Overview
This article highlights the definitions and significance of A1C (hemoglobin A1C) and eAG (estimated average glucose) in managing diabetes, focusing on how they help assess blood sugar control. A1C reflects average blood sugar levels over two to three months, which can feel overwhelming. On the other hand, eAG provides a more relatable daily glucose average, making it easier to understand your health journey.
Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes are crucial steps toward achieving optimal health outcomes for individuals with diabetes. It's understandable to feel a mix of emotions as you navigate this path. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way, encouraging you to share your experiences and connect with others who understand your challenges. Together, we can foster a community of support and understanding.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding key metrics like A1C and estimated average glucose (eAG) is crucial for effective care. A1C serves as a vital indicator of long-term blood sugar control, while eAG translates this percentage into a more relatable daily average. This translation makes it easier for you to grasp your glucose levels. As healthcare professionals increasingly emphasize these metrics, the conversation around diabetes care is evolving. Innovative approaches and lifestyle changes are at the forefront, highlighting the importance of your journey.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by the implications of abnormal results, which can be significant. This underscores the need for proactive management strategies to prevent complications and enhance your overall health. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, measurements, relationships, and lifestyle adjustments associated with A1C and eAG. Our goal is to empower you to take charge of your diabetes journey, reminding you that you're not alone in this experience.
What Are A1C and eAG? Defining Key Terms in Diabetes Management
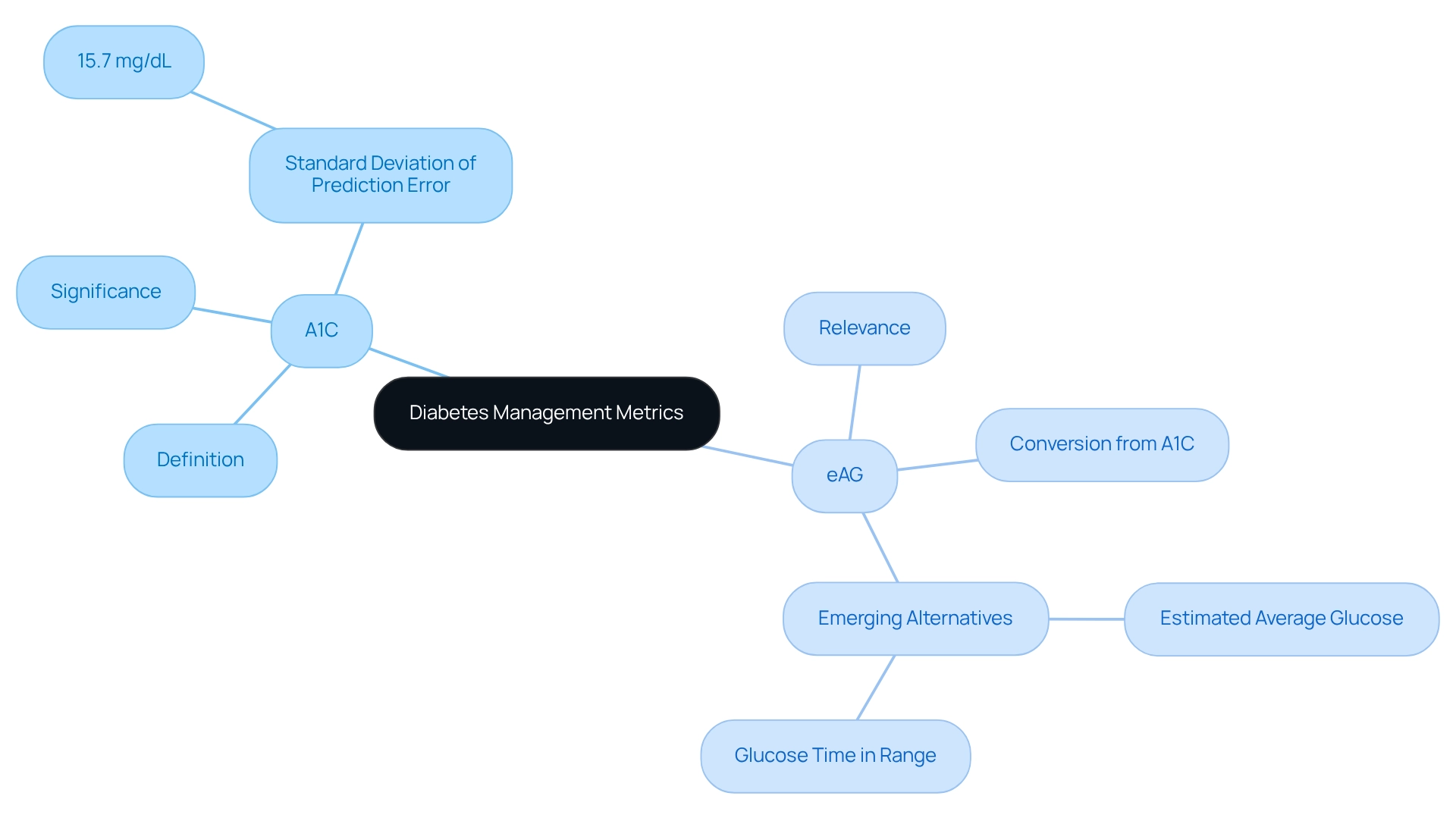
A1C, or hemoglobin A1C, is an important blood test known as a1c eag that assesses the average blood sugar readings over the previous two to three months. It serves as a vital marker for blood sugar management, reflecting how effectively an individual's diabetes is being controlled. On the other hand, eAG, or estimated average glucose, converts the A1C percentage into a daily average blood glucose level, expressed in familiar units such as mg/dL or mmol/L. This conversion assists individuals in better comprehending their glucose management in a more relatable context.
Both A1C and a1c eag are essential metrics for evaluating long-term glucose control and informing treatment decisions. It's understandable to feel uncertain about these numbers, but recent statistics show that the standard deviation of prediction error for the relationship between A1C and average glucose (AG) is approximately 15.7 mg/dL. This highlights the variability that can occur in individual assessments, underscoring the significance of consistent monitoring and consultation with healthcare professionals to customize management strategies effectively.
Emerging discussions within the medical community are exploring alternatives to A1C as the primary measure of glycemic control, such as estimated average glucose and glucose time in range. These alternatives may offer a more comprehensive view of blood sugar management, although they are not yet universally accessible to all patients. As blood sugar management progresses, understanding the implications of a1c eag is essential for achieving optimal health outcomes.
Vivian Fonseca emphasizes, "Translating the hemoglobin A1C assay..." highlighting the importance of A1C testing in managing blood sugar levels. In 2025, the importance of a1c eag in managing blood sugar conditions continues to expand, with healthcare professionals emphasizing their roles in directing treatment strategies and enhancing patient education. Real-world examples illustrate how these metrics impact diabetes management, empowering individuals to take charge of their health through informed decision-making. However, it's crucial to remember that the information provided here is not medical advice and should not be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition.
You are encouraged to consult your doctor or healthcare team for personalized health needs. You're not alone in this journey; support is available every step of the way.
How A1C Levels Are Measured and What They Reveal About Blood Sugar Control
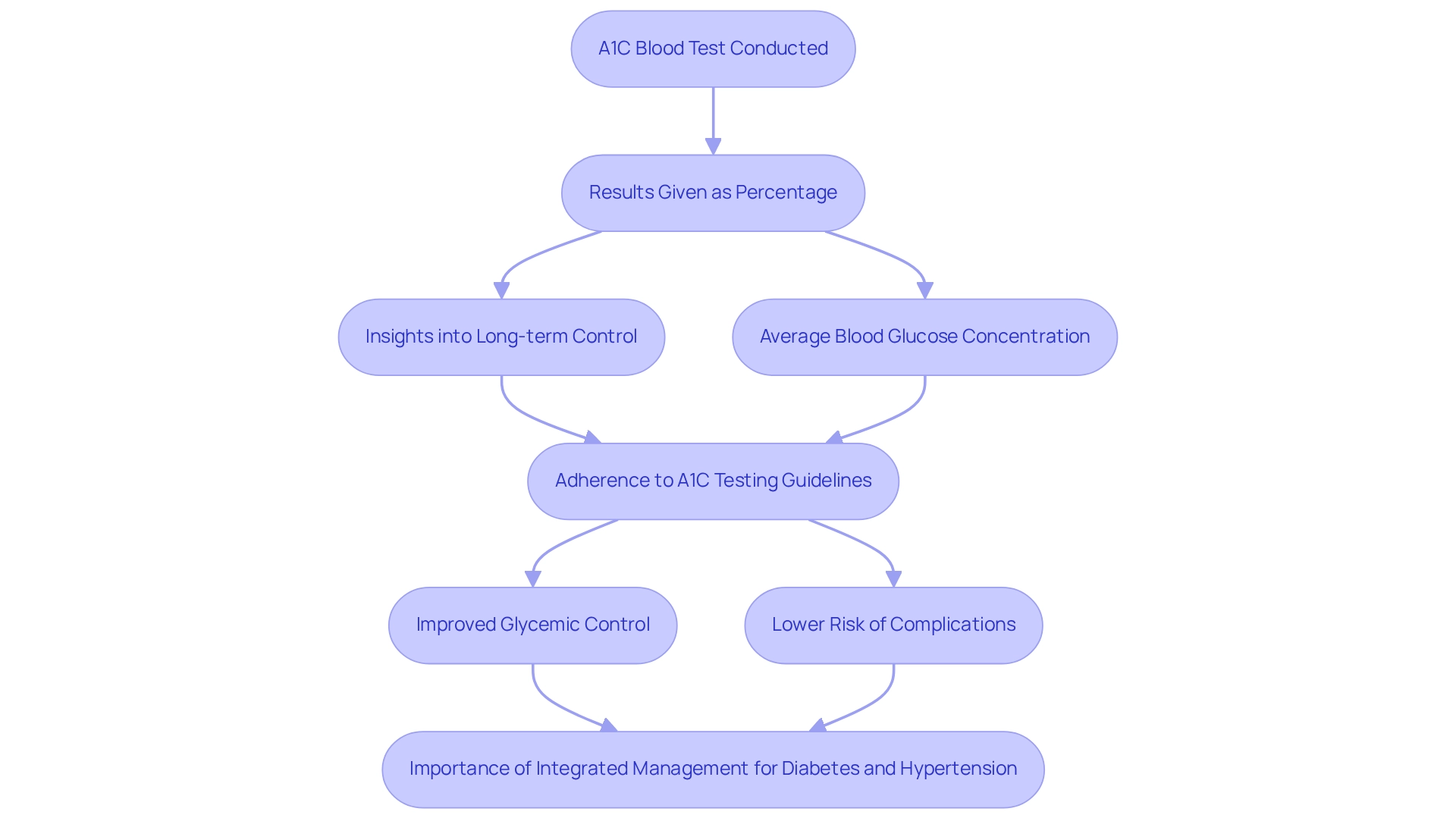
A1C values are determined through a simple blood test, typically conducted in a healthcare provider's office or a laboratory. The results are given as a percentage, representing the proportion of hemoglobin that has become glycated, or coated with sugar. For instance, an A1C value of 7% indicates an average blood glucose concentration of approximately 154 mg/dL.
This measurement is vital for effective blood sugar management, offering insights into long-term control.
At T2DSolutions, we recognize the importance of consistently tracking A1C EAG levels for individuals managing their condition and their healthcare providers. This tracking allows for the assessment of how well management strategies are working over time. In fact, statistics show that adhering to A1C testing guidelines is significantly linked to improved glycemic control and a lower risk of complications.
A study by Outcome Health demonstrated that following testing frequency recommendations correlates with better glycemic control and a reduced risk of future complications.
Moreover, a significant number of individuals with this condition also face high blood pressure, with 80.6% showing systolic blood pressure readings of 130 mmHg or higher. This connection underscores the need for integrated management strategies that effectively address both blood sugar issues and hypertension. The case study titled "High Blood Pressure and Diabetes Management" highlights this critical intersection, emphasizing the necessity for comprehensive care approaches.
Real-life examples illustrate the importance of A1C EAG testing in maintaining blood sugar control. Patients who actively engage with their healthcare teams and adhere to testing recommendations often report better health outcomes. Insights from the case study "Patient Engagement and Monitoring Care" reveal that effective communication and emotional support from healthcare providers significantly enhance patient self-care behaviors, leading to improved adherence to monitoring practices.
Furthermore, it is important to note that between 2017 and 2018, 5,293 children and teenagers aged 10 to 19 years were newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. This statistic highlights the increasing prevalence of the condition among younger populations and emphasizes the importance of A1C monitoring, especially concerning A1C EAG in this demographic.
In summary, understanding how A1C levels, particularly A1C EAG, are assessed and what they signify regarding blood sugar regulation is essential for anyone navigating the complexities of managing this condition. Regular A1C EAG testing not only informs treatment adjustments but also empowers individuals to take charge of their health journey. T2DSolutions is dedicated to providing resources and support for newly diagnosed individuals, ensuring they have the tools needed for effective disease management.
Understanding the Relationship Between A1C and Estimated Average Glucose (eAG)
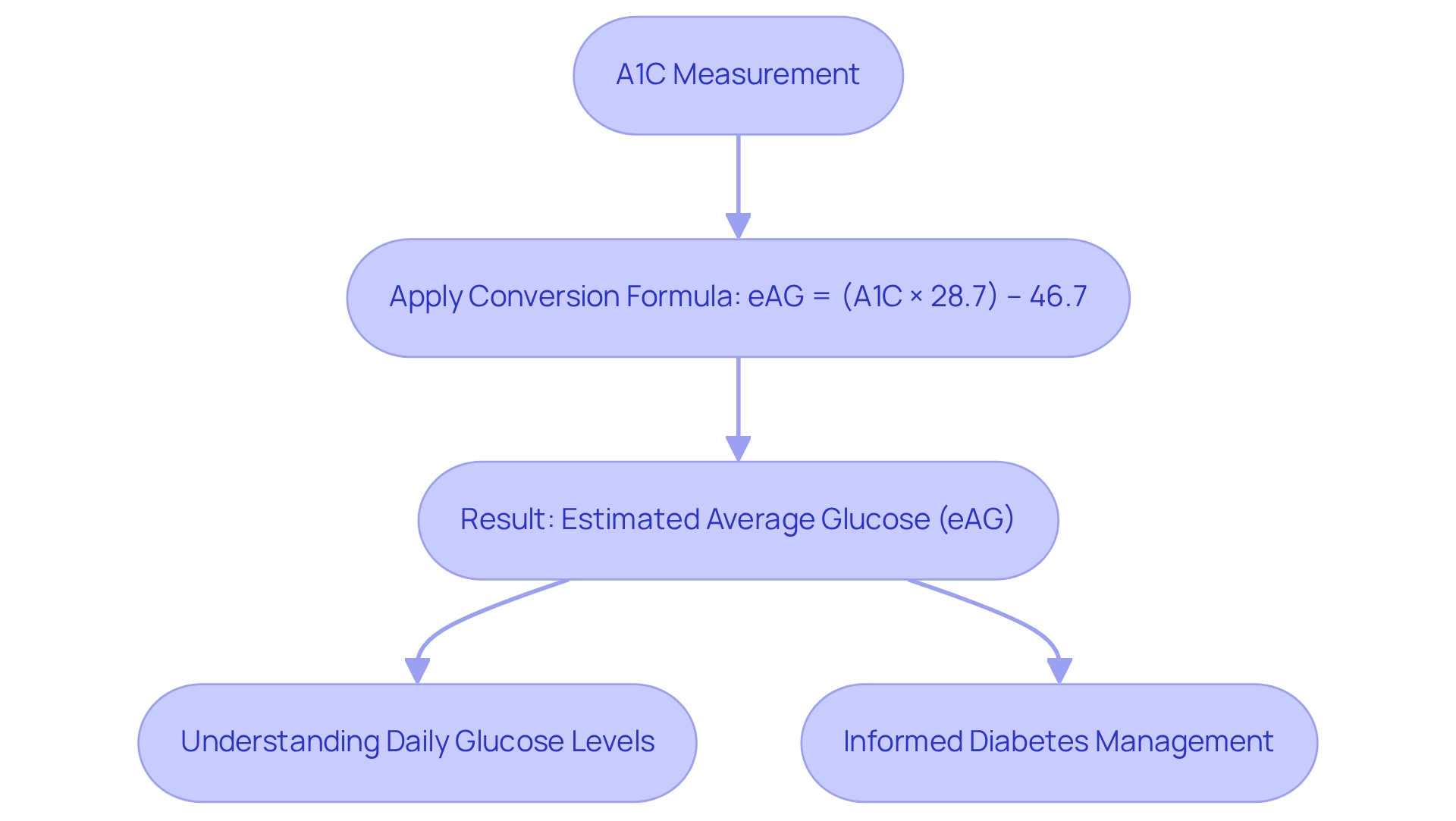
The connection between A1C and estimated average glucose (eAG) is made easy with a simple formula: eAG = (A1C × 28.7) – 46.7. This equation allows you to convert your A1C percentage into an estimated average glucose amount, offering a clearer perspective on managing your blood sugar. For instance, an A1C of 6.5% translates to an eAG of about 140 mg/dL.
Understanding the relationship between A1C and eAG is crucial for you as a patient. It links lab results to your daily glucose readings, empowering you to make informed decisions about your diabetes management. Recent statistics highlight that regularly monitoring A1C measurements, also known as A1C eAG, which represent a weighted average of glucose readings over the past four months, is essential for maintaining glycemic control within target ranges. The American Diabetes Association stresses the importance of quarterly A1C EAG measurements to ensure your glucose levels remain stable.
It's also important to be aware that the lower limit of agreement for the DCCT population was -74 mg/dL, indicating some variability in glucose measurements.
Moreover, the American Diabetes Association's introduction of the A1C EAG conversion calculator has greatly improved diabetes management. This tool helps healthcare professionals present A1C results in familiar units, fostering more effective discussions about glucose management with you. By converting A1C percentages into eAG values, you gain a clearer insight into how your glucose measurements relate to your daily life.
As Dr. Robert J. Heine, MD, stated, "The current results support the reporting of the measured A1C as eAG."
At T2DSolutions, we understand the importance of these conversions and are committed to providing resources that help newly diagnosed individuals navigate their diabetes management effectively. Grasping your eAG levels can lead to better health outcomes. For example, knowing that an A1C of 7% corresponds to an eAG of approximately 154 mg/dL can help you recognize the implications of your readings and adjust your management strategies accordingly.
This knowledge encourages a proactive approach to managing your blood sugar, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes. The introduction of the eAG/A1C conversion calculator aims to enhance conversations about glucose control between healthcare professionals and you, promoting a better understanding and management of your eAG. We invite you to explore T2 Solutions for more information on diabetes management and educational resources. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Lifestyle Changes to Lower A1C: Practical Tips for Better Diabetes Management
To effectively lower A1C levels, you can make several impactful lifestyle changes, and T2DSolutions is here to support you on this journey:
-
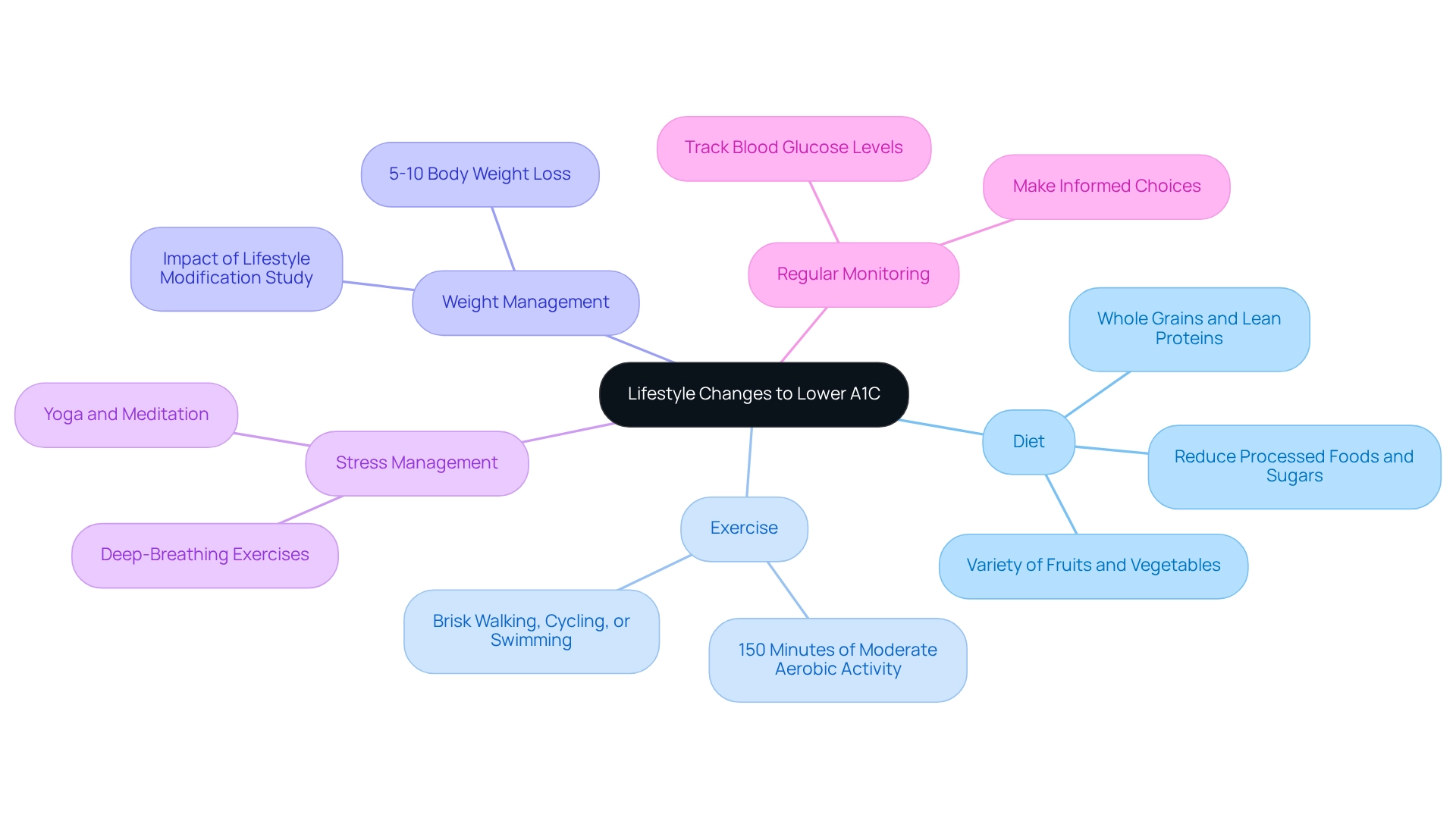
Diet: It's important to focus on a balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, and a variety of fruits and vegetables. Reducing processed foods and sugars is essential for maintaining stable blood glucose levels. Remember, small changes can make a big difference.
-
Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Regular physical activity helps with weight management and enhances insulin sensitivity, which is vital for glucose control. As Dr. Jong Ryeal Hahm noted, "a significant improvement of glycemic control was achieved by a simple educational emphasis of 'you have to do more exercise and control your daily diet' in a number of type 2 diabetic patients."
-
Weight Management: Even modest weight loss—around 5-10% of your body weight—can lead to significant improvements in A1C readings. This is especially important for those with Type 2 Diabetes. In fact, a study titled 'Impact of Lifestyle Modification on Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes' revealed that 35.3% of participants experienced a remarkable reduction in A1C readings after making lifestyle changes.
-
Stress Management: Incorporate relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises. Managing stress is crucial, as increased stress can negatively impact blood sugar regulation. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but taking time for yourself can truly help.
-
Regular Monitoring: Consistently tracking your blood glucose levels allows you to see how your lifestyle changes are influencing your A1C. This practice empowers you to make informed choices about your diet and exercise routines.
At T2DSolutions, we aim to provide educational resources and community support to those recently diagnosed, helping you navigate these lifestyle changes effectively. Recent studies highlight that lifestyle changes can lead to significant improvements in glycemic control. For instance, a study conducted during the pandemic in Japan found that patients who modified their lifestyle experienced notable changes in both glycemic control and body weight.
These findings underscore the importance of adopting healthy habits and the need for future studies to collect data on lifestyle changes and their impact on metabolic control.
Implementing these strategies not only helps in reducing A1C values but also enhances your overall well-being, contributing to better A1C levels. Diabetes instructors emphasize that practical advice, such as meal organization and setting achievable fitness goals, can significantly impact managing the condition effectively. Real-life examples show that individuals who commit to dietary modifications and consistent physical activity often notice substantial improvements in their A1C measurements. You're not alone in this journey; lifestyle changes are a fundamental aspect of diabetes management, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions About A1C and eAG: Clearing Up Common Misunderstandings
- What is a normal A1C measurement? A normal A1C level is considered to be below 5.7%. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% suggest prediabetes, a crucial phase where intervention can help prevent the progression to diabetes. An A1C level of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of diabetes. For individuals aged 60 and older, normal A1C ranges are defined as 4.4% to 6.6%, reflecting the importance of age-specific considerations in diabetes management.
Can A1C readings vary? Yes, A1C readings can fluctuate due to various factors, including dietary choices, physical activity, and stress. This variability highlights the importance of regular monitoring to capture a comprehensive picture of blood sugar control over time.
-
How often should I get tested? It is generally recommended that individuals with diabetes have their A1C tested at least twice a year. However, if there are changes in treatment or if blood glucose readings are not well managed, more frequent testing may be necessary. In 2025, guidelines suggest that patients should consult with their healthcare providers to determine the optimal testing frequency based on their individual circumstances.
-
Does A1C indicate daily blood sugar readings? While A1C provides an average of blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, it does not capture daily fluctuations. This means that a single A1C result may not fully represent a patient's day-to-day blood sugar management. Understanding this difference is essential for effective management of blood sugar levels.
Common misconceptions about A1C and eAG: Many individuals incorrectly assume that A1C is a direct measure of daily blood glucose readings, when in reality, it represents an average. Additionally, some may think that a single high A1C reading indicates immediate health risks, while it is crucial to consider trends over time. It's important to note that a range of 5.7–6.4% implies a person may have prediabetes, and over 6.5% signifies a more serious condition. Education on these points is vital, especially considering that average medical expenses for individuals with diagnosed blood sugar issues are 2.6 times greater than those without the condition. This emphasizes the significance of managing A1C levels to potentially lower these costs.
Real-world examples of patient education show that programs aimed at educating patients about A1C testing frequency have led to positive outcomes. For instance, community health initiatives offering workshops on blood sugar management have effectively raised awareness about the importance of regular A1C testing, resulting in improved health outcomes for participants. The high number of individuals with prediabetes, estimated at 97.6 million Americans aged 18 and older in 2021, underscores the urgent need for preventive measures and education to reduce the progression to diabetes.
Expert answers to frequently asked questions: Healthcare professionals emphasize that understanding A1C and eAG is crucial for effective diabetes management. They encourage individuals to inquire about their A1C results and to discuss any concerns regarding their testing frequency with their healthcare team. This proactive approach promotes improved communication and empowers individuals on their health journey.
What Do Abnormal A1C and eAG Results Mean? Understanding the Implications for Your Health
Abnormal A1C and a1c eag results are critical indicators of inadequate blood sugar control, significantly increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and neuropathy. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by these statistics, which reveal that a staggering percentage of diabetes patients struggle with uncontrolled A1C measurements. This underscores the urgent need for effective a1c eag management strategies. When A1C values exceed the recommended target range, consulting a healthcare provider is essential to evaluate and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Effective strategies may include dietary changes, increased physical activity, and adjustments to a1c eag medications. For instance, a case study highlighted the importance of understanding HbA1c values among healthcare professionals. While HbA1c remains a valuable tool, its effectiveness is enhanced within a collaborative healthcare team setting. This teamwork ensures that healthcare providers, including nurses and pharmacists, accurately interpret A1C results and work together to optimize patient care.
Moreover, the implications of abnormal A1C and eAG results extend beyond immediate health concerns. Elevated A1C values can lead to serious complications. Recent findings indicate that 80.6% of U.S. adults with diagnosed blood sugar issues have a systolic blood pressure of 130 mmHg or greater or are on medication for hypertension. It's crucial to maintain blood pressure below 130/80 mmHg to prevent complications of hyperglycemia. This connection emphasizes the importance of managing both blood sugar and cardiovascular health.
The total estimated costs of diagnosed cases in the U.S. in 2022 was $413 billion, illustrating the significant economic impact of managing this illness. Regular follow-up and monitoring are essential to mitigate long-term complications and enhance overall health. Engaging with specialists in blood sugar management can provide valuable insights into effectively managing high A1C levels.
As one expert noted, 'Virtualizing a clinical trial to fill in the gaps in old, sparse data using advanced data science methods is the next best thing we can do today.' Understanding the nuances of A1C and a1c eag results is vital for tailoring individualized treatment plans that promote better health outcomes. By prioritizing these strategies, you can take proactive steps toward managing your condition and reducing the risk of complications.
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to being your comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support. We encourage newly diagnosed patients to explore our resources to better understand their A1C and a1c eag results. Remember, you're not alone in this journey—subscribe to stay updated on the latest diabetes management strategies and resources available through T2D Solutions.
Conclusion
Understanding A1C and estimated average glucose (eAG) is pivotal for anyone navigating the complexities of diabetes management. A1C serves as a key indicator of long-term blood sugar control, while eAG provides a more relatable context, enabling individuals to grasp their glucose levels in everyday terms. Regular monitoring of these metrics is essential. Not only do they inform treatment plans, but they also empower you to take charge of your health.
Adopting lifestyle changes can significantly lower A1C levels and enhance overall well-being. Key strategies include:
- Maintaining a balanced diet
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Managing weight
- Implementing stress reduction techniques
These proactive measures, along with consistent monitoring, create a foundation for improved glycemic control and reduced risk of complications.
Moreover, it’s crucial to understand the implications of abnormal A1C and eAG results for effective diabetes management. High levels can indicate inadequate blood sugar control, which necessitates immediate action and collaboration with healthcare providers. By prioritizing education and open communication, you can navigate your diabetes journey more effectively, fostering better health outcomes.
In summary, knowledge and proactive management are the cornerstones of successful diabetes care. By embracing the insights gained from A1C and eAG metrics, along with implementing lifestyle modifications, you can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the risks associated with diabetes. Taking these steps not only enhances your personal health but also contributes to a broader understanding of diabetes management in the community. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is A1C and why is it important?
A1C, or hemoglobin A1C, is a blood test that measures the average blood sugar levels over the previous two to three months. It is a vital marker for blood sugar management and indicates how effectively an individual's diabetes is being controlled.
What does eAG stand for and how does it relate to A1C?
eAG stands for estimated average glucose. It converts the A1C percentage into a daily average blood glucose level, expressed in common units like mg/dL or mmol/L, making it easier for individuals to understand their glucose management.
How are A1C and eAG used in diabetes management?
Both A1C and eAG are essential metrics for evaluating long-term glucose control and guiding treatment decisions. They help individuals and healthcare providers assess how well diabetes management strategies are working over time.
What is the standard deviation of prediction error for the relationship between A1C and average glucose?
The standard deviation of prediction error for the relationship between A1C and average glucose is approximately 15.7 mg/dL, highlighting the variability that can occur in individual assessments.
Are there alternatives to A1C for measuring glycemic control?
Yes, the medical community is exploring alternatives to A1C, such as estimated average glucose and glucose time in range. These alternatives may provide a more comprehensive view of blood sugar management, although they are not yet universally available to all patients.
How is the A1C value determined?
A1C values are determined through a simple blood test conducted in a healthcare provider's office or a laboratory. The results are given as a percentage, indicating the proportion of hemoglobin that has become glycated.
What does an A1C value of 7% indicate?
An A1C value of 7% indicates an average blood glucose concentration of approximately 154 mg/dL.
Why is tracking A1C EAG levels important?
Consistently tracking A1C EAG levels is vital for individuals managing diabetes, as it allows assessment of the effectiveness of management strategies over time and correlates with improved glycemic control and reduced risk of complications.
What is the connection between diabetes and high blood pressure?
A significant number of individuals with diabetes also face high blood pressure, with 80.6% showing systolic blood pressure readings of 130 mmHg or higher. This highlights the need for integrated management strategies that address both blood sugar and hypertension.
What demographic shows an increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes?
Between 2017 and 2018, 5,293 children and teenagers aged 10 to 19 years were newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, emphasizing the importance of A1C monitoring in this demographic.
