Overview:
The article focuses on the American Diabetes Association (ADA) A1C recommendations for diabetes management, emphasizing the importance of individualized A1C targets to optimize treatment outcomes. It supports this by detailing how personalized A1C goals, informed by factors such as age and health status, can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve overall management, highlighting the necessity of regular monitoring and tailored strategies for effective diabetes care.
Introduction
Managing diabetes effectively requires a deep understanding of key metrics, with A1C levels standing out as a critical indicator of long-term blood sugar control. This essential blood test not only reflects a patient's average glucose levels over the past two to three months but also serves as a cornerstone for tailoring individual diabetes management plans.
With the rise in diabetes-related complications and escalating healthcare costs, it is imperative for patients to comprehend their A1C results and the implications for their health. This article delves into the significance of A1C in diabetes management, exploring:
- Recommended targets
- Individualization of goals
- Potential risks associated with elevated levels
- Practical strategies for achieving optimal outcomes
By equipping patients with the necessary knowledge and resources, the aim is to foster informed decision-making and enhance overall well-being in the journey of diabetes management.
Understanding A1C: The Cornerstone of Diabetes Management
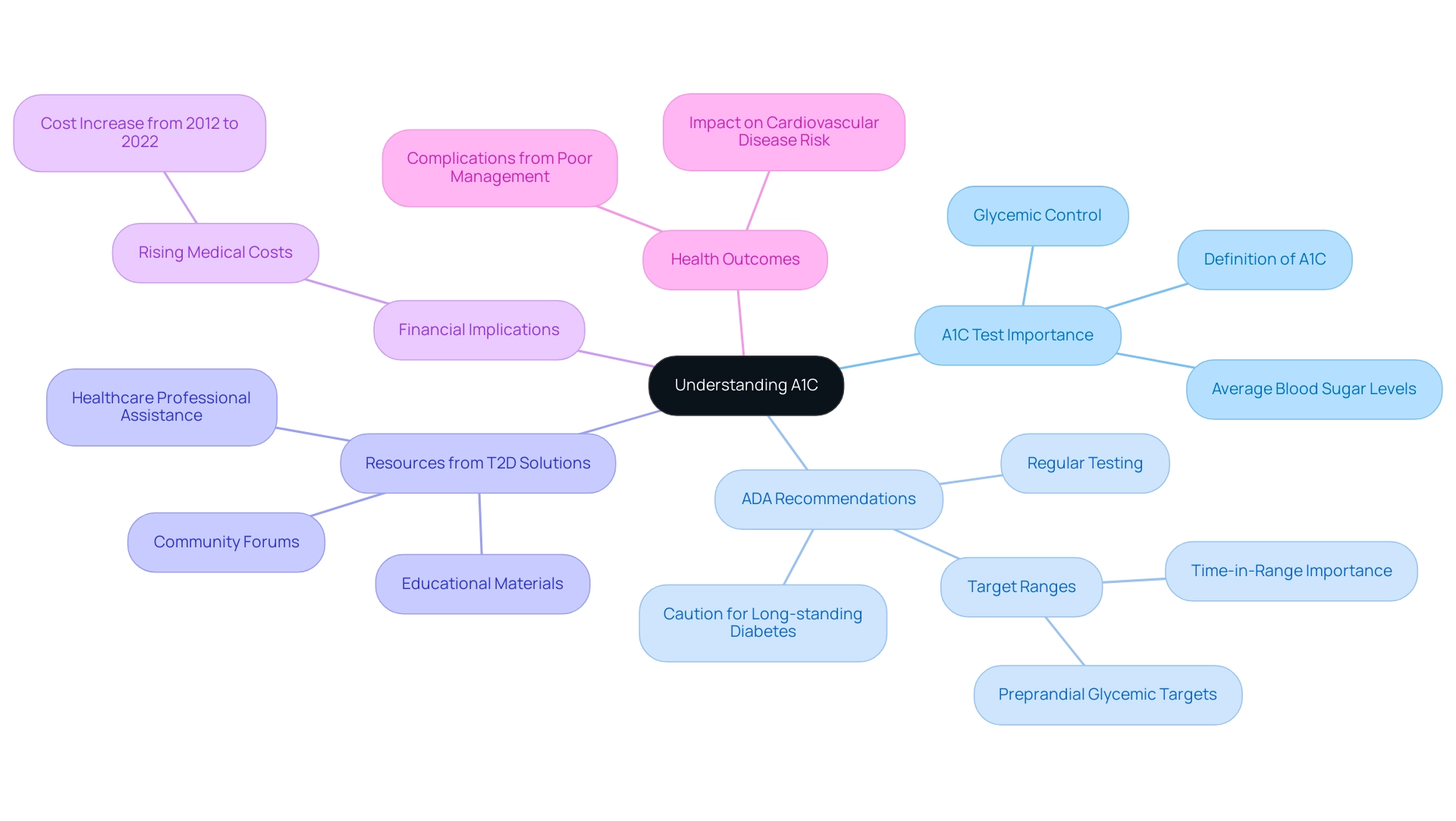
A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, is a crucial blood test that provides insight into average blood sugar levels over the preceding two to three months. This measurement is expressed as a percentage, where higher values indicate elevated average blood glucose levels, reflecting the individual's glycemic control. Comprehending A1C results is crucial in assessing the effectiveness of a management plan, particularly for newly diagnosed individuals seeking assistance through T2D Solutions, which may include ADA A1C recommendations.
Regular testing of A1C is essential to adhere to ADA A1C recommendations, as it enables healthcare providers to track progress and make informed decisions regarding treatment adjustments. T2D Solutions provides a variety of resources, including educational materials and community forums, to assist individuals in understanding their A1C results and the implications for their health. Recent research highlights the importance of keeping A1C levels within target ranges to reduce complications related to blood sugar disorders, especially for individuals with prolonged conditions and cardiovascular disease risk.
In fact, the excess medical costs per individual related to this condition increased from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022, highlighting the financial implications of effective management. Additionally, experts like Saboo B. emphasize the urgent need for time-in-range as a target in type 2 management, reinforcing the importance of ADA A1C recommendations. The ADA's revision of preprandial glycemic targets in 2015 illustrates the need to adapt treatment plans to minimize risks, particularly for individuals with long-standing conditions and cardiovascular disease risk.
Regular A1C evaluations, following ADA A1C recommendations from specialists, can enhance individual treatment approaches, ensuring that individuals receive customized care that meets their specific needs and conditions. Through T2D Solutions, individuals can access assistance from healthcare professionals and connect with others in the community who share similar experiences, making it easier to navigate these essential aspects of managing the condition.
ADA A1C Recommendations: Setting Targets for Effective Management
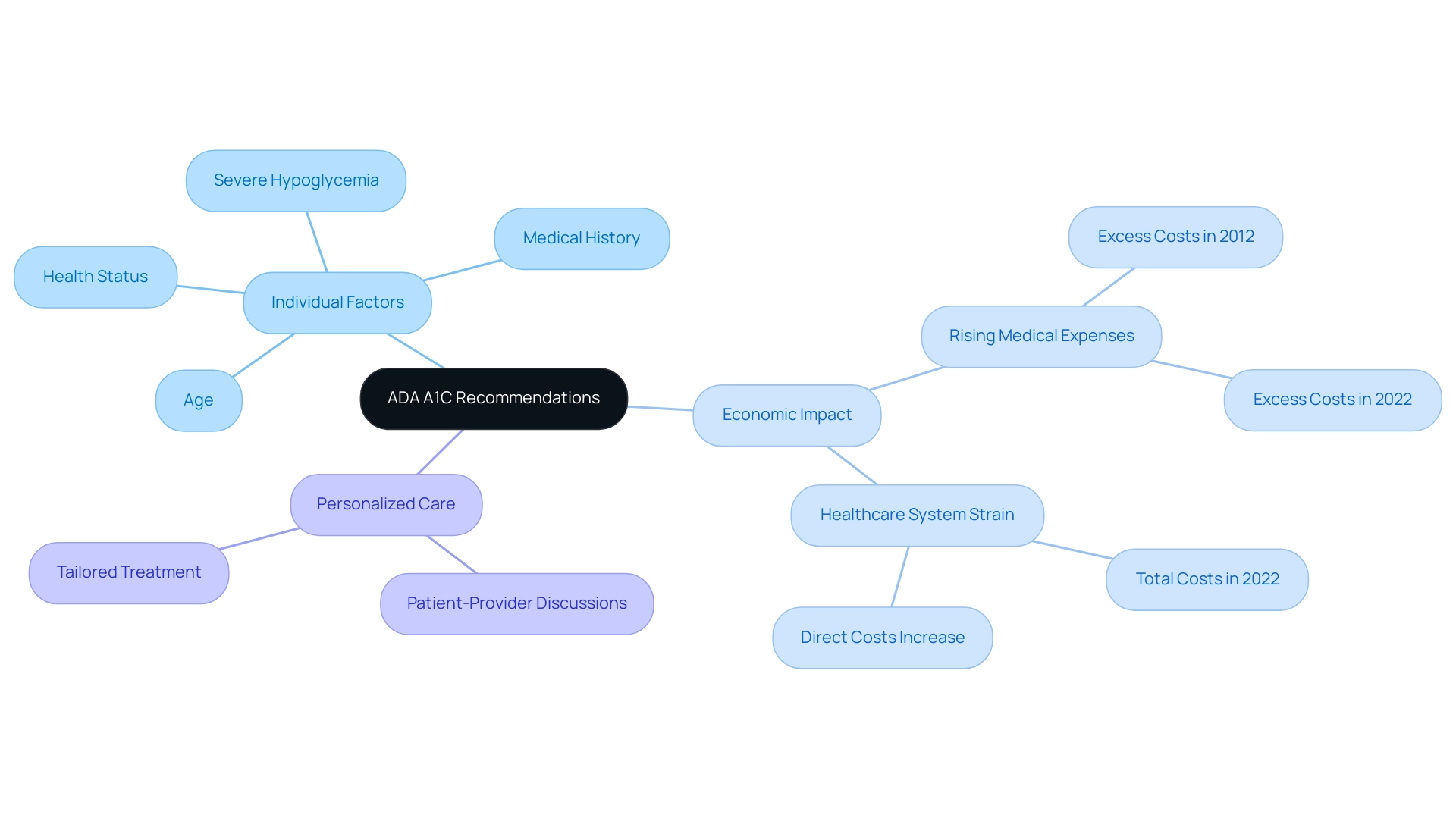
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) offers ADA A1C recommendations suggesting that most adults with the condition aim for an A1C level below 7%. However, it is crucial to recognize that individual targets may differ significantly based on a variety of factors, including age, overall health status, and specific medical history. For instance, individuals who have experienced severe hypoglycemia or who have a limited life expectancy may benefit from a higher target, which can help mitigate risks associated with stringent glycemic control.
A recent analysis indicates that the excess medical expenses per individual related to this health condition increased from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022, highlighting the economic strain encountered by individuals and the healthcare system alike. This economic impact is further detailed in the updated tables (9.3 and 9.4), which reflect changes in costs for several agents utilized in blood sugar management. Therefore, it is essential for patients to engage in discussions with their healthcare providers to establish ADA A1C recommendations that are tailored to their unique circumstances.
As healthcare expenses keep rising—amounting to an estimated $413 billion in 2022, with direct costs growing from $227 billion in 2012 to $307 billion—it becomes increasingly important to implement effective management strategies that prioritize personalized care. According to Dr. Jane Smith, a specialist in blood sugar regulation, 'Setting personalized A1C targets is crucial in managing the condition effectively, as it allows for a more tailored approach to treatment.' The ADA's guidelines provide a framework, but the ADA A1C recommendations highlight the importance of individualization for optimizing outcomes for individuals.
T2DSolutions seeks to act as an all-encompassing resource center for individuals recently diagnosed with Type 2 and Type 3 conditions, providing education, community support, and tools for monitoring A1C levels to assist people in effectively managing their plans. Additionally, we encourage visitors to subscribe for updates on new content and resources that will be available on T2D Solutions. A case study emphasizing an individual who effectively controlled their condition through personalized ADA A1C recommendations underscores the significance of this tailored approach.
Individualizing A1C Goals: Factors to Consider for Optimal Care
T2DSolutions is committed to supporting newly diagnosed individuals in understanding and managing their A1C goals effectively. Establishing suitable A1C goals in diabetes management, guided by ADA A1C recommendations, requires thoughtful evaluation of several factors, including:
- Age
- Duration of diabetes
- Existence of comorbid conditions
- Likelihood of complications
For example, younger individuals with a longer life expectancy may gain from more rigorous A1C targets, as attaining tighter control may lessen the likelihood of long-term complications.
Conversely, older individuals, who may have a higher risk of hypoglycemia or other health issues, might prioritize higher A1C targets to minimize potential adverse effects. Recent findings underscore that factors such as baseline A1C, body mass index (BMI), diabetes duration, and the total number of medications do not predict A1C outcomes, indicating that individualized approaches are essential. Notably, individuals with diabetes receiving a combination of oral antidiabetic drugs were 2.3-fold more likely to achieve good glycemic control compared to those using insulin and oral antidiabetics.
Additionally, individuals on monotherapy were 4.8-fold more likely to achieve good glycemic control, highlighting the importance of treatment strategies in relation to A1C goals. T2DSolutions will provide educational materials and community support to help individuals engage in thorough discussions with healthcare professionals, determining the most suitable targets based on ADA A1C recommendations while considering personal health priorities and lifestyle. As echoed by diabetes care professionals, 'Individualizing ADA A1C recommendations is vital to effectively manage diabetes and align treatment with patient-specific health considerations.'
Furthermore, self-management behaviors significantly impact glycemic control; for example, adherence to medication was reported at 53.4%, emphasizing the importance of individual engagement. This personalized approach not only enhances client engagement but also promotes better adherence to treatment regimens, which is positively correlated with achieving good glycemic control.
The Consequences of A1C Levels: Understanding Risks and Complications
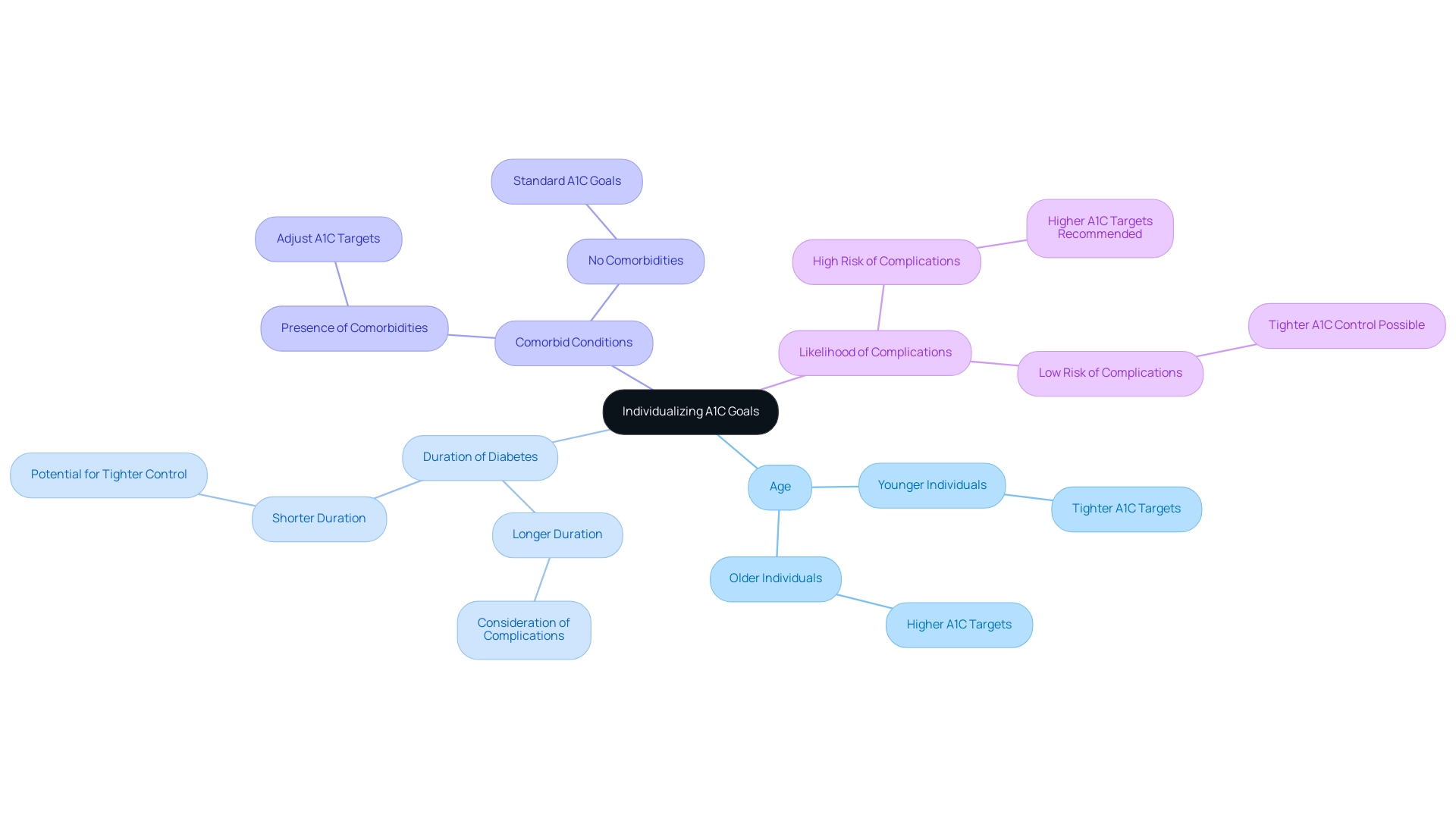
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your new comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support. As you navigate your journey as a newly diagnosed patient, we are committed to providing you with valuable insights and resources. According to ADA A1C recommendations, elevated A1C levels are strongly correlated with an increased likelihood of diabetes-related complications, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Neuropathy
- Nephropathy
- Retinopathy
Notably, research indicates that an A1C level exceeding 8% is associated with a significantly heightened chance of these complications. For instance, recent findings indicate that elevated HbA1c levels in the non-diabetic range are linked to a 51% increased likelihood of developing colorectal cancer. Furthermore, the Canarian Health Service, with contributions from authors like Reina G. Roa, emphasizes the importance of maintaining A1C levels below established targets according to ADA A1C recommendations, to substantially diminish the likelihood of encountering such complications and thereby enhancing overall quality of life.
Consistent observation of A1C levels and applying proactive management strategies are essential to follow ADA A1C recommendations for reducing these concerns. As highlighted by Jennifer Sargent, Primary Handling Editor, in collaboration with the Nature Medicine team, ongoing vigilance in monitoring ADA A1C recommendations is vital for patient health management. Furthermore, recent studies have demonstrated a weak significant interaction between center and A1C category regarding the likelihood of composite cardiovascular disease (CVD), indicating that geographic factors may influence these dangers.
Studies examining lung cancer incidence rates indicate that no significant trends were observed across varying HbA1c levels, with the study reporting specific incidence rates and the number of events for participants with known blood sugar issues. This implies that although A1C is an essential measure, it may not act as a conclusive indicator for all cancer probabilities, highlighting the need for thorough assessment strategies that take various elements into account in managing blood sugar levels.
Stay tuned for more updates as we continue to build our resources, and don’t forget to subscribe to receive emails when new content is published!
Strategies for Achieving Your A1C Goals: Practical Tips and Tools
To effectively achieve your A1C goals, consider the ADA A1C recommendations along with the following strategies:
- Regular Monitoring: Consistent tracking of your blood glucose levels is crucial. This practice helps you understand how various foods and activities influence your readings, which is essential for informed decision-making.
Notably, in a meta-analysis of over 95,000 subjects, the relative cardiovascular event risk was found to be 1.33 for impaired fasting glucose and 1.58 for individuals with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), underscoring the health risks associated with poor glucose management.
- Healthy Eating: Prioritize a balanced diet that includes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
Consulting a registered dietitian can provide you with personalized meal planning tailored to your specific needs. As noted by the Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group, metformin and lifestyle interventions are associated with modest incremental costs compared with placebo interventions, highlighting the cost-effectiveness of lifestyle changes.
-
Physical Activity: Strive for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week. Engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity and effectively lower blood sugar levels. Additionally, Ceriello et al. found that oscillating glucose is more harmful to endothelial function than chronic hyperglycemia, emphasizing the importance of stable glucose levels.
-
Medication Adherence: It is vital to take your prescribed medications as directed.
If you have any questions or concerns, engage in an open dialogue with your healthcare provider.
- Support Systems: Actively participating in support groups or counseling can offer valuable opportunities to share experiences and strategies with others living with the condition.
Furthermore, as part of Td Solutions, we strive to deliver a comprehensive resource hub that provides educational materials, community support, and guidance customized to the needs of individuals with Type 2 and Type 3 conditions. These multifaceted approaches not only aim to reach A1C targets but also align with ADA A1C recommendations to contribute to sustained glycemic control, which is paramount given that diabetes significantly impacts overall health and mortality.
Conclusion
Achieving and maintaining optimal A1C levels is a fundamental aspect of effective diabetes management. The insights provided throughout the article emphasize the importance of understanding A1C as a key indicator of long-term blood sugar control. Regular monitoring of A1C levels, along with individualized goal-setting based on personal health factors, plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
The American Diabetes Association's recommendations highlight the necessity of tailoring A1C targets to suit each patient's unique circumstances, acknowledging that a one-size-fits-all approach is inadequate. By engaging in informed discussions with healthcare providers, patients can establish personalized A1C goals that align with their health status and lifestyle choices.
Furthermore, practical strategies such as:
- Consistent blood glucose monitoring
- Healthy eating
- Regular physical activity
- Medication adherence
- Leveraging support systems
are essential for achieving these targets. As diabetes management evolves, T2DSolutions remains committed to equipping individuals with the resources and community support necessary for navigating their journey effectively.
In summary, understanding and managing A1C levels not only enhances individual health outcomes but also mitigates the broader economic impact of diabetes. With the right knowledge and tools, patients can take proactive steps towards better health, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced healthcare costs.



