Introduction
Navigating the complexities of diabetes management involves understanding various lifestyle choices, including the impact of alcohol on blood sugar levels. Alcohol can exert both hyperglycemic and hypoglycemic effects, complicating the health landscape for individuals with diabetes.
With recent studies shedding light on the intricate relationship between alcohol consumption and diabetes risk, it becomes essential for patients to be informed and proactive.
This article delves into the nuances of alcohol's effects on blood sugar, offers guidelines for safe consumption, and highlights the importance of education and continuous monitoring in managing diabetes effectively.
By equipping individuals with knowledge and strategies, T2DSolutions aims to empower those affected by Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes to make informed decisions regarding their health and lifestyle.
The Complex Relationship Between Alcohol and Blood Sugar Levels
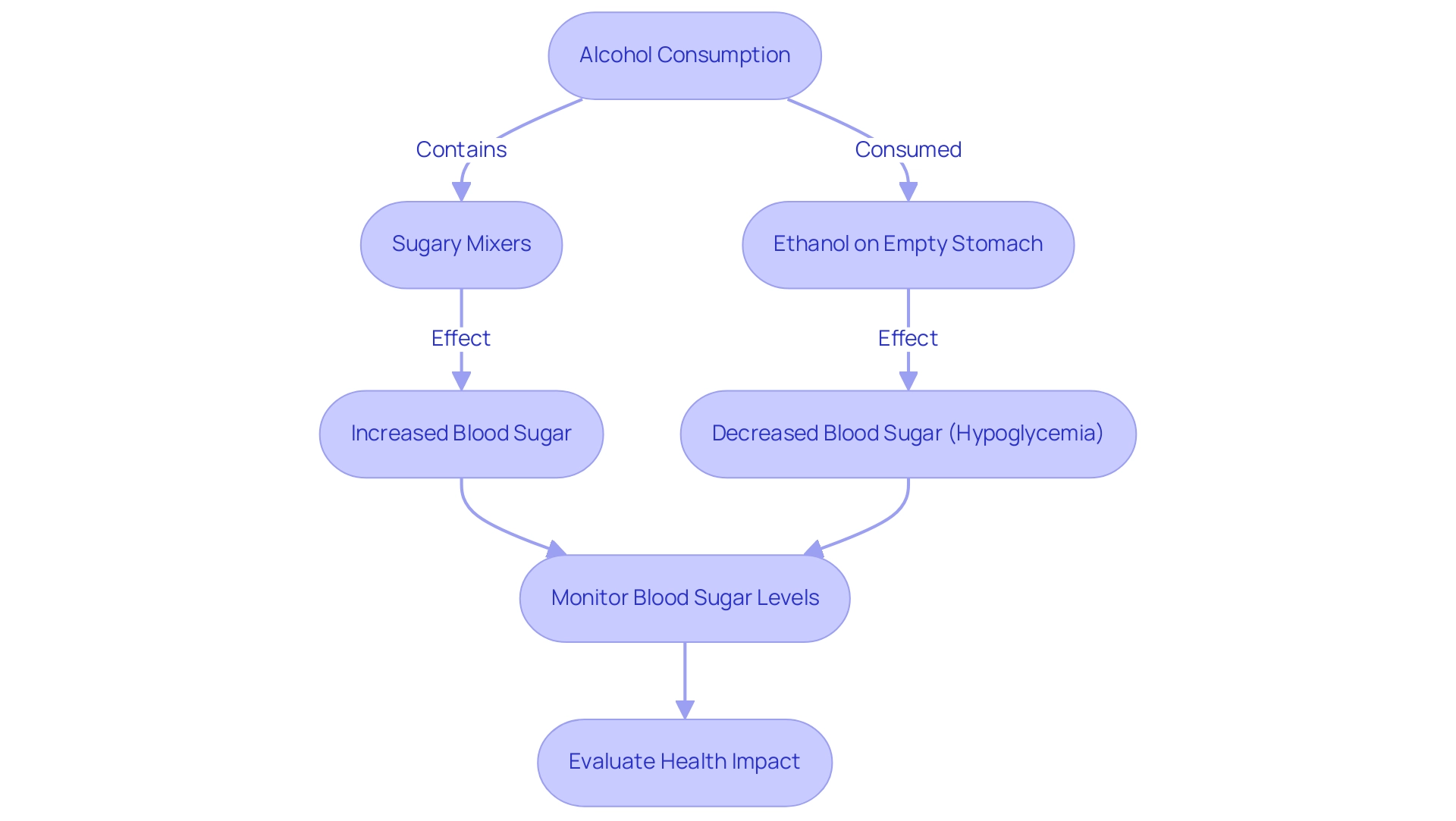
At T 2 Solutions, we are excited to announce the launch of our new educational resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes management. We acknowledge that beverage intake can considerably affect alcohol and blood sugar levels, demonstrating both hyperglycemic (increasing glucose) and hypoglycemic (decreasing glucose) effects. When ethanol is ingested, it is primarily processed by the liver, which can disrupt alcohol and blood sugar levels through its effect on glucose production.
For instance, moderate consumption of alcohol and blood sugar levels may see a temporary increase, especially when alcoholic beverages contain sugary mixers. On the other hand, excessive consumption of beverages containing ethanol—especially on an empty stomach—can trigger hypoglycemia, which can impact alcohol and blood sugar levels, as the liver prioritizes metabolizing these drinks over producing glucose.
In our dedication to offering extensive resources for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar regulation, we emphasize a meta-analysis titled 'Meta-Analysis of Beverage Consumption and Type 2 Blood Sugar Risk,' which employed rigorous methods to evaluate biases in research related to these substances. This study examined information from 477,200 individuals, revealing 12,556 new instances of the condition. The analysis highlighted the complexity of the connection between beverage intake and health risk, revealing that effects can vary based on diabetes type, medications, and individual health conditions.
Dolly O Baliunas, the corresponding author of the study, emphasizes the implications of these findings, stating, 'Because former drinkers may be inspired to abstain due to health concerns, they may actually be at increased risk of developing health issues, known as the sick-quitter effect.' Consequently, it is essential for individuals with blood sugar issues to carefully track their glucose levels in relation to alcohol and blood sugar levels before, during, and after beverage intake to evaluate its particular effect on their health. Comprehending these dynamics is essential for the efficient management of alcohol and blood sugar levels and for making informed choices regarding beverage consumption, aligning with T2DSolutions' mission to assist newly diagnosed patients in navigating their health journey.
Additionally, T2DSolutions will offer community support initiatives to foster connections among patients, providing a platform for shared experiences and resources.
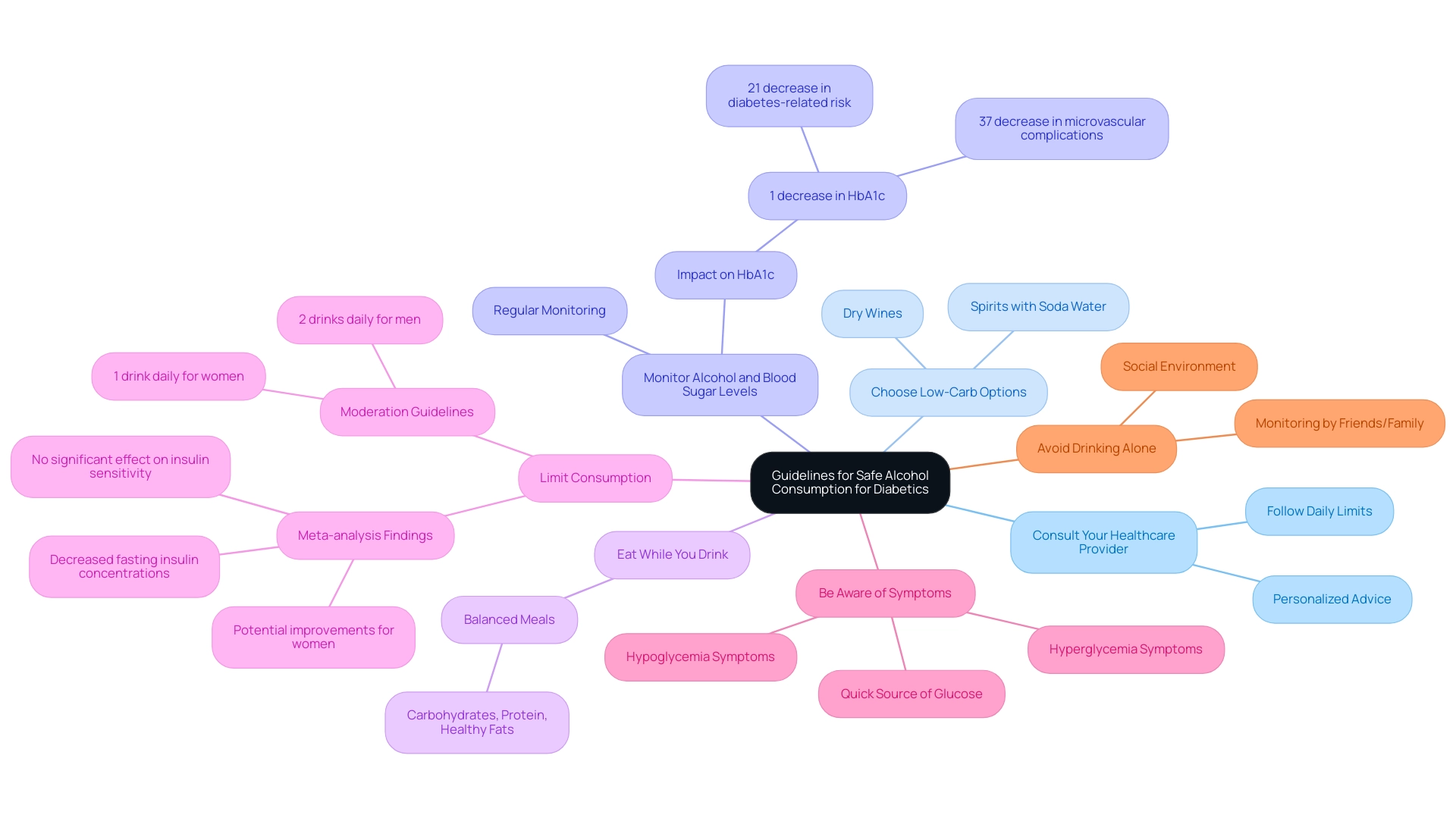
Guidelines for Safe Alcohol Consumption for Diabetics
-
Consult Your Healthcare Provider: It is essential to engage in a discussion about your alcohol consumption with your healthcare provider or diabetes educator. This conversation allows for personalized advice tailored to your specific health needs, ensuring a safer approach to drinking. As Lisa Hodgson, RDN, CDN, CDCES, FADCES, advises, it is best to follow daily recommended consumption limits to manage alcohol and blood sugar levels.
-
Choose Low-Carb Options: Opting for low-sugar beverages, such as dry wines or spirits mixed with soda water, can significantly minimize carbohydrate intake. This choice is crucial for effectively managing both alcohol and blood sugar levels.
-
Monitor Alcohol and Blood Sugar Levels: It is vital to regularly monitor alcohol and blood sugar levels before, during, and after drinking. A 1% decrease in HbA1c correlates with a 21% decrease in the risk of any diabetes-related endpoint and a 37% decrease in the risk of microvascular complications, highlighting the significance of understanding how different types and quantities of beverages, particularly alcohol and blood sugar levels, can affect your sugar levels.
-
Eat While You Drink: Consuming food alongside beverages can aid in stabilizing blood sugar levels. It is advisable to focus on balanced meals that comprise carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats, as this can help mitigate the effects of beverages on alcohol and blood sugar levels.
-
Limit Consumption: Moderation is crucial for individuals with diabetes. The American Diabetes Association suggests restricting beverage consumption to one drink daily for women and two for men. Adhering to these guidelines can help minimize risks related to the impact of alcohol and blood sugar levels during beverage consumption. Notably, the findings from a meta-analysis concluded that moderate beverage consumption did not significantly affect insulin sensitivity or fasting glucose levels, but did decrease fasting insulin concentrations and HbA1c, particularly showing potential improvements in insulin sensitivity for women regarding alcohol and blood sugar levels.
-
Be Aware of Symptoms: Being informed about the symptoms of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia is critical. Always ensure that you have a quick source of glucose available to address any emergencies that may arise from alcohol and blood sugar levels.
-
Avoid Drinking Alone: It is advisable to drink in a social environment where others can assist in monitoring your condition. This approach provides an extra layer of safety, as friends or family can help in case of any adverse reactions related to alcohol and blood sugar levels.
As T2DSolutions launches as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, we encourage you to stay informed. Subscribe to receive updates and empower yourself with the necessary knowledge to manage your health effectively, including understanding the implications of alcohol and blood sugar levels.
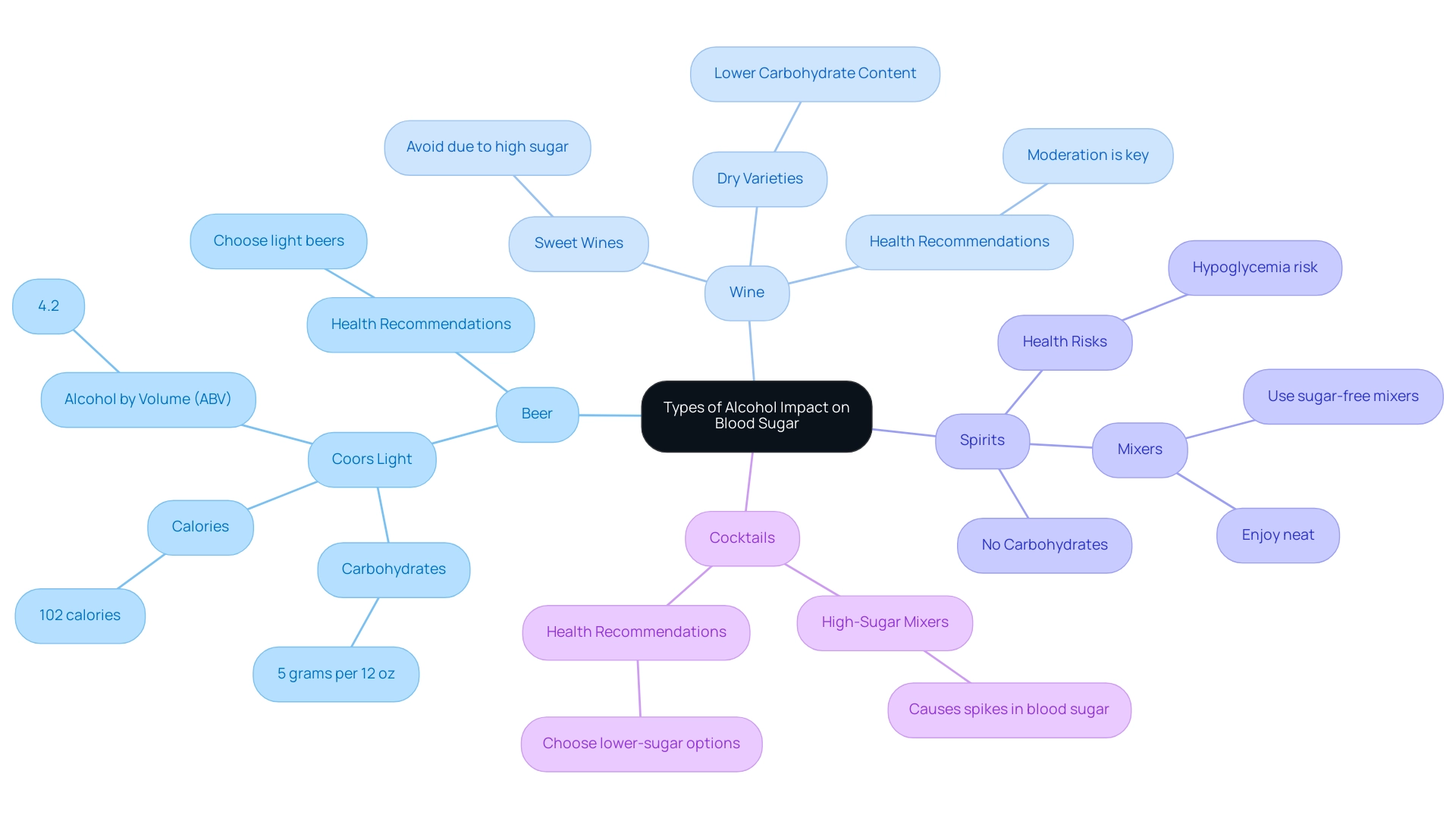
Understanding the Impact of Different Types of Alcohol
-
Beer: Traditional beers often contain significant carbohydrates, which can affect alcohol and blood sugar levels. For individuals controlling their alcohol and blood sugar levels, choosing light beers with a lower carbohydrate content is advisable. For instance, Coors Light, a popular choice, contains only 5 grams of carbs per 12-ounce serving, along with 102 calories and a volume of 4.2%. Its crisp and refreshing qualities make it a viable option for those on less restrictive diets. As a reminder, 'I am not judging anyone and I am not asking anyone to join me'—the goal is to make informed choices that suit individual health needs. This information is part of the resources T2D Solutions is dedicated to offering for improved diabetes management, including guides and articles on beverage consumption.
-
Wine: When considering wine, dry varieties are generally more suitable for diabetics due to their lower carbohydrate content. Sweet wines, however, can cause an increase in alcohol and blood sugar levels, and therefore should be avoided. Nutritionists often emphasize the importance of moderation and caution when selecting wines to ensure they align with dietary needs. It's also essential to keep in mind the American Heart Association's recommendation for alcohol consumption: men should limit themselves to two drinks per day, while women should limit to one. T2DSolutions aims to offer comprehensive guidance on these choices to support informed decision-making, especially for newly diagnosed patients.
-
Spirits: Distilled liquors such as vodka, gin, and whiskey contain no carbohydrates, offering a lower-risk choice for glucose management. However, caution is warranted when consuming these spirits, as they are often mixed with high-sugar mixers. To maintain better control over glucose levels, consider using sugar-free mixers or enjoying spirits neat, as these choices can help manage alcohol and blood sugar levels. Furthermore, it’s crucial to recognize that hypoglycemia may happen after a night of consuming alcohol, which introduces another layer of risk for individuals managing alcohol and blood sugar levels. T2DSolutions will include these vital considerations in its resource materials, ensuring patients have the information they need.
-
Many cocktails are crafted with syrups and high-sugar mixers that can cause significant spikes in alcohol and blood sugar levels. It is crucial to inquire about the ingredients before ordering and to choose lower-sugar options whenever possible. By making informed choices and being aware of carbohydrate content, individuals can enjoy social occasions while managing their health effectively. T2DSolutions is committed to assisting newly diagnosed patients in navigating these challenges with extensive educational resources, including FAQs and practical tips on diabetes management.
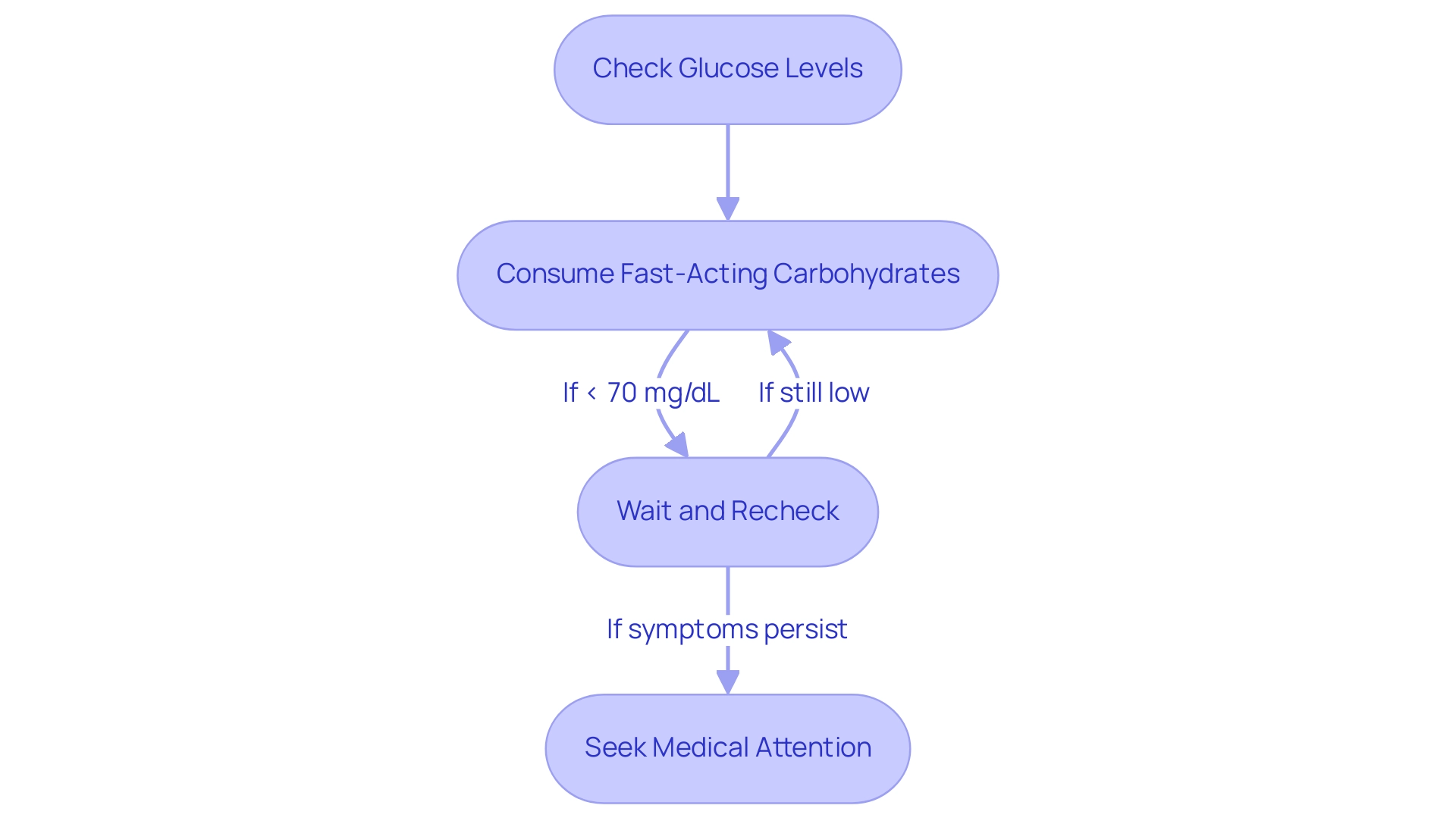
Recognizing and Managing Alcohol-Induced Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia presents with symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, sweating, and trembling, which can significantly impact a person's well-being, particularly in relation to alcohol and blood sugar levels. If you suspect you are experiencing hypoglycemia following drinking, it is crucial to act promptly:
- Check Glucose Levels: Use a glucometer to evaluate your current glucose levels.
- Consume Fast-Acting Carbohydrates: If your levels are below 70 mg/dL, promptly ingest 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets, fruit juice, or candy.
- Wait and Recheck: Allow 15 minutes to pass, then recheck your blood sugar levels. If they remain low, consume an additional 15 grams of carbohydrates.
- Seek Medical Attention: If symptoms persist or escalate, it is imperative to seek medical assistance without delay.
Comprehending these steps is crucial, particularly considering recent discoveries indicating that alcohol and blood sugar levels can cause lactate levels to rise to 6.27 mmol/L in instances of severe hypoglycemia, highlighting the possible severity of this condition. As Hideaki Kaneto notes, "Case report of severe hypoglycemic alcoholic ketoacidosis: A possible pitfall in diagnosis of ketoacidosis," highlighting the complexities in diagnosing such conditions. Additionally, a systematic review titled "Drug-Induced Hypoglycemia: A Systematic Review" identified various drugs that can contribute to hypoglycemia, emphasizing the need for awareness of multiple potential causes.
Expert insights emphasize the importance of recognizing these symptoms early to prevent further complications.
Planning Ahead for Social Situations
-
Choose Your Venues Wisely: When selecting social venues, prioritize establishments that offer nutritious food options. This enables improved control over your overall dietary intake and assists you in managing your beverage consumption more effectively. Venues that emphasize healthier choices can facilitate the maintenance of stable alcohol and blood sugar levels while socializing.
-
Communicate Your Needs: It is crucial to openly discuss your dietary restrictions with friends or hosts before attending social gatherings. By clearly outlining your requirements regarding beverage consumption, you enable your support system to assist you in making healthier choices throughout the event.
-
Practice Moderation: Establish a clear plan regarding the number of alcoholic beverages you intend to consume before the event starts. Sticking to a predetermined limit can help mitigate the risk of excessive drinking, which is particularly important for maintaining balanced alcohol and blood sugar levels. As noted by S.E. Ramsey, "This work was supported in part by award number R01AA017418 from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism to S.E. Ramsey," highlighting the importance of informed decision-making in alcohol consumption for those with diabetes.
-
Bring Your Snacks: To maintain energy levels, consider bringing along nutritious snacks to social events. Having nutritious options readily available can help you manage your alcohol and blood sugar levels while still enjoying the social aspects of drinking.
-
Know Your Limits: Understanding how beverages impact your body is essential. Be vigilant about your body's signals, and do not hesitate to decline additional drinks if you feel it necessary. Acknowledging your limits is essential for maintaining your health and well-being during social interactions involving beverages.
In a case study titled "Assessment and Intervention for At-Risk Drinking," it was found that outpatient medical settings provide an opportunity to assess at-risk drinking among patients, particularly focusing on their alcohol and blood sugar levels, using validated questionnaires. This demonstrates the efficacy of incorporating substance evaluations into the management of alcohol and blood sugar levels, emphasizing the significance of these approaches.
As T2DSolutions launches as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 conditions education and community support, we encourage newly diagnosed patients to engage with our content. By subscribing, you can stay informed about the latest strategies and resources to help manage your health, including how to navigate social situations involving beverages.
The Importance of Education and Continuous Monitoring
-
Stay Informed: Regular participation in diabetes education programs is crucial for acquiring the knowledge necessary to manage your condition effectively. These classes offer valuable insights into how lifestyle choices, including alcohol consumption, impact alcohol and blood sugar levels. Alcohol and blood sugar levels can be affected, causing both high and low sugar levels depending on the amount consumed and whether it is taken with food. As highlighted by Leslie Kolb, the guidance provided by education and support systems for managing this condition is invaluable in navigating these complexities.
-
Utilize Technology: Embrace the use of management applications that assist in monitoring glucose levels, medication schedules, and beverage consumption. This technological integration not only aids in daily management but also helps identify patterns in alcohol and blood sugar levels fluctuations.
-
Maintain Communication with Healthcare Providers: Consistent follow-ups with your healthcare team are essential to address any emerging concerns and to adapt your management plan as necessary. Regular check-ups can lead to timely interventions, particularly in preventing acute complications associated with blood sugar issues, such as hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, which accounted for approximately 267,000 and 202,000 emergency department visits respectively in 2020.
-
Connect with Support Networks: Engaging in support groups allows you to exchange experiences and strategies with individuals facing similar challenges. These interactions can offer emotional support and practical guidance on managing beverage intake in relation to alcohol and blood sugar levels. Resources such as local health associations or online forums can provide additional support and information.
-
Be Flexible with Your Management Plan: It is vital to remain adaptable in your approach to managing alcohol and blood sugar levels for better health. Changes in your health status or recommendations from healthcare professionals may necessitate adjustments in your strategies. The case study on emergency department visits related to diabetes underscores the critical health challenges faced by adults with diabetes, particularly concerning acute complications such as hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Conclusion
Understanding the effects of alcohol on blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals managing Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes. The dual nature of alcohol—capable of causing both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia—highlights the need for careful monitoring and informed decision-making. By recognizing the intricate relationship between alcohol consumption and diabetes risk, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health effectively.
Guidelines for safe alcohol consumption, such as:
- Consulting healthcare providers
- Choosing low-carb options
- Monitoring blood sugar levels
serve as essential strategies for those looking to enjoy social occasions without compromising their health. Additionally, awareness of the specific impacts of different types of alcohol can empower individuals to make choices that align with their dietary needs.
Education and continuous monitoring are vital components of effective diabetes management. By leveraging available resources, participating in educational programs, and utilizing technology, individuals can gain valuable insights into their condition and tailor their approaches to alcohol consumption accordingly. Engaging with support networks further enhances this journey, providing community and shared experiences that can ease the management process.
Ultimately, the goal is to foster a balanced lifestyle that accommodates social interactions while prioritizing health. By remaining informed and vigilant, individuals with diabetes can navigate the complexities of alcohol consumption, ensuring that their choices contribute positively to their overall well-being.



