Overview
The article provides an in-depth tutorial on the American Diabetes Association guidelines for managing Type 2 Diabetes, emphasizing the importance of diagnosis, lifestyle changes, nutrition, physical activity, and emotional support. It supports this by detailing specific management strategies, such as dietary recommendations, exercise regimens, and the necessity of self-monitoring blood glucose levels, all aimed at empowering patients to effectively control their condition.
Introduction
Type 2 Diabetes presents a growing challenge in contemporary healthcare, marked by a significant rise in diagnosis rates, particularly among younger populations. Understanding the nuances of this condition—ranging from its diagnosis and classification to effective management strategies—is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. As the economic burden of diabetes continues to escalate, it becomes increasingly important to address risk factors and implement comprehensive management plans that encompass:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Nutritional guidance
- Physical activity
- Emotional support
This article delves into the multifaceted approach needed for effectively managing Type 2 Diabetes, offering insights into the latest guidelines and strategies that can empower individuals on their health journey.
Understanding the Diagnosis and Classification of Type 2 Diabetes
Condition 2 Mellitus is mainly identified through specific blood sugar measurements, which include the following criteria:
- A fasting plasma glucose level of 126 mg/dL or higher
- A 2-hour plasma glucose level of 200 mg/dL or greater during an oral glucose tolerance test
- An A1C level of 6.5% or higher
Recognizing the unique traits of this condition, such as insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency, is essential as it distinguishes this ailment from the other form. This differentiation is crucial for understanding treatment options and management strategies as outlined in the American Diabetes Association guidelines for type 2 diabetes.
Recent studies indicate a significant rise in the occurrence of the second classification of diabetes, particularly among children and adolescents aged 10 to 19 years across various racial and ethnic groups, with non-Hispanic Black individuals experiencing the highest incidence rates. The economic impact of diabetes is also notable, with excess medical costs per person associated with diabetes increasing from $10,179 to $12,022 from 2012 to 2022. Moreover, conditions such as impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and impaired fasting glycaemia (IFG) act as important warning signs suggesting an increased risk of developing 2nd stage blood sugar issues, although progression is not guaranteed.
By identifying and addressing risk factors—such as age, family history, physical inactivity, and ethnic background—highlighted in case studies, we can take proactive steps toward preventing the onset of the second type of diabetes. T2DSolutions seeks to be your all-encompassing resource for diabetes control and education, offering essential information, including personalized treatment choices and support services, as you navigate your health journey.

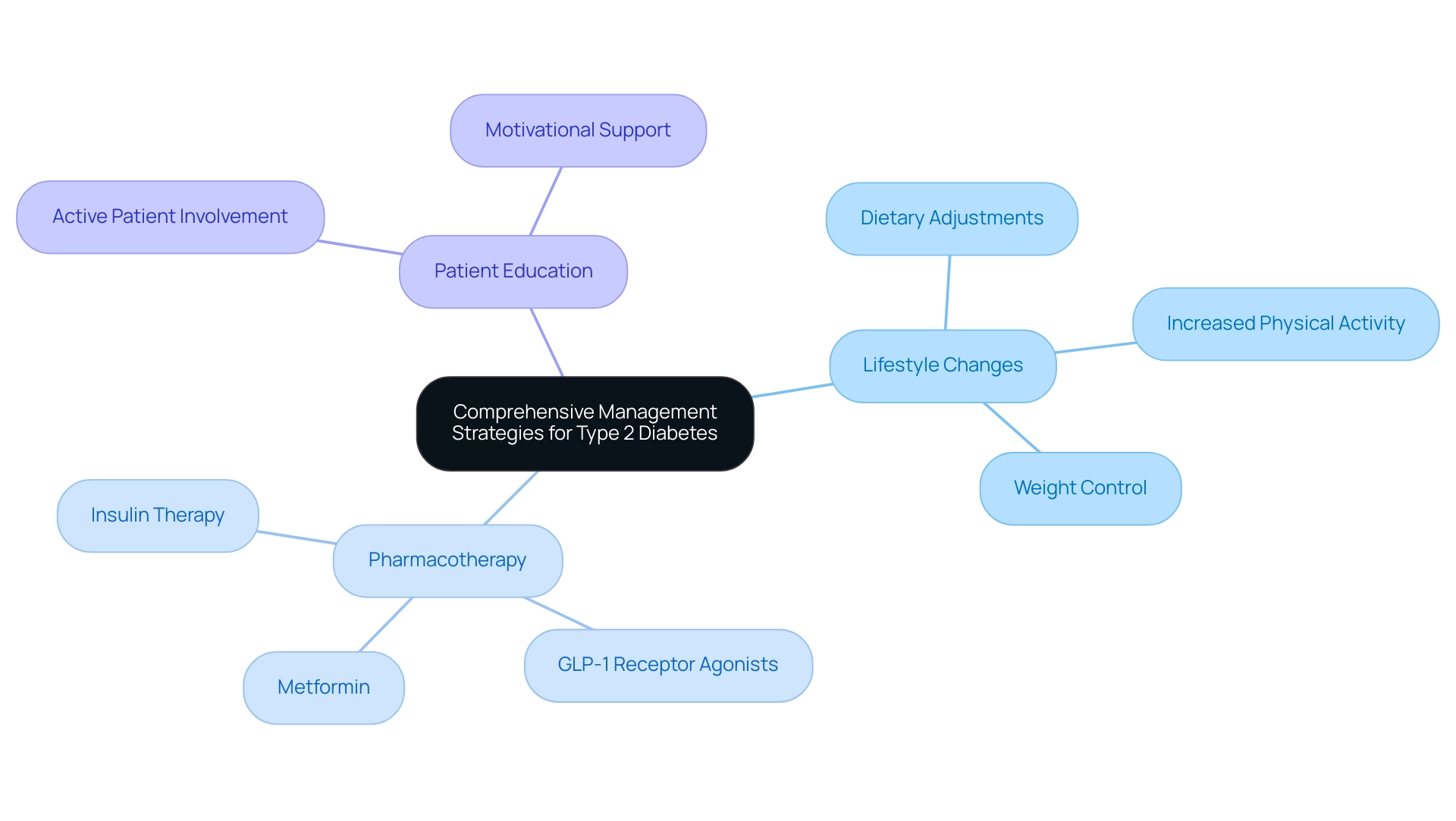
Comprehensive Management Strategies for Type 2 Diabetes
The strategies outlined in the American Diabetes Association guidelines for type 2 diabetes include several crucial approaches, prominently featuring lifestyle changes such as:
- Dietary adjustments
- Increased physical activity
- Effective weight control
A pivotal study, the PREDIMED-Plus Trial, highlights that combining a Mediterranean diet with exercise can lead to significant weight reduction and improved glucose metabolism, underscoring the critical role of lifestyle changes. Significantly, the PREDIMED Study Post-hoc Reports indicate that condition 2 can be avoided even without substantial weight loss in high-risk individuals utilizing the Mediterranean diet, with risk reduction varying from 30% to 50% in comparison to the control group.
For patients who may require additional support, pharmacotherapy is also a consideration. Medications such as:
- Metformin
- GLP-1 receptor agonists
- Insulin therapy
can be tailored to the individual based on their unique health profiles. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and A1C is vital for personalizing treatment and preventing complications.
Furthermore, the American Diabetes Association guidelines for type 2 diabetes emphasize the significance of patient education and support, encouraging active patient involvement in their care plans. As Ronald B. Goldberg, M.D., notes, 'Patient involvement is crucial for fostering motivation and achieving better health outcomes.' Encouraging discussions about the benefits observed from lifestyle changes can help patients stay motivated, particularly those who may feel discouraged by incremental progress.
This comprehensive method, integrating lifestyle changes with medication when needed, is essential for the effective control of the condition associated with insulin resistance.
The Role of Nutrition in Diabetes Management
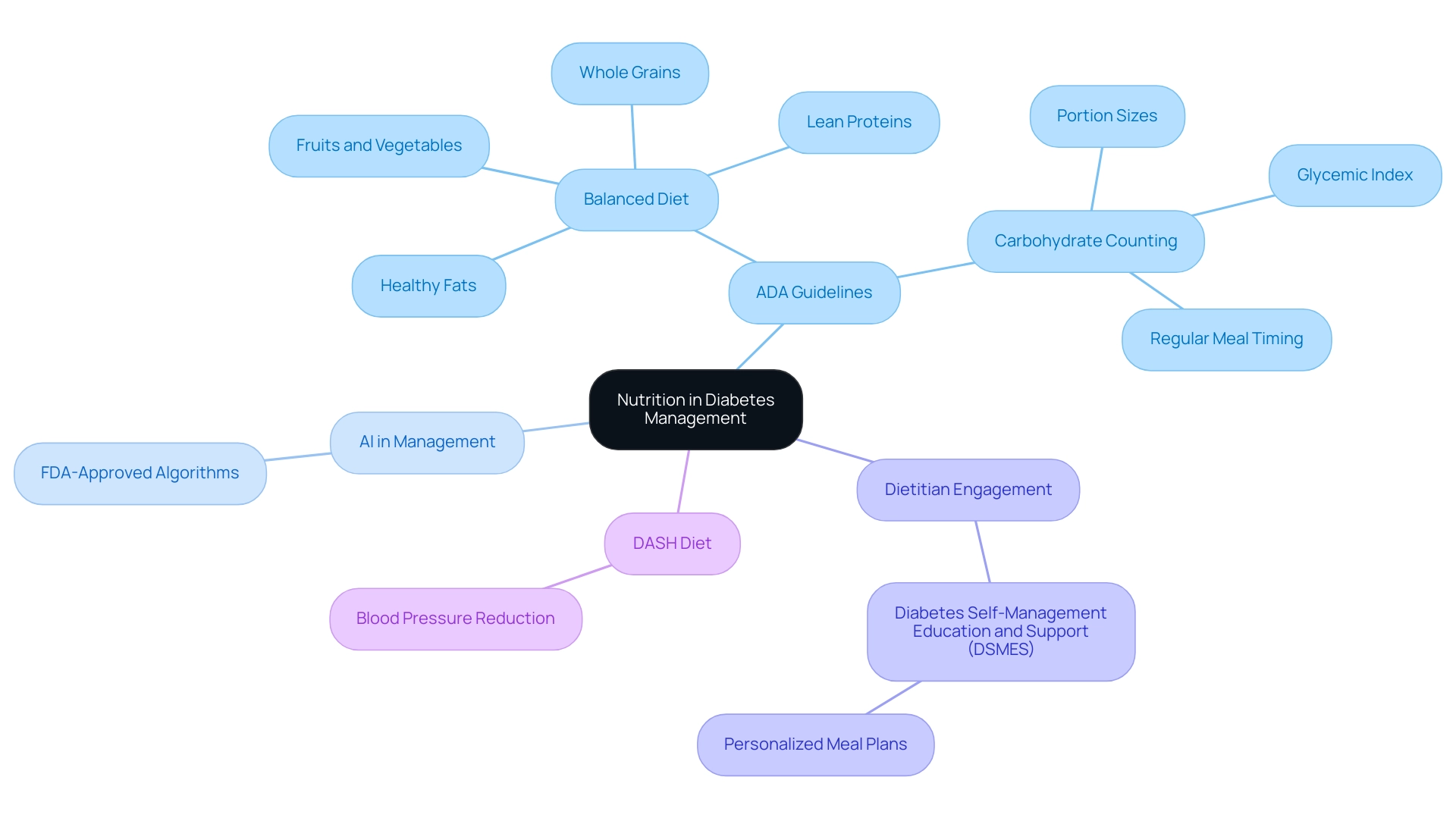
Nutrition plays a crucial role in the control of Type 2 condition, and following the American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines is vital for effective care. The ADA advocates for a balanced diet that includes:
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
- A variety of fruits and vegetables
In particular, carbohydrate counting is highlighted as a critical strategy for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels; understanding portion sizes and the glycemic index of foods is fundamental.
Recent updates indicate that the application of FDA-approved artificial intelligence algorithms can further enhance the management of carbohydrate intake, making this approach more accessible and effective for patients. As noted by the American Association Professional Practice Committee, 'Recommendation 12.6 was updated to indicate the application of FDA-approved artificial intelligence algorithms.' Regular meal timing and moderation in portion sizes are also vital in preventing blood glucose spikes.
Additionally, fat intake should primarily come from monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats while limiting saturated and trans fats. Engaging with a registered dietitian through Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support (DSMES) services can lead to the development of personalized meal plans tailored to individual health needs and preferences. This tailored approach not only improves compliance with dietary recommendations but can also significantly contribute to better health outcomes.
Additionally, the DASH diet has been demonstrated in extensive, randomized, controlled studies to significantly lower blood pressure, highlighting the significance of dietary oversight in managing blood sugar conditions. At T2DSolutions, we aim to provide newly diagnosed patients with access to the ADA guidelines and additional resources to support their journey towards effective management of their condition.
Importance of Physical Activity
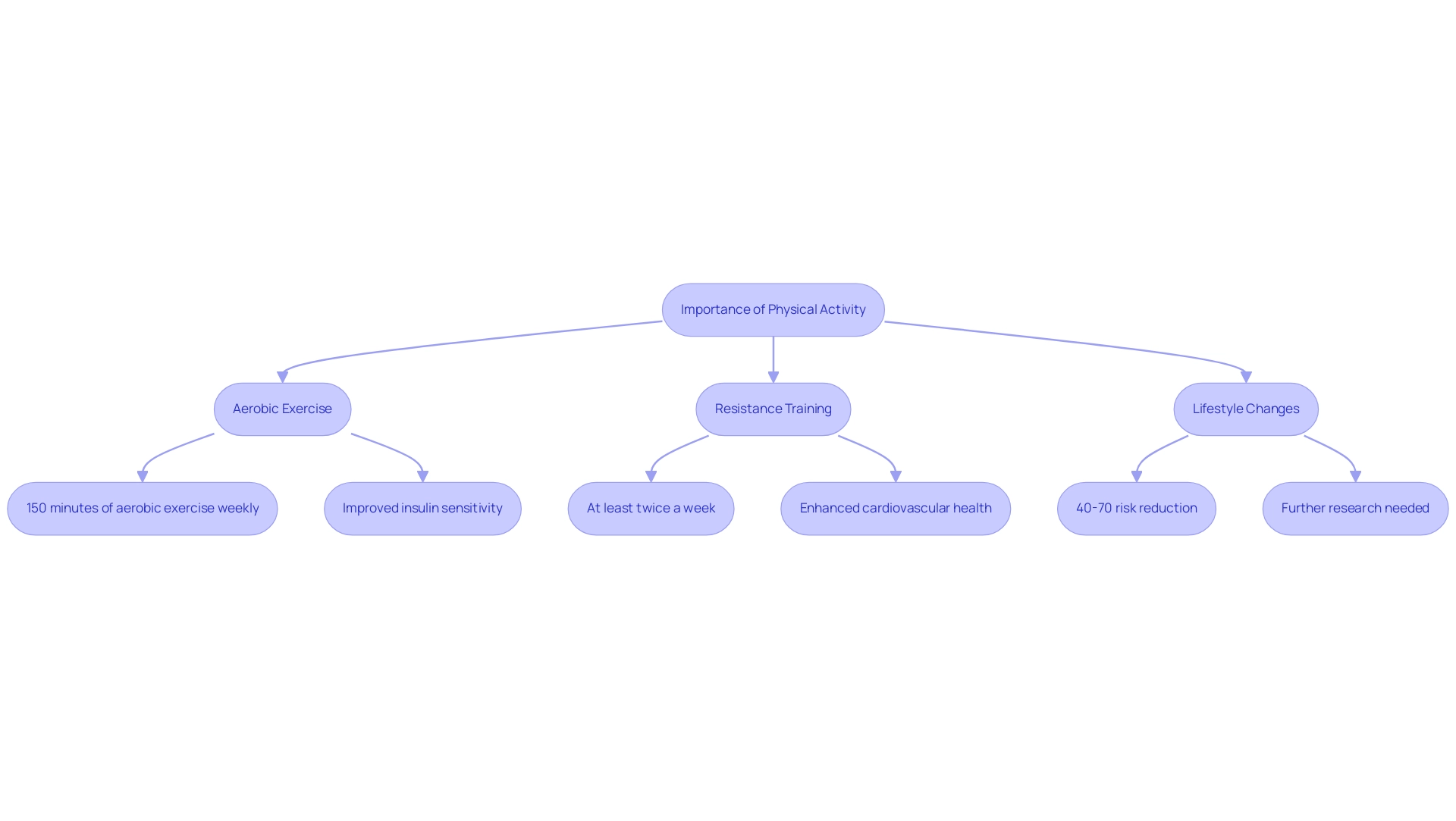
at&t Solutions, we are dedicated to offering newly diagnosed patients extensive resources for managing type 2 and type 3 diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association guidelines for type 2 diabetes, individuals with the second form of the condition should participate in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly. Activities such as brisk walking or cycling are ideal and should be spread across at least three days.
In addition to aerobic exercise, incorporating resistance training at least twice a week is crucial for enhancing muscle strength and improving insulin sensitivity. Research indicates that structured lifestyle interventions focusing on weight loss and increased physical activity can reduce the risk of developing type 2 conditions by 40% to 70% in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance. Significantly, both the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study and the U.S. Diabetes Prevention Program have shown that lifestyle changes can lower the occurrence of the condition by 58%.
As Barry Braun, Ph.D., FACSM, points out, 'Engagement in regular physical activity enhances blood glucose management and can prevent or postpone the onset of type 2.' Despite the known benefits of exercise for type 2 glucose management, optimal exercise recommendations according to the American Diabetes Association guidelines for type 2 diabetes remain unclear, highlighting the need for further research. Regular physical activity is not only essential for managing weight but also plays a significant role in enhancing cardiovascular health, alleviating stress, and improving overall mood.
These diverse advantages highlight the importance of physical activity as a crucial element of effective health control. At&t Solutions, we provide customized resources and assistance to help you manage your condition journey. Subscribe to our updates to stay informed about new content and resources designed specifically for you.
Monitoring and Self-Management
Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) is a crucial element of successful condition control, and T2D Solutions is here to assist you in this journey. By empowering individuals to track their blood sugar patterns, SMBG facilitates informed decisions regarding dietary choices, physical activity, and medication adjustments. According to the American Diabetes Association guidelines for type 2 diabetes, patients are recommended to undergo A1C testing every three months and are also encouraged to monitor their daily blood glucose based on personal needs.
At T2D Solutions, we provide resources and tools to help you keep a detailed log of these readings, allowing you to recognize trends and engage in meaningful discussions with your healthcare team. This proactive self-management strategy not only promotes accountability but also enables timely modifications to treatment plans. A significant finding from a multicase study on insulin-treated individuals revealed that motivations for SMBG often extend beyond long-term glycemic control, encompassing routines and preparations for healthcare appointments.
Overall, 86% of participants viewed the SMBG data as having equal or greater importance than the HbA1c data, emphasizing the vital role of SMBG in controlling blood sugar. Furthermore, it is important to note that there is significant variation in individual practices regarding SMBG, with many not adhering to recommended testing frequencies. Such insights emphasize the necessity of customizing SMBG practices to optimize management outcomes.
With T2D Solutions, you can access a community of support and educational resources that can help you effectively manage your SMBG practices and overall health care.
![]()
Emotional and Psychological Support
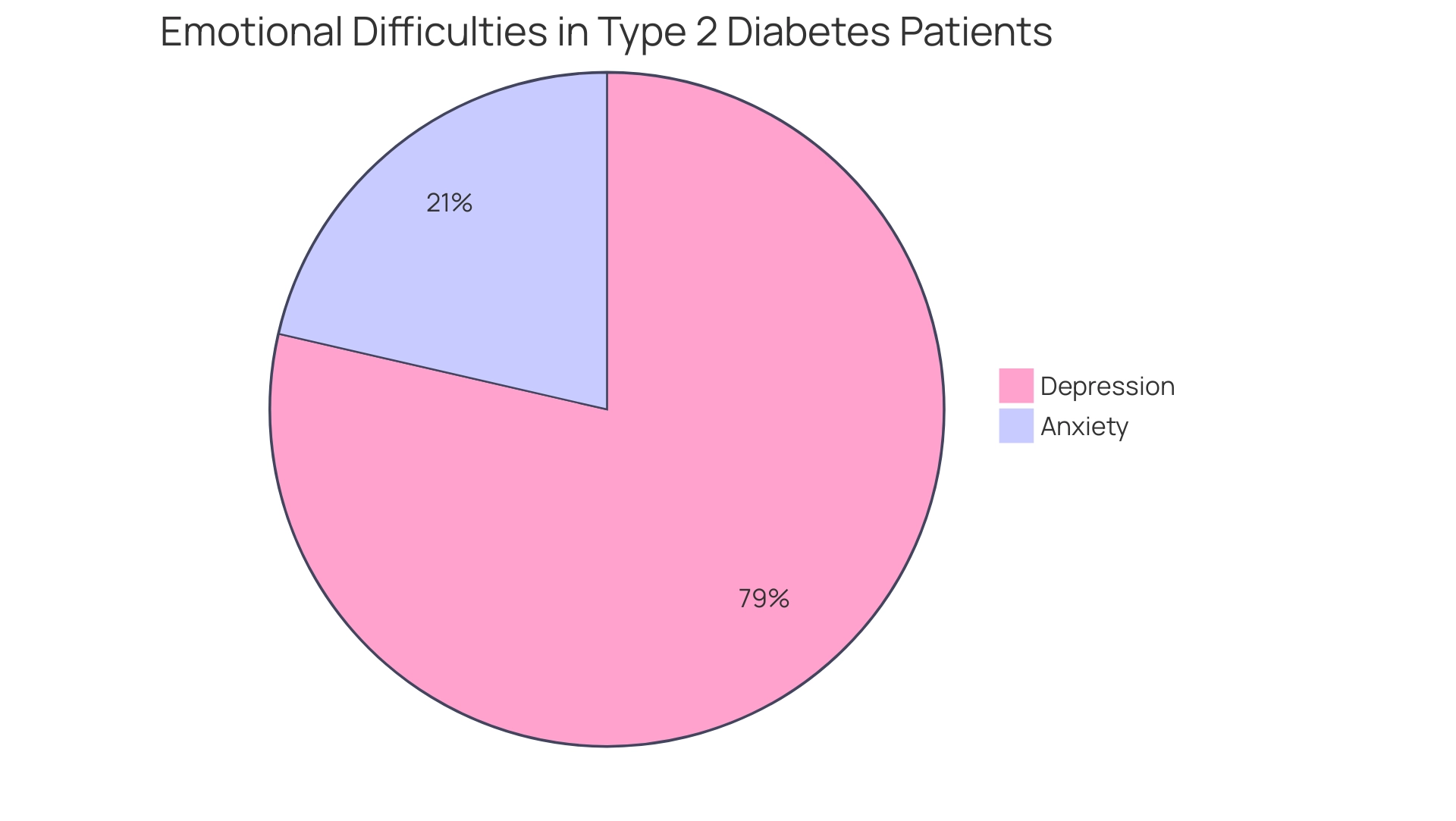
Managing a chronic condition like type 2 mellitus often brings about considerable emotional difficulties, including anxiety and depression. Recent findings indicate that among individuals with a family history of mental health issues:
- 21.4% reported experiencing anxiety
- 78.6% reported depression
Recognizing the intricate interplay between mental health and chronic illness, Td Solutions is proud to serve as a new resource hub dedicated to providing education and community support for individuals managing Type 2 and Type 3 conditions.
The management of the condition is highlighted by the American Diabetes Association guidelines for type 2 diabetes, which emphasize the importance of incorporating emotional and psychological support. In addition to seeking professional counseling and participating in support groups, improving knowledge and health education is crucial for reducing anxiety and depression in T2DM patients. Furthermore, a recent study utilizing cross-lagged panel structural equation modeling revealed bi-directional negative associations between anxiety, depression, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among patients with the condition.
This highlights the critical need for tailored support systems that address both the physical and emotional aspects of diabetes care. As noted by author Kalpana Sharma, 'Many factors are associated with anxiety and depression so these factors are needed to be considered while planning and implementing the program for the risk groups.' The findings from the case study titled 'Factors Associated with Anxiety and Depression in Diabetes Patients' emphasize the importance of regular screening and integrated care, identifying significant associations between anxiety and factors like living status and educational level, while depression was linked to smoking habits and satisfaction with treatment.
By adhering to the American Diabetes Association guidelines for type 2 diabetes, T2D Solutions aims to empower newly diagnosed patients with the necessary tools and support to effectively manage their physical and mental health.
Conclusion
Type 2 Diabetes requires a comprehensive understanding of its diagnosis, management strategies, and the importance of emotional support. Effective management begins with accurate diagnosis through blood glucose measurements, which is critical for differentiating Type 2 Diabetes from other forms. The rising incidence, particularly among younger populations, highlights the urgency of addressing risk factors and implementing preventive measures.
Lifestyle modifications serve as the cornerstone of diabetes management, with evidence supporting the benefits of:
- Dietary changes
- Increased physical activity
- Weight management
The integration of pharmacotherapy may be necessary for some individuals, but the emphasis on patient education and active participation in one’s health journey cannot be overstated. Nutrition, particularly through balanced diets and carbohydrate counting, plays a vital role in maintaining optimal blood sugar levels.
Moreover, physical activity is essential, not only for weight control but also for improving overall health and well-being. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care, while the acknowledgment of emotional and psychological challenges underscores the need for integrated support systems.
Ultimately, the multifaceted approach to managing Type 2 Diabetes—encompassing lifestyle changes, nutritional guidance, physical activity, and emotional support—aims to empower individuals in their health journey. By recognizing the interconnectedness of these elements, patients and healthcare providers can work collaboratively to mitigate the impacts of this condition, fostering a healthier future for those affected by Type 2 Diabetes.



