Overview:
The article focuses on how individuals with diabetes can safely consume alcoholic beverages while managing their condition. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the effects of alcohol on blood sugar levels, recommending practices such as consulting healthcare providers, monitoring glucose levels, and choosing low-carb drink options to mitigate risks like hypoglycemia and weight gain.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of alcohol consumption can be particularly challenging for individuals managing diabetes. As the relationship between alcohol and blood sugar levels becomes increasingly understood, it is essential for those affected to grasp how their choices can impact their health. From the potential for hypoglycemia to the nuances of carbohydrate counting, the implications of drinking extend beyond mere enjoyment.
This article delves into the critical aspects of alcohol consumption for diabetics, offering insights into:
- Safe drinking practices
- The benefits and risks associated with moderate intake
- Guidance on selecting diabetic-friendly beverages
By fostering a comprehensive understanding of these topics, individuals can make informed decisions that support their overall diabetes management and well-being.
The Relationship Between Alcohol and Diabetes: Understanding the Basics
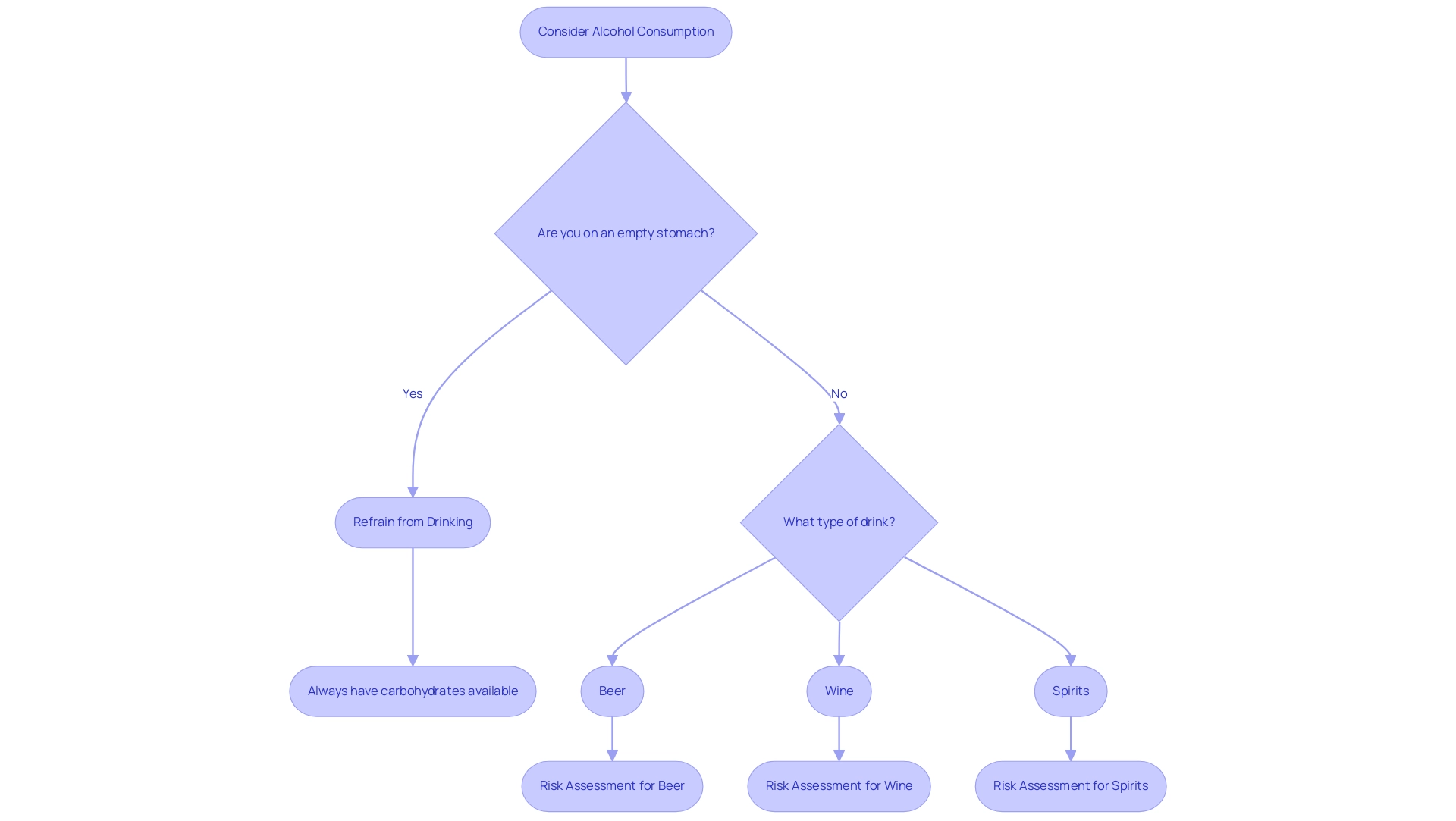
The relationship between alcoholic beverages and diabetes can significantly influence blood sugar levels, often causing an initial increase followed by a subsequent decline, particularly when ingested on an empty stomach. This fluctuation is critical for effective diabetes management, especially for those newly diagnosed, as it can lead to hypoglycemia, which requires immediate attention. Heavy consumption of alcoholic beverages and diabetes, defined as 16 or more standard drinks per day, can increase the risk for ketoacidosis in diabetics, making it essential to monitor intake carefully.
Numerous alcoholic beverages and diabetes can be influenced by the different levels of sweeteners and carbohydrates they comprise, which contribute to a person's total carbohydrate consumption. Therefore, those managing blood sugar levels should be aware of the potential interactions between alcoholic beverages and diabetes medications, as certain medications may exacerbate the effects of alcoholic beverages, leading to increased risks of complications. To encourage safe consumption, it is recommended to:
- Refrain from drinking on an empty stomach
- Always have a source of carbohydrates available in case of low blood glucose events
Comprehending these dynamics is vital for sustaining stable blood glucose levels and ensuring effective management of the condition. At&T Solutions, we are dedicated to enhancing management of the condition through education and community support. We offer resources including educational articles, community forums, and tools for monitoring consumption and its effects on blood sugar, assisting individuals in managing these significant health considerations.
Recent studies in 2024 have further emphasized the importance of these considerations, highlighting the need for ongoing awareness and adaptability in managing this condition.
Safe Drinking Practices for People with Diabetes: Tips and Guidelines
Individuals with diabetes can adopt several key practices to consume beverages safely and effectively manage their condition:
-
Consult Your Healthcare Provider: It is crucial to engage in a conversation with your healthcare professional about beverage intake, as they can provide personalized advice based on your health status and medication regimen.
-
Monitor Blood Glucose Levels: Regularly checking blood glucose levels before and after drinking is vital. This practice aids in understanding how spirits interact with your body and affects glucose levels.
-
Eat Before and While Drinking: Consuming food prior to and during beverage intake can help reduce blood glucose fluctuations. A balanced meal or snacks can slow the absorption of spirits and reduce its impact on blood sugar levels.
-
Stay Hydrated: It is important to drink water alongside alcoholic beverages. Staying hydrated not only helps prevent dehydration but also mitigates some of the negative effects of drinking.
-
Limit Consumption: Adhering to recommended beverage limits—generally one standard drink per day for women and two for men—is advisable. Opt for lower-calorie alcoholic options when possible, as they can have less impact on overall health.
Healthcare providers suggest displaying a standard drink chart to precisely assess their intake of beverages, a method that has been demonstrated to enhance awareness and encourage responsible drinking habits. Significantly, binge drinking happens in approximately half of teenagers and adults who partake in drinking, highlighting the necessity of careful intake, particularly for individuals managing blood sugar levels. As cultural attitudes towards beverages evolve, recognizing the need to drink less than socially acceptable levels can be beneficial, aligning with public health interventions tailored to specific cultural contexts.
With the awareness that recipes for cocktails often surpass one standard drink’s worth of spirits, it becomes even more essential for individuals with blood sugar issues to be vigilant about their selections and drinking habits. Moreover, T2DSolutions will offer additional resources and community assistance to help individuals manage beverage intake and blood sugar control effectively, promoting a more knowledgeable approach to their health.

Benefits and Risks of Alcohol Consumption for Diabetics
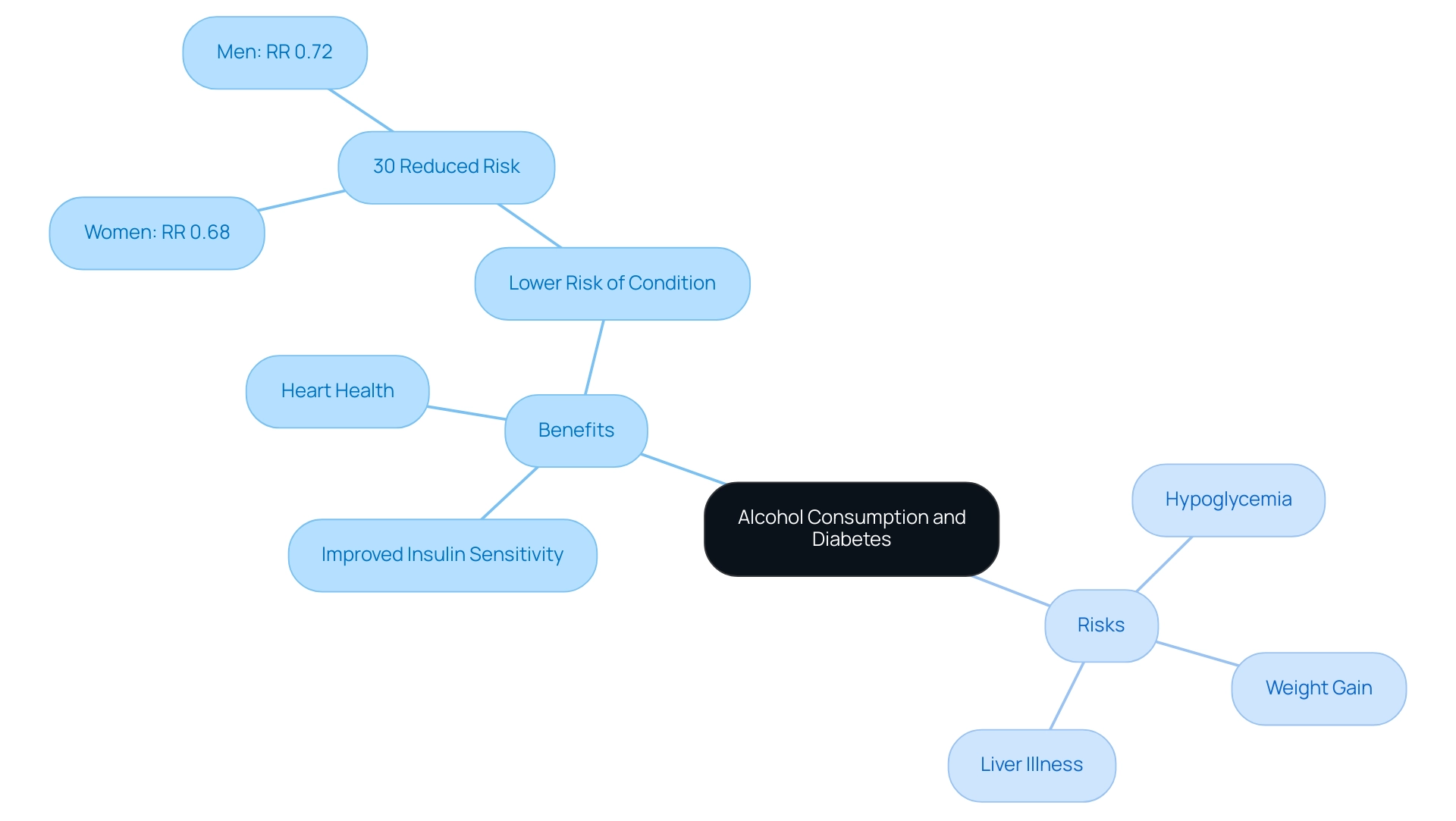
Moderate intake of beverages can offer specific benefits for individuals controlling blood sugar levels, especially regarding improving insulin sensitivity and encouraging heart health. Studies suggest that moderate consumption is linked to a 30% lower risk of developing the condition, with relative risks of 0.72 for men and 0.68 for women, indicating that responsible intake may play a positive role in managing the illness. The aim of the research was to analyze the connection between beverage intake and type 2 disease risk using lifetime abstinence as the reference category.
However, it is essential to carefully weigh these potential benefits against significant risks. For individuals with blood sugar issues, the consumption of alcoholic beverages and diabetes can lead to hypoglycemia, weight gain, and poor dietary choices that may accompany drinking, which can exacerbate their condition. Moreover, individuals with high blood sugar levels face an increased risk of liver illness, requiring a careful strategy regarding alcoholic beverages and diabetes.
Specialists highlight the necessity for a tailored evaluation of alcoholic beverages and diabetes, as personal health condition and blood sugar management must be considered when establishing safe levels of intake. T2DSolutions is here to provide support and resources to help newly diagnosed patients navigate these complexities, offering educational materials and community assistance focused on management. As Rosana Norman noted, 'We thank the core group of the Comparative Risk Assessment within the GBD 2005 Study for Alcohol for their support and comments on the general methodology and an earlier version of this article.'
The case study by Wei (2000) involving over 8,600 participants highlighted the complexity of the substance's effects on blood sugar regulation, reinforcing the necessity of informed decision-making regarding alcoholic beverages and diabetes. For more information and resources on managing alcohol consumption as part of your care plan, visit T2DSolutions.
Carbohydrate Counting and Alcohol: What Diabetics Need to Know
T2DSolutions is dedicated to offering newly diagnosed individuals essential information on managing their condition, including the effect of alcoholic drinks on blood sugar levels. Alcoholic drinks differ greatly in carbohydrate levels, directly impacting those controlling their blood sugar. For instance, beer and sweet wines can have carbohydrate counts exceeding 10 grams per serving, while spirits like vodka and gin generally contain minimal to no carbohydrates.
It is vital for individuals with diabetes to read nutrition labels when available and incorporate these counts into their overall dietary intake. A recent survey indicated that average monthly spending on beverages among consumers aged 21 and older rose from $25 to $38 early in 2022. Notably, participants with an income of $100,000 or more increased their spending on beverages by 31% from April to June 2022, while those with incomes under $50,000 saw a 17% decrease in spending.
This trend necessitates awareness of the substance's nutritional impact, which T2DSolutions aims to address. Moreover, the Ready-to-Drink (RTD) market, which has experienced sales triple since 2018, highlights how flavor affects consumer decisions; this is especially pertinent for individuals controlling blood sugar levels when choosing alcoholic beverages. For effective blood glucose management, particularly when planning meals that contain beverages, monitoring carbohydrate consumption is crucial.
Nutritionists advise that individuals with blood sugar issues remain vigilant about the carbohydrate content in their alcoholic choices, as this can facilitate improved blood sugar control and overall health outcomes. T2DSolutions will act as a thorough resource for navigating these dietary considerations, providing tools such as:
- Personalized meal planning
- Educational resources on alcohol's effect on blood sugar management
- A supportive community for sharing experiences and strategies

Choosing the Right Alcoholic Beverages: Diabetic-Friendly Options
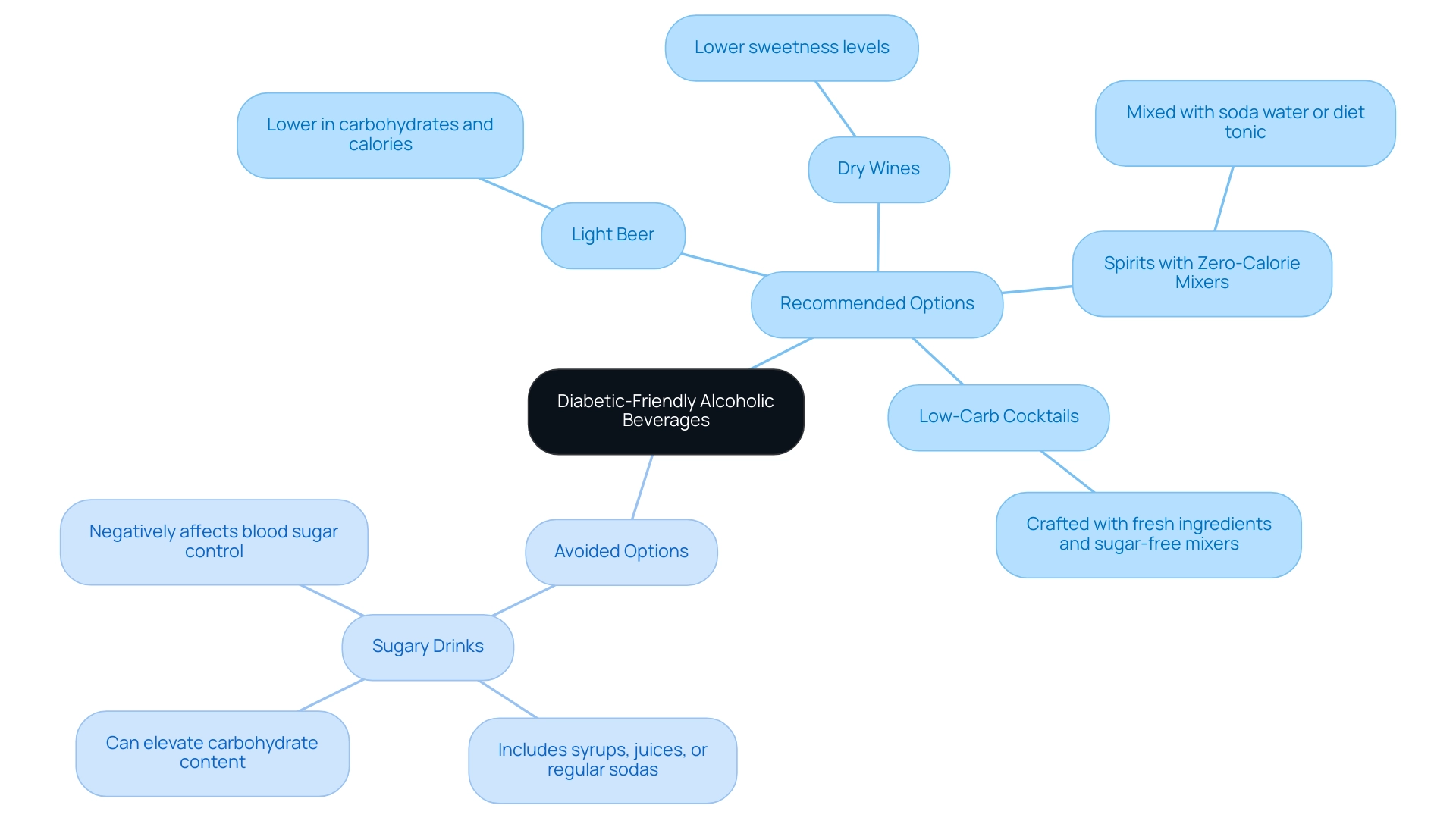
When choosing alcoholic beverages and diabetes-friendly options, individuals managing diabetes should consider the following choices that align with their dietary needs:
-
Light Beer: Typically lower in carbohydrates and calories, light beer provides a refreshing option without significantly affecting blood glucose levels.
-
Dry Wines: Both red and white dry wines are suggested as they have lower levels of sweetness compared to sweeter varieties. This makes them a more suitable option for diabetic individuals.
-
Spirits with Zero-Calorie Mixers: Spirits like vodka, gin, or tequila can be enjoyed when mixed with soda water or diet tonic water, effectively minimizing carbohydrate intake while maintaining flavor.
-
Low-Carb Cocktails: Opt for cocktails crafted with fresh ingredients and sugar-free mixers. These beverages can offer a fulfilling experience without the extra sweeteners that complicate managing blood glucose.
Avoid Sugary Drinks: It is crucial to steer clear of cocktails that include syrups, juices, or regular sodas, as these can substantially elevate carbohydrate content and negatively affect blood sugar control.
As emphasized by Dr. Sharita E. Warfield, adopting healthier lifestyle choices early can improve overall quality of life and prevent complications associated with blood sugar issues. This is particularly important given the 21% rise in Type 1 condition prevalence among individuals younger than 20 between 2001 and 2009. Current trends indicate a growing awareness of the importance of low-carb drink options in the context of alcoholic beverages and diabetes management effectively.
Additionally, case studies on changes in SSB-attributable burdens over time reveal the significant health impacts of sugary drinks, reinforcing the advice to avoid sugary cocktails.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of alcohol consumption is crucial for individuals managing diabetes. This article highlights the significant relationship between alcohol and blood sugar levels, emphasizing the importance of safe drinking practices and the potential benefits and risks associated with moderate intake. By consulting healthcare providers, monitoring blood sugar, and choosing diabetic-friendly beverages, individuals can navigate the challenges of alcohol while prioritizing their health.
Moreover, the article underscores the necessity of carbohydrate counting in alcohol consumption. Recognizing the varying carbohydrate content in different alcoholic beverages enables better blood sugar management. With options like light beer, dry wines, and spirits mixed with zero-calorie mixers, individuals can enjoy social occasions without compromising their health.
In summary, informed decision-making regarding alcohol consumption is essential for effective diabetes management. By embracing safe practices and understanding the impact of alcohol on blood sugar levels, individuals can enjoy a balanced lifestyle while maintaining their health priorities. T2DSolutions remains committed to providing resources and support to empower those navigating these important health considerations.



