Introduction
Navigating the complexities of alcohol consumption can be particularly challenging for individuals managing diabetes. While social occasions often include drinking, understanding how alcohol affects blood sugar levels is essential for maintaining health and preventing complications.
From the immediate impacts of different alcoholic beverages on glucose control to the long-term implications of excessive consumption, the relationship between alcohol and diabetes is multifaceted. This article delves into key considerations for diabetics, including:
- Safe drinking choices
- The importance of monitoring blood sugar levels
- Strategies for managing alcohol intake in social settings
By equipping individuals with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions, it becomes possible to enjoy social interactions while prioritizing health and well-being.
The Impact of Alcohol on Blood Sugar Control in Diabetics
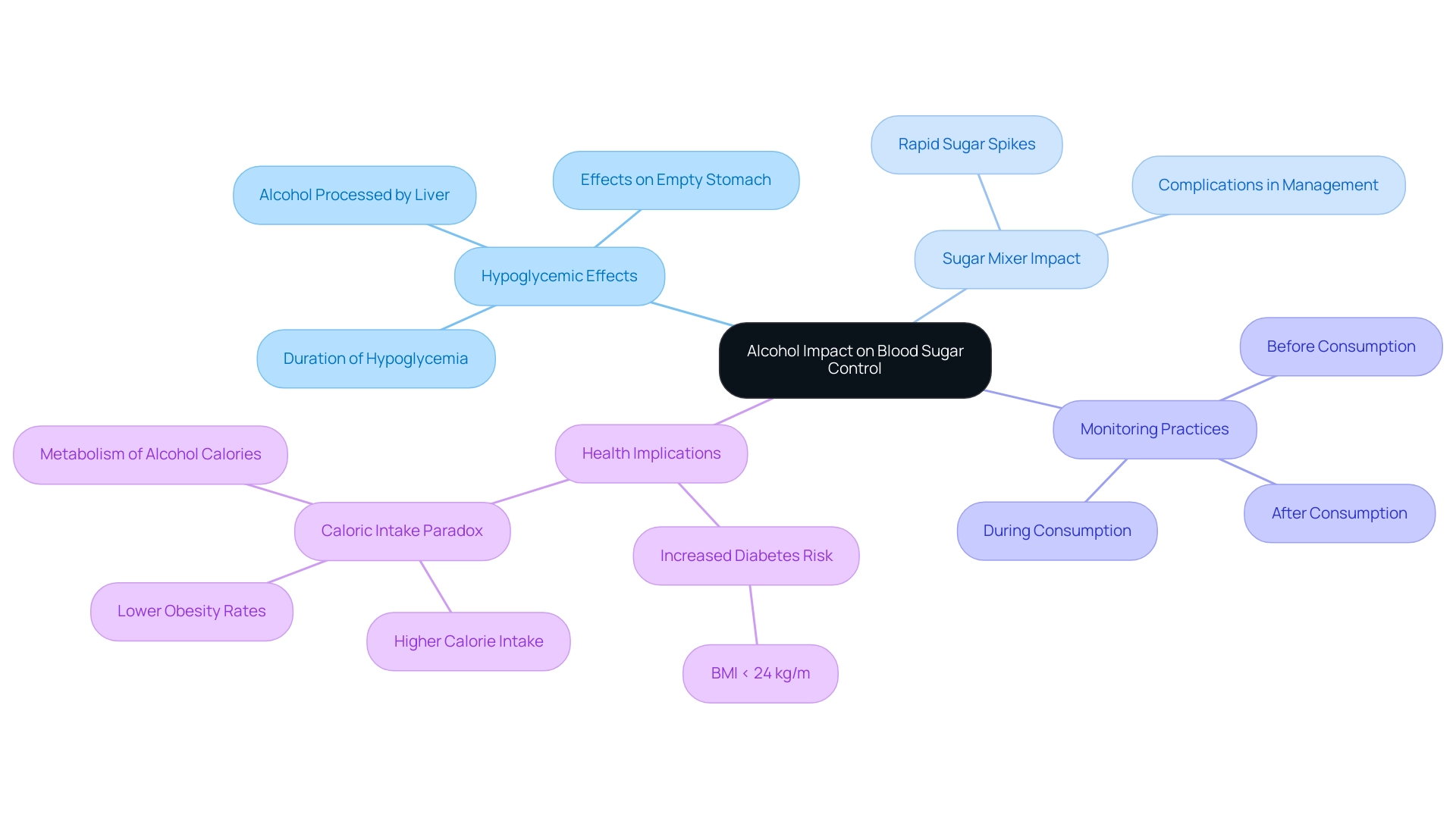
At T2DSolutions, we acknowledge that beverage intake can markedly impact glucose levels, influencing both short-term and long-term diabetes control. When consumed, alcohol for diabetics is primarily processed by the liver, which can lead to a decrease in glucose levels, particularly if taken on an empty stomach. This hypoglycemic effect may continue for several hours, necessitating vigilant monitoring of glucose levels.
Conversely, drinks high in sugar or combined with sweet mixers can cause rapid spikes in sugar levels, complicating management efforts. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals with blood sugar issues to closely monitor their glucose levels before, during, and after consuming beverages, especially alcohol for diabetics, to understand their unique physiological responses.
Recent studies indicate a pronounced connection between excessive beverage intake and increased risk of blood sugar disorders, particularly among individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of less than 24 kg/m. This emphasizes the crucial need for targeted interventions aimed at reducing beverage consumption as a preventative measure against diabetes. In fact, the study suggests that the peak reduction for women equated to almost two pints of 4% ABV lager per day, emphasizing the need for careful monitoring of beverage consumption.
Moreover, the complexities of caloric intake related to beverage consumption warrant further examination. A case study titled 'Caloric Intake and Obesity in Beverage Consumers' revealed that individuals in the highest consumption category reported a greater calorie intake yet exhibited lower obesity rates. This paradox indicates that the body may process calories from beverages differently, potentially resulting in heightened thermogenesis and decreased fat storage, although further research is needed to confirm this theory.
In light of these findings, it is crucial to consider the broader implications of such drinks on overall health, including their potential contribution to weight gain and their impact on adherence to health management plans. As Mary West noted in her observations on August 16, 2021, understanding these dynamics is crucial for effective management of the condition. Therefore, at T2DSolutions, we encourage individuals with blood sugar issues to approach beverage consumption with caution, especially when it comes to alcohol for diabetics, ensuring that their choices align with their health goals and management strategies.
We are dedicated to offering resources, including educational materials and community support, to assist you in navigating the complexities of alcohol for diabetics and its effects on health. Stay tuned for more insights and resources dedicated to supporting your health management journey.
Choosing the Right Alcohol: Best Options for Diabetics
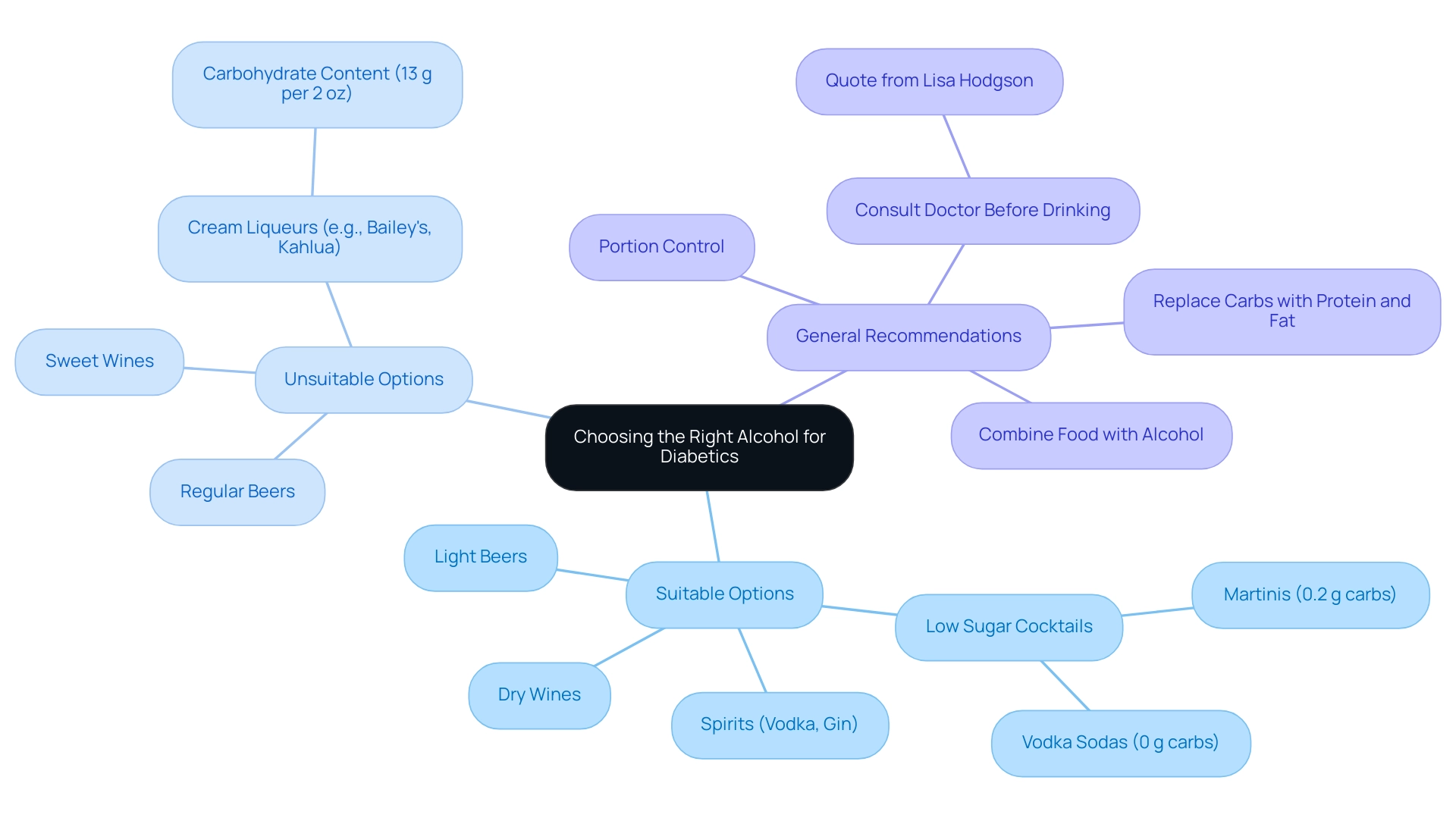
Atd Solutions, we understand that for individuals managing diabetes, selecting the right alcohol for diabetics is crucial. It is important to choose options that are lower in carbohydrates and to recognize that drinking habits, specifically alcohol for diabetics, should be individualized based on personal health needs. Suitable choices for alcohol for diabetics include:
- Dry wines
- Spirits like vodka or gin
- Light beers
as opposed to sweet wines, cocktails, or regular beers, which tend to have higher carbohydrate levels.
For example, cream liqueurs such as Bailey’s Irish Cream and Kahlua can contain around 13 grams of carbohydrates per 2 oz (60 mL) serving, making them less ideal. We recommend steering clear of mixers rich in sweetness, like sodas or fruit juices, and instead thinking about sugar-free mixers or drinking straight spirits, as these options are better for managing glucose levels when consuming alcohol for diabetics. Additionally, low-sugar cocktail options, like:
- Martinis containing 0.2 g of total carbs
- Vodka sodas with 0 g
provide enjoyable alternatives for alcohol for diabetics who are monitoring their carbohydrate intake.
Portion control is also essential; larger amounts of spirits can result in erratic glucose variations. Combining food with alcohol for diabetics can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Nutritionist Lisa Hodgson emphasizes the need for individuals to consult their doctors before engaging in moderate drinking.
Furthermore, substituting a portion of carbohydrates with protein and fat may help enhance cholesterol levels in individuals with type 2. By making informed choices and being mindful of carbohydrate content, individuals with blood sugar concerns can enjoy social occasions while effectively managing their health, including the option of alcohol for diabetics. For more information and resources on managing this condition, we encourage you to subscribe to t2d solutions and stay updated on our educational initiatives.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels Before and After Drinking
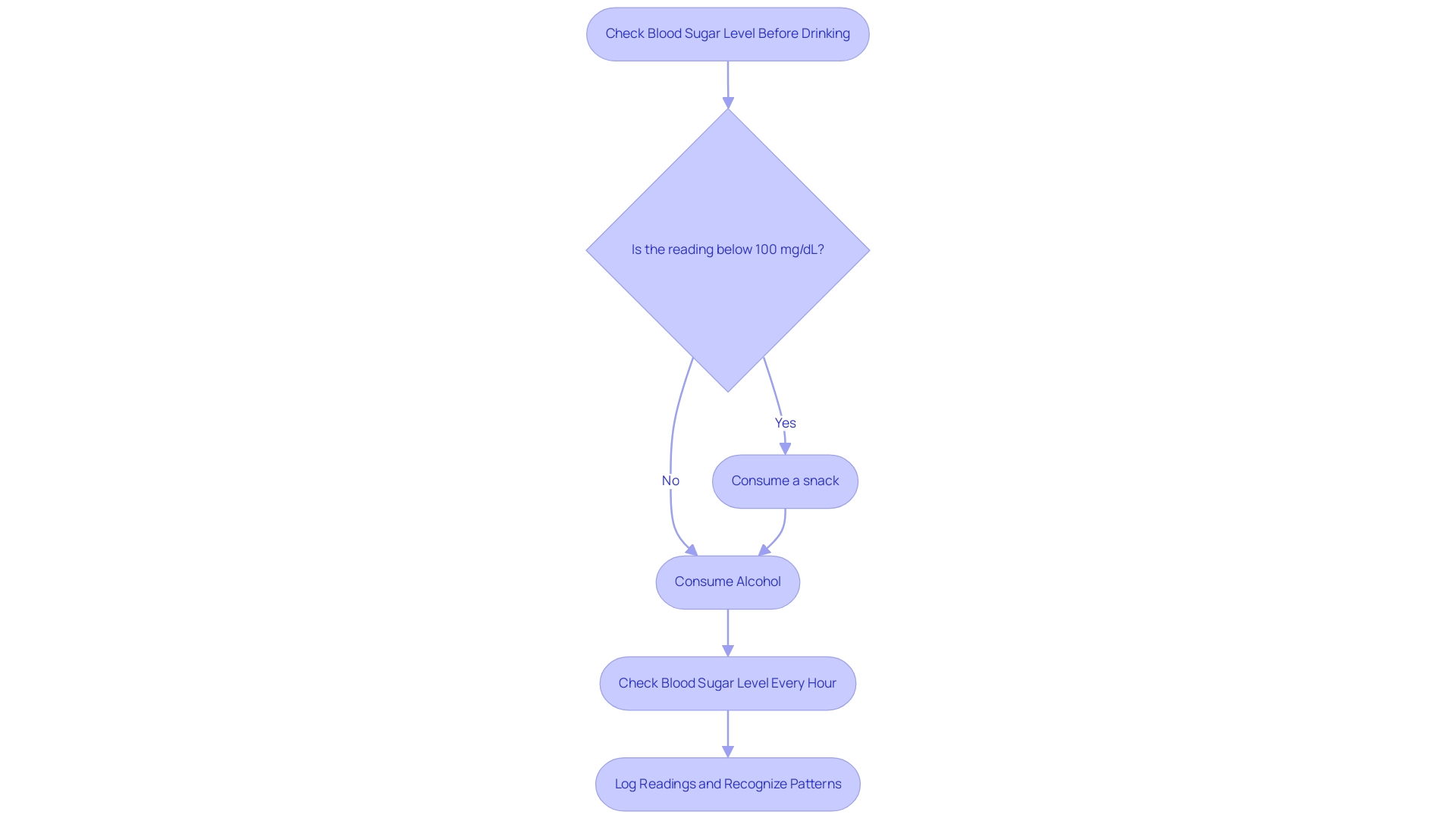
For individuals managing diabetes, it is essential to monitor glucose levels before consuming alcohol for diabetics. If the reading is below 100 mg/dL, it is advisable to consume a snack beforehand to mitigate the risk of hypoglycemia. After consumption, glucose levels should be closely observed, ideally every hour for several hours, as alcohol for diabetics can continue to affect glucose levels even after drinking has stopped.
As stated by Robert M. Swift, M.D., Ph.D., a specialist in the area, 'Tracking glucose levels is essential for avoiding hypoglycemic incidents, especially when alcohol for diabetics is consumed.' Keeping a detailed log of these readings not only aids in recognizing patterns but also informs future drinking choices, allowing for timely responses to any negative effects. Statistics indicate that hypoglycemia can occur in a significant percentage of diabetics after beverage consumption, emphasizing the importance of managing alcohol for diabetics.
Furthermore, a case study named 'Moderate Drinking and Type 2 Diabetes Risk' indicates that although moderate drinking might reduce the risk of developing type 2 conditions in women, individuals with blood sugar concerns should remain vigilant about alcohol for diabetics and follow advised consumption limits. For more information and assistance regarding management of the condition, consider visiting T2DSolutions, a new resource hub dedicated to providing education and community support for individuals managing type 2 and type 3 related issues.
Understanding Alcohol Labels and Nutritional Information
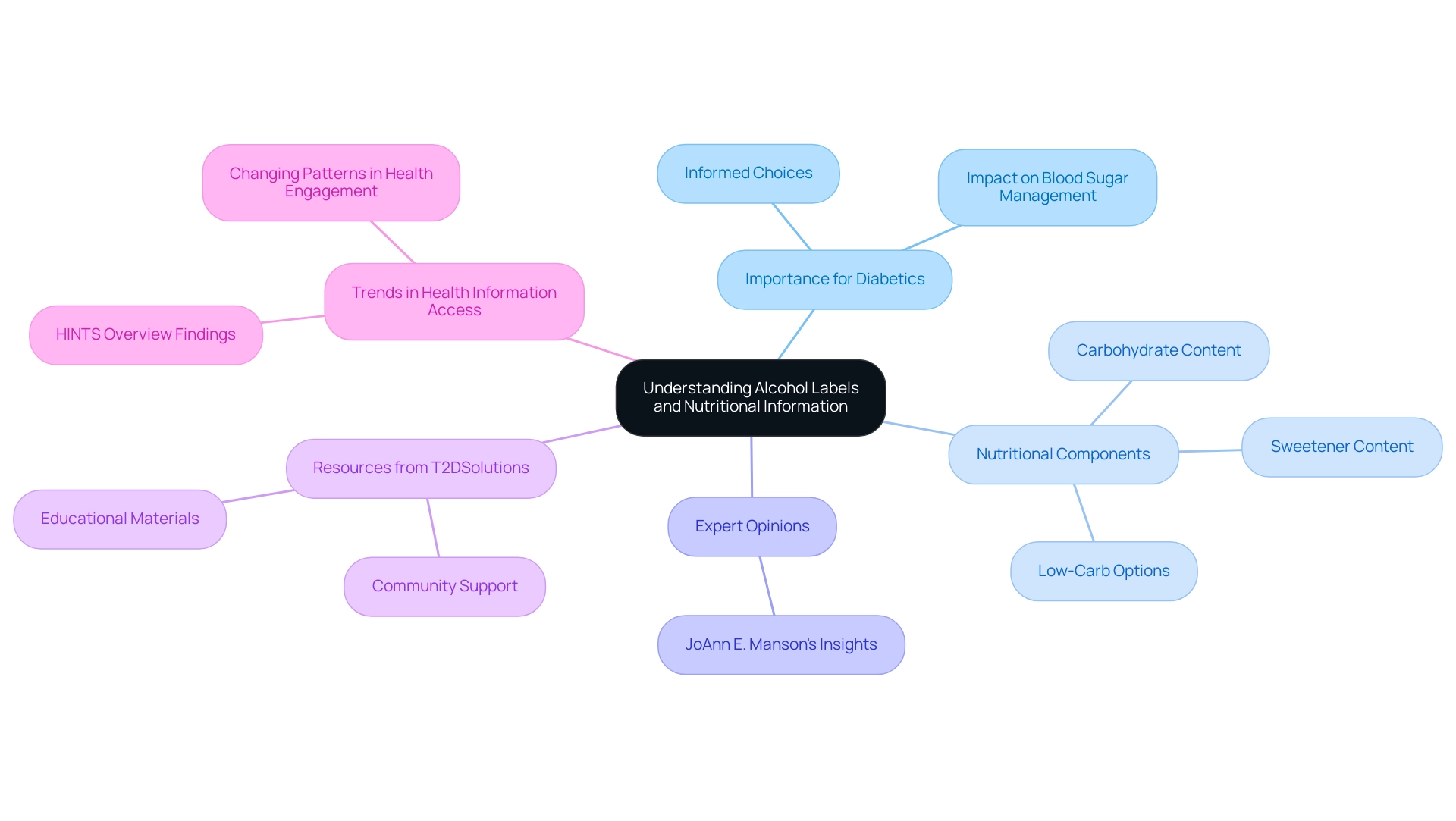
For people controlling blood sugar, comprehending beverage labels is crucial. According to NHS studies, which enrolled over 116,000 women and more than 40,000 male and female nurses, recognizing the relationship between alcohol for diabetics and diabetes management is crucial. At T2DSolutions, we are committed to empowering patients through education and community support.
When reviewing nutritional information, pay particular attention to the carbohydrate and sweetener content listed in the facts. Some alcoholic beverages will directly state their carbohydrate content, while others may require a deeper look at the ingredient list. Choosing drinks marked as 'low-carb' or 'no added sugar' can significantly influence sugar management.
As Joann E. Manson, MD, DrPH from Harvard Medical School states, "Understanding the nutritional information in alcoholic beverages is vital for making informed choices about alcohol for diabetics that can influence glucose levels." Familiarizing oneself with common terminology and standard serving sizes can facilitate better choices, especially in social settings. By diligently reading labels, diabetics can effectively gauge a drink's potential effect on their blood glucose levels, which is essential for making informed choices about alcohol for diabetics.
Furthermore, findings from the HINTS Overview survey underscore evolving trends in health information access and usage, especially concerning beverage labels and blood sugar management, highlighting the necessity of remaining informed. As T2DSolutions launches as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 glucose regulation education, we aim to provide the latest updates and resources, including guidance on nutrition and alcohol for diabetics, to support your management journey.
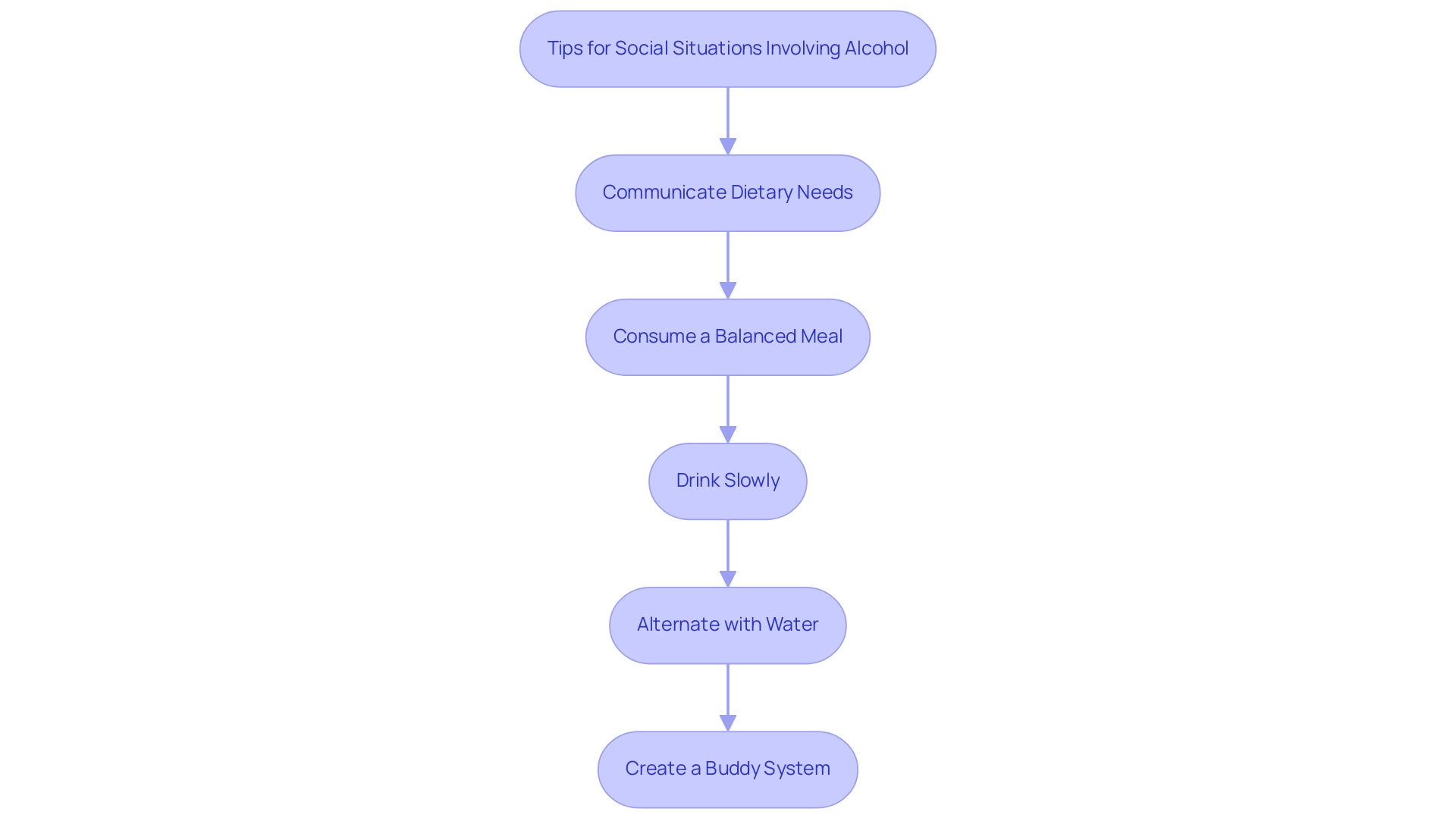
Tips for Social Situations Involving Alcohol
As T2DSolutions launches as a new resource hub for diabetes education and community support, individuals managing diabetes can benefit from careful planning when attending social gatherings. It is essential to communicate dietary needs to friends or hosts prior to the event, which may also involve bringing low-carbohydrate options if the available choices are limited. Consuming a balanced meal before the event can significantly mitigate potential spikes in blood sugar levels.
In fact, the average CRP level for participants with no beverage consumption was noted to be 0.64 g/mL ± 0.80, indicating the health implications of beverage consumption. T2DSolutions offers guidance on strategies for consuming alcohol for diabetics, such as:
- Drinking slowly
- Alternating alcoholic beverages with water
Creating a buddy system, where a reliable friend helps in monitoring beverage consumption, adds an essential layer of support.
As highlighted in the Diabetes Prevention Program study, greater alcohol consumption was associated with lower levels of insulin secretion, underscoring the importance of careful planning and monitoring of alcohol for diabetics in social situations. By being well-prepared and utilizing the resources provided by T2DSolutions, individuals with diabetes can enjoy social interactions while prioritizing their health and safety.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of alcohol consumption while managing diabetes requires a thoughtful approach. Understanding the immediate and long-term effects of alcohol on blood sugar control is crucial for maintaining health. It is imperative to choose alcoholic beverages that are lower in carbohydrates and sugars, while also being aware of how different drinks can affect blood glucose levels. Monitoring these levels before, during, and after drinking is essential to prevent hypoglycemia and manage overall health effectively.
In social settings, careful planning and communication about dietary needs can lead to a more enjoyable experience without compromising health. Strategies such as:
- Consuming a balanced meal beforehand
- Selecting appropriate drink options
- Staying hydrated
can greatly mitigate risks associated with alcohol consumption. Moreover, understanding nutritional labels and making informed choices can empower individuals to manage their diabetes more effectively while still participating in social occasions.
Ultimately, with the right knowledge and resources, it is possible for individuals with diabetes to enjoy the social aspects of drinking responsibly. Staying informed and prepared enables better decision-making, allowing for a balanced approach to alcohol consumption that aligns with personal health goals. By prioritizing health and utilizing available support systems, individuals can navigate social situations confidently, ensuring their well-being remains intact.



