Overview:
The article focuses on the importance of the A1C test in managing blood sugar levels and how A1C medicine can aid in treatment and monitoring. It emphasizes that regular A1C testing is crucial for effective diabetes management, as it informs healthcare providers about necessary treatment adjustments and highlights the significance of lifestyle changes and medication options to improve A1C levels and overall health outcomes.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of diabetes management requires a solid understanding of critical tools such as the A1C test. This essential measure, which reflects average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, plays a pivotal role in both diagnosing diabetes and guiding treatment strategies.
As healthcare professionals emphasize the need for regular A1C testing, patients are encouraged to engage actively with their results to optimize their management plans. With the rising costs associated with diabetes care—estimated at a staggering $413 billion in 2022—effective A1C monitoring becomes not just a health necessity but also a financial imperative.
This article delves into the importance of A1C testing, the lifestyle changes and medications that can help manage levels, and the factors influencing test accuracy, providing a comprehensive resource for those looking to take control of their diabetes journey.
Understanding the A1C Test: Importance and Functionality
The A1C test, known as glycated hemoglobin, serves a critical function in managing blood sugar by measuring the average glucose levels over the preceding two to three months. This test is presented as a percentage; higher percentages are indicative of less effective blood sugar control. Its role extends beyond diagnosis; it is vital for evaluating the effectiveness of A1C medicine treatment plans.
Healthcare professionals utilize A1C medicine results to make informed decisions regarding necessary treatment adjustments and ongoing monitoring. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), individuals diagnosed with this condition should undergo an A1C test at least biannually. Increased frequency may be warranted when treatment plans change or when glycemic targets are not being met.
These recommendations highlight the significance of regular monitoring in managing the condition effectively. T2DSolutions is dedicated to assisting newly diagnosed patients with extensive resources and community support, enabling them to comprehend the importance of A1C testing and overall health care. T2DSolutions offers educational initiatives such as workshops and online resources that provide information on managing the condition, including diet and exercise guidance tailored for individuals based on their A1C levels and the use of A1C medicine.
The financial consequences of dealing with the condition are substantial, as additional healthcare expenses per individual linked to it rose from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022. This highlights the need for comprehensive healthcare strategies. As Roopa Naik states, 'Disclosure: Roopa Naik declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.'
Additionally, the overall direct and indirect projected expenses of diagnosed blood sugar conditions in the United States in 2022 amounted to $413 billion, highlighting the significance of efficient oversight strategies, including the use of A1C medicine for regular testing. T2DSolutions seeks to assist these strategies through its educational programs, aiding patients in navigating the complexities of health condition oversight and potentially lowering their healthcare expenses.
Managing A1C Levels: Lifestyle Changes and Medication Options
Effective oversight of A1C values requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Dietary adjustments
- Physical activity
- Weight control
- A1C medicine
Individuals should focus on a balanced diet that emphasizes:
- Whole grains
- An array of fruits and vegetables
- Lean proteins
while minimizing the intake of processed foods and sugars. Current research underscores that regular physical activity—specifically, aiming for 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week—can lead to marked improvements in glycemic control.
Significantly, at six months, participants in dietary studies reached a median physical activity rate of 15.7 metabolic equivalent hours per week, emphasizing the potential for lifestyle modifications to enhance health outcomes. Moreover, weight control plays a vital part; even slight decreases in body weight have been linked to substantial improvements in A1C scores. Medication, such as A1C medicine options including Metformin, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and insulin therapy, remains a crucial element of blood sugar control.
In light of recent findings, including that 26% of participants prescribed sulfonylureas experienced a reduction in dosage after 12 months, it is crucial to consult healthcare providers to tailor a treatment plan that reflects individual health needs and preferences. This complex approach not only seeks to enhance A1C levels but also corresponds with new findings regarding the financial impact of blood sugar disorders, which reached an estimated $413 billion in the United States in 2022, highlighting the urgent necessity for effective A1C medicine solutions.
Furthermore, T2DSolutions is debuting as a fresh resource center focused on Type 2 and Type 3 conditions education and community assistance, offering recently diagnosed individuals valuable insights and tools for effective oversight.
This hub will provide educational articles, support groups, and interactive tools designed to assist patients in their health journey. As the site is 'coming soon,' we encourage you to subscribe for updates and be among the first to access these resources. As Dr. Bazzano pointed out, 'Minimizing random error in dietary intake assessments using 24-hour recall is essential for accurately understanding the impact of diet on blood sugar control.'
This insight highlights the significance of accurate dietary assessments in the overall control of A1C values with the help of A1C medicine.
Interpreting A1C Results: What Do the Numbers Mean?
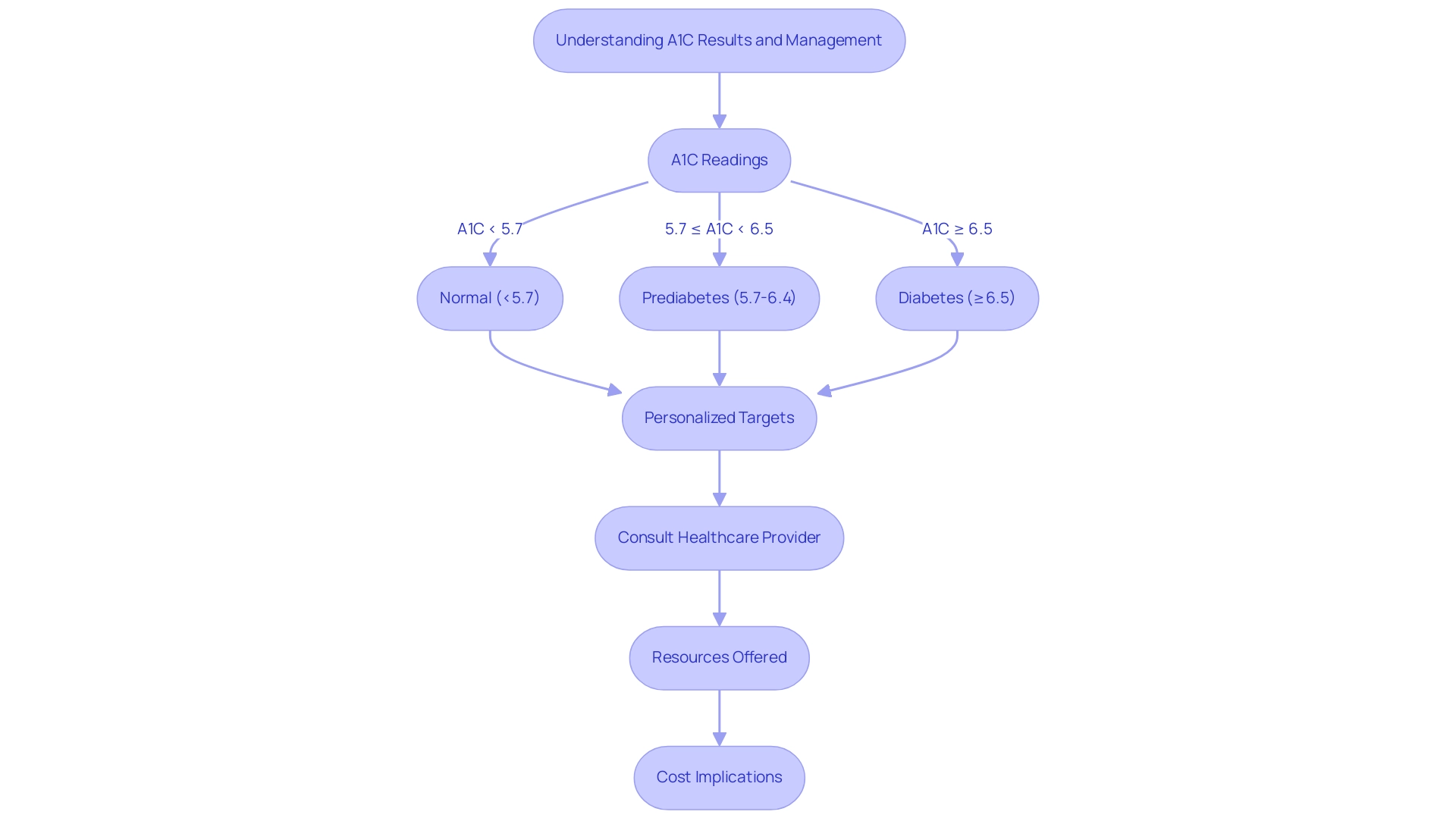
As a recently diagnosed individual, comprehending A1C values is essential in the management of a1c medicine for this condition. An A1C reading below 5.7% is regarded as normal, while readings between 5.7% and 6.4% suggest prediabetes. A rate of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis, with a suggested target for a1c medicine generally below 7% for those identified.
However, personalized targets may vary significantly based on individual factors, including age, overall health, and medical history. The American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee emphasizes a uniform approach to interpreting these results, highlighting that, 'There remains strong consensus that establishing a uniform approach to diagnosing GDM will benefit people with GDM, caregivers, and policymakers.' This consensus extends to A1C interpretation, underscoring the necessity for patients to discuss their results with healthcare providers to understand their implications fully.
At T2DSolutions, launching soon, we are dedicated to offering extensive resources to assist you in your health journey, including advice on A1C measurements and treatment strategies. Our forthcoming platform will provide tools like:
- Personalized tracking systems
- Educational resources
- Community support forums
to assist you in navigating health challenges effectively. Recent statistics indicate that efficient oversight of A1C levels can greatly impact healthcare expenses associated with glucose intolerance, which rose from $10,179 per individual in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022.
This underscores the urgent need for effective A1C medicine management to mitigate rising costs. Experts like Cheryl D. Fryar and Qiuping Gu from the National Center for Health Statistics stress the importance of ongoing monitoring and individualized treatment strategies, particularly with a1c medicine. For those diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), awareness of A1C monitoring implications is essential, as evidenced by the case study 'Lifelong Screening for Conditions Post-GDM,' which indicates that GDM can signal underlying β-cell dysfunction, increasing the risk of developing type 2 health issues post-delivery.
Continuous monitoring and personalized treatment approaches are essential for effectively managing the condition and reducing associated complications, and T2 Solutions strives to be your dependable partner in this effort.
Current Guidelines and Controversies in A1C Testing
t D Solutions is proud to announce the launch of a new resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 sugar-related conditions education and community support. As a recently diagnosed individual, grasping the significance of regular A1C medicine testing is essential for effective control of blood sugar levels. Current guidelines established by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) indicate that individuals diagnosed with the condition should undergo A1C testing at least twice annually if they are meeting their treatment goals.
Conversely, for those not achieving these goals, testing should occur quarterly. This organized method is based on the need for regular monitoring to ensure effective oversight. In addition to A1C testing guidelines, T2 Solutions will provide a variety of resources, including:
- Educational materials
- Community forums
- Access to healthcare professionals dedicated to supporting your health journey
According to the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, the prevalence of this condition continues to rise, underscoring the urgency of effective management strategies. The conversation around optimal A1C targets continues to evolve, with many experts advocating for personalized strategies that consider individual risk factors and health profiles. As noted by Saboo B., 'Time-in-range as a target in type 2 conditions: An urgent need,' this highlights the importance of an interprofessional healthcare team to optimize outcomes.
Furthermore, recent data indicates that during 2017-2018, approximately 18,169 children and adolescents under 20 years were diagnosed with type 1 and 5,293 with type 2. This notable rise in incidence rates, especially among non-Hispanic Black youth, illustrates the critical need for effective A1C medicine testing and control strategies. This nuanced understanding of A1C medicine testing protocols and the accompanying controversies is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers as they work collaboratively to manage the condition effectively.
Stay tuned for more resources and insights as we continue to expand our offerings at T2DSolutions.
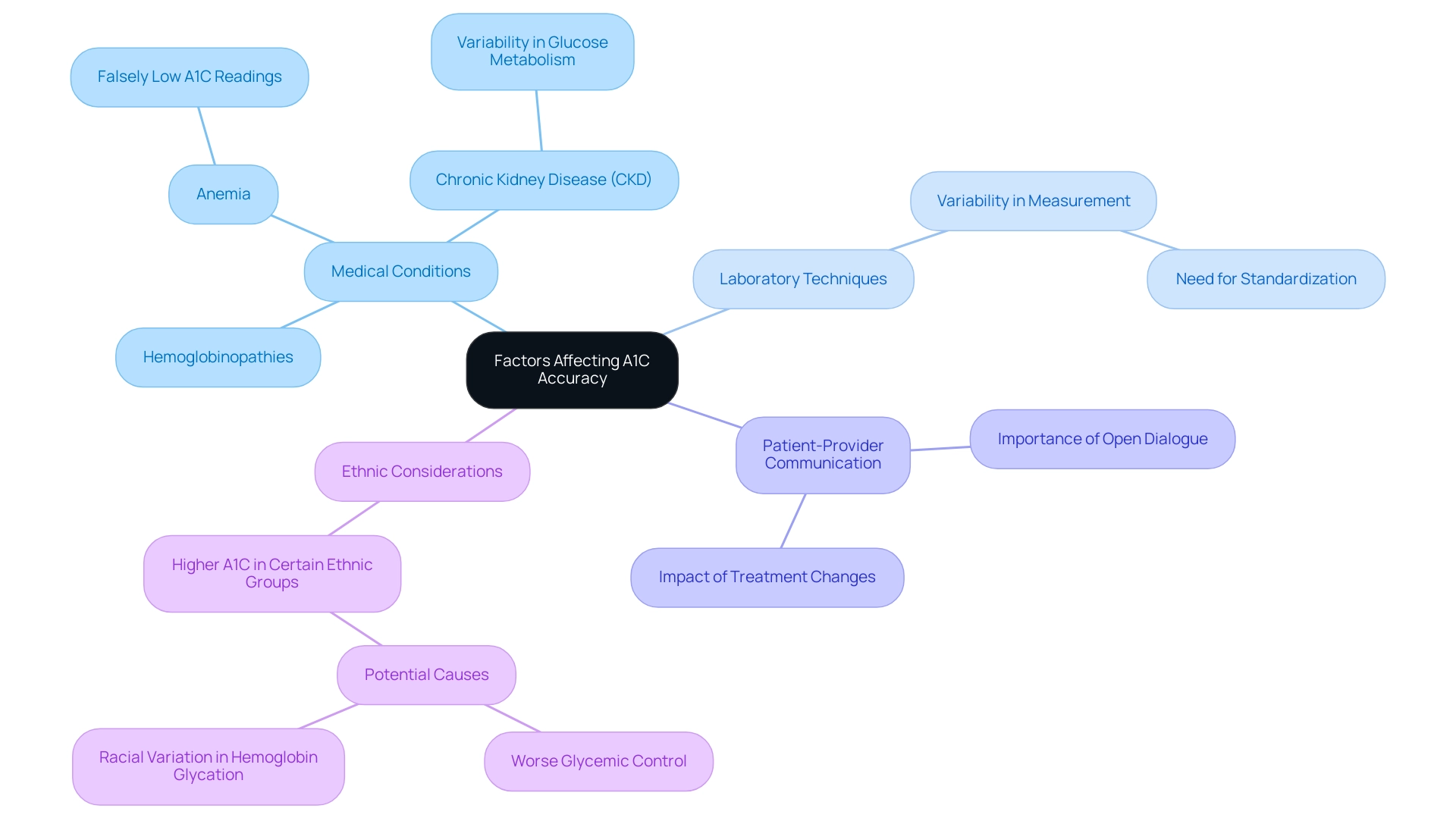
Factors Affecting A1C Accuracy: What You Need to Know
Comprehending the elements that influence A1C test outcomes is essential for effective control, and T2D Solutions seeks to offer valuable educational materials on a1c medicine. A variety of factors can significantly affect the accuracy of A1C test results, particularly certain medical conditions. Conditions like anemia, chronic kidney disease (CKD), and hemoglobinopathies are known to skew A1C results.
For instance, patients experiencing anemia may present falsely low A1C readings, while those with CKD could exhibit variability in glucose metabolism that complicates interpretation. Furthermore, variations in laboratory techniques used for measuring A1C can introduce discrepancies, underscoring the necessity for standardization across testing facilities. Dr. Woo emphasizes that 'effective communication between patients and healthcare providers is crucial,' as health issues or changes in treatment plans can profoundly affect A1C results. Regular monitoring and open dialogue with healthcare teams are vital for ensuring that A1C test results are accurately interpreted and effectively utilized in a1c medicine for managing diabetes.
Recent studies suggest that the maximum white blood cell (WBC) count can reach up to 11.6 (IQR 8.4–16.4), which may also affect glucose concentrations and, in turn, A1C results.
Clinicians must consider various factors—including ethnicity, as some studies suggest that A1C concentrations may be higher in certain ethnic groups compared to Caucasians—when assessing A1C and glucose measurements. A case study titled 'Clinical Implications of Discordant Glucose Levels' found that higher-than-expected glucose levels were associated with factors such as anemia and high-dose glucocorticoid treatment, indicating stress hyperglycemia in critically ill patients. By integrating this knowledge, T2 Solutions aims to empower patients with information regarding a1c medicine that can help avoid inappropriate management decisions and improve overall diabetes care.
Conclusion
Regular A1C testing is an essential component of diabetes management, providing critical insights into average blood glucose levels over recent months. This test not only aids in diagnosing diabetes but also serves as a benchmark for evaluating treatment effectiveness. The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals with diabetes undergo A1C testing at least twice a year, with increased frequency for those not meeting their glycemic targets. By actively engaging with A1C results, patients can better tailor their management strategies, potentially leading to improved health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Effective management of A1C levels involves a multifaceted approach, combining lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise with appropriate medication. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, and weight management are fundamental to achieving and maintaining optimal A1C levels. Furthermore, understanding the implications of A1C results is crucial for making informed decisions about treatment plans and lifestyle adjustments, which can ultimately influence both health and financial well-being.
The complexities surrounding A1C testing, including factors that may affect test accuracy, highlight the importance of ongoing dialogue between patients and healthcare providers. Conditions like anemia and chronic kidney disease can skew results, making it vital for patients to communicate openly about their health status. As the landscape of diabetes management continues to evolve, resources like T2DSolutions aim to empower individuals with the knowledge and tools necessary for effective diabetes care. By prioritizing regular A1C testing and understanding its implications, patients can take significant strides towards better managing their diabetes and improving their overall quality of life.



