Overview
The article focuses on the significance of understanding A1C glucose conversion for effective diabetes management, emphasizing its role in monitoring average blood glucose levels over time. It explains that regular A1C testing and conversion to average glucose readings are essential for patients to assess their treatment effectiveness and make informed lifestyle adjustments, ultimately reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding and monitoring A1C levels is paramount. A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, provides a snapshot of average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, serving as a crucial indicator for healthcare professionals to evaluate treatment effectiveness.
With alarming statistics revealing that a significant proportion of adults with diabetes are not achieving optimal A1C levels, the need for comprehensive management strategies has never been more urgent. This article delves into the importance of A1C testing, the conversion between A1C and daily glucose levels, and effective strategies for improvement, all while emphasizing the role of patient education and support in navigating the complexities of diabetes care.
By fostering a proactive approach to A1C monitoring, individuals can take significant strides toward better health outcomes and reduced risk of complications.
Understanding A1C: The Key to Diabetes Management
A1C, commonly referred to as glycated hemoglobin, is an essential blood test that assesses your average blood glucose amounts over the previous two to three months and is crucial for understanding a1c glucose conversion. Expressed as a percentage, the A1C glucose conversion measurement indicates the degree of glucose binding to hemoglobin; a higher percentage signifies elevated blood glucose amounts. This measurement plays a crucial role in blood sugar control through a1c glucose conversion by providing healthcare professionals with insights into the effectiveness of a patient's current treatment plan, enabling them to make informed adjustments as needed.
Regular monitoring of A1C readings is essential for preventing complications associated with diabetes, particularly when considering the a1c glucose conversion, as 80.6% of U.S. adults with diagnosed diabetes have a systolic blood pressure of 130 mmHg or higher, or are on medication for high blood pressure. This emphasizes the significance of thorough management strategies that tackle both blood pressure and a1c glucose conversion. Recent studies, including a subgroup analysis of A1C values and cardiovascular outcomes, found that the A1C glucose conversion >8% is consistently associated with increased cardiovascular risk across various patient populations.
For instance, the study indicated that while patients taking antipsychotics showed no significant cardiovascular events with an A1C ≤6%, those not on such medications exhibited a similar risk profile to the overall study. Ann L Albright, PhD, RD, from the Division of Diabetes Translation at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate A1C thresholds, noting that the choice of thresholds will depend on the interventions likely to be employed and the trade-offs between sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value. Therefore, a proactive approach to A1C monitoring, which includes a1c glucose conversion, not only aids in managing the condition but also significantly reduces the likelihood of long-term health complications.
At ATd Solutions, we provide resources and tools to help you understand and monitor your A1C levels effectively. Stay tuned for upcoming articles and support services designed to assist you in your health management journey.
A1C to Glucose Conversion: How It Works
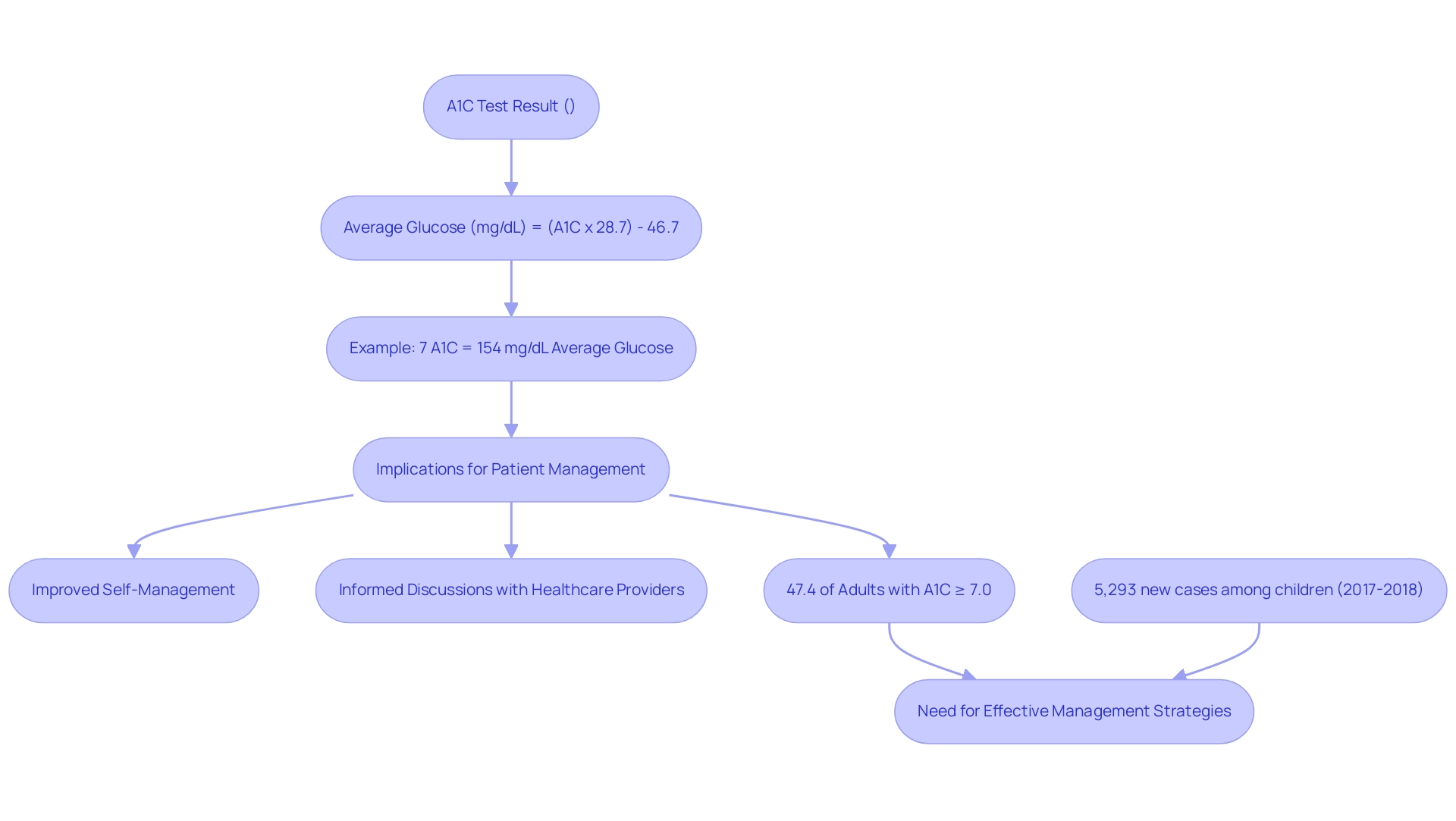
As T2DSolutions launches as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, it provides crucial information for newly diagnosed patients. The A1C test result is commonly expressed as a percentage, while average glucose concentrations are typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). The following formula can be employed for A1C glucose conversion to convert A1C values to average glucose readings:
Average Glucose (mg/dL) = (A1C x 28.7) - 46.7
For instance, an A1C of 7% corresponds to an average glucose measurement of approximately 154 mg/dL. This A1C glucose conversion is vital for patients, as it bridges the gap between A1C results and daily glucose levels, thereby enhancing self-management strategies. T2DSolutions aims to support newly diagnosed patients not only through educational content like this but also by offering community forums, access to healthcare professionals, and personalized resources.
Current research underscores the significance of integrating A1C monitoring with healthy lifestyle changes, which can lead to substantial improvements in overall health and well-being. Notably, among adults diagnosed with the condition, 47.4% had an A1C value of 7.0% or higher, indicating a pressing need for effective management strategies. Furthermore, during 2017–2018, there were 5,293 newly diagnosed cases of type 2 condition among children and adolescents aged 10 to 19, highlighting the prevalence of this illness across different age groups.
Understanding the A1C glucose conversion not only aids in daily monitoring but also encourages more informed discussions with healthcare providers regarding treatment and lifestyle adjustments. As Dr. Mathias Ried-Larsen stated, among adults with type 2 conditions diagnosed for less than 10 years, lifestyle interventions have shown benefits in glycemic control, emphasizing the importance of lifestyle changes in conjunction with A1C monitoring. The case study titled 'A1C Levels in Adults with Diabetes' illustrates that a significant portion of adults with this condition are not achieving optimal blood sugar control, further underlining the urgency for improved strategies for handling this health issue.
T2DSolutions is dedicated to tackling these challenges by offering the essential resources and community assistance for effective health oversight.
The Importance of Regular A1C Testing and Self-Monitoring
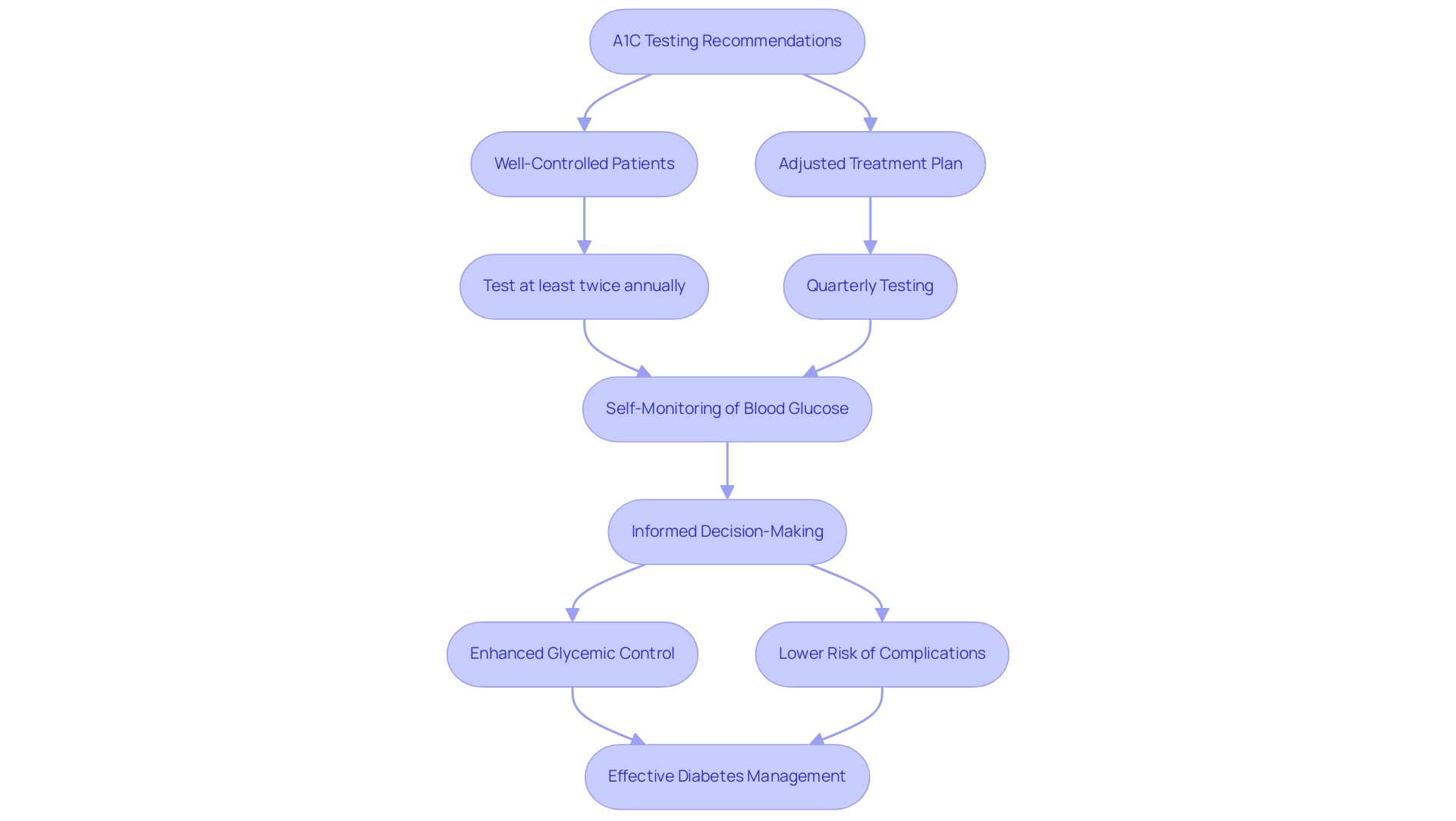
At T2DSolutions, a brand new resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education, we understand that effective diabetes management is crucial for newly diagnosed patients. For optimal care, it is essential for patients to have their A1C values tested at least twice annually to ensure accurate A1C glucose conversion, provided their condition is well-controlled. In cases where there have been adjustments to the treatment plan, quarterly testing is recommended.
Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose readings at home plays a critical role in this process and is a key focus of our resource hub. It empowers patients to understand how various factors—such as diet, physical activity, and medication—affect their blood sugar levels. This knowledge allows for informed decision-making regarding lifestyle and treatment adjustments.
By incorporating regular testing for A1C glucose conversion with ongoing self-monitoring, patients can gain a thorough understanding of their condition. This dual approach not only enhances glycemic control but also lowers the risk of complications; a recent study showed that only 3% of patients developed chronic kidney disease (CKD) and 1% developed ischemic heart disease (IHD) when adhering to testing frequency recommendations. Furthermore, the advantages of self-monitoring are emphasized by findings that show a substantial percentage of nondiabetic patients undergoing HbA1c testing, which raises concerns about overutilization and highlights the need for targeted strategies in managing blood sugar.
Additionally, a case study titled 'Adjusting Glycemic Targets for Hypoglycemia Unawareness' illustrates that patients experiencing hypoglycemia unawareness may benefit from raising their glycemic targets, ultimately improving their awareness and reducing future episodes. As one expert stated, 'Our results illustrated the potential link between adherence to testing frequency recommendations and better glycemic control and lower risk of subsequent complications.' At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to offering the resources and assistance required for effective diabetes care.
Subscribe now to stay up to date with our upcoming content and resources designed to assist you on your journey.
Interpreting A1C Results: What They Mean for Your Health
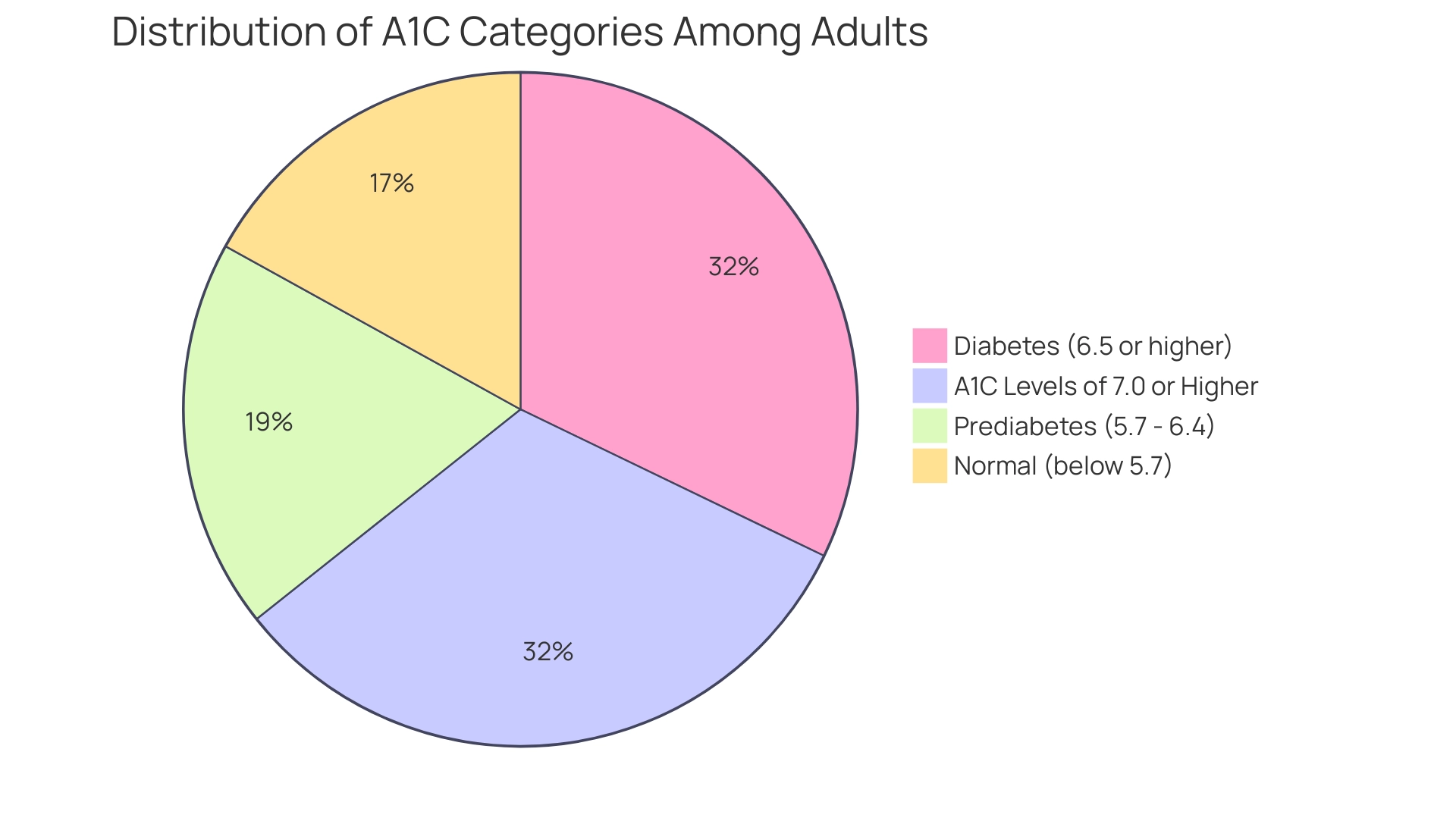
A1C results are classified into distinct categories based on A1C glucose conversion:
- Normal (below 5.7%)
- Prediabetes (5.7% - 6.4%)
- Diabetes (6.5% or higher)
Each classification carries significant health implications, highlighting the urgency of effective glucose management. Notably, higher A1C levels correlate with an elevated risk of diabetes-related complications, including neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular diseases.
Recent studies indicate that among adults with this condition, 47.4% exhibit an A1C value of 7.0% or higher, showcasing a troubling trend in glycemic control. Additionally, 80.6% of adults with diagnosed blood sugar issues had a systolic blood pressure of 130 mmHg or above or were on medication for elevated blood pressure, highlighting the relationship between A1C control and overall well-being. The occurrence of type 2 diabetes has notably risen among all racial and ethnic groups from 2002 to 2018, highlighting the need for effective strategies for control.
T2DSolutions is dedicated to empowering health care through education, community support, and resources customized for newly diagnosed patients. Our platform provides a range of educational resources, community support events, and direct access to healthcare professionals, ensuring that patients have the tools they need for effective oversight. Understanding these categories allows patients and caregivers to engage in informed discussions with healthcare providers regarding potential treatment adjustments related to A1C glucose conversion.
As Dr. Ann L Albright from the CDC notes, 'The selection of specific thresholds will ultimately depend on the interventions likely to be employed and the tradeoffs between sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value.' This insight highlights the significance of interpreting A1C results through the lens of A1C glucose conversion, considering personal health objectives and risks, and reinforcing the mission of T2 Solutions to provide comprehensive support for those navigating their diabetes care journey. Furthermore, the case study titled 'A1C Levels in Adults with Diabetes' reveals a concerning trend in glycemic control across various age groups, further emphasizing the need for improved strategies.
Testimonials from users highlight the positive impact of T2D Solutions on their management journey, illustrating the effectiveness of our resources in real-world scenarios.
Strategies for Managing and Improving Your A1C Levels
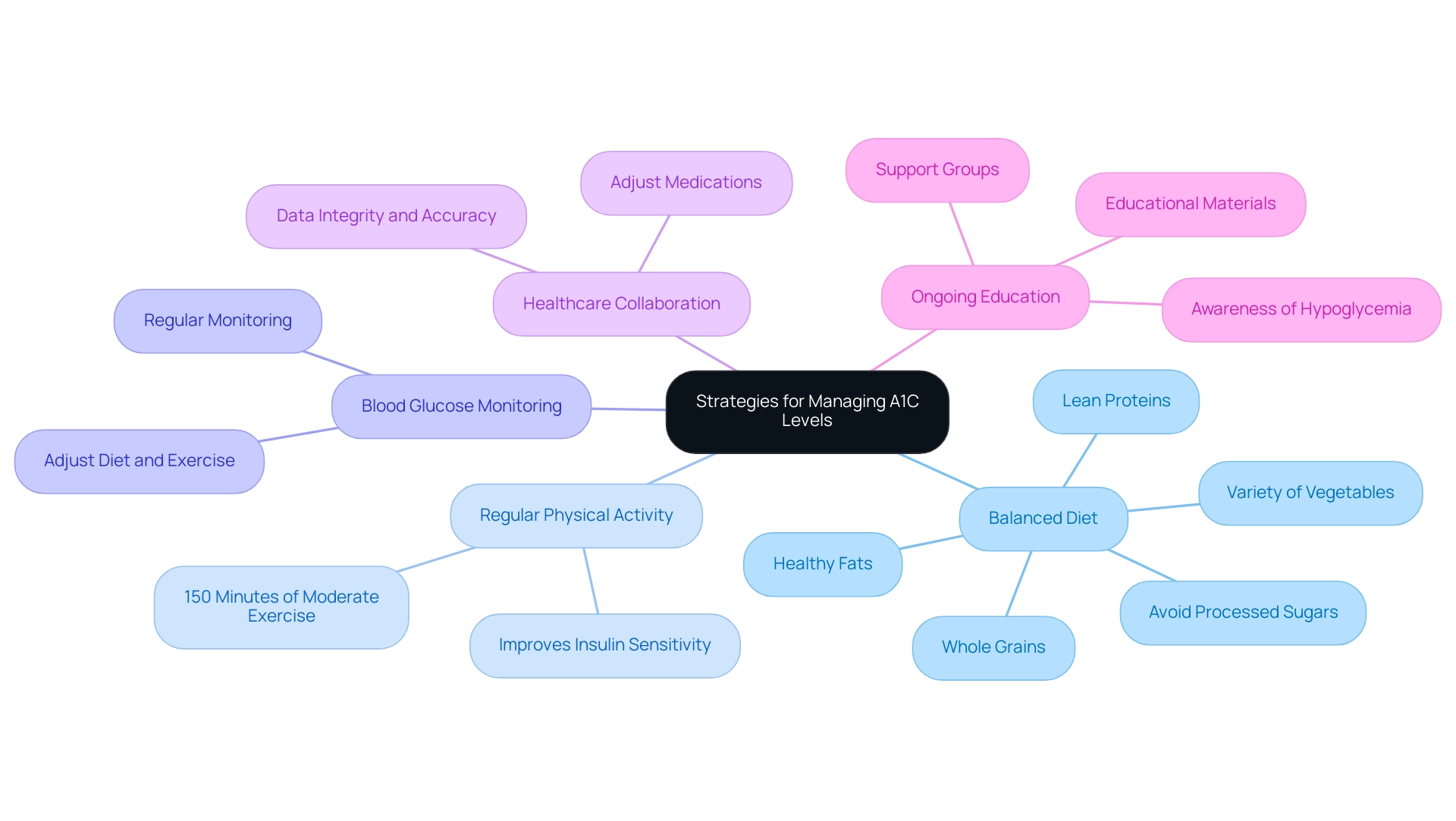
T2DSolutions is proud to introduce a new resource hub dedicated to providing comprehensive education and support for individuals managing Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes. To effectively enhance A1C values, consider implementing the following comprehensive strategies:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a balanced diet that includes whole grains, a variety of vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It's essential to steer clear of processed sugars, which can cause spikes in blood glucose. Nutritionists emphasize that a well-rounded diet plays a vital role in the a1c glucose conversion for managing A1C levels.
- Regular Physical Activity: Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Participating in regular physical activity not only helps with weight regulation but also improves insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for glucose control.
- Blood Glucose Monitoring: Regularly monitor your blood glucose levels to identify how different foods and activities influence your readings. This practice is vital for making informed adjustments to your diet and exercise regimen.
- Healthcare Collaboration: Work closely with a healthcare provider to adjust medications as needed. Personalized medication oversight can significantly impact your ability to achieve A1C targets, especially considering that 74.6% of Non-Hispanic Whites fail to reach the A1C target of <7%. O.E. and S.R., as guarantors of this work, emphasize the importance of data integrity and accuracy in managing this condition effectively.
- Ongoing Education: Stay informed about diabetes care through resources such as support groups and educational materials. Recent formal training programs have been developed to increase awareness of hypoglycemia and proactive prevention strategies, which are critical for newly diagnosed patients.
T2DSolutions will offer a variety of resources, including educational articles, interactive tools, and community support groups to assist you on your journey. We encourage you to subscribe for updates to receive the latest information and resources directly in your inbox. By implementing these strategies and utilizing the resources available through T2DSolutions, you can expect substantial improvements in A1C levels and achieve effective a1c glucose conversion for overall health. T2DSolutions is dedicated to being your complete resource in this journey, emphasizing the significance of continuous glucose monitoring, as underscored in research by Hermanns et al., which benefits hypoglycemia control. Furthermore, the economic consequences of blood sugar regulation are significant, with total expenses in the U.S. reaching an estimated $413 billion in 2022. This situation underscores the pressing need for effective prevention and management strategies to alleviate the financial burden associated with diabetes.
Conclusion
Understanding A1C levels is fundamental to effective diabetes management, as they serve as a key indicator of average blood glucose over time. Regular A1C testing not only helps healthcare professionals evaluate treatment efficacy but also empowers patients to take control of their health. The relationship between A1C results, daily glucose levels, and overall health underscores the necessity for proactive monitoring and lifestyle adjustments.
Implementing comprehensive strategies such as:
- Maintaining a balanced diet
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Collaborating closely with healthcare providers
can lead to significant improvements in A1C levels. The alarming statistics regarding the proportion of individuals with diabetes not achieving optimal A1C levels highlight the urgent need for better management practices and patient education.
Ultimately, the integration of A1C monitoring with self-management strategies can substantially reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. By utilizing available resources and staying informed, individuals can navigate their diabetes management journey with greater confidence and success. T2DSolutions is committed to supporting this journey, providing the tools and knowledge necessary for improved health outcomes.



