Overview:
The article focuses on understanding A1C levels and their implications for diabetes management across different age groups. It emphasizes that A1C targets vary by age—less than 7.5% for children, below 7% for adults, and between 7.5% to 8% for older adults—highlighting the importance of tailored management strategies to optimize health outcomes and prevent complications associated with diabetes.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding A1C levels is paramount for effective health outcomes. A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, serves as a crucial indicator of average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, guiding both patients and healthcare providers in monitoring diabetes control.
With rising diabetes prevalence and the significant economic burden associated with the condition, the importance of regular A1C testing cannot be overstated. This article delves into the intricacies of A1C testing, including:
- its implications for different age groups
- the impact of lifestyle choices
- common misconceptions that can hinder effective management
By exploring these facets, individuals can better navigate their diabetes journey, armed with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions and improve their overall health.
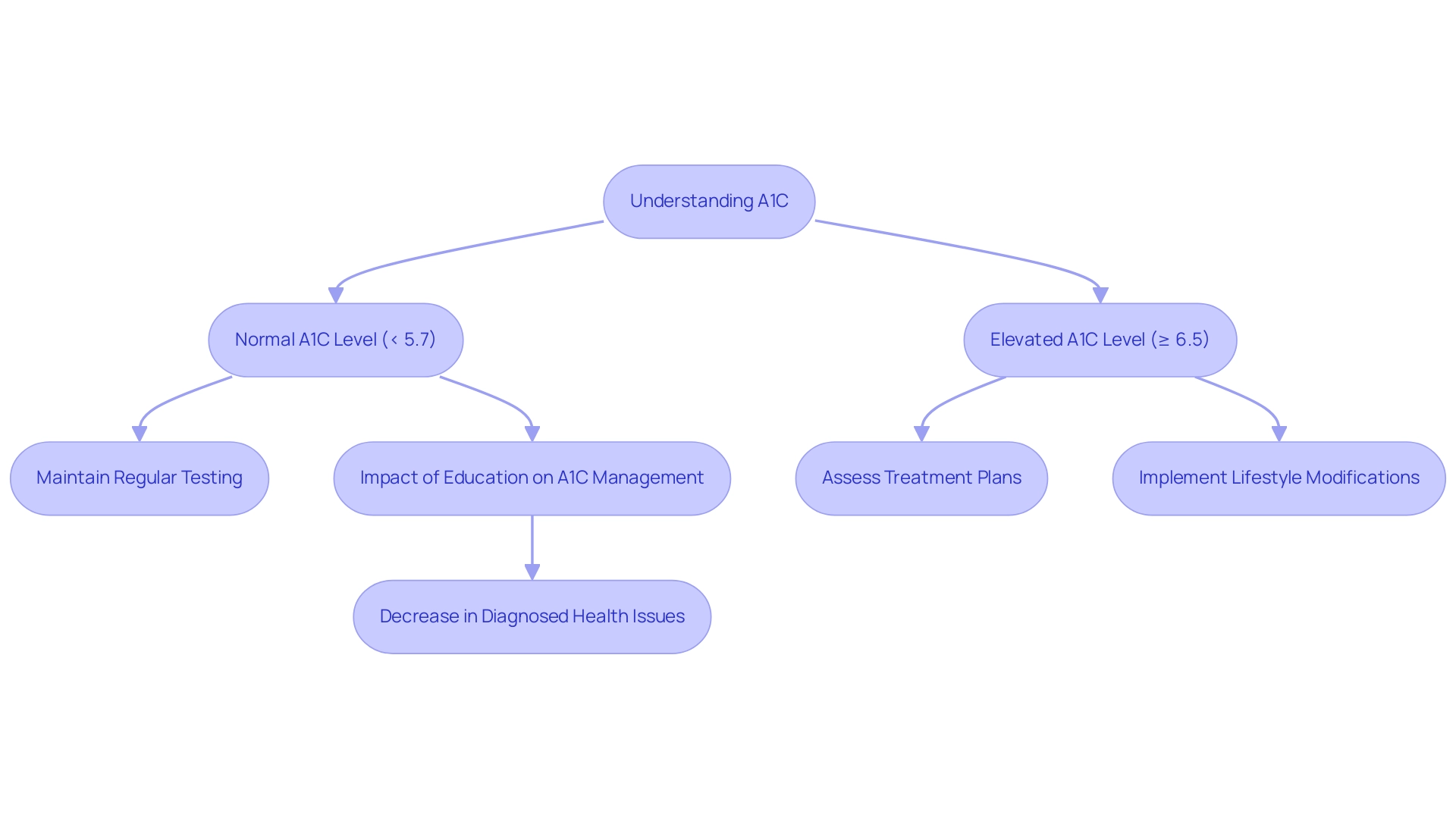
Understanding A1C: What It Is and Why It Matters
A1C, commonly referred to as glycated hemoglobin, is an essential blood test that indicates an individual’s average blood sugar readings over the past two to three months. This measurement plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar, offering insights into how effectively glucose concentrations are being controlled. The A1C test results are shown as a percentage; a higher percentage indicates increased blood sugar amounts.
According to current guidelines:
- An A1C level below 5.7% is considered normal.
- Levels equal to or above 6.5% are indicative of a blood sugar condition.
At T2 Solutions, we emphasize the importance of regular A1C testing for individuals diagnosed with this condition, as it allows healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of treatment plans and lifestyle modifications. This ongoing evaluation is crucial for making necessary adjustments to prevent potential complications associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
Recent research has highlighted the significance of reaching and sustaining target A1C levels by age group, with suggestions indicating a minimum 7–10% reduction in excess weight for young individuals facing overweight and obesity concerning glucose regulation. This statistic highlights the significance of lifestyle modifications in controlling A1C levels. Furthermore, T2 Solutions acknowledges that the occurrence of diagnosed health issues related to blood sugar varies greatly with educational level; it dropped from 14.6% in adults with a high school diploma or less to 7.3% in those with a bachelor’s degree or higher, illustrating the impact of education on effective control of the condition.
Furthermore, T2 Solutions is dedicated to offering innovative insights and the latest updates in health management, which are crucial for patients navigating their health journeys. The economic strain of this condition is significant, with direct and indirect expenses amounting to $413 billion in the United States in 2022, highlighting the essential requirement for effective strategies in handling this illness. By understanding these metrics and accessing the latest resources from T2 Solutions, patients can engage in proactive management of their condition, supported by our commitment to education and community support.
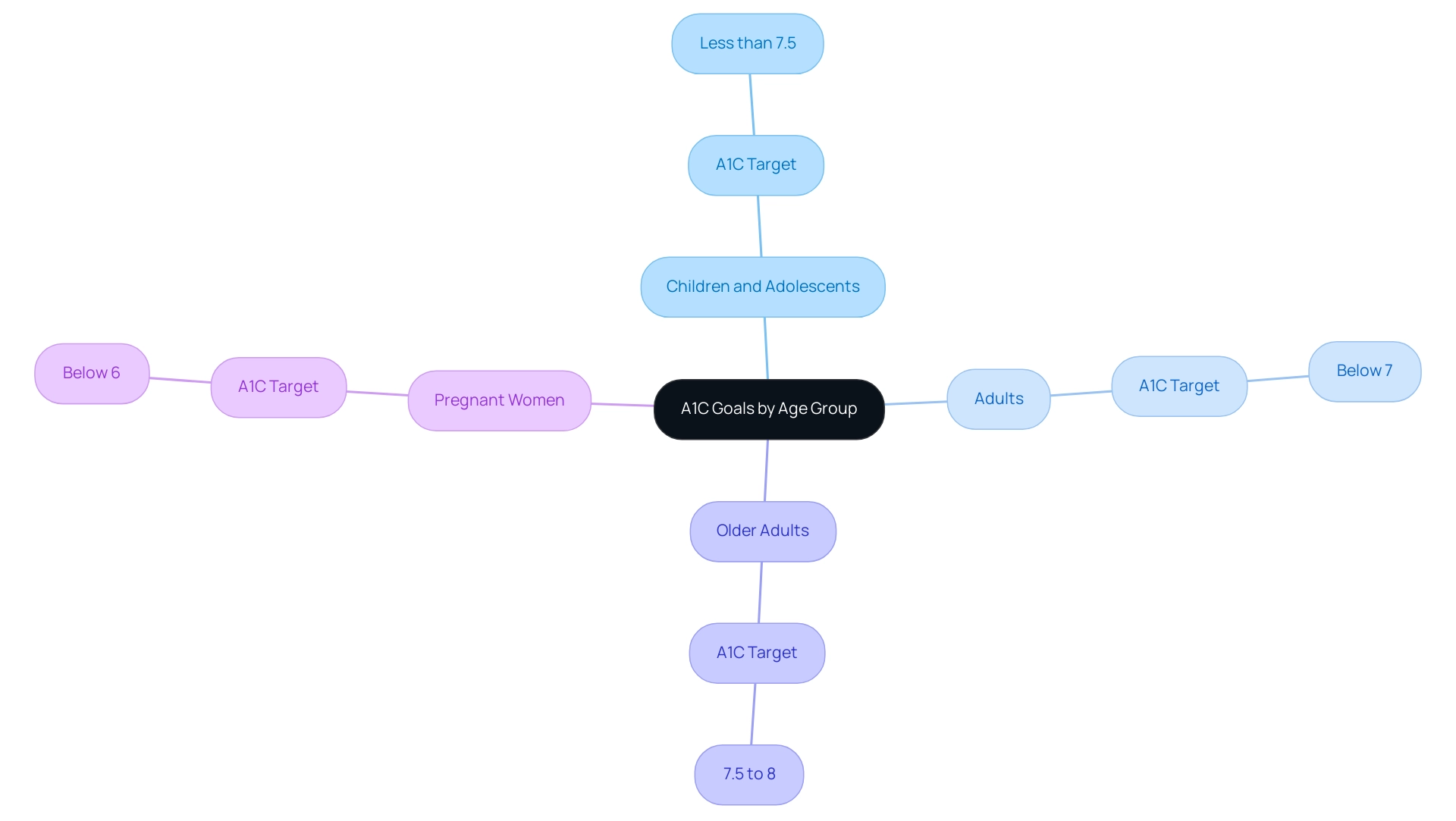
A1C Goals by Age Group: Tailoring Diabetes Management
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support. As a new site, we are dedicated to offering valuable information to assist you in managing your condition effectively. A crucial element of diabetes management is understanding A1C measurements and goals, which differ considerably across various age groups, emphasizing the significance of A1C levels by age group to meet specific health needs and risks.
The recommended targets for A1C values are as follows:
- Children and Adolescents (under 18 years): An A1C level of less than 7.5% is advisable for this group, as it aids in preventing complications while supporting healthy growth and development.
- Adults (18-65 years): For most adults, the optimal A1C target is below 7%. This target strikes a balance between effective management of blood sugar levels and minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Older Adults (over 65 years): A1C targets for older adults may be adjusted to a range of 7.5% to 8%. This adjustment helps mitigate the risk of complications while considering the increased likelihood of significant health issues. Individualized care is essential, taking into account life expectancy, overall health, and cognitive function.
- Pregnant Women: In pregnancy, an A1C goal of below 6% is generally recommended to reduce the risk of complications for both mother and child.
These A1C levels by age group provide a framework for developing treatment plans and lifestyle modifications, empowering individuals to manage their condition effectively and lower the risk of long-term complications. According to recent findings from the National Center for Health Statistics, the prevalence of undiagnosed blood sugar issues has increased from 1.6% in adults in the underweight or normal weight category to 2.8% in those in the overweight category and 7.9% in adults with obesity. This statistic highlights the need for tailored management strategies across age groups.
As noted by leading endocrinologists, addressing the distinct A1C levels by age group is crucial for optimizing care and ensuring better health outcomes for patients across all ages. Furthermore, the case study titled 'Trends in Diabetes Prevalence Over Time' indicates that the age-adjusted prevalence of total metabolic disorders increased from 9.7% in 1999–2000 to 14.3% in August 2021–August 2023, illustrating the growing public health concern regarding these conditions. Don't forget to subscribe to stay updated on our latest content and resources as we continue to grow.
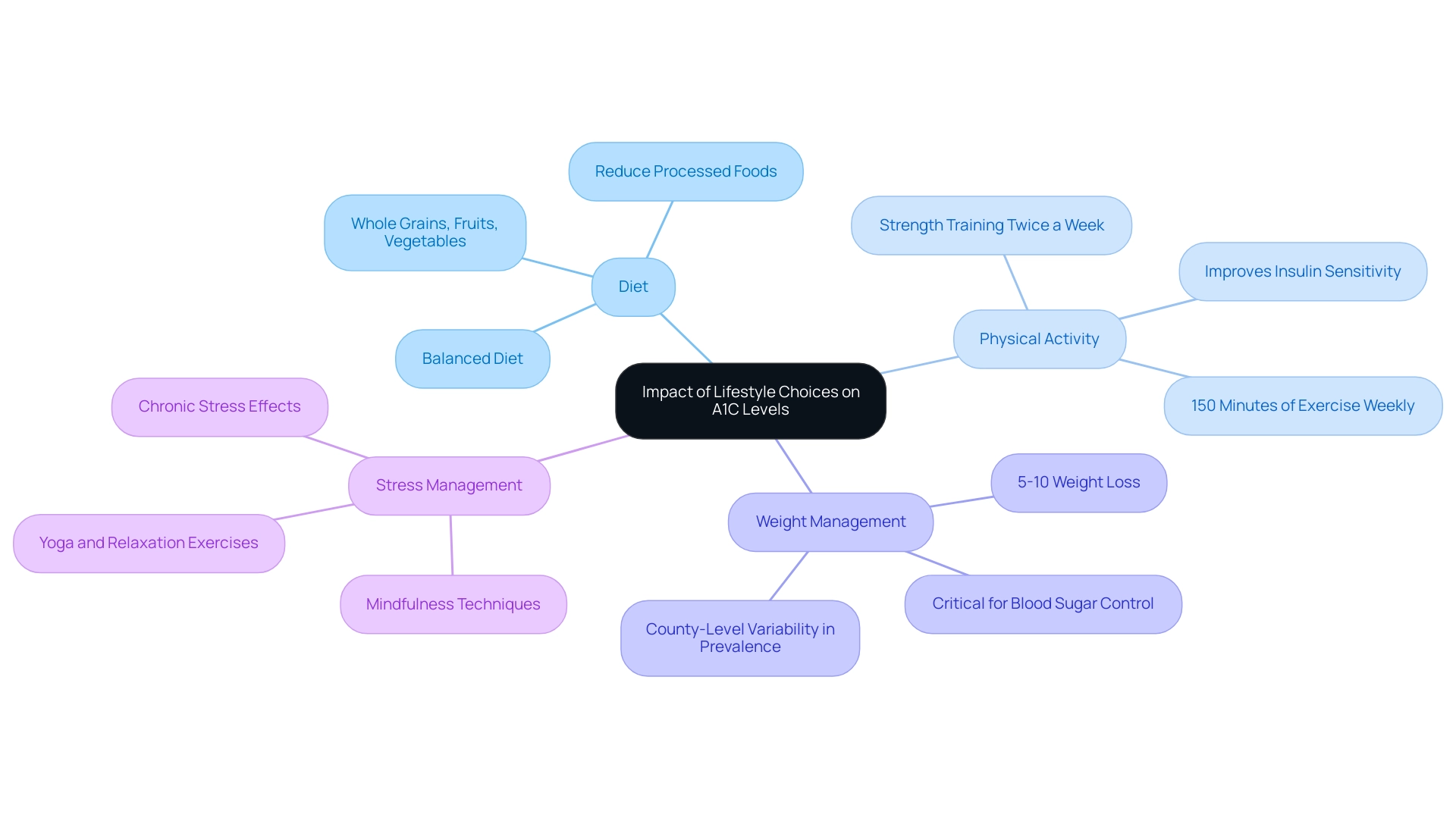
The Impact of Lifestyle Choices on A1C Levels
Managing a1c levels by age group is significantly influenced by lifestyle choices for individuals with type 2 diabetes. The following factors are particularly significant:
-
Diet: A balanced diet composed of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential for regulating blood sugar.
It is essential to reduce the consumption of processed foods and sugars, as these can cause fluctuations in glucose. Nutritionists stress that a well-structured diet can significantly influence blood sugar control, making it a foundational aspect of managing the condition. For further details on controlling A1C values, visit T2DSolutions, a new resource center focused on education and support for those with blood sugar issues. -
Physical Activity: Participating in regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps in reducing blood sugar amounts. The World Health Organization recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, complemented by strength training exercises on at least two days. Recent studies indicate that individuals who incorporate consistent exercise into their routines can achieve better results in A1C levels by age group.
The odds ratio (OR) for ACA enrollees having an uncontrolled A1C was 1.093, highlighting the importance of lifestyle choices in managing the condition effectively. -
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is critical for improving a1c levels by age group. Research shows that a modest weight loss of 5-10% can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar control.
This is especially pertinent considering the growing occurrence of the condition, with county-level studies indicating an increase in diagnosed cases from 6.3% in 2004 to 8.3% in 2021 across the United States. The variability in prevalence across counties underscores the need for localized public health strategies to address diabetes management. -
Stress Management: Chronic stress is known to raise blood sugar amounts, making it essential to adopt stress-reducing techniques.
Practices such as mindfulness, yoga, and relaxation exercises can be beneficial in managing stress, thus contributing positively to blood sugar levels.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is vital for identifying patterns that relate to lifestyle choices and their effects on a1c levels by age group. This proactive approach enables timely adjustments to management strategies, ensuring that individuals can maintain optimal health.
T2DSolutions will offer tools and community assistance to help individuals in these monitoring efforts.
The significance of these lifestyle factors is emphasized by the WHO, which reports that up to 50% of individuals who have succumbed to COVID-19 were affected by vascular and metabolic disorders, including other chronic conditions. Furthermore, the WHO recommends that individuals aged 45 and older, along with younger individuals at greater risk, undergo more frequent screenings for blood sugar conditions. By emphasizing nutrition, physical activity, and general well-being, people can make educated decisions that greatly influence their overall condition and a1c levels by age group, aided by the resources offered at T2DSolutions.
Understanding A1C Testing Frequency
The suggested frequency of A1C testing differs based on personal situations and management needs.
For Individuals with Diabetes:
- Patients who maintain stable blood sugar levels and have effectively managed their diabetes may only require A1C testing every 6 months.
- Conversely, individuals who struggle to meet their blood sugar targets or who have experienced changes in their treatment plan are advised to test their A1C every 3 months.
For Prediabetes:
- For individuals diagnosed with prediabetes, testing is generally recommended every 1-2 years, contingent on specific risk factors and the guidance of healthcare providers.
During Pregnancy:
- Pregnant women diagnosed with diabetes should undergo more frequent A1C testing, typically every trimester. This enables efficient oversight of their well-being and their baby's health.
Regular A1C testing is essential as it offers a continuous assessment of blood sugar control. This practice facilitates timely adjustments to treatment plans, which is essential for preventing complications. Additionally, the 2024 Standards of Care emphasizes the importance of person-first and inclusive language in managing the condition, as stated by the American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee:
'The 2024 Standards of Care includes revisions to incorporate person-first and inclusive language.'
Furthermore, ongoing research into blood sugar disorders classification may lead to a better understanding of the pathophysiology of β-cell dysfunction, ultimately enhancing personalized treatment strategies. In a pertinent case study titled 'Lifelong Screening for Glucose Intolerance Post-GDM,' it was emphasized that women diagnosed with gestational glucose intolerance mellitus (GDM) should be monitored for prediabetes and type 2 hyperglycemia throughout their lives, as this condition indicates a higher risk for the latter. This highlights the essential importance of regular A1C testing in the control of A1C levels by age group across different groups.
It is also recommended that screening for blood sugar issues should begin at age 35 and be repeated at least every 3 years if results are normal. Furthermore, for young individuals with excess weight and type 2 conditions, a reduction in weight of at least 7–10% is recommended, which can greatly influence A1C values and overall care.
![]()
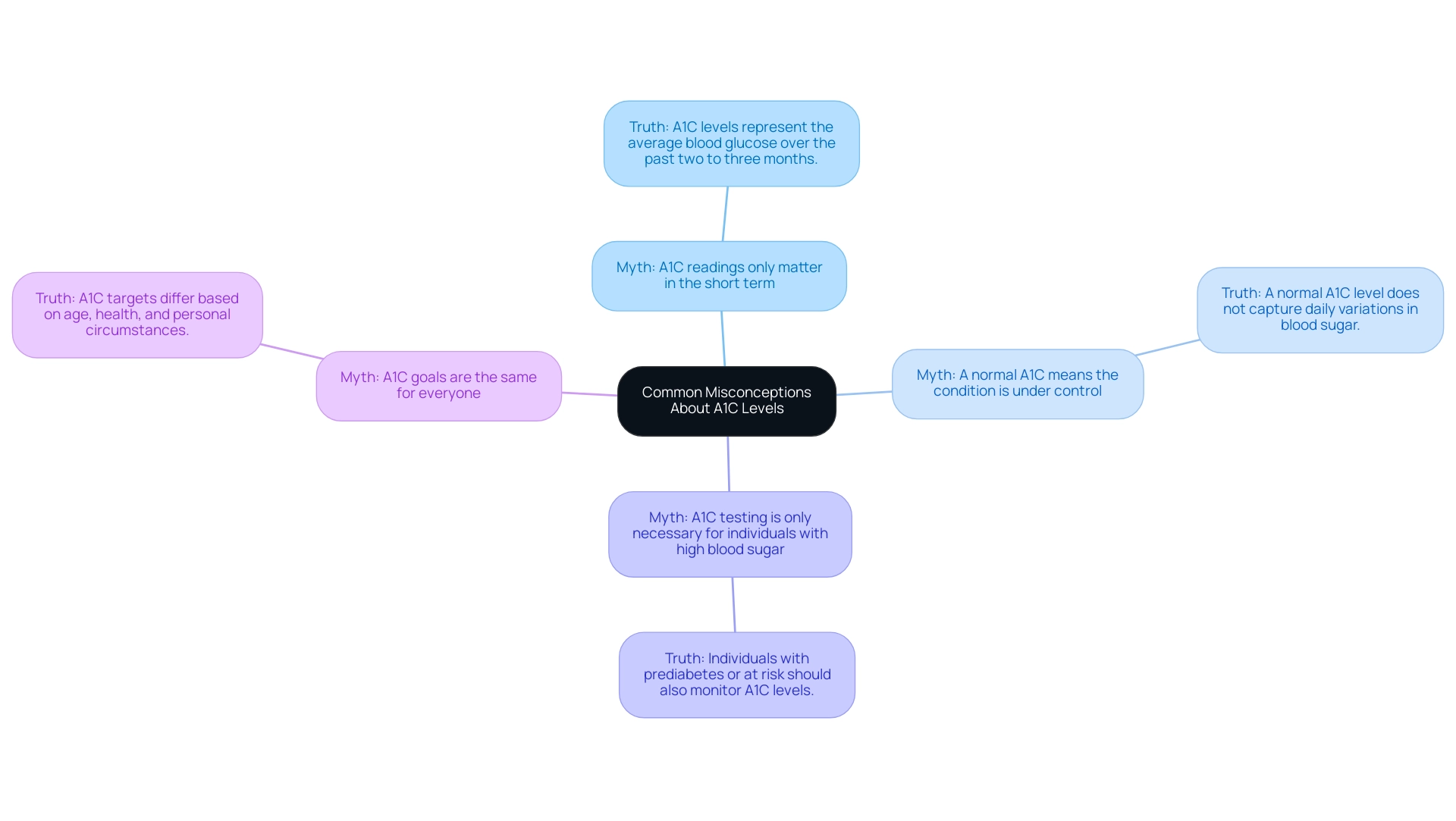
Common Misconceptions About A1C Levels
A variety of myths persist regarding A1C testing and its interpretation in the care of blood sugar conditions. Below are some prevalent misconceptions, along with clarifying truths:
- Myth: A1C readings only matter in the short term.
-
Truth: A1C levels represent the average blood glucose over the past two to three months, making it a crucial metric for evaluating long-term glycemic control and overall diabetes management.
-
Myth: A normal A1C means the condition is under control.
-
Truth: Although a normal A1C level is encouraging, it does not capture the daily variations in blood sugar. Continuous monitoring is essential for a thorough understanding of one’s health management.
-
Myth: A1C testing is only necessary for individuals with high blood sugar.
-
Truth: Individuals diagnosed with prediabetes or those at risk for developing diabetes should also have their A1C levels monitored. This proactive approach helps individuals remain informed about their health status and make necessary lifestyle adjustments.
-
Myth: A1C goals are the same for everyone.
- Truth: A1C targets differ based on various factors including age, overall health, and personal circumstances. This emphasizes the significance of personalized approaches tailored to individual needs.
By clarifying these prevalent misunderstandings, individuals can better navigate their health strategies, leading to informed choices and enhanced health results. Addressing these myths is vital, particularly as this condition remains a leading cause of complications such as end-stage kidney disease, which accounted for 39.2% of cases in 2019. This statistic highlights the gravity of blood sugar control and its complications.
As emphasized by David B. Sacks, 'The notable decrease in microvascular complications with lower A1C and the absence of sample lability, along with several other benefits, have resulted in the suggestion by some organizations that A1C be utilized for screening and diagnosis of this condition.' Additionally, in 2019, 61,522 individuals developed end-stage kidney disease with the primary factor being high blood sugar, highlighting the critical need for effective A1C monitoring and oversight.
As T2DSolutions emerges as a new resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, we are committed to empowering diabetes management through education, community support, and innovative insights. Stay tuned for more updates as we continue to develop this platform, and consider subscribing to receive emails when new content is published.
Conclusion
Understanding A1C levels is essential for effective diabetes management, as it serves as a vital indicator of average blood sugar control over time. Regular A1C testing, tailored to individual needs and age groups, is crucial for monitoring diabetes and making necessary adjustments to treatment plans. The article highlights the significance of lifestyle choices—such as diet, exercise, weight management, and stress reduction—in influencing A1C levels and overall health.
Moreover, dispelling common misconceptions about A1C testing is pivotal for empowering individuals to take charge of their diabetes management. Recognizing that A1C levels reflect long-term trends rather than short-term fluctuations is essential for informed decision-making. The economic burden of diabetes underscores the need for proactive management strategies, making it imperative for individuals to stay educated and engaged in their health journeys.
In summary, understanding and monitoring A1C levels, combined with a commitment to healthy lifestyle choices, can lead to improved health outcomes for those managing diabetes. By leveraging resources like T2DSolutions, individuals can enhance their knowledge and support networks, ultimately fostering better diabetes care and management.



