucial; drinking water can help counteract dehydration and lessen the intoxicating effects of beverages. -
Limit Intake:
Adhere to moderate drinking guidelines, which recommend a maximum of one drink per day for women and two for men. This approach helps reduce the risk of complications associated with managing blood sugar levels, particularly in relation to A1C alcohol. -
Plan Ahead:
If you expect to drink, consult your healthcare provider to modify your blood sugar medication and meal plan accordingly. This preparation is vital for maintaining optimal glycemic control.
Adopting these practices enables individuals with blood sugar issues to engage in social situations without compromising their health. According to recent studies, only 25.5% of patients following SMBG recommendations consume less than 0.1 drinks, while 22.7% consume between 0.1–0.9 drinks, 21.5% consume 1–1.9 drinks, and 20.4% consume 2–2.9 drinks. This emphasizes the significance of informed decisions in beverage consumption.
As noted by I.C.S., 'However, more intervention studies with a longer intervention period are necessary to confirm the results,' emphasizing the need for ongoing research to enhance consumption strategies for individuals with blood sugar issues. By being proactive and informed, individuals can successfully navigate the complexities of alcohol consumption and health management, including understanding A1C alcohol, with T2D Solutions as their trusted resource. Be sure to subscribe to T2D Solutions to stay updated on the latest resources and support available for your diabetes management journey.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between A1C levels and alcohol consumption is vital for effective diabetes management. A1C serves as a key indicator of blood sugar control, and maintaining levels below the recommended threshold can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. The nuances of how different types of alcohol can affect blood sugar levels highlight the importance of making informed choices. Moderate alcohol intake may even offer some benefits, but excessive consumption poses serious risks, including hypoglycemia.
Choosing the right alcoholic beverages—such as dry wines or light beers—while avoiding sugary options can help manage blood sugar levels effectively. Additionally, implementing strategies like:
- Monitoring blood sugar before and after drinking
- Eating while consuming alcohol
- Staying hydrated
are essential practices for individuals with diabetes. Each of these steps contributes to a proactive approach to managing A1C levels without sacrificing social enjoyment.
As diabetes continues to be a pressing health concern, resources like T2DSolutions play a crucial role in providing education and support for those navigating these challenges. By staying informed and making mindful choices, individuals can successfully balance their social lives with their health needs, ensuring better outcomes in their diabetes management journey.



