Overview
Understanding A1C diabetes levels is crucial for diagnosing and managing diabetes, with normal levels below 5.7%, prediabetes between 5.7% and 6.4%, and diabetes confirmed at 6.5% or higher. The article emphasizes the significance of the A1C test in reflecting long-term blood sugar control and guiding treatment decisions, highlighting its role in preventing complications associated with diabetes.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding the nuances of the A1C test is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. This test, which measures average blood glucose levels over the previous two to three months, serves not only as a diagnostic tool but also as a key indicator for monitoring the effectiveness of treatment strategies.
With A1C levels offering insights into long-term glycemic control, they can significantly influence decisions regarding lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, the need for accessible education and resources becomes increasingly vital.
T2DSolutions emerges as a comprehensive platform dedicated to empowering individuals navigating their diabetes journey, providing essential tools and community support to foster better health outcomes. Understanding A1C levels is not just about managing a condition; it is about taking proactive steps towards a healthier future.
Understanding the A1C Test: Purpose and Importance
The A1C test is a vital tool that assesses your average blood glucose readings and determines your A1C diabetes level over the preceding two to three months. It serves a dual purpose: diagnosing and monitoring the condition effectively. Typically, an A1C diabetes level below 5.7% is classified as normal, while an A1C diabetes level ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% suggests prediabetes.
An A1C diabetes level of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of blood sugar disorder. Understanding your A1C diabetes level results is paramount, as it enables you and your healthcare provider to make informed decisions about your treatment plan and necessary lifestyle changes. This test not only reflects how well your blood sugar has been managed but also plays a crucial role in preventing the long-term complications linked to the condition, which is essential for maintaining a healthy A1C diabetes level and ultimately contributing to overall health and well-being.
As T2DSolutions launches as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 conditions education, we emphasize the importance of monitoring the A1C diabetes level to help newly diagnosed patients navigate their health journey effectively. T2DSolutions will offer educational articles, community forums, and tools for monitoring A1C diabetes level, ensuring that patients have the resources they need to manage their condition. With excess medical costs per person related to this condition rising from $10,179 to $12,022 between 2012 and 2022, monitoring your A1C diabetes level becomes increasingly important for managing healthcare expenses.
As Roopa Naik highlights, understanding the A1C diabetes level is crucial for effective control of blood sugar levels. Furthermore, a recent case study titled 'Statistical Analysis of Diabetes Data' highlights the trends and factors affecting the prevalence of the condition, underscoring the role of A1C testing in understanding these trends related to A1C diabetes level.
A1C vs. Blood Sugar: Key Differences and Insights
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes management. Here, you will find valuable information, tools, and community support tailored to your needs. The A1C diabetes level test serves as an essential tool for assessing blood sugar control over an extended period, typically indicating glucose readings from the past two to three months.
In contrast, daily blood glucose tests offer a snapshot of your current glucose measurements, which can fluctuate significantly throughout the day due to factors such as food intake, physical activity, and medication adherence. For example, an A1C diabetes level of 7% correlates to an average blood glucose concentration of approximately 154 mg/dL. This correlation highlights the significance of comprehending both types of measurements in diabetes care.
Monitoring the A1C diabetes level offers insight into long-term glycemic control, while daily glucose tests allow for immediate adjustments and interventions. Recent studies indicate that the mean absolute errors for prediction equations of A1C and blood glucose levels range between 2.32 and 3.30 percentage points, emphasizing the need for accurate monitoring. As Lara J. Akinbami noted, 'All material appearing in this report is in the public domain and may be reproduced or copied without permission; citation as to source, however, is appreciated.'
Moreover, a case study on a two-step strategy for GDM diagnosis emphasizes practical applications of glucose monitoring techniques, demonstrating how effective oversight can lead to improved health outcomes. Thus, a comprehensive approach that includes both metrics, particularly the A1C diabetes level, is essential for effective diabetes care, ensuring that patients can maintain optimal health outcomes.
Don't forget to subscribe to our newsletter to stay updated on the latest resources and support available through T2D Solutions!
Factors Affecting A1C Levels: What You Need to Know
A range of elements can greatly affect your a1c diabetes level, including dietary choices, physical activity, stress control, and existing health conditions. Consuming a diet rich in refined carbohydrates, for instance, can lead to increased a1c diabetes level readings, whereas engaging in regular physical activity is associated with lower a1c diabetes level values. According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines, it is essential to measure the a1c diabetes level twice yearly for stable individuals and at least four times for those experiencing glucose fluctuations, emphasizing the significance of monitoring in relation to lifestyle changes.
T2DSolutions is dedicated to empowering condition oversight through comprehensive education and community support, ensuring that newly diagnosed individuals have access to vital resources. As a new resource hub, T2D Solutions will soon offer a range of educational materials and community initiatives aimed at fostering engagement and support among patients. Moreover, underlying health conditions such as anemia and kidney disease can skew the A1C diabetes level test results, leading to potentially inaccurate assessments of glycemic control.
As mentioned by glycemic control specialist Roopa Naik, Hemoglobin A1c is a valuable tool in overseeing metabolic disorders and other glycemic regulation issues, but it operates most effectively in an interprofessional healthcare team setting. This highlights the importance of a thorough strategy for handling blood sugar issues that takes into account all contributing elements. Furthermore, studies suggest that expanding healthcare coverage, particularly Medicaid, could enhance A1C results among uninsured or underinsured populations, emphasizing the role of policy in diabetes management.
For optimal A1C diabetes level readings, it is crucial to understand and address these variables through tailored dietary and exercise plans, as well as regular monitoring and consultation with healthcare professionals. Notably, the DCCT extension into the EDIC study demonstrated long-term cardiovascular risk and mortality benefits for patients maintaining lower a1c diabetes levels, reinforcing the importance of effective glycemic control.
Effective Strategies to Lower Your A1C Levels
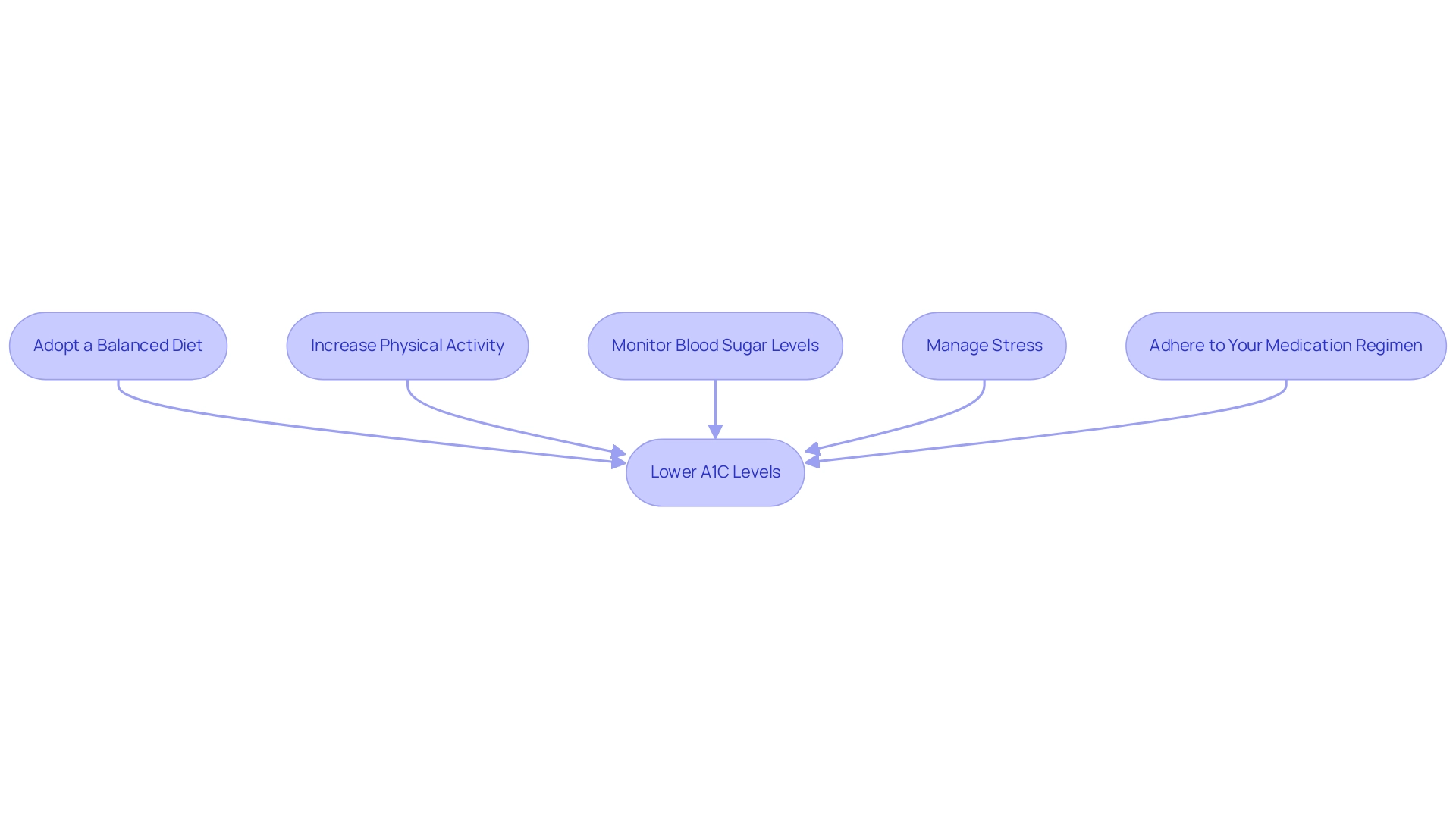
To effectively reduce your A1C readings, consider implementing the following strategies:
-
Adopt a Balanced Diet: Emphasize whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. It is crucial to minimize the intake of processed foods and sugars. Research indicates that individuals with a poor diet, even those who are food secure, experience significantly elevated A1C diabetes levels. As Amanda Crowe mentions, 'having a poor diet (not consuming sufficient nutritious foods) is significantly linked to an increased A1C diabetes level,' emphasizing the importance of nutrition in blood sugar control. For further guidance on nutrition, T2DSolutions will soon offer comprehensive resources tailored for patients, including meal planning guides and educational articles on healthy eating habits.
-
Increase Physical Activity: Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week, such as brisk walking or cycling. Consistent physical activity not only assists in weight control but also plays a crucial part in enhancing insulin sensitivity, which can lead to decreases in A1C diabetes levels. T2DSolutions will offer exercise suggestions specifically tailored for individuals managing Type 2 and Type 3 conditions, including video tutorials and customized fitness plans.
-
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly checking your blood glucose levels is essential for identifying patterns and making necessary adjustments to your control plan. Consistent monitoring can empower you to make informed decisions regarding diet and exercise. T2DSolutions will soon feature tools to assist with effective monitoring, such as blood sugar tracking apps and resources on interpreting results.
-
Manage Stress: Incorporating relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation can be beneficial in managing stress, which has been shown to negatively impact blood sugar control. Minimizing stress using these techniques can improve overall control of blood sugar levels. Expect to find stress reduction resources at T2Solutions that cater to the unique challenges faced by newly diagnosed patients, including guided meditation sessions and stress relief workshops.
-
Adhere to Your Medication Regimen: Collaborate with your healthcare team to ensure your medications are tailored to your specific needs. Proper medication adherence is a cornerstone of effective control of blood sugar levels and the management of A1C diabetes level reduction.
As we prepare to launch T2DSolutions, it’s important to note that the economic burden of this condition is substantial, with direct costs rising from $227 billion in 2012 to $307 billion in 2022. This highlights the significance of strategies that can effectively decrease the A1C diabetes level and thereby reduce long-term healthcare expenses. By adopting these methods and utilizing the resources provided by T2DSolutions, patients can significantly improve their health outcomes and overall quality of life.
Effective leadership not only benefits individual health but also addresses the rising economic impact of diabetes, as highlighted by the case study on the economic effect of diabetes, which underscores the necessity of implementing these strategies.
Interpreting A1C Results: Normal vs. Dangerous Levels
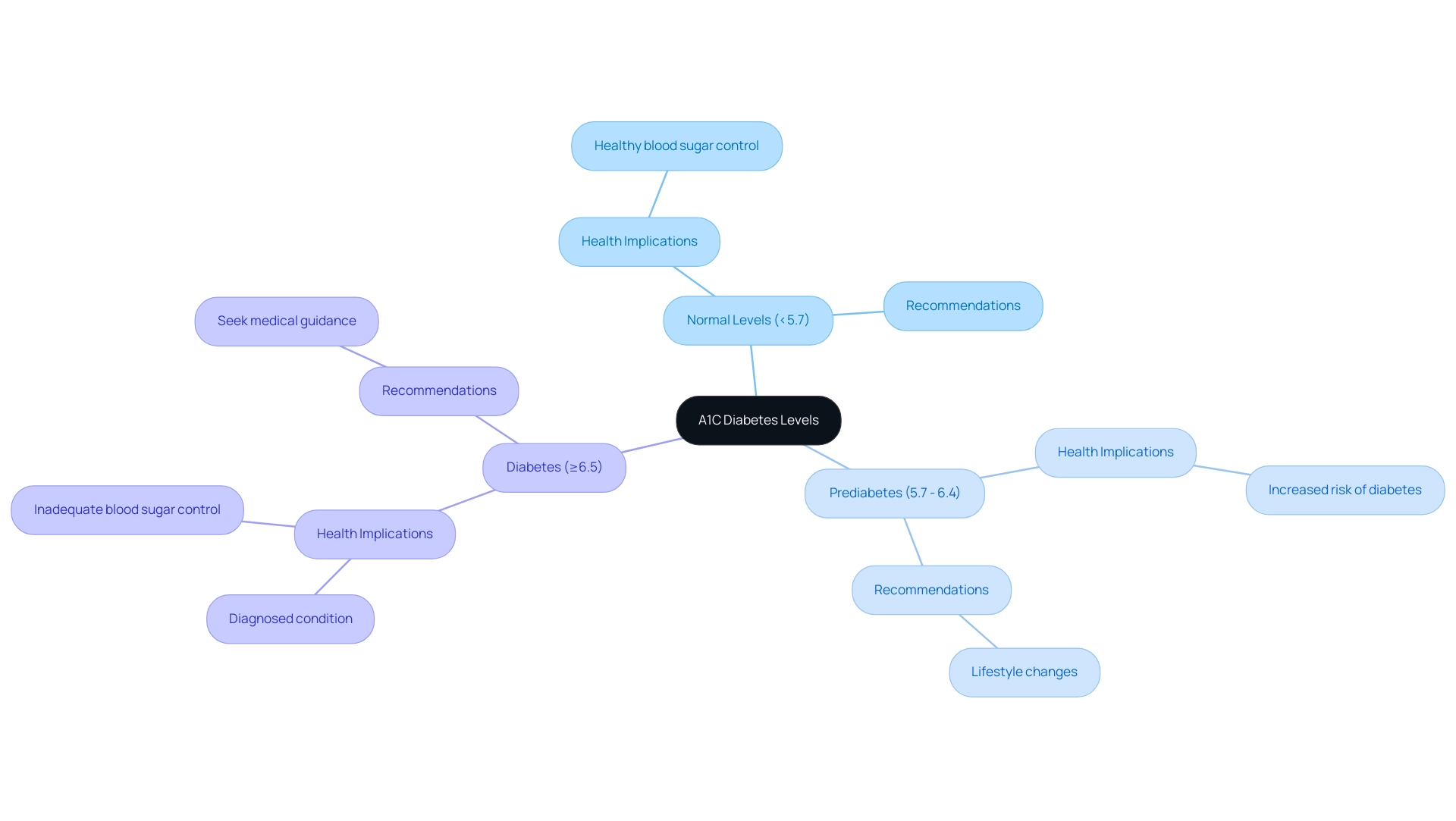
The A1C diabetes level results are classified into three main groups, each signifying different degrees of blood sugar control and related health risks.
- A normal A1C diabetes level below 5.7% reflects healthy blood sugar readings, suggesting effective glycemic management.
- Prediabetes: A1C values ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate an increased risk of advancing to a diabetic condition, highlighting the necessity for lifestyle changes to reduce the risk related to A1C diabetes level.
- An A1C diabetes level of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of this condition.
It is important to note that an A1C diabetes level above 8% can indicate inadequate blood sugar control, which substantially heightens the risk of diabetes-related complications. Recognizing these categories not only aids individuals in understanding their current health status but also serves as a catalyst for taking proactive measures to manage their condition effectively.
In light of the urgent need for education and support highlighted by the increasing prevalence of the condition, T2 Solutions offers a comprehensive resource hub for newly diagnosed patients. This includes:
- Educational articles
- Community forums for peer support
- Personalized guidance to help navigate management of the condition
With an estimated annual number of newly diagnosed cases including 18,169 children and adolescents with type 1 condition, understanding the A1C diabetes level is paramount.
As Roopa Naik states, 'Hemoglobin A1c is a valuable tool in managing diabetes mellitus and other glycemic control disorders, but it functions best in an interprofessional healthcare team environment to be effective.' The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study further underscores the necessity for proactive management and lifestyle changes, reinforcing the value of T2D solutions as an essential resource for both education and community support.
Conclusion
Understanding and monitoring A1C levels is fundamental for effective diabetes management. The A1C test not only facilitates the diagnosis of diabetes but also serves as a vital tool for tracking long-term glycemic control. By recognizing the significance of A1C results, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their treatment plans and lifestyle modifications, ultimately preventing the complications associated with diabetes.
Various factors, including diet, physical activity, and stress management, can influence A1C levels. Adopting a balanced diet, increasing physical activity, and effectively managing stress are all strategies that can contribute to lowering A1C levels. Regular monitoring of blood glucose and adhering to prescribed medications further empower individuals to maintain optimal health outcomes.
As diabetes prevalence continues to rise, platforms like T2DSolutions play an essential role in providing education and support for those navigating their diabetes journey. By equipping patients with the necessary resources, T2DSolutions fosters an environment where individuals can engage with their health proactively. Ultimately, understanding A1C levels and implementing effective management strategies not only enhance personal well-being but also address the broader economic implications of diabetes care.



