Overview:
The article focuses on understanding A1C goals for diabetics, emphasizing the importance of personalized A1C targets and effective management strategies to minimize health risks. It explains that while a general A1C target of under 7% is recommended for most adults, individual factors such as age and health conditions should be considered to tailor these goals, thus enhancing overall diabetes management and reducing the likelihood of complications.
Introduction
The A1C test is a pivotal tool in the management of diabetes, providing critical insights into a patient's average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. This test not only helps healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of treatment plans but also plays a significant role in predicting the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
With established guidelines categorizing A1C levels into normal, prediabetes, and diabetes ranges, understanding these metrics is essential for patients navigating their health journey. As diabetes prevalence continues to rise, the need for accurate monitoring and personalized management strategies has never been more pressing.
This article delves into the importance of the A1C test, how to interpret results, the necessity of individualized targets, and the limitations of the test, providing a comprehensive overview for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Understanding the A1C Test: Importance and Functionality
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support. Here, you will find a variety of educational resources, support groups, and tools designed to help you manage your condition effectively. The A1C test, commonly referred to as glycated hemoglobin, quantifies the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it.
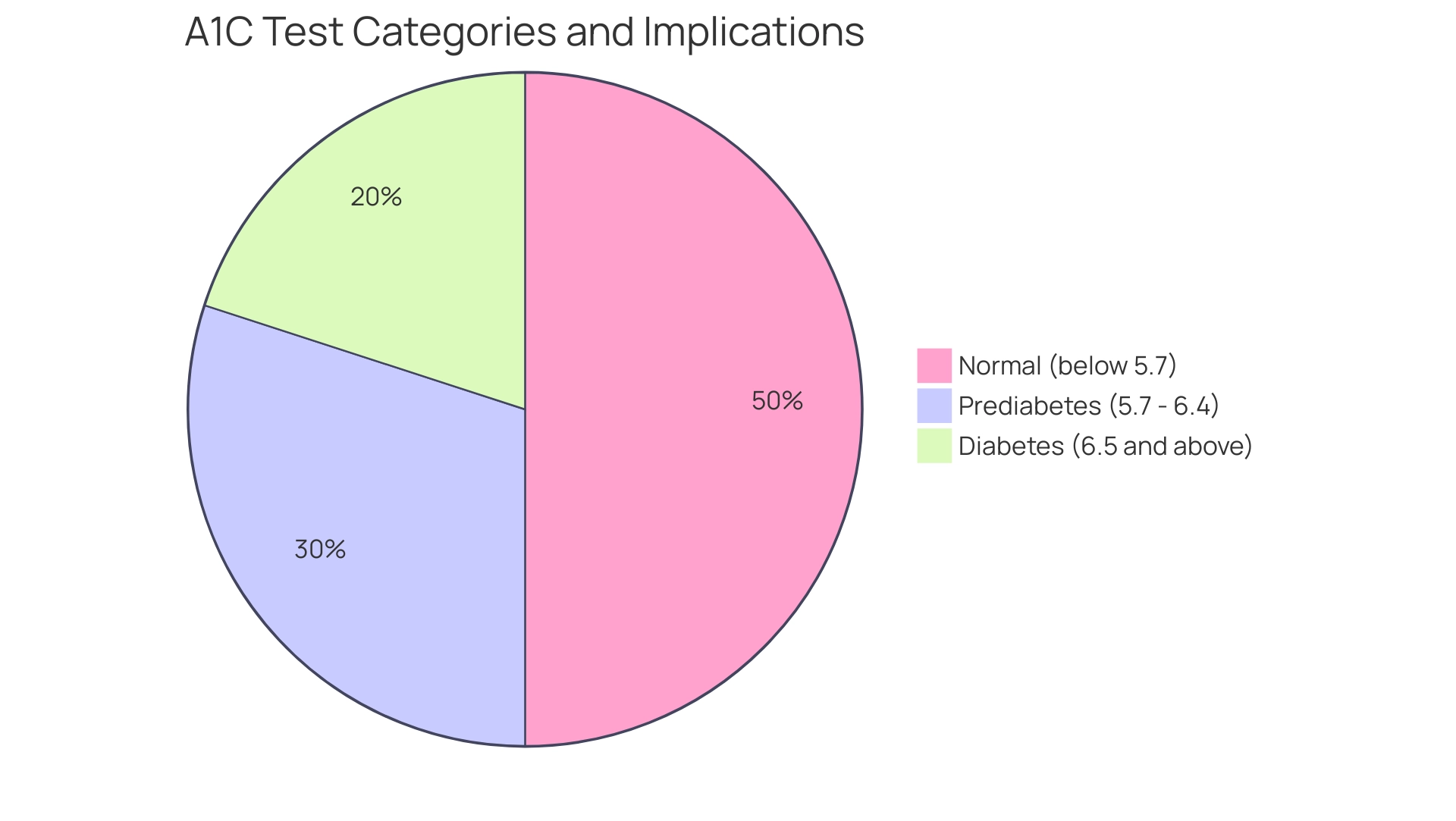
This test provides a dependable mean of your blood glucose readings over the prior two to three months, making it a crucial element in the management of the condition. By assessing A1C values, healthcare professionals can ascertain the efficacy of your treatment strategy and measure the risk of possible complications associated with blood sugar issues. According to established guidelines, a normal A1C measurement is generally considered to be below 5.7%.
Values between 5.7% and 6.4% suggest a condition of prediabetes, whereas an A1C measurement of 6.5% or above signifies a diagnosis of diabetes. Understanding these ranges is crucial, as patients with A1C levels exceeding 8% face a 5% increased odds of experiencing cardiovascular events. Moreover, previous severe hypoglycemia was noted in 447 (4.0%) of case subjects compared to 520 (1.2%) of control subjects, emphasizing extra risks linked to the care of individuals with blood sugar issues.
R. James Dudl, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Southern California, highlights the significance of the A1C test in preventive care, stating, 'The A1C test is an essential instrument in evaluating long-term glucose regulation and risk assessment for individuals with diabetes-related conditions.' Additionally, a case study titled 'Performance of A1C for Predicting Diabetes' demonstrated that the AUC for visit-detected cases during 6 years of follow-up was 0.827, showcasing A1C's effectiveness in long-term prediction of the condition. This highlights the significance of tracking A1C values and establishing A1C goals for diabetics as part of a comprehensive diabetes management strategy, which T2D Solutions is committed to assisting as we introduce our resources for newly diagnosed patients.
We encourage you to subscribe and stay updated as we roll out new content and tools tailored to your needs.
Interpreting A1C Results: What the Numbers Mean
A1C results are expressed as a percentage, offering a comprehensive view of average blood glucose readings over the preceding two to three months. For instance, an A1C reading of 7% is indicative of an average glucose measurement around 154 mg/dL. Elevated A1C percentages signify inadequate blood glucose control, thereby heightening the risk for complications, including neuropathy and cardiovascular diseases.
In fact, the hospitalization rate for hypoglycemia stands at 2.2 per 1,000 adults with diabetes, highlighting the potential dangers of poor A1C management. As indicated by specialists, the A1C test assesses glucose concentrations over a span of time, offering more insights about blood sugar than a single blood sugar examination. This underscores the necessity for patients to engage in discussions with their healthcare providers regarding the A1C goals for diabetics.
Furthermore, administering insulin after meals can help ensure appropriate dosing based on carbohydrate intake, which is a practical strategy for managing blood glucose levels. Comprehending these outcomes is essential for identifying suitable oversight strategies and applying required lifestyle adjustments to reduce health risks linked to blood sugar issues.
As T2D Solutions introduces itself as a fresh resource center for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar education and community assistance, we urge recently diagnosed individuals to make use of this platform for thorough advice on achieving A1C goals for diabetics and overall care.
T2D Solutions will provide a range of resources, including:
- Articles
- Webinars
- Support groups
These resources are aimed at assisting patients in managing their health journey. We also invite you to subscribe for updates to receive the latest content and resources as they become available. The recent case study titled 'Trends in Prevalence of Diagnosed and Undiagnosed Diabetes' illustrates the rising occurrence of the condition, emphasizing the significance of monitoring A1C goals for diabetics.
Personalizing A1C Goals: Tailoring Targets for Individual Needs
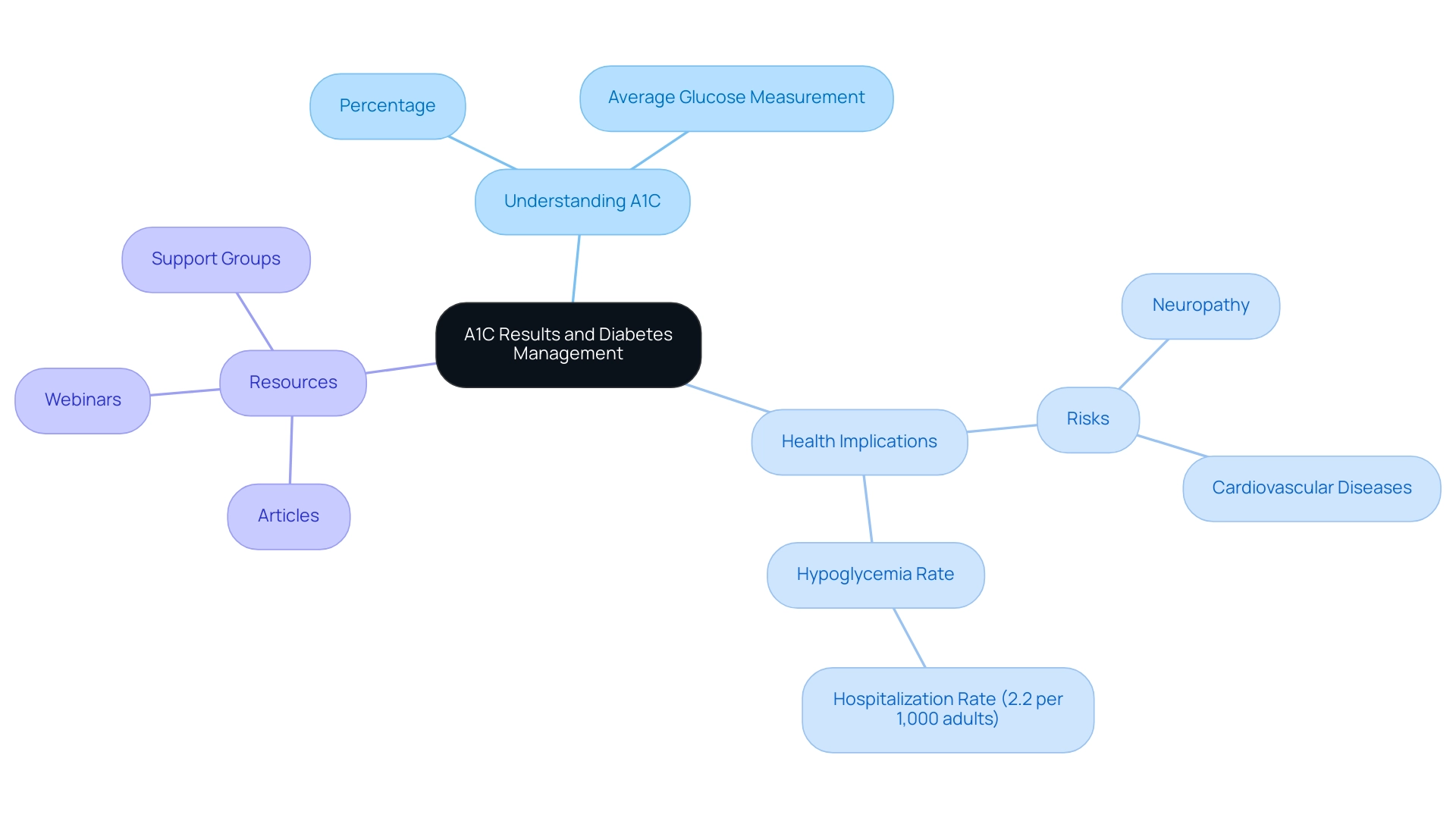
Customizing A1C goals for diabetics is crucial for efficient control, as it takes into account various factors such as age, duration of the condition, coexisting health issues, and personal lifestyle choices. Research indicates that older adults, especially those with a history of severe hypoglycemia, may benefit from less stringent A1C targets. For instance, the odds ratio for HbA1c ≥ 8.0% in the 76+ age group is 0.99 (95% CI 0.93–1.05), suggesting that older adults may not face significantly increased risks at this threshold.
While a general recommendation suggests maintaining A1C goals for diabetics below 7% for most adults, it is crucial for individuals to engage in discussions with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate target based on their unique circumstances. This customized method not only improves overall health oversight but also substantially lowers the risk of complications. Furthermore, the introduction of age-dependent HbA1c targets in 2016 has been associated with changes in clinician behavior, indicating a shift towards more personalized care.
As noted by Jenny Staab, PhD,
And, we would like to acknowledge the guidance on the use of the various data sources, highlighting the importance of expert input in establishing personalized care strategies.
This personalized focus aligns with the evolving recommendations regarding A1C goals for diabetics, further emphasizing the necessity of individualized plans in managing blood sugar. T2DSolutions aims to support newly diagnosed patients by providing access to educational materials and community resources that can help them understand and effectively manage their A1C goals for diabetics.
By leveraging the expertise available through Td Solutions, patients can receive tailored guidance that aligns with their specific health needs, similar to how personalized approaches have proven effective in other areas of healthcare, such as the case study on electronic triggers for cancer diagnosis delays.
Limitations of the A1C Test: Challenges in Diabetes Management
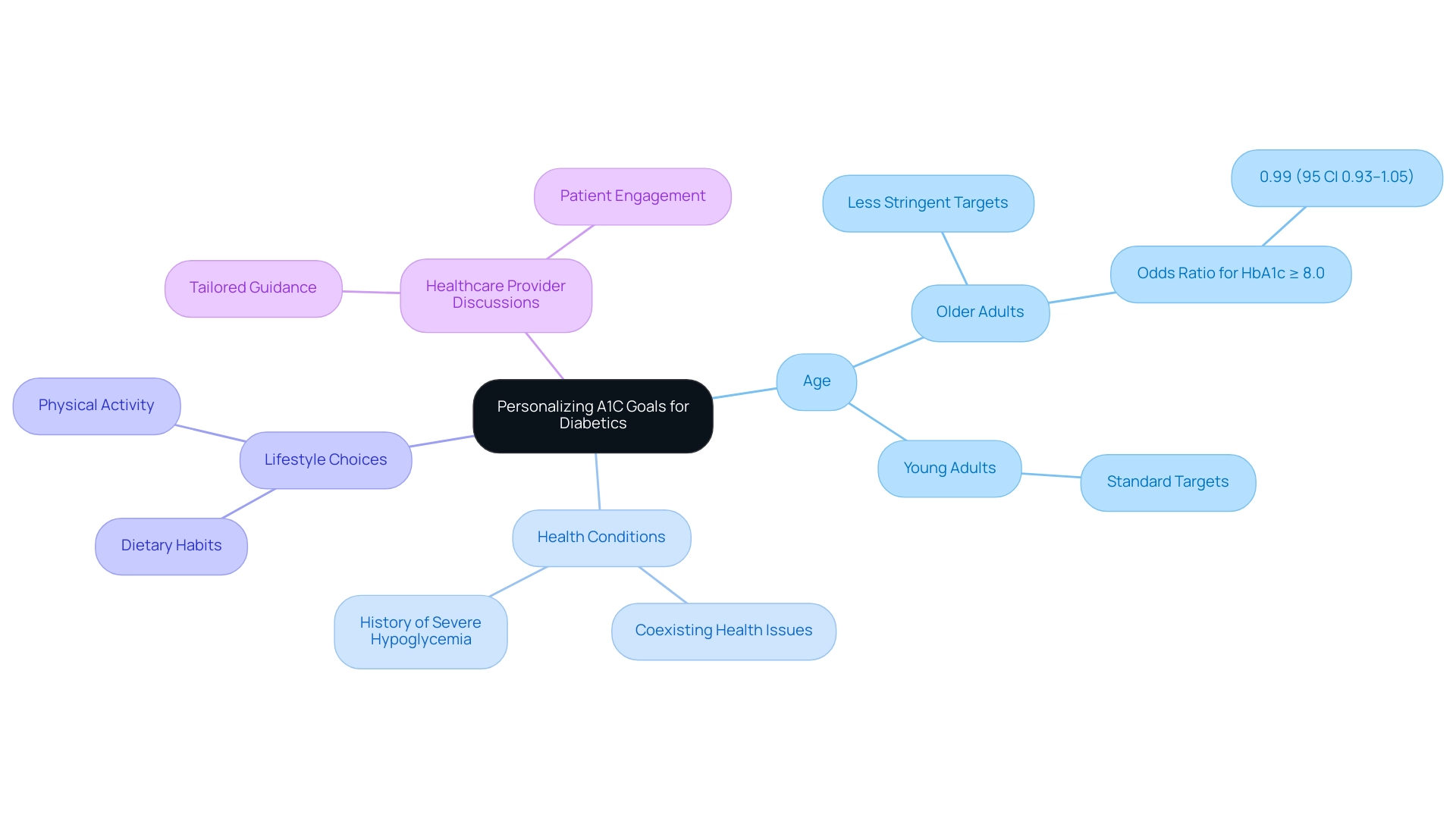
The A1C test acts as a vital element in blood sugar control, and it is important to recognize the A1C goals for diabetics while also acknowledging its restrictions. Various medical conditions, including anemia and hemoglobinopathies, can distort A1C results, leading to potential misinterpretations of a patient’s glycemic control. Furthermore, the test may not quickly indicate rapid changes in blood glucose levels, which can be essential for effective control of the condition.
Recent discussions highlight the necessity of considering A1C time in range (TIR) when contemplating treatment intensification. Findings suggest that a TIR below 20% is associated with a hazard ratio of 1.07 for peripheral vascular progression, emphasizing the need for careful monitoring. As noted in expert findings, 'Our findings suggest A1C TIR should be considered when thinking about intensification of treatment.'
Additionally, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) has revised its glycemic targets to establish A1C goals for diabetics, reflecting evolving guidelines based on studies like ADAG, which underscores the implications of A1C testing limitations. Consequently, it is imperative for patients to complement A1C testing with regular blood glucose monitoring using a glucometer. Participating in frequent conversations with healthcare providers about their overall approach is crucial.
As part of T2D Solutions, we aim to provide resources and community support to help individuals navigate these complexities. A comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, education, and self-monitoring is vital for effectively managing the condition and achieving optimal health outcomes.
Current Guidelines for A1C Management: Best Practices for Diabetics
T2DSolutions is committed to assisting newly diagnosed individuals in their journey towards effective control of their condition. Current clinical guidelines suggest that adults with the condition aim for A1C goals for diabetics of under 7% to effectively minimize the risk of complications related to it. This target is crucial, as it aligns with evidence suggesting that even older adults can experience significant benefits from lifestyle interventions, similar to those observed in younger populations.
Participants in the Look AHEAD trial demonstrated improvements in multimorbidity, with a reduction in the number of chronic conditions and enhanced physical function, significantly contributing to their quality of life. This reinforces the importance of thorough management of the condition, regardless of age. Healthcare professionals must consider the diverse needs of older adults when establishing and prioritizing treatment goals.
Regular monitoring of A1C levels, typically recommended every 3 to 6 months, is vital for evaluating the effectiveness of the treatment plan. Lifestyle modifications—including adherence to a balanced diet, consistent physical activity, and compliance with prescribed medications—are essential strategies for achieving A1C goals for diabetics. Additionally, understanding the cost changes for glucose management agents is important for treatment planning, as it can influence the accessibility and adherence to prescribed therapies.
By adopting these best practices and maintaining a collaborative approach with healthcare providers, individuals with this condition can achieve improved health outcomes and preserve their quality of life. T2DSolutions will provide ongoing education and support, ensuring you stay informed and empowered in your diabetes management journey. To stay updated on new content and resources, we encourage you to subscribe to T2D Solutions.
Conclusion
The A1C test is an indispensable tool in the effective management of diabetes, offering insights into a patient’s average blood glucose levels over the preceding months. Understanding the significance of A1C results, including the distinctions between normal, prediabetes, and diabetes ranges, is crucial for patients. This knowledge empowers individuals to engage meaningfully with their healthcare providers, facilitating informed decisions about their treatment plans and lifestyle adjustments.
Personalized A1C targets play a vital role in diabetes management, taking into account individual factors such as age and coexisting health conditions. This tailored approach not only enhances overall care but also helps mitigate the risks associated with diabetes. However, it is essential to recognize the limitations of the A1C test, including its susceptibility to misinterpretation due to various medical conditions and its inability to reflect rapid blood glucose fluctuations. Therefore, combining A1C monitoring with regular blood glucose checks is critical for a comprehensive management strategy.
In light of these considerations, adhering to current clinical guidelines, engaging in lifestyle modifications, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers are paramount for achieving optimal health outcomes. T2DSolutions is committed to equipping individuals with the necessary resources and support to navigate their diabetes journey effectively. By prioritizing education and community engagement, patients can empower themselves to manage their condition proactively and improve their quality of life.



