Overview
An A1C level of 6.2% indicates prediabetes, which raises the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, necessitating proactive management strategies. The article emphasizes the importance of lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and a supportive network to effectively manage this level, highlighting educational resources and community support as essential tools for individuals seeking to lower their A1C and improve overall health.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding A1C levels is crucial for both individuals and healthcare providers. An A1C level of 6.2% signals a prediabetes condition, placing individuals at an increased risk for type 2 diabetes and related health complications.
With the rising incidence of diabetes across diverse populations, proactive measures are essential to mitigate these risks. This article delves into effective strategies for managing and lowering A1C levels, including:
- The role of medication
- The importance of regular testing
- The necessity of building a supportive network
By exploring these facets, individuals can gain valuable insights and tools to navigate their health journey with greater confidence and efficacy.
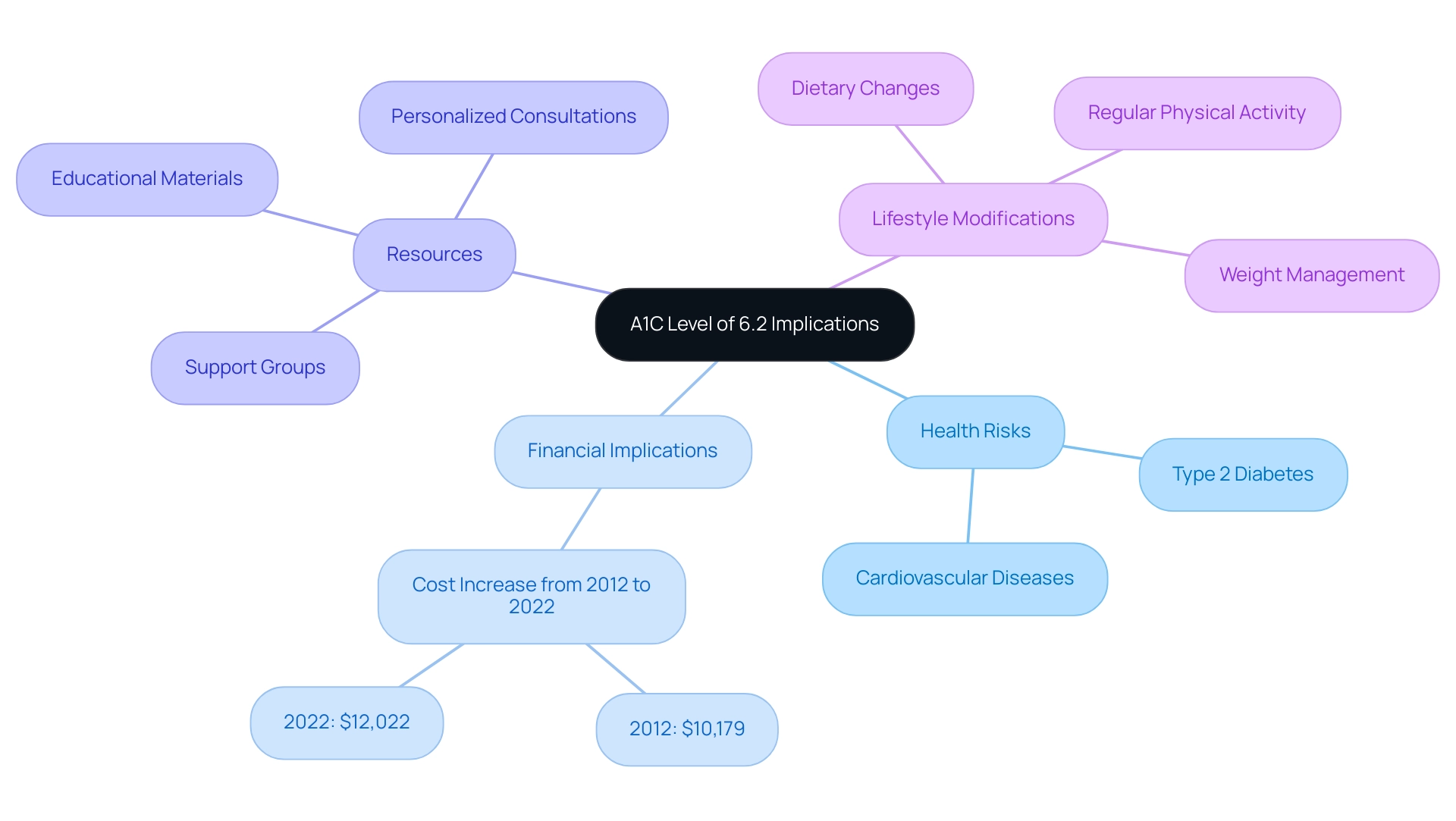
Understanding the Implications of an A1C Level of 6.2
An A1C level of 6.2% is classified as prediabetes, indicating that blood sugar amounts are elevated but not yet within the range for a type 2 condition diagnosis. This level corresponds to an average blood glucose level of approximately 135 mg/dL over the preceding two to three months. Individuals with an A1C level of 6.2% face an increased risk of developing not only type 2 conditions but also cardiovascular diseases.
The financial implications are significant, as excess medical costs per individual related to the condition rose from $10,179 to $12,022 from 2012 to 2022. Furthermore, the incidence of type 2 sugar-related illness has significantly risen across all racial and ethnic groups from 2002 to 2018, highlighting the urgency for preventive measures. T2DSolutions is dedicated to empowering individuals with elevated A1C levels through education and community support, offering resources such as:
- Educational materials
- Support groups
- Personalized consultations
It is crucial for these individuals to engage in regular monitoring and implement lifestyle modifications aimed at reversing this trend, such as:
- Dietary changes
- Regular physical activity
- Weight management
The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study highlights the significance of wellness education and preventive actions, especially for young individuals at risk, showing substantial rises in the occurrence of both type 1 and type 2 conditions among children and adolescents. Consulting with healthcare professionals is essential to tailor an effective management plan that addresses individual health needs, thereby promoting overall well-being and reducing the risk of progression to a chronic condition.
Act now to remain connected with Td Solutions for the latest updates and resources that assist your journey in managing your health.
Effective Strategies for Managing and Lowering Your A1C Level
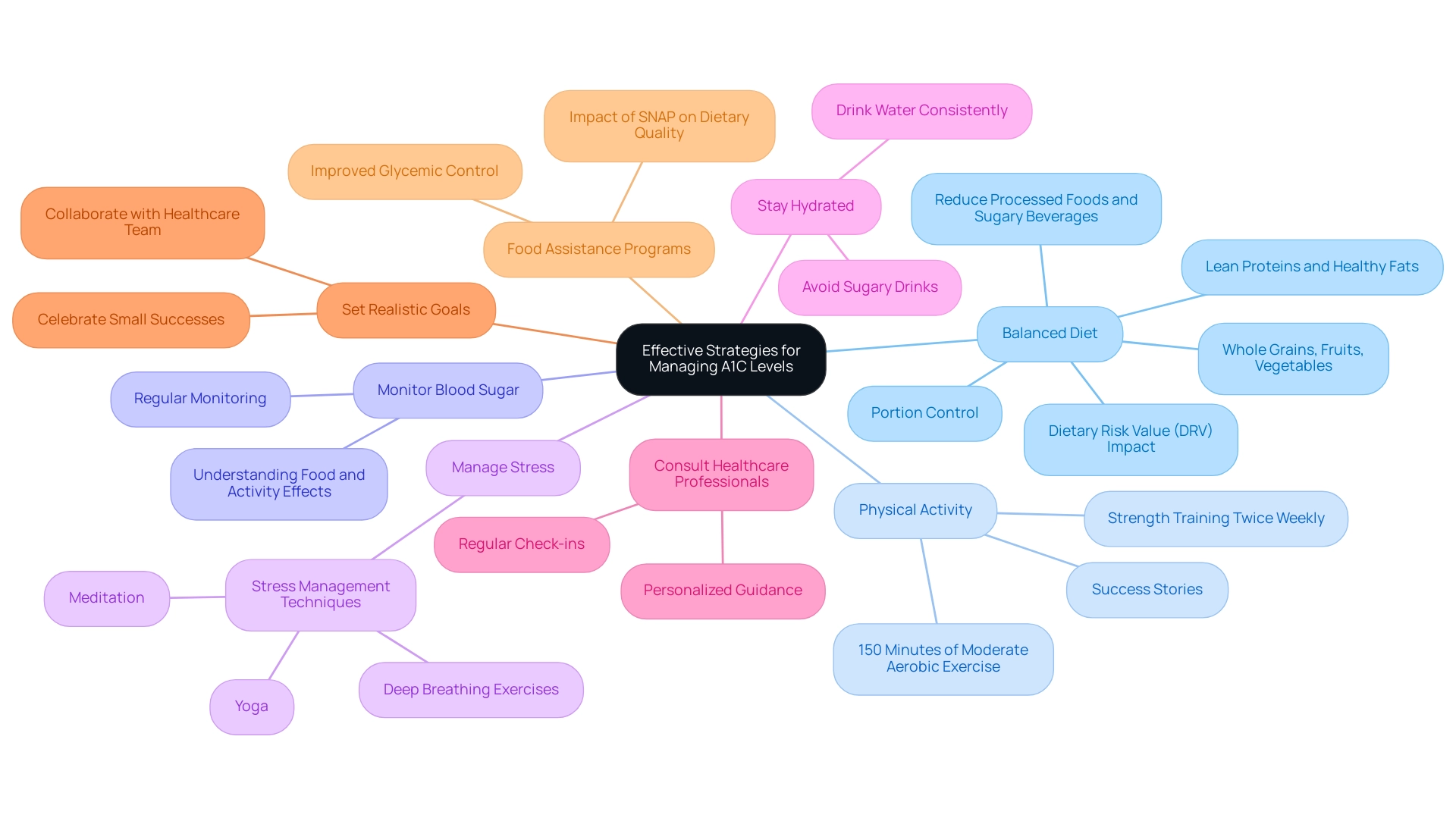
As T2DSolutions gets ready to launch as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, it is essential to effectively manage and reduce your A1C level of 6.2. Consider the following strategies:
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: Emphasize a diet abundant in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Reducing intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-carbohydrate snacks is crucial. Portion control is essential to avoid spikes in blood sugar, as studies suggest that reduced carbohydrate and increased fat intakes are associated with elevated hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) readings. Additionally, a higher Dietary Risk Value (DRV) score, reflecting improved dietary quality, has been inversely associated with %HbA1c by − 0.023% (or 0.23 mmol/mol; 95% CI − 0.035%, − 0.012%; < 0.001), reinforcing the need for careful dietary choices.
-
Increase Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week—activities such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling are beneficial. Incorporating strength training exercises at least twice weekly can further enhance your health outcomes. Current research emphasizes the importance of physical activity in managing A1C values, showcasing success stories that illustrate how it can help achieve an A1C level of 6.2.
-
Monitor Blood Sugar Concentrations: Regular monitoring of blood sugar concentrations, as advised by your healthcare provider, is essential. Comprehending how different foods and activities affect your measurements enables prompt modifications to your management plan.
-
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can elevate blood sugar levels, making stress management techniques—such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises—essential to your wellness regimen.
These practices not only promote emotional well-being but also enhance glycemic control.
-
Stay Hydrated: Consistently drinking water throughout the day promotes overall health and hydration. Avoid sugary drinks, as they can lead to increased blood sugar levels.
-
Consult Healthcare Professionals: Regular check-ins with healthcare providers, including certified diabetes educators, can provide personalized guidance tailored to your needs. This support may encompass medication adjustments and access to educational resources to empower your management journey.
-
Set Realistic Goals: Collaborate with your healthcare team to establish achievable, measurable goals for your A1C levels and overall well-being.
Acknowledging and celebrating small successes can help sustain motivation throughout your journey to improved well-being.
Including food assistance programs, such as SNAP, may also enhance dietary quality and outcomes among food-insecure individuals. The analysis revealed that among food insecure adults, those receiving SNAP benefits had significantly reduced odds of poor glucose control, suggesting that economic assistance may help improve dietary quality and health outcomes.
Stay tuned for more resources and strategies from T2DSolutions, and consider subscribing to receive updates on how to manage your condition effectively.
The Role of Medication in A1C Management
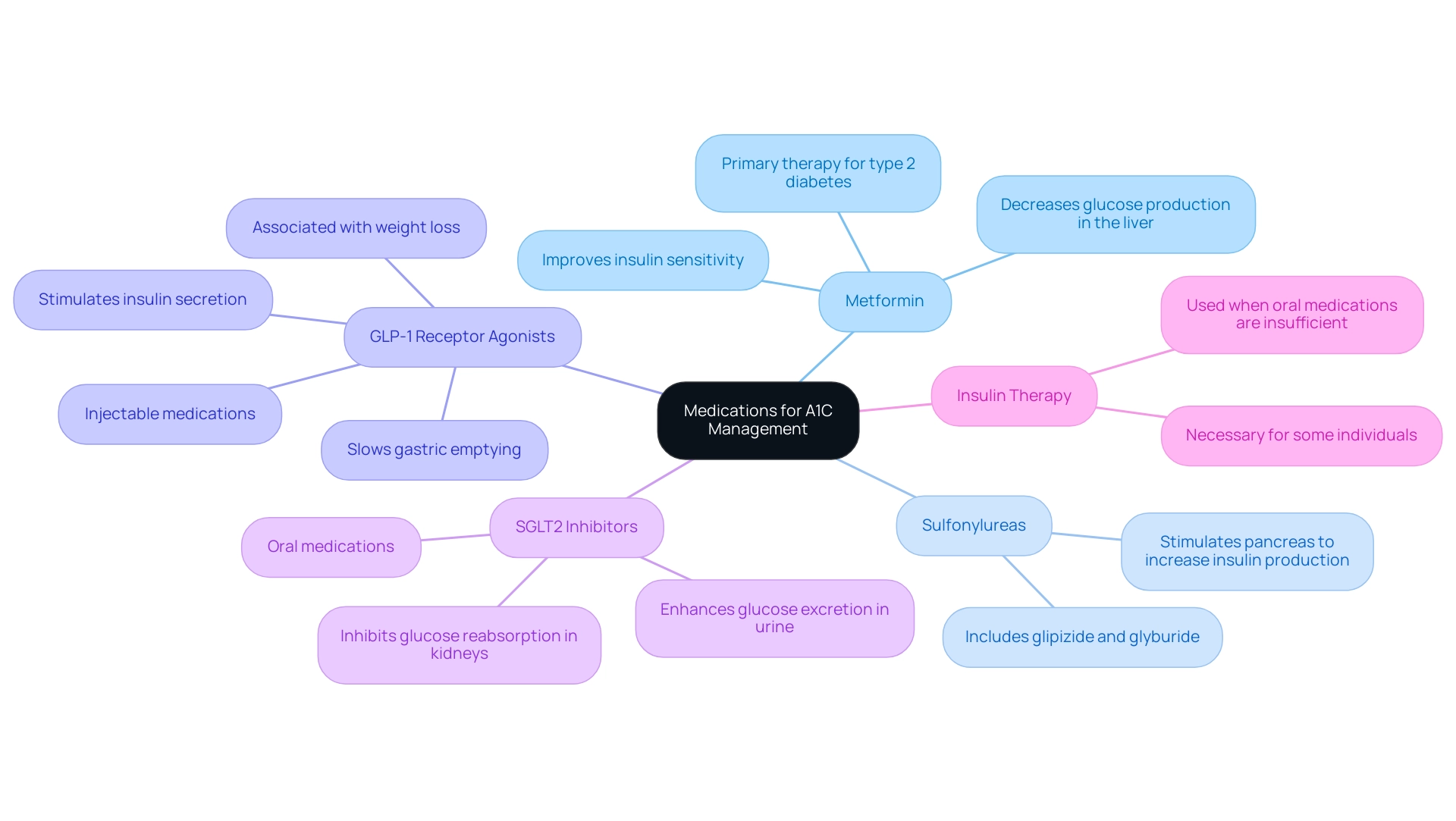
For individuals with a1c level of 6.2, several medication options are available for those who may need extra assistance in managing their blood sugar. T2D Solutions, as a new resource hub for educational purposes related to blood sugar management, offers valuable insights and support to help navigate these options effectively. The main categories of blood sugar medications include:
- Metformin: Acknowledged as the primary therapy for type 2 sugar imbalance, Metformin effectively reduces blood sugar amounts by improving insulin sensitivity and decreasing glucose production in the liver.
- Sulfonylureas: This class of medications, which includes glipizide and glyburide, works by stimulating the pancreas to increase insulin production, thereby lowering blood sugar levels.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These injectable medications promote blood sugar control by stimulating insulin secretion and slowing gastric emptying. They are also associated with weight loss, which can be beneficial for many patients.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: By inhibiting the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, these oral medications enhance glucose excretion in the urine, effectively lowering blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Therapy: Some individuals may need insulin therapy to achieve adequate blood sugar control, particularly if lifestyle modifications and oral medications do not suffice.
It's important to note that this condition was the eighth leading cause of death in the United States in 2021, underscoring the critical need for effective management strategies. As Dr. Qiuping Gu noted, the age-adjusted prevalence of total blood sugar disorders increased from 9.7% in 1999–2000 to 14.3% in August 2021–August 2023, highlighting the urgency in addressing treatment for patients with an a1c level of 6.2. Additionally, the increasing occurrence of type 1 and type 2 conditions in youth, particularly among non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander groups, reflects a growing public health challenge that necessitates early intervention strategies.
Consulting healthcare professionals is essential to tailor a medication regimen that aligns with individual health needs and circumstances. The evolving landscape of blood sugar regulation further emphasizes the need for personalized management strategies. T2D Solutions aims to provide educational resources and community support to assist newly diagnosed patients in understanding their treatment options and managing their condition effectively.
Importance of Regular A1C Testing
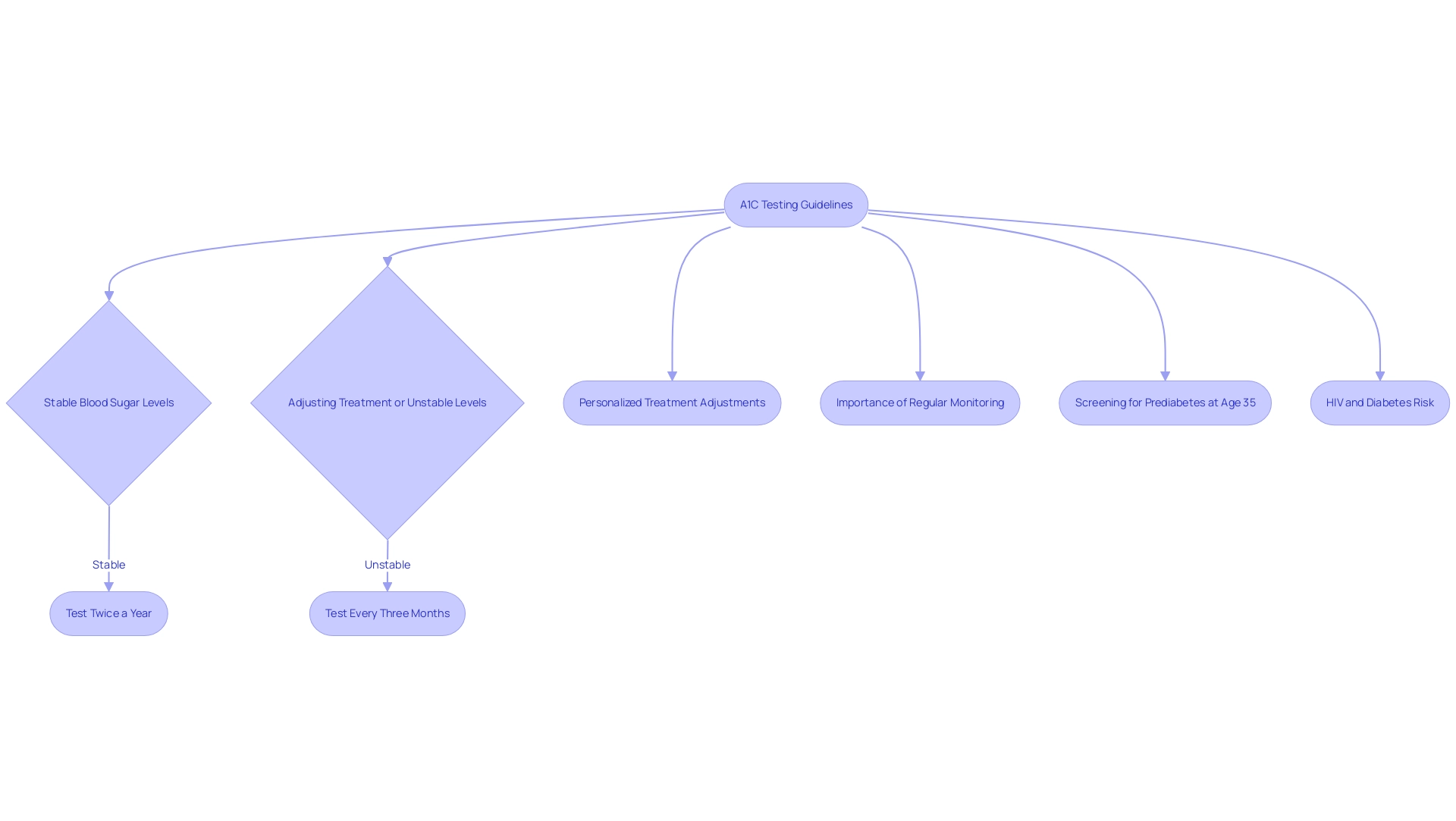
Regular A1C testing serves as a cornerstone for individuals managing blood sugar levels, particularly for those aiming to maintain an A1C level of 6.2 or prediabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, individuals with the condition should undergo A1C testing at least twice a year, provided their blood sugar levels remain stable. For those adjusting their treatment regimens or failing to achieve their glycemic targets, more frequent testing is essential—typically every three months.
At T2DSolutions, we recognize the critical role that A1C monitoring plays in diabetes management. Our platform aims to provide comprehensive resources and community assistance to help individuals understand their A1C results and make informed decisions about their health. This ongoing monitoring of A1C levels, particularly an A1C level of 6.2, enables individuals to evaluate their blood sugar management trends over time, facilitating the identification of necessary adjustments to their treatment plans.
Furthermore, a comprehensive understanding of A1C results, such as an A1C level of 6.2, equips healthcare providers with crucial insights, allowing them to deliver personalized advice and support. As stated by the American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, 'insulin dosing adjustments should be made according to meal composition,' highlighting the importance of tailoring treatment based on A1C outcomes. It's also important to note that screening for prediabetes and type 2 conditions should begin at age 35 for asymptomatic individuals, reinforcing the relevance of A1C testing in a broader demographic.
Additionally, individuals with HIV face a higher risk of developing diabetes, particularly when on certain antiretroviral therapies, where the A1C test may not be reliable. This highlights the need for customized screening protocols and preventive medical care. Ultimately, this proactive approach to monitoring not only enhances individual health management but also contributes to improved overall health outcomes.
Regular testing aligns with the guidelines established for 2024, reinforcing its role in effective health management. At T2D Solutions, we are dedicated to assisting you in your journey towards improved health management.
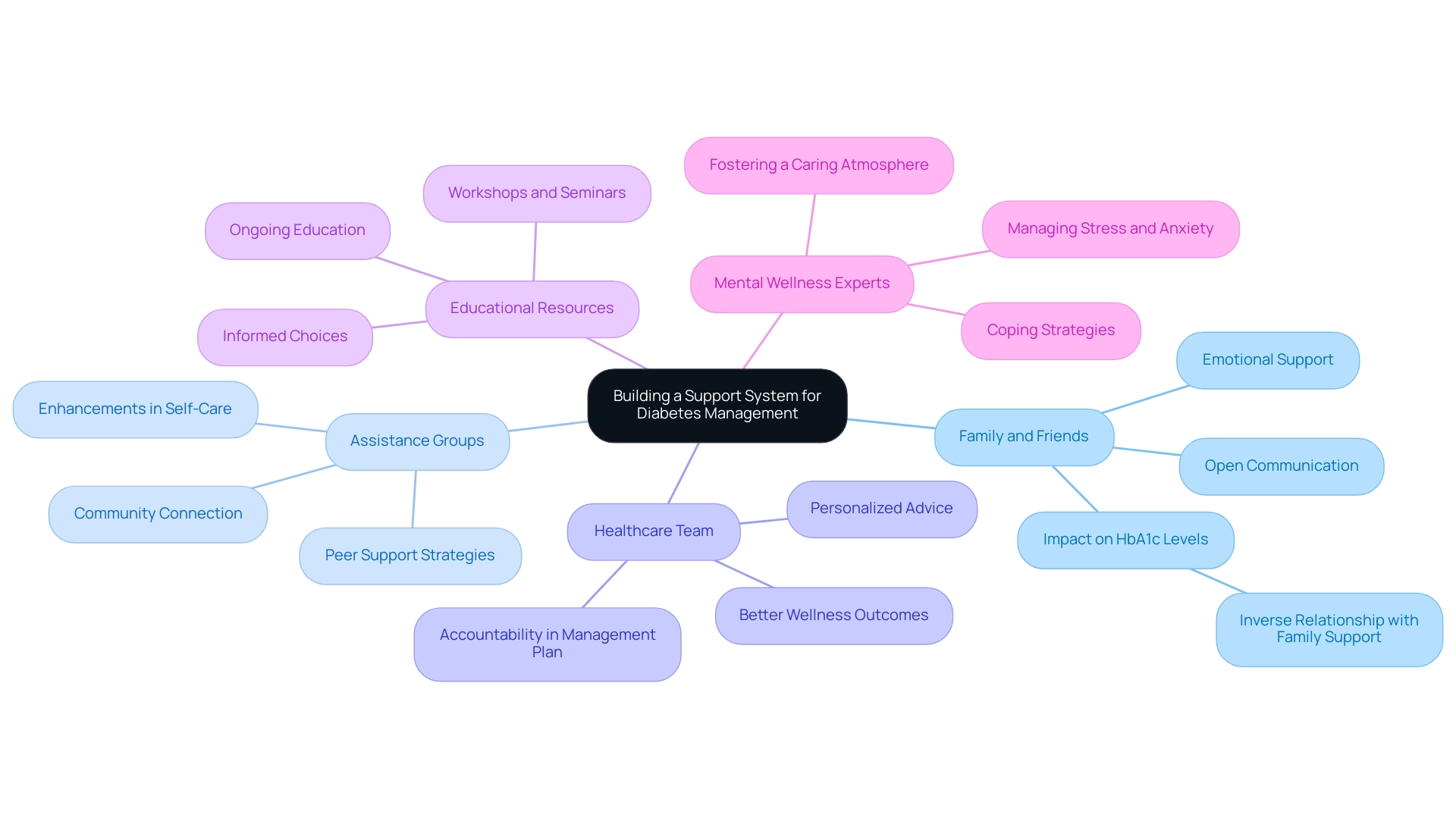
Building a Support System for Diabetes Management
Managing blood sugar levels presents various challenges, and creating a strong network is essential for long-term success. As you begin this journey, T2DSolutions is here to act as your complete resource center for Type 2 and Type 3 glucose management education and community assistance. We are excited to announce that T2DSolutions is coming soon, and you can subscribe now to stay up to date and receive emails when new content is published!
The following avenues can help you build an effective assistance network:
-
Family and Friends: Involve your family and friends in your health management journey. Openly communicate your goals and challenges to them, fostering an environment of understanding and encouragement. Shiva Heidari emphasizes that there is a significant inverse relationship between family assistance and HbA1c levels, highlighting the critical role loved ones play in managing the condition. Involving family members not only helps with emotional well-being but can also lead to improved health results, potentially lowering long-term medical expenses related to managing blood sugar conditions.
-
Assistance Groups: Think about participating in a group for individuals with blood sugar issues, either face-to-face or virtually. These groups provide opportunities to connect with individuals facing similar challenges, allowing for the sharing of experiences and insights that can serve as motivation and foster a sense of community. Research indicates that group participation can lead to enhancements in self-care and glycemic control. Moreover, studies suggest that incorporating peer support strategies can be an effective method for long-term management of the condition.
-
Healthcare Team: Cultivating a strong relationship with your healthcare providers—including a certified health educator, dietitian, and physician—is essential. They offer personalized advice, resources, and encouragement that keep you accountable in your management plan. Engaging your healthcare team effectively can lead to better wellness outcomes.
-
Educational Resources: Utilize educational materials, workshops, and seminars centered on managing diabetes-related health. Ongoing education enables you to make informed choices regarding your well-being and adjust to new strategies as necessary. Staying informed is a key component of successful management of the condition.
-
Mental Wellness Experts: If you find the emotional aspects of managing diabetes-related issues overwhelming, consider seeking assistance from a mental wellness expert. They can provide coping strategies for managing stress, anxiety, or depression associated with diabetes. Addressing mental health is an essential aspect of fostering a caring atmosphere.
Establishing a nurturing assistance network, along with the educational resources available at T2 Solutions, can significantly enhance your capacity to manage your health and achieve an A1C level of 6.2 while maintaining a healthier lifestyle. The effectiveness of peer assistance has been documented in studies like the 'Train-the-Trainer Program for Peer Assistance in Diabetes Management,' which demonstrated that participants who engaged in peer assistance maintained an A1C level of 6.2 over time, while those who did not showed a decline. This underscores the tangible advantages of a strong support network in managing the condition.
Furthermore, research funded by the American Academy of Family Physicians Foundation and the Asia Diabetes Foundation emphasizes that these strategies, devoid of conflicts of interest, can lead to better health outcomes for individuals managing diabetes.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing an A1C level of 6.2% is essential for preventing the progression to type 2 diabetes and related health complications. The article emphasizes the importance of proactive measures, including:
- Adopting a balanced diet
- Increasing physical activity
- Monitoring blood sugar levels
Each of these strategies plays a critical role in effectively managing A1C levels and overall health.
In addition to lifestyle changes, the significance of medication and regular A1C testing cannot be overstated. Medications like Metformin and SGLT2 inhibitors provide essential support for those struggling to manage their blood sugar levels through diet and exercise alone. Regular testing allows for timely adjustments to treatment plans, ensuring that individuals remain on track toward healthier A1C levels.
Furthermore, establishing a robust support system enhances the journey toward effective diabetes management. Engaging family and friends, participating in support groups, and collaborating with healthcare professionals can provide the necessary encouragement and resources to navigate the challenges of diabetes management successfully.
Overall, a holistic approach that combines lifestyle modifications, medication, regular monitoring, and a strong support network is vital for those with an A1C level of 6.2%. By taking these steps, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and improve their overall health outcomes. The commitment to managing A1C levels today can pave the way for a healthier tomorrow.



