Overview:
A1C drugs play a crucial role in diabetes management by helping patients maintain optimal blood glucose levels through various oral and injectable medications. The article outlines how these medications, including metformin and GLP-1 receptor agonists, function to lower A1C levels, while emphasizing the importance of lifestyle changes and regular healthcare monitoring to enhance treatment effectiveness and patient outcomes.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of diabetes management requires a comprehensive understanding of the various A1C-lowering medications available. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, especially among populations that may be unaware of their condition, the role of effective pharmacological interventions becomes increasingly critical.
This article delves into the essential classes of medications, including oral and injectable options, and highlights their mechanisms of action and potential interactions. It also emphasizes the importance of integrating lifestyle changes with medication for optimal A1C control.
With insights from recent advancements in diabetes treatments, this resource aims to empower individuals with knowledge and strategies to enhance their diabetes management and improve overall health outcomes.
Overview of A1C-Lowering Medications for Diabetes
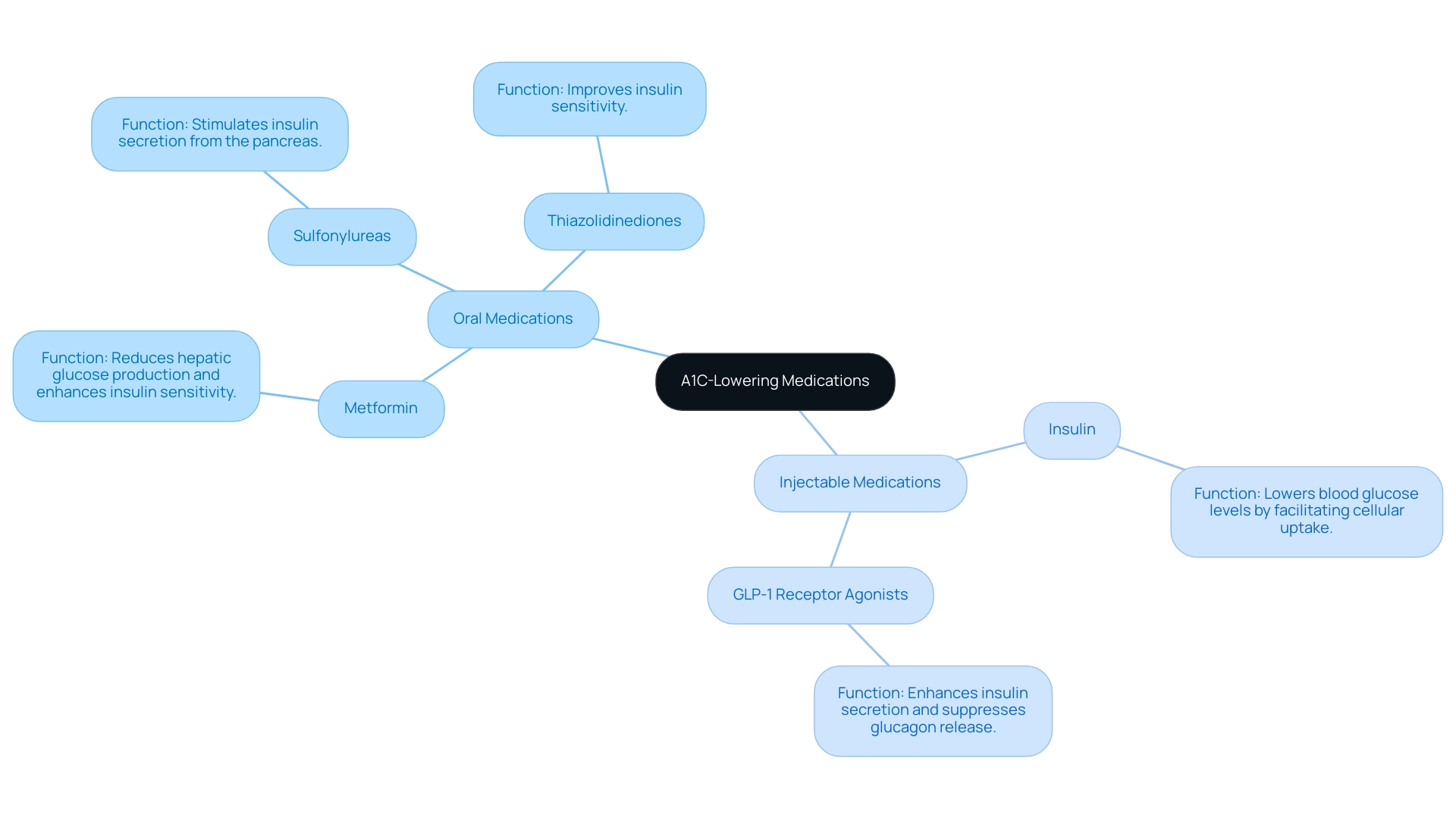
As part of the launch of T2D Solutions, a new resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, we emphasize the critical role of A1C drugs in effective diabetes management. T2DSolutions aims to empower individuals recently diagnosed with comprehensive resources and support. These treatments, such as A1C drugs, allow patients to maintain optimal blood glucose levels and are broadly categorized into oral and injectable options.
Oral treatments, such as:
- Metformin
- Sulfonylureas
- Thiazolidinediones
are commonly prescribed due to their ease of administration and effectiveness. For instance, metformin primarily reduces hepatic glucose production and enhances insulin sensitivity, while sulfonylureas stimulate insulin secretion from the pancreas. Conversely, injectable drugs include:
- Insulin
- GLP-1 receptor agonists
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels by facilitating cellular uptake, while GLP-1 receptor agonists enhance insulin secretion and suppress glucagon release for improved glycemic control. In 2020, the crude rate of emergency department visits for hypoglycemia was 8.6 per 1,000 adults, highlighting the importance of effective health care to prevent such critical situations. It is also crucial to conduct further carefully designed OAD trials to explore the combinations of OAD drug use and their impact on A1C levels when considering A1C drugs.
Comprehending these different types of medications and their functions is crucial for recently diagnosed individuals, enabling them to make knowledgeable choices regarding their health strategies. Moreover, a study on Continuous Glucose Monitoring has shown enhanced glucose control and patient results, highlighting a practical use of effective treatment for the condition. For more resources and support, we invite you to subscribe to T2 Solutions and stay updated on the latest information and community initiatives.
Key Classes of Medications: GLP-1 Agonists and SGLT2 Inhibitors
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your all-inclusive resource center for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar control. As we get ready to launch shortly, we are dedicated to offering you vital information on effective treatments for managing blood sugar levels, including notable categories of A1C drugs used for controlling A1C levels.
-
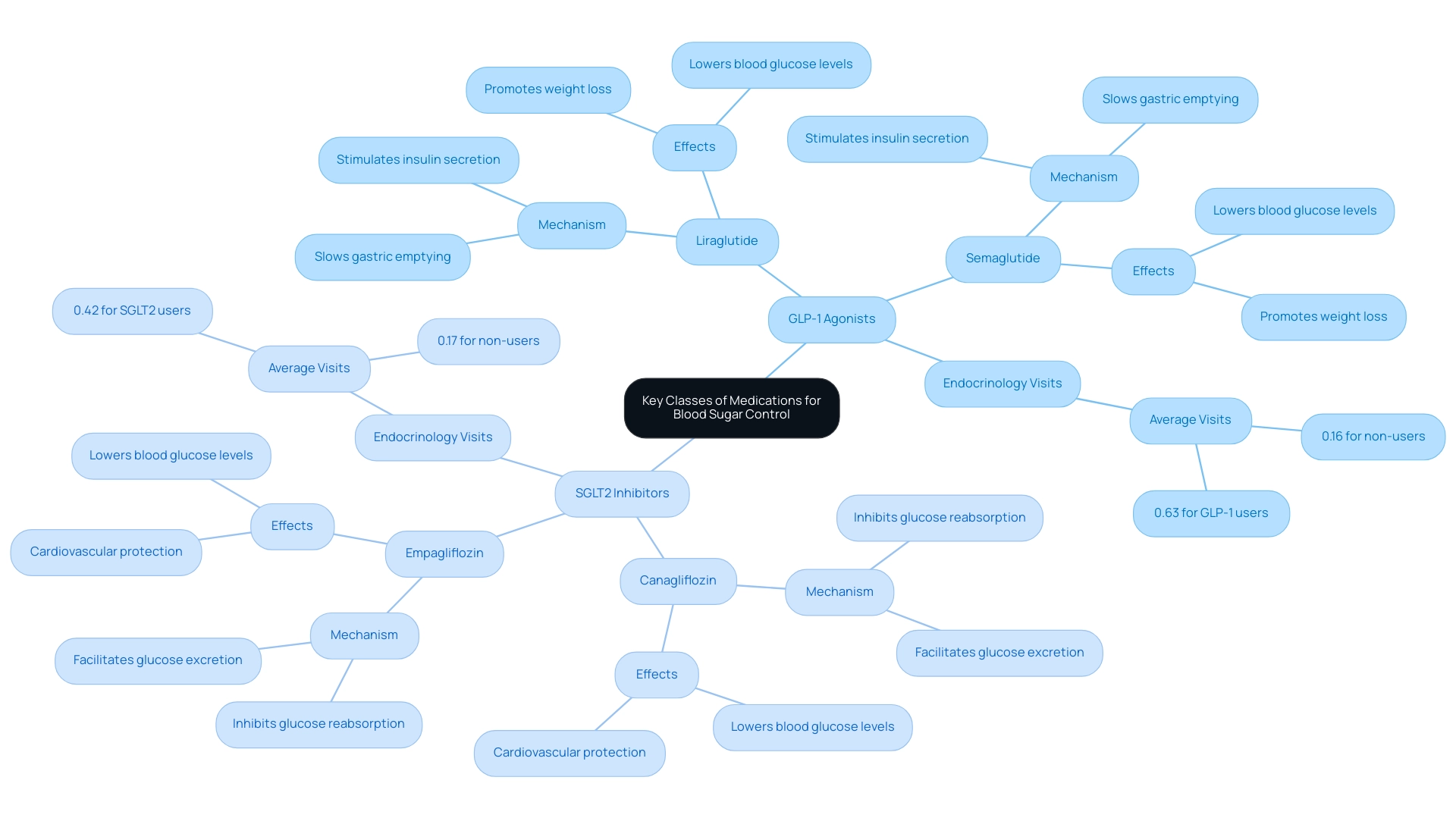
GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors are two key categories that play a vital role in managing blood sugar levels.
- GLP-1 agonists, such as liraglutide and semaglutide, stimulate insulin secretion in response to meals while slowing gastric emptying, leading to lower blood glucose levels and weight loss.
- SGLT2 inhibitors, including canagliflozin and empagliflozin, work by inhibiting glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, facilitating glucose excretion through urine.
Both types of treatments not only effectively reduce A1C levels but also include A1C drugs that provide substantial cardiovascular and renal protection—essential elements of managing blood sugar.
Research highlights the significance of these treatments, with patients on SGLT2 inhibitors attending an average of 0.42 endocrinology visits compared to 0.17 for those not using this therapy. Similarly, GLP-1 receptor agonists have shown a higher frequency of endocrinology visits at an average of 0.63. This emphasizes the necessity of regular monitoring and engagement with healthcare providers for optimal treatment plans.
As noted by Ziyad Al-Aly from the Clinical Epidemiology Center, 'Effective management of the condition requires not only pharmacological intervention but also consistent follow-up with healthcare professionals.'
Stay tuned for more updates as we approach our launch, and subscribe to receive emails when new content, including comprehensive guides on health treatments, is published!
Understanding Medication Interactions and Side Effects
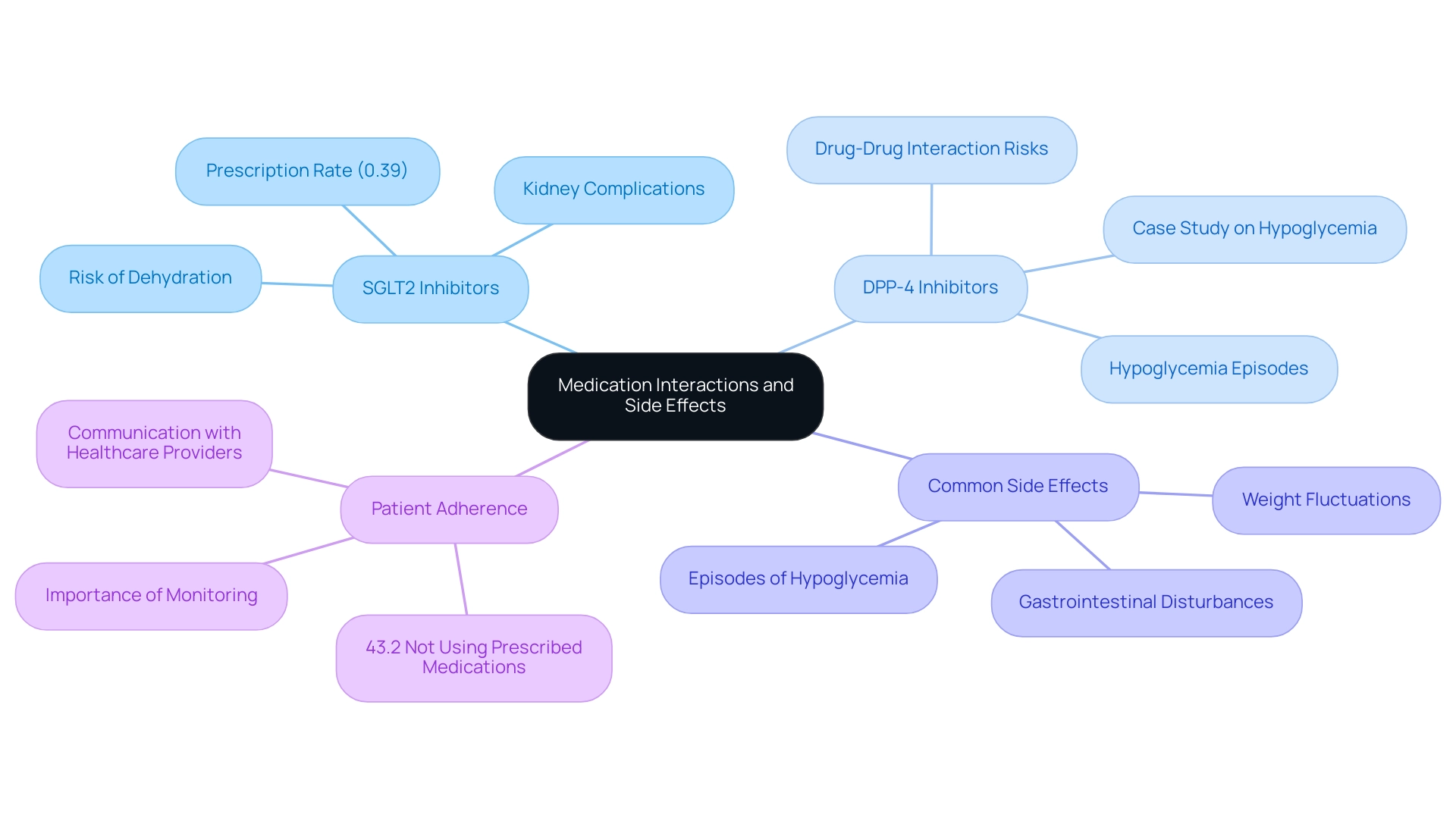
Individuals undergoing treatment for blood sugar issues must stay alert regarding possible interactions involving their prescriptions, supplements, and specific foods. For instance, the use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors—prescribed in only 0.39% of the study population—alongside diuretics can elevate the risk of dehydration and kidney complications. Recent findings reveal that a significant portion of patients with diabetes—43.2%—did not utilize prescribed medications for managing glucose, blood pressure, or lipid levels, highlighting the critical importance of adherence and monitoring.
As Puneet Kaur Chehal, PhD, notes, consistent monitoring and communication with healthcare providers regarding side effects are crucial to effective management of the condition. Additionally, Kiki et al.'s examination of possible drug interactions in individuals with type 2 underscores the necessity for awareness of these interactions.
Common side effects associated with diabetes medications include:
- Gastrointestinal disturbances
- Episodes of hypoglycemia
- Fluctuations in weight
A case study on hypoglycemia associated with drug interactions among individuals using dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors further emphasizes the necessity of managing these risks. Utilizing a computerized drug interaction monitoring system is recommended to bolster patient safety and minimize serious interactions.
Being aware of these possible side effects and interactions can greatly improve health supervision and assist in avoiding complications.
Integrating Lifestyle Changes with Medication for Optimal A1C Control
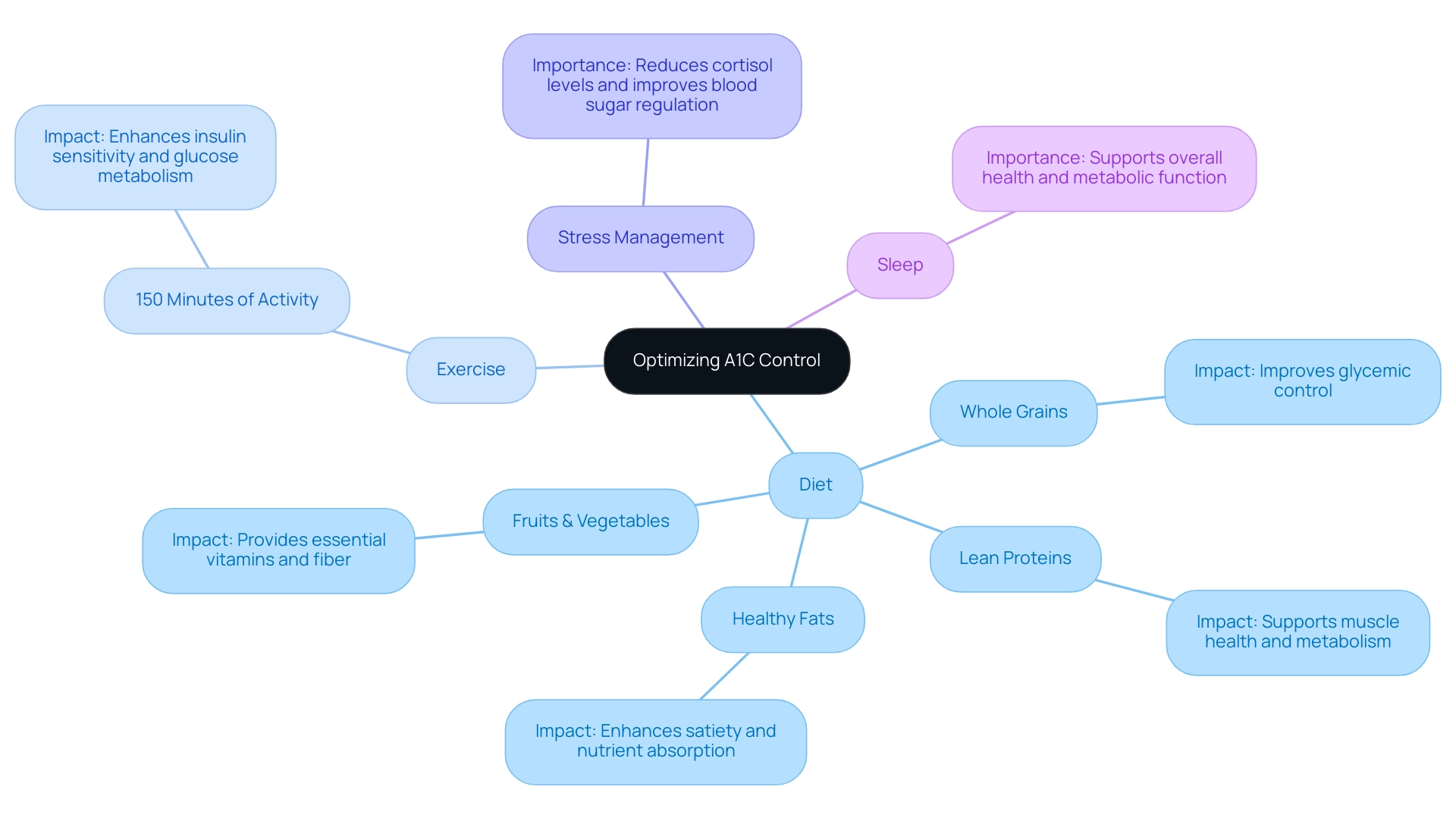
Incorporating lifestyle changes is paramount for attaining optimal A1C control. Patients are encouraged to adopt a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables. Recent studies have shown that making these dietary adjustments significantly impacts A1C levels.
For instance, a study focusing on lifestyle modifications highlighted that:
- 35.3% of participants with mild to moderate uncontrolled type 2 conditions experienced a notable decrease in HbA1c levels after three months, with an average reduction of -0.74%.
- Engaging in regular physical activity—aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week—can substantially enhance insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
This aligns with the findings that structured exercise training led to significant improvements in the prevalence of uncontrolled cardiovascular risk factors post-intervention, underscoring the dual benefits of exercise for both A1C control and cardiovascular health.
Stress management techniques and sufficient sleep also contribute critically to effective care for blood sugar regulation. As emphasized by specialist Mathias Ried-Larsen, further research is needed to assess the generalizability and durability of these findings, particularly in the context of lifestyle changes.
T2DSolutions, a new site launching soon, is committed to empowering patients through education and community support, providing comprehensive resources to help you integrate these lifestyle modifications effectively.
We encourage you to subscribe for updates and access our educational materials as we build our resource hub. A cooperative strategy that incorporates A1C drugs, lifestyle changes, and consistent oversight can promote effective control of blood sugar levels.
Recent Advances in Diabetes Medications and Their Impact on A1C
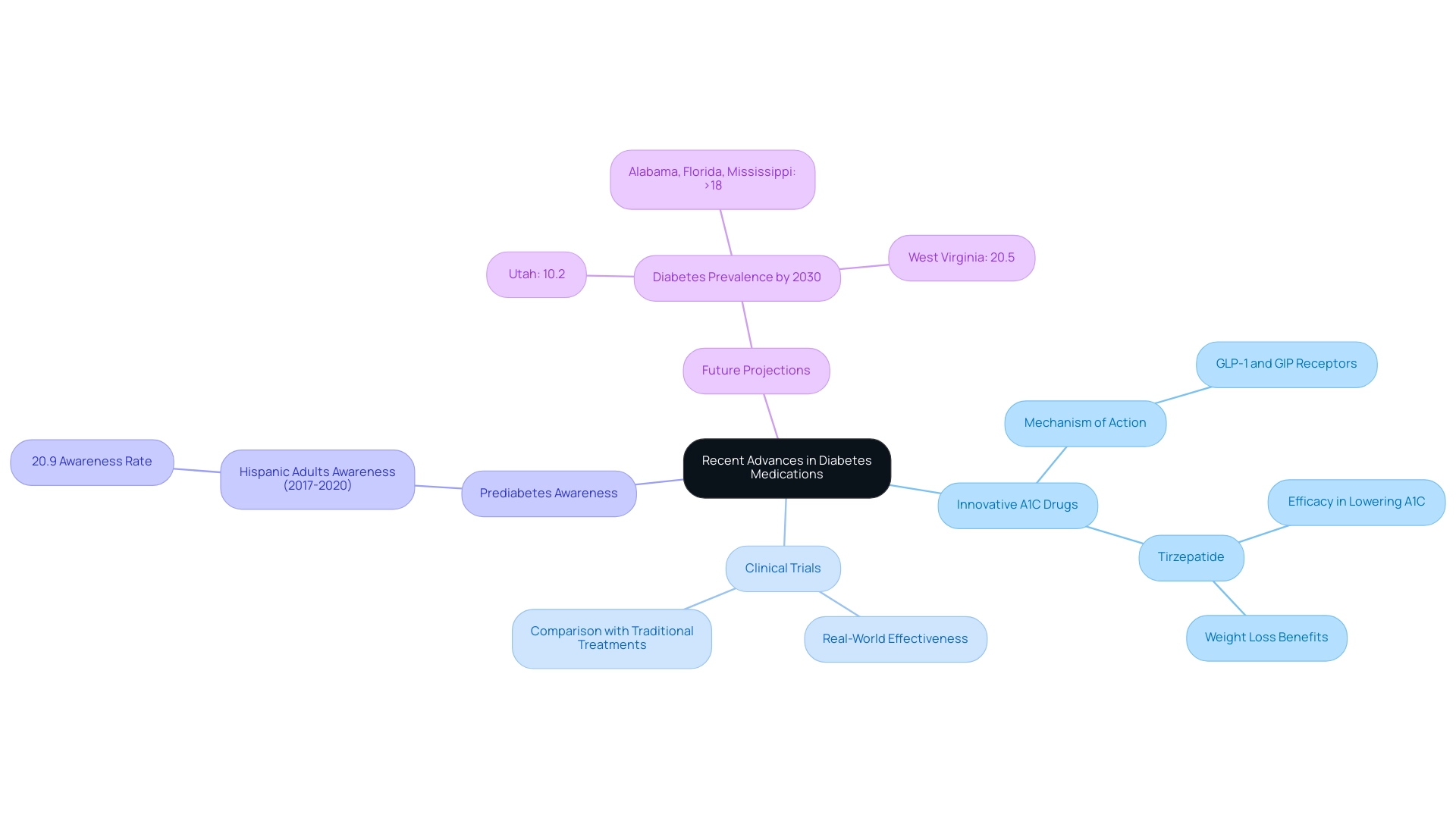
As we launch T2DSolutions, a site that will soon be your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 health education and community support, we are excited to share valuable information and resources tailored to your needs. Recent advancements in treatments for blood sugar control have introduced innovative a1c drugs that specifically target pathways involved in glucose regulation. A notable example of a1c drugs is tirzepatide, which engages both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, demonstrating significant efficacy in lowering A1C levels.
Clinical trials show that patients using tirzepatide, which is categorized among a1c drugs, not only experience significant reductions in A1C but also benefit from weight loss, improving overall health care. This is especially significant as, from 2017 to 2020, only 20.9% of Hispanic adults were aware of their prediabetes, emphasizing the need for enhanced awareness in managing the condition. By 2030, the condition is predicted to affect 10.2% of Utah's population and over 18% in Alabama, Florida, and Mississippi, underscoring the urgency of advancements in treatments like tirzepatide.
According to recent clinical trial results, tirzepatide has consistently outperformed traditional treatments in real-world effectiveness, positioning it among the leading a1c drugs and marking a substantial step forward in managing blood sugar. In 2021, it was estimated that 29.4 million adults had diagnosed blood sugar conditions, illustrating the significance of new treatments in addressing this widespread issue. As the field of treatment evolves, ongoing research into these medications offers encouraging opportunities for enhanced individual outcomes and quality of life.
We encourage newly diagnosed patients to engage in discussions with their healthcare providers to explore these advanced treatment options and tailor strategies to their unique health needs. Stay tuned for upcoming content that will further support your journey in diabetes management.
Conclusion
Understanding the various A1C-lowering medications available is crucial for effective diabetes management. This article has explored key classes of medications, including oral options like metformin and injectable treatments such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors. Each medication class has distinct mechanisms of action that contribute to controlling blood glucose levels, highlighting the importance of personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs.
The integration of lifestyle changes alongside pharmacological interventions cannot be overstated. Adhering to a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress are essential components that enhance the effectiveness of medication. Studies have shown that these lifestyle modifications can lead to significant improvements in A1C control, reinforcing the idea that a holistic approach is vital for achieving optimal health outcomes.
Recent advancements in diabetes treatments, such as tirzepatide, offer new hope for patients seeking effective management strategies. These innovations not only lower A1C levels but also promote weight loss, addressing multiple facets of diabetes care. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, staying informed about these advancements and actively engaging with healthcare providers will empower patients to make informed decisions about their treatment options.
In conclusion, effective diabetes management is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a thorough understanding of medications, awareness of potential interactions, and a commitment to lifestyle changes. By embracing a comprehensive approach, individuals can significantly enhance their diabetes management, improve their quality of life, and mitigate the risks associated with this chronic condition.



