Overview:
The article focuses on the interactions between alcohol consumption and insulin levels, highlighting that moderate alcohol intake may enhance insulin sensitivity, while excessive consumption can lead to insulin resistance and increased diabetes risk. This is supported by research indicating that the type of alcoholic beverage consumed significantly affects blood sugar levels, with sweetened drinks posing greater risks and emphasizing the need for individuals managing diabetes to monitor their intake and consult healthcare providers for personalized guidance.
Introduction
Understanding the intricate relationship between alcohol consumption and insulin levels is vital for individuals managing diabetes. As research reveals, the effects of alcohol on blood sugar can vary significantly depending on the type and quantity consumed.
While moderate drinking may offer some benefits, excessive intake poses serious risks, including:
- Heightened insulin resistance
- Unpredictable blood sugar fluctuations
This article delves into the complexities of alcohol's impact on diabetes management, providing essential guidelines for:
- Safe consumption
- Recognizing hypoglycemia symptoms
- The importance of consulting healthcare providers
With the right knowledge and strategies, individuals can navigate social situations while maintaining their health and well-being.
The Relationship Between Alcohol Consumption and Insulin Levels
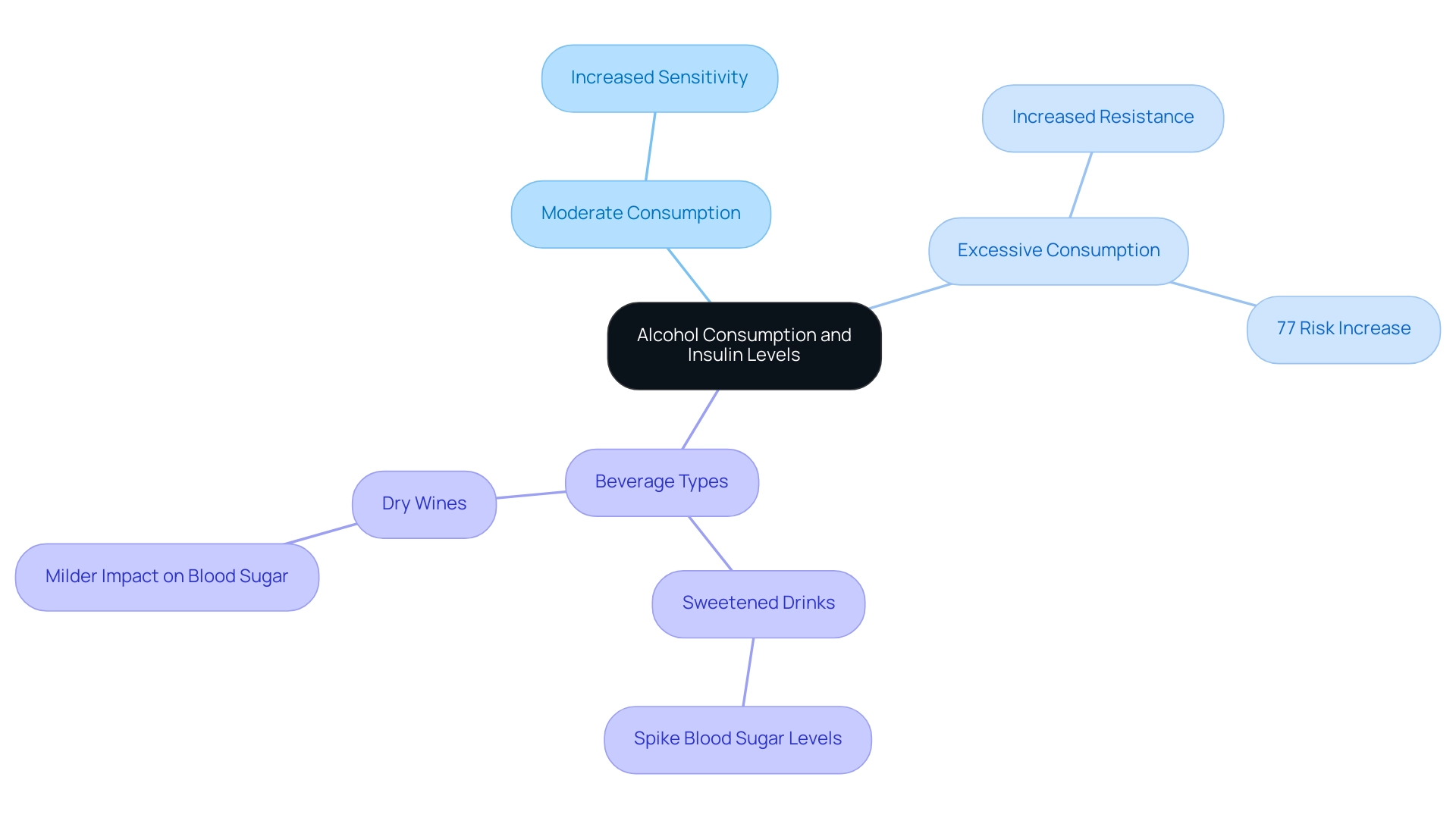
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your newly launched resource hub developed by the T2DSolutions Content Team, dedicated to providing comprehensive education and community support for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes management. Our platform aims to empower newly diagnosed patients with essential information, including the intricate effects of beverage intake on alcohol and insulin levels and sensitivity. Research indicates that while moderate intake may enhance insulin sensitivity in some individuals, excessive consumption is linked to increased insulin resistance.
Significantly, a recent sensitivity analysis revealed a 77% increase in risk of diabetes-related issues linked to high beverage consumption, especially for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) below 24 kg/m². It’s vital for individuals overseeing glucose control to comprehend these dynamics, as the interaction between alcohol and insulin can interfere with secretion and result in unpredictable sugar fluctuations. Furthermore, the choice of alcoholic beverage is significant as it relates to alcohol and insulin; sweetened drinks may spike blood sugar levels, while dry wines typically have a milder impact.
As we create our content, we encourage you to subscribe to remain informed about our latest insights, research findings, and guidance customized to your needs in health management.
Managing Alcohol Intake: Guidelines for Diabetics
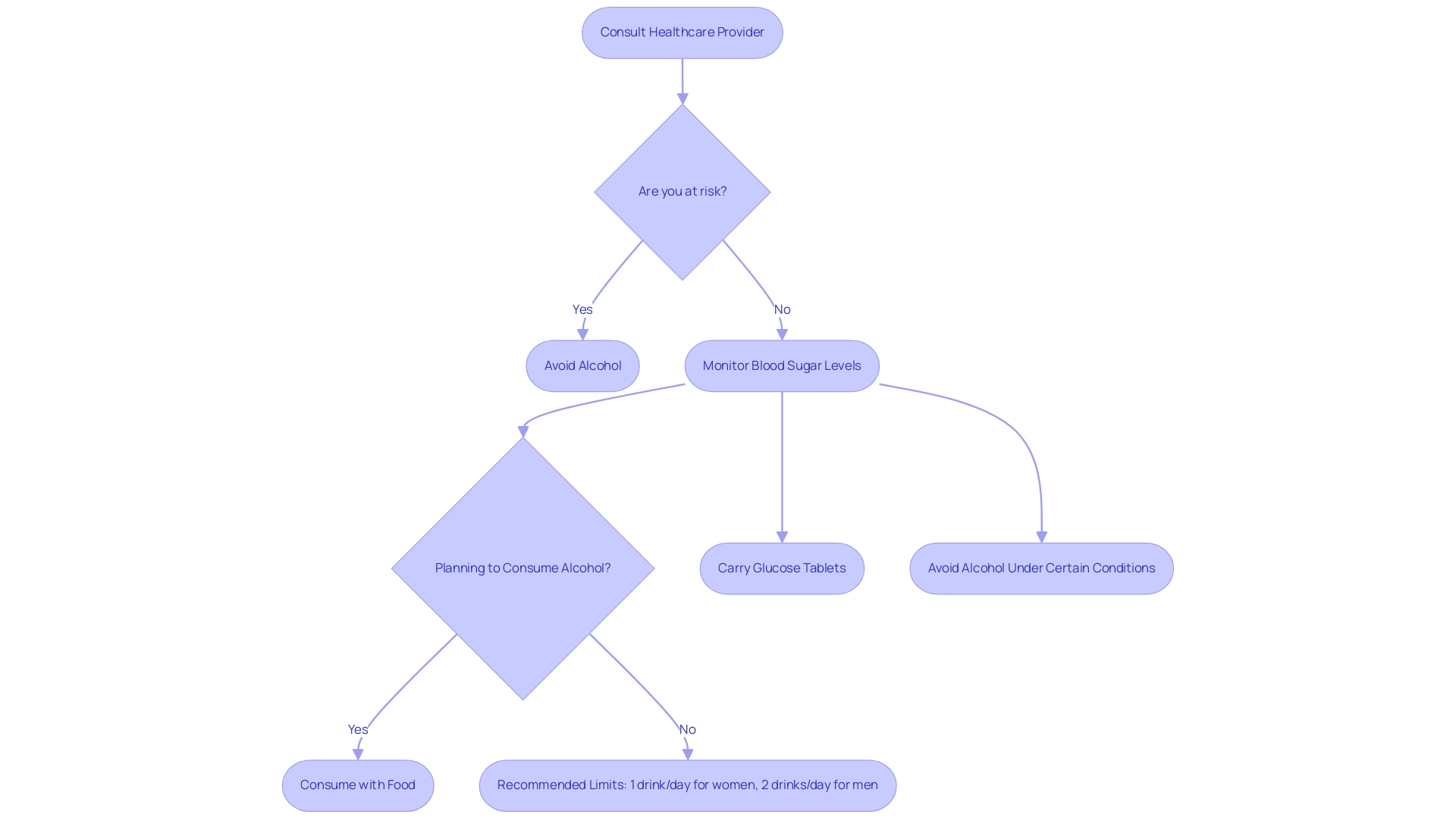
Individuals diagnosed with diabetes must adhere to specific guidelines concerning alcohol and insulin intake to safeguard their health. It is crucial to consult a healthcare provider prior to drinking alcohol and insulin, as they can evaluate individual risks and determine appropriate limits. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels before and after consuming beverages is essential, especially those that contain alcohol and insulin, as fluctuations can occur.
In fact, binge drinking occurs in about half of adolescents and adults who drink, underscoring the importance of responsible consumption. When deciding to drink, it is advisable to consume alcohol and insulin alongside food to help reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. Recommended beverage limits are:
- Up to one drink per day for women
- No more than two drinks per day for men, as stated by StayWell Custom Communications.
Selecting beverages with lower sugar content is also important; options such as dry wines or spirits mixed with calorie-free mixers are preferable. Additionally, it is prudent to carry glucose tablets or snacks to manage potential hypoglycemic episodes effectively. It is also important to be aware of specific circumstances under which individuals should avoid consuming it altogether, such as:
- When taking medications that interact with it
- Having certain medical conditions, as outlined in the case study titled 'When to Avoid Alcohol.'
Following these guidelines can greatly improve the management of blood sugar levels while allowing for the safe intake of alcohol and insulin. For more information and comprehensive resources on beverage consumption and diabetes management, visit t2d solutions, which will serve as a valuable hub for newly diagnosed patients seeking education and community support.
The Impact of Different Types of Alcohol on Blood Sugar
The impact of alcohol and insulin on glucose levels is significantly influenced by the type of beverage consumed. Generally, beer and sweet wines contain higher carbohydrate levels, which can lead to noticeable increases in sugar levels. In contrast, distilled spirits like vodka, gin, and whiskey typically contain little to no carbohydrates, making them safer options for individuals who are monitoring their glucose levels.
However, caution is warranted as mixers can introduce substantial sugar content; therefore, choosing sugar-free alternatives is highly recommended. According to Lisa Hodgson, a registered dietitian nutritionist, 'One study found that women who drink moderately have a lower risk of developing type 2 conditions than women who do not drink.' It's important to note that this study has limitations, and while moderate drinking may present potential benefits, individuals with blood sugar issues should remain cautious and follow recommended intake limits.
The case study titled 'Moderate Drinking and Type 2 Diabetes Risk' suggests that while some studies indicate moderate beverage intake may lower the risk of developing type 2 blood sugar issues in women, the findings are not definitive. Moreover, the Peth biomarker can stay identifiable in the bloodstream for as long as four weeks following beverage intake, highlighting the importance for individuals with blood sugar issues to be cautious about their decisions. By diligently reading labels and selecting low-carb alcoholic beverages, individuals can better manage their sugar levels and avoid unintended spikes associated with alcohol and insulin.
Comprehending the impacts of alcohol and insulin on glucose levels is essential for effective management of this condition. For additional resources and assistance, think about checking out t2d solutions, your all-encompassing center for education on the condition.

Recognizing Symptoms of Hypoglycemia After Drinking
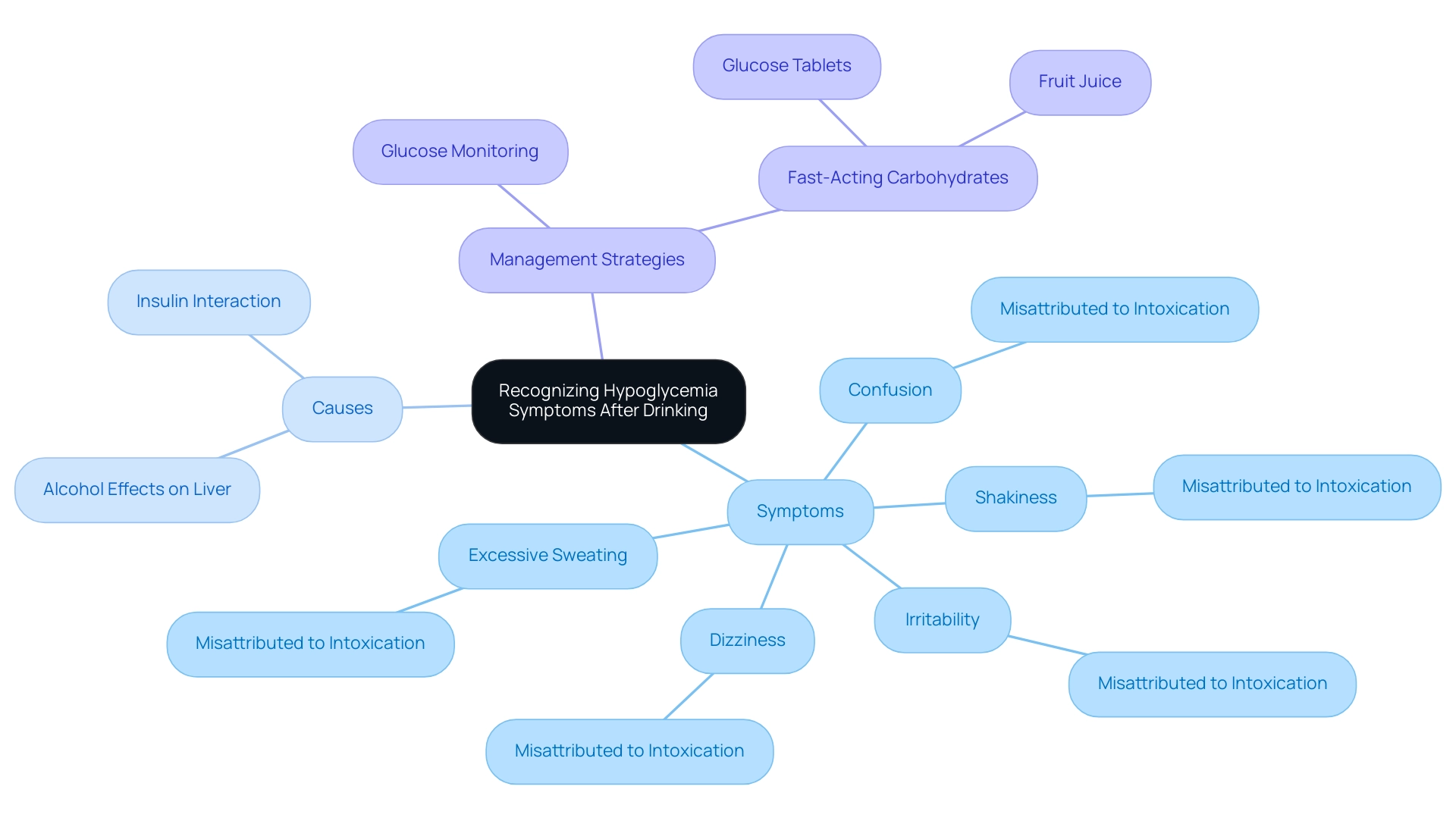
Hypoglycemia may manifest through a range of symptoms, including shakiness, dizziness, confusion, irritability, and excessive sweating. After consuming alcohol, individuals may mistakenly attribute these sensations to intoxication rather than recognizing the possibility of dangerously low blood sugar levels. Alcohol can interfere with the liver's capacity to release glucose into the bloodstream, especially when considering the effects of alcohol and insulin, resulting in a heightened risk of hypoglycemia, particularly for those managing blood sugar levels.
This misinterpretation can have serious consequences for those managing diabetes. It is imperative for individuals to remain vigilant, particularly when these symptoms arise post-drinking. Timely glucose monitoring is essential, as prompt identification of hypoglycemia allows for swift intervention.
Consuming fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice, can effectively elevate blood sugar levels. Education about these symptoms and their implications is not just beneficial; it is a potentially life-saving aspect of managing this condition. T2DSolutions aims to assist individuals in navigating these complexities, offering a comprehensive resource for understanding how beverage intake affects blood sugar management.
Recent findings underscore the importance of distinguishing between hypoglycemia symptoms and signs of intoxication, as both can present similarly but require different responses. Significantly, estimates indicate that 95% or more individuals with substance use disorder have low sugar levels, emphasizing the commonality of this issue. T2DSolutions provides resources like educational materials and community support to assist newly diagnosed patients in comprehending the effects of alcohol and insulin on their blood sugar levels and managing their condition effectively.
As Thornton PS mentions in his review on hypoglycemia, understanding these symptoms is crucial in managing this condition effectively. Furthermore, the case study titled 'Prognosis of Non-Diabetic Hypoglycemia' emphasizes that the prognosis of hypoglycemia varies depending on the underlying cause, underscoring the need for careful evaluation and management to improve patient outcomes. Through T2DSolutions, newly diagnosed patients can access vital information and community support to aid in their condition management journey.
Planning for Alcohol Consumption: A Diabetes Management Strategy
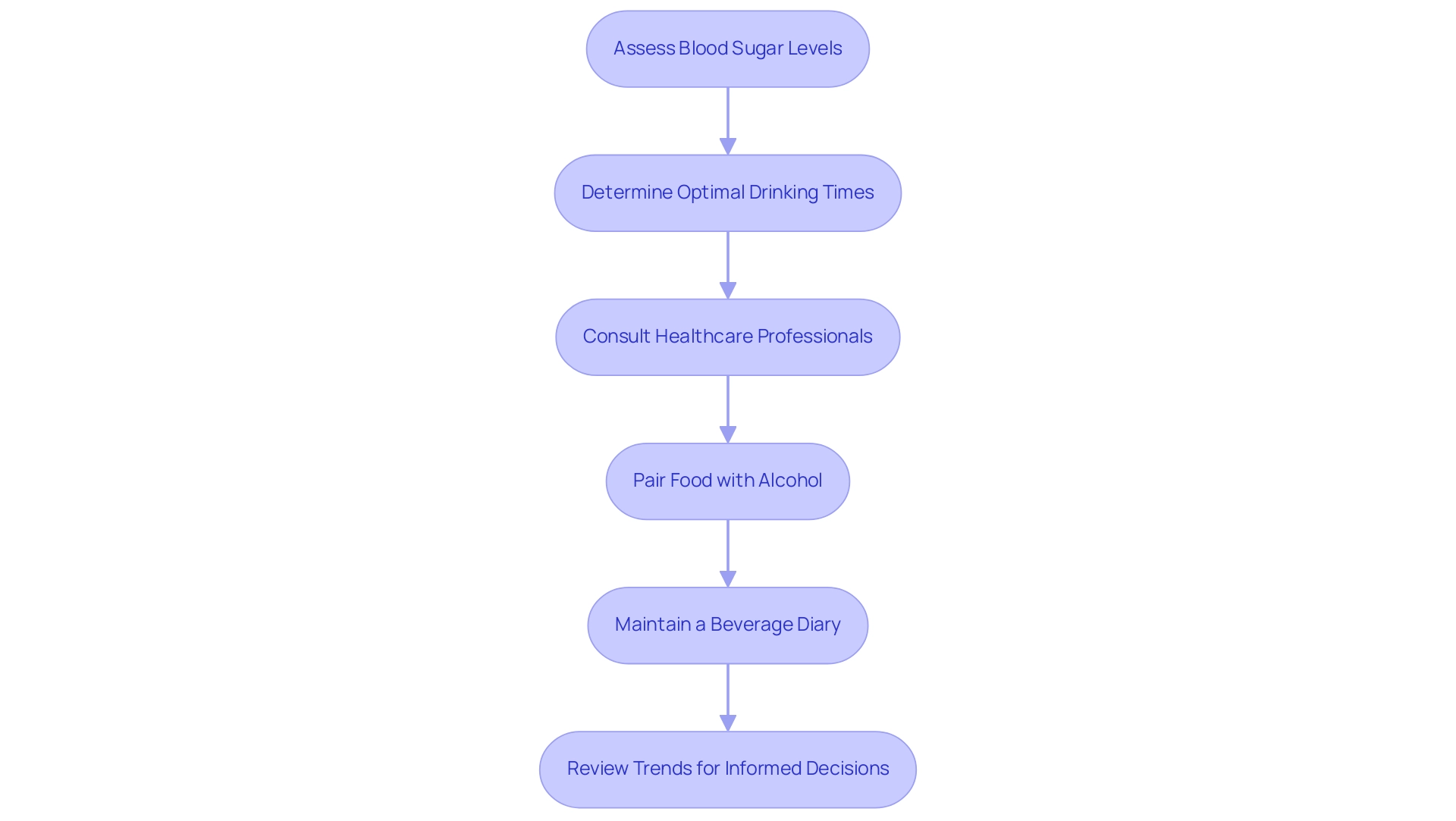
For individuals with diabetes, it is essential to formulate a comprehensive plan when considering beverage consumption, particularly in relation to alcohol and insulin. This strategy begins with assessing current blood sugar levels and determining optimal drinking times for alcohol and insulin, especially when blood sugar is stable. To reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, it is advisable to pair food options with beverages that involve alcohol and insulin.
Moreover, discussing with healthcare professionals regarding alcohol and insulin consumption is essential for ensuring that individual drinking strategies correspond with overall health management. Notably, statistics show that 53.8% of male participants have type 2 diabetes, highlighting the importance of tailored advice for this demographic. Maintaining a thorough diary of beverage intake and its following impacts on blood sugar can aid in recognizing personal trends, resulting in more educated decisions in the future.
Ang Huang notes that,
These studies indicate that mild-moderate beverage consumption might protect against liver inflammation and fibrosis in MASLD by exerting anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Additionally, a case study titled 'Role of Type 2 Diabetes in Alcohol Consumption Effects' found that in non-excessive drinkers without T2DM, mild-moderate drinking was negatively associated with liver fibrosis. However, in those with T2DM, no significant relationship was noted regarding alcohol and insulin, suggesting that the condition may alter the impacts of beverages on liver health.
Lastly, Gunawardena et al. examined the impact of a mobile application on health management, showcasing contemporary strategies that promote effective management practices. Thus, comprehending these dynamics is essential for effective management of blood sugar and safe intake of spirits.
As T2DSolutions initiates as a new resource center for health education and community support, individuals can discover further guidance on handling beverage intake in relation to their condition, ensuring they possess the tools required for informed decision-making.
Consulting Healthcare Providers About Alcohol
a2d Solutions, we acknowledge the significance of open conversations between individuals with blood sugar concerns and their healthcare providers about beverage intake. As a new resource center focused on Type 2 and Type 3 education and community support, we aim to empower recently diagnosed patients with the knowledge they require for effective management. Engaging in these essential conversations allows healthcare professionals to offer tailored advice that considers each patient's medical history, current medications, and overall health status.
By addressing beverage consumption, patients can establish safe limits and necessary precautions, enabling them to participate in social occasions without jeopardizing their health. Moreover, healthcare providers play a crucial role in monitoring potential interactions between medications and substances, ensuring a holistic approach to diabetes management that encompasses lifestyle choices. A recent randomized controlled trial in the UK demonstrates the effectiveness of personalized interventions in managing drinking habits, emphasizing the need for ongoing support.
As noted by the authors, 'All follow‐up data were collected and managed by a researcher who was masked to allocation status,' demonstrating the rigor of the study's methodology. Furthermore, initiatives like 'Project U Connect' underscore effective intervention strategies for beverage consumption, reinforcing our commitment to providing personalized advice for diabetics. ATd Solutions, we offer a variety of resources, including educational materials and support groups, to assist you in your journey.
We invite you to subscribe to our updates to stay informed about new content and initiatives. Fostering an open dialogue about alcohol and insulin consumption is a key aspect of effective diabetes management.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between alcohol consumption and insulin levels is crucial for individuals managing diabetes. This article highlights the importance of moderation, emphasizing that:
- While moderate drinking may provide some benefits,
- Excessive intake can lead to heightened insulin resistance and unpredictable blood sugar fluctuations.
Adhering to guidelines for safe consumption and recognizing symptoms of hypoglycemia are essential for effective diabetes management.
The type of alcohol consumed plays a significant role in its effect on blood sugar levels. Low-carb options, such as dry wines and spirits, are generally safer choices compared to sweeter beverages. It is vital to:
- Monitor blood sugar levels before and after drinking
- Consume alcohol with food to mitigate the risk of hypoglycemia
Consulting healthcare providers for personalized advice is also a critical step in ensuring safe alcohol consumption.
By equipping individuals with the knowledge and strategies outlined in this article, the path to safely navigating social situations while managing diabetes becomes clearer. With careful planning and responsible drinking, individuals can enjoy their social lives without compromising their health. Staying informed and proactive in diabetes management will lead to more stable blood sugar levels and overall well-being.



