Overview
In this article, we explore the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI), a crucial tool in diabetes management that can truly make a difference in your daily life. Understanding how GMI is calculated and applied can empower you to take control of your health. GMI estimates average blood sugar levels by utilizing continuous glucose monitoring data, providing a dynamic view of your glucose control. This perspective can lead to improved health outcomes, and studies have shown significant reductions in GMI over short periods, all while maintaining a safe distance from increased hypoglycemia risks.
It's natural to feel overwhelmed when navigating diabetes management, but you're not alone in this journey. Knowing that GMI can help you gain insights into your health can be comforting. As you learn more about how to use this information, remember that there are resources and support available to guide you along the way. We are here to support you every step of the way, ensuring you have the tools you need to succeed.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, the emergence of the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) represents a significant evolution in how individuals monitor and understand their glucose levels. This innovative metric, derived from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data, offers a real-time perspective on average blood glucose levels. It provides a dynamic alternative to traditional measurements like HbA1c, which can often feel overwhelming.
As patients and healthcare providers increasingly recognize the importance of GMI, its potential to enhance treatment plans and improve health outcomes becomes clear. This tool empowers individuals to take charge of their diabetes management journey, making informed decisions that can lead to better health. You're not alone in this journey; many are discovering the benefits of GMI.
This article delves into the intricacies of GMI, exploring its benefits, limitations, and future implications in the evolving landscape of diabetes care. We are here to support you every step of the way as you navigate this important aspect of your health.
What is the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI)?
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to being a comprehensive resource hub for diabetes education and community support. Understanding the diabetes GMI is crucial for those who have recently been diagnosed. This novel metric approximates an individual's average blood sugar levels over time, specifically derived from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data. It estimates the laboratory-measured HbA1c level, which reflects average sugar levels over the past two to three months.
The formula for calculating GMI is straightforward:
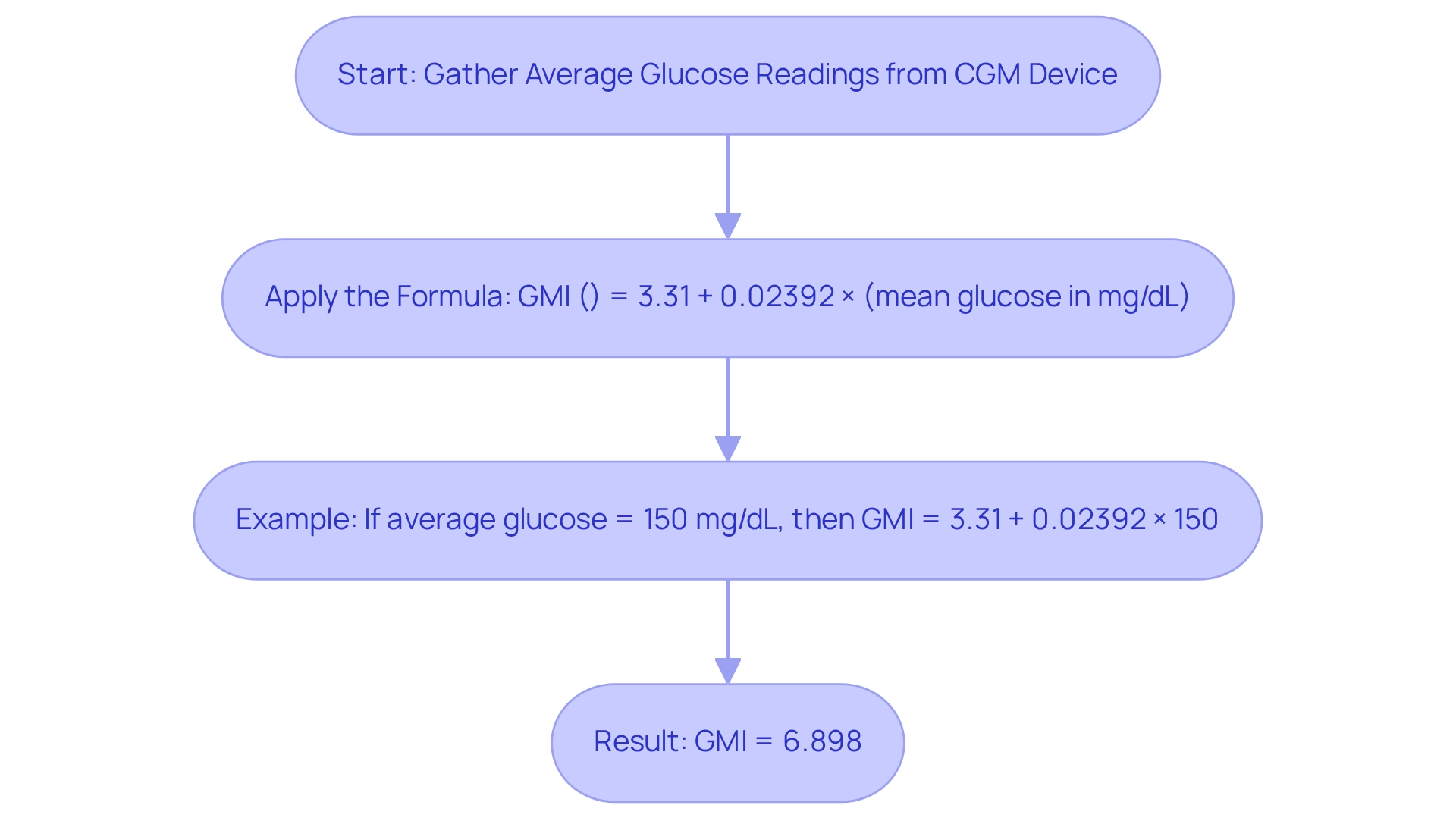
GMI (%) = 3.31 + 0.02392 × (mean glucose in mg/dL).
This metric is especially beneficial for individuals managing their blood sugar levels, as it provides a more dynamic and real-time perspective on glucose control compared to traditional methods. Recent studies indicate that diabetes GMI can decrease from 8.5% to 7.8% within just 2 to 4 weeks, without a significant increase in hypoglycemia. This highlights its potential for effective blood sugar management.
The adoption of the term 'Glucose Management Indicator' marks a shift towards a more positive and empowering approach to care for those with blood sugar challenges. D.B.R., President of the American Association of Diabetes Educators, remarked, "It will be up to the appropriate committees of any professional organization to consider further action regarding the suggestions pertaining to the use of GMI made in this Perspective." This change underscores the importance of community and collaboration in improving health outcomes through shared knowledge and support.
Additionally, recent case studies, such as those examining the effects of obstructive sleep apnea on diabetes care, show that conditions like these can complicate glycemic control. The variability in diabetes GMI and HbA1c measurements noted in these studies emphasizes the need for personalized strategies for patients with comorbid conditions. It is clear that diabetes GMI can be an essential tool in addressing these complexities.
As continuous glucose monitoring technology becomes more widespread, understanding diabetes GMI and its calculation method is vital for newly diagnosed patients. By utilizing diabetes GMI, individuals can gain valuable insights into their blood sugar control, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes. At T2DSolutions, we are here to provide additional resources and support to help you navigate your health journey effectively.
The Importance of GMI in Diabetes Management
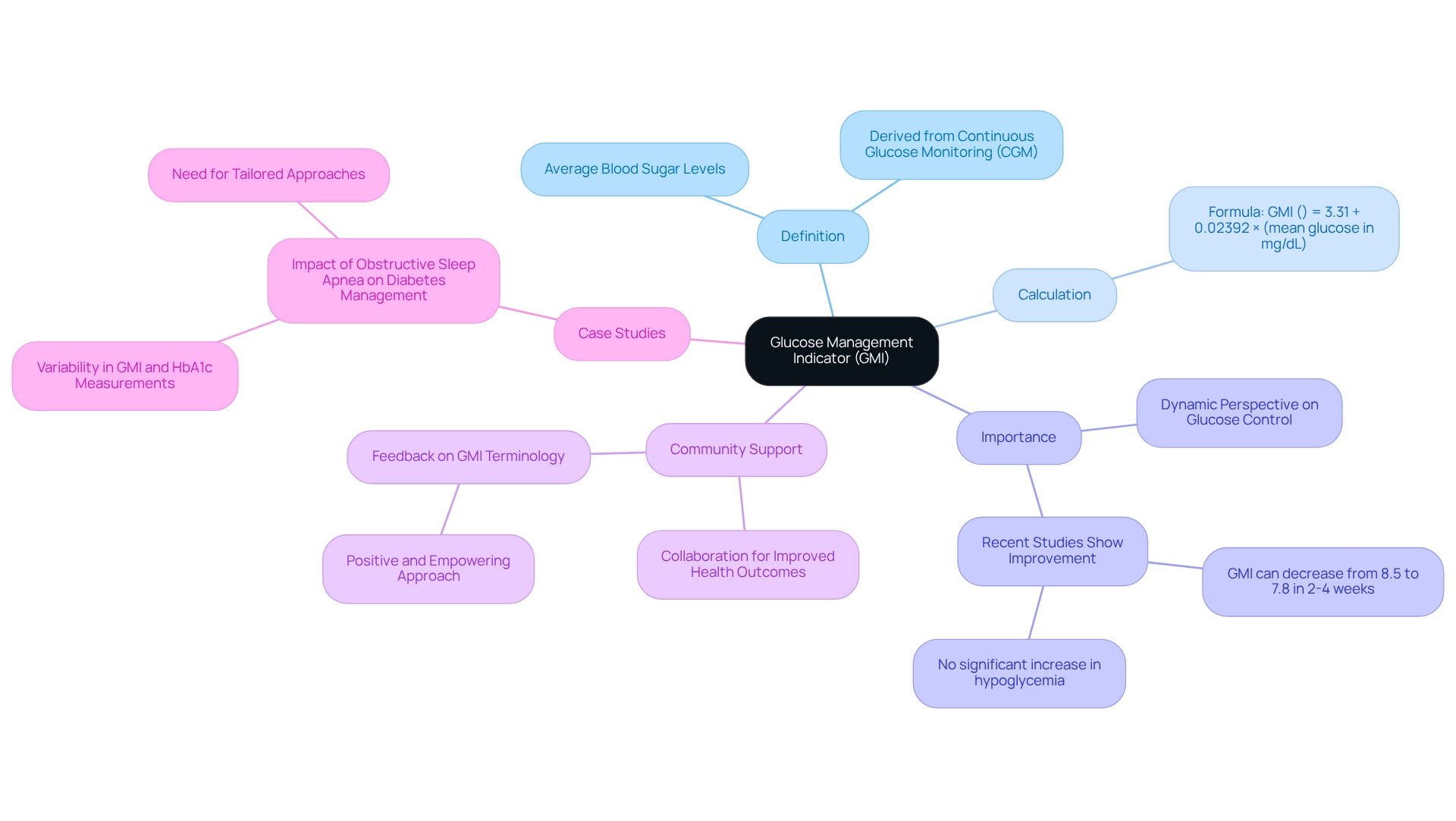
Diabetes GMI plays a vital role in effectively managing blood sugar conditions, offering both healthcare providers and patients a reliable estimate of average blood sugar levels. A lower diabetes GMI indicates better sugar management, which is associated with a reduced risk of complications related to blood sugar disorders. By utilizing diabetes GMI, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment plans, monitor patient progress, and make timely adjustments to therapies as needed.
At T2DSolutions, we understand the importance of diabetes GMI in blood sugar control. We strive to provide educational materials that help patients comprehend and apply this metric effectively. This metric is particularly beneficial for those using Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems, as it offers real-time insights into their diabetes GMI management. For example, a recent case study titled "Influence of Physiological Factors on Glycemic Control" highlighted how various physiological factors, including age and comorbidities, significantly affect glycemic levels.
These findings underscore the need for refining diabetes GMI calculation formulas to enhance personalized insights into glycemic control. Larger, multi-centric studies could lead to more accurate assessments. Further research is crucial to understand the clinical implications of GMI across diverse populations.
Moreover, studies indicate that achieving optimal management of diabetes is more complex than merely meeting individual glycemic goals. For instance, only about 10% of adults with type 1 diabetes are likely to be optimally managed, highlighting the challenges faced in care. As Elizabeth Selvin from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health notes, 'These results suggest that diabetes GMI may not be a reliable metric of glycemic control and should be interpreted cautiously in clinical practice.'
Integrating diabetes GMI into blood sugar management not only aids in reducing complications but also enhances treatment strategies by providing a clearer view of a patient's glucose levels over time. Additionally, laboratory HbA testing typically costs around $10 per test, which is an essential consideration for patients managing their condition. At T2DSolutions, we are committed to promoting a comprehensive approach to diabetes management that empowers patients to take an active role in their care, ultimately improving health outcomes.
We encourage you to explore our resources for more information on diabetes GMI and its impact on diabetes care. Remember, you're not alone in this journey—we are here to support you every step of the way.
How to Calculate GMI: The Formula Explained
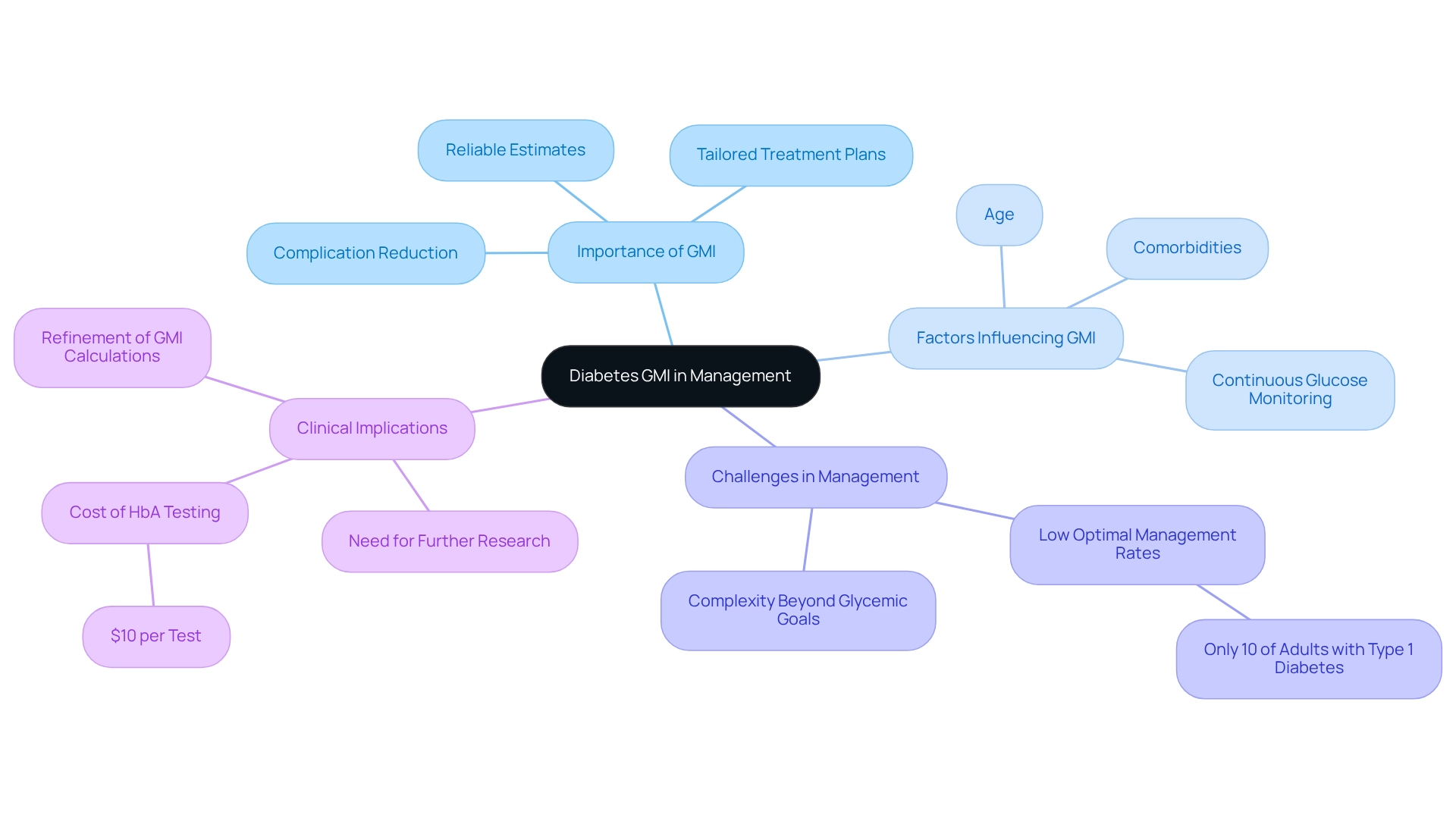
Calculating your diabetes GMI is essential for understanding your blood sugar management over time. To calculate your GMI, you will need the average sugar readings collected from a Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) device. The formula for calculating GMI is as follows:
GMI (%) = 3.31 + 0.02392 × (mean glucose in mg/dL).
For instance, if your average glucose level is 150 mg/dL, the calculation would proceed like this:
GMI = 3.31 + 0.02392 × 150 = 3.31 + 3.588 = 6.898%.
This result reflects your estimated HbA1c level, offering a comprehensive view of your glucose management. Understanding your diabetes GMI is crucial, as it serves as a significant measure for evaluating treatment effectiveness and diagnosing prediabetes and other related conditions. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends reducing the A1C goal to 6.5% for individuals with a brief duration of the condition and extended life expectancy, highlighting the importance of diabetes GMI in evaluating treatment outcomes.
Recent studies suggest that diabetes GMI can uncover clinically meaningful discrepancies in sugar control. E. Selvin observed that "there was clinically significant discordance in over one-third of participants." This finding underscores the importance of diabetes GMI in guiding adjustments to blood sugar control strategies. By utilizing diabetes GMI, both clinicians and patients can make informed decisions based on real-time glucose data, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
As you navigate your health journey, monitoring your diabetes GMI can empower you to take proactive steps toward better well-being.
At T2DSolutions, we are committed to providing resources and support for newly diagnosed patients. Our platform will offer educational materials and community support to help you understand and manage your diabetes GMI effectively. Subscribe to stay informed about the latest diabetes care resources offered by T2DSolutions, and take the first step toward improved health today.
GMI vs. HbA1c: Understanding the Differences
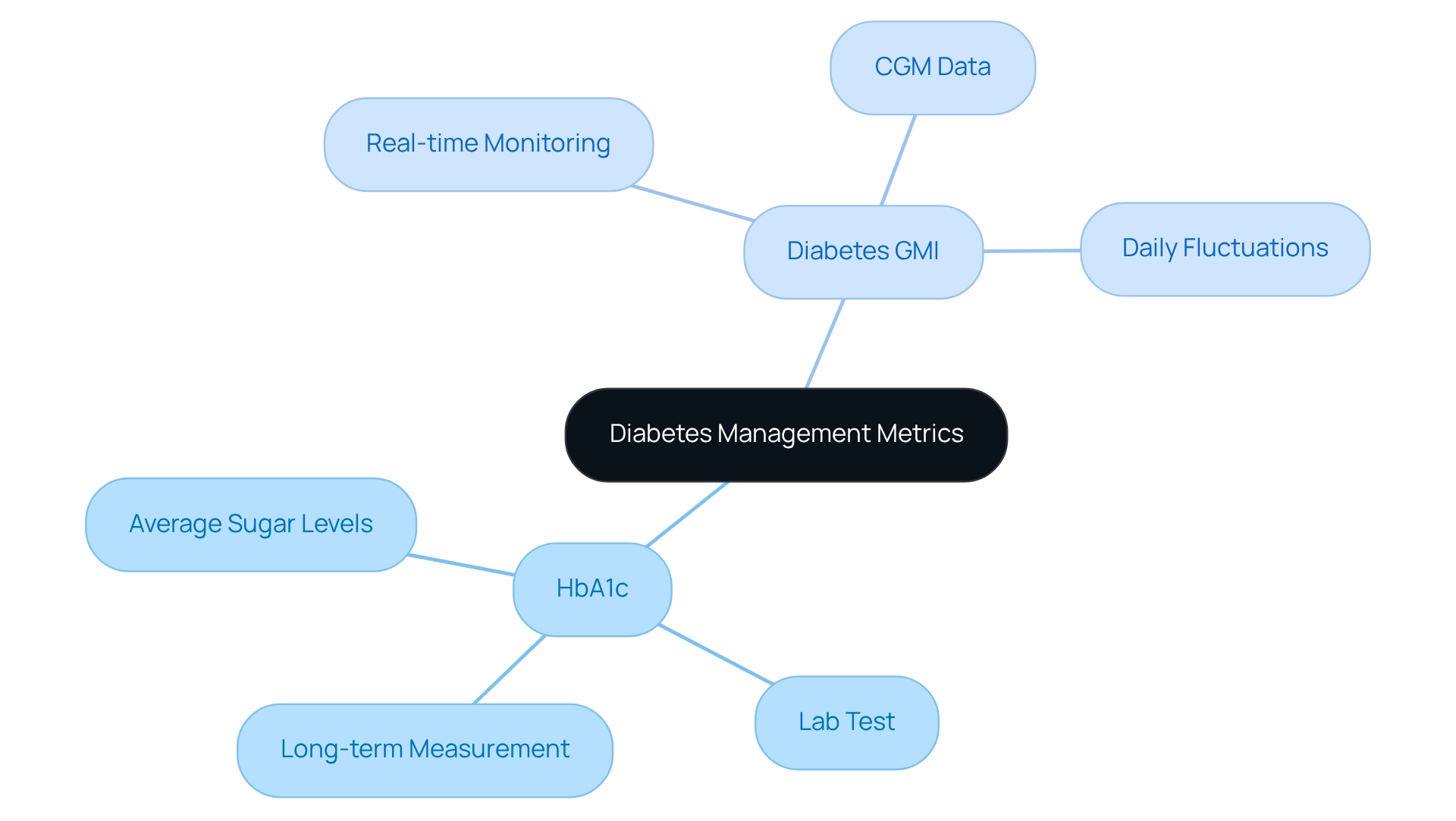
Understanding your health can feel overwhelming, especially when it comes to managing diabetes. Two important metrics to consider are the Diabetes GMI and Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). While both are crucial for evaluating sugar regulation, they differ significantly in how they are measured and used.
HbA1c is a laboratory test that measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in your blood. This test provides an average of your sugar levels over the past two to three months, making it a key tool in clinical settings to assess long-term sugar regulation. It serves as a cornerstone of diabetes care guidelines, helping healthcare providers understand your overall control.
On the other hand, diabetes GMI is derived from real-time data collected through Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems. This innovative approach offers a more immediate and dynamic evaluation of your sugar levels, reflecting daily fluctuations. For those who consistently monitor their glucose, diabetes GMI can provide insights that align closely with your daily lifestyle, making it a valuable resource for real-time management.
Recent studies indicate that individuals who meet all seven glycemic targets typically require an average total daily insulin dose of about 0.53±0.18 units per kg. This highlights the challenges many face in achieving optimal health outcomes. While HbA1c targets are important, they do not capture the full picture of glycemic control. Striving to meet all seven glycemic objectives, as recommended by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), can be a significant challenge, underscoring the need for a comprehensive understanding of your condition.
It's also vital to recognize that health care disparities exist, emphasizing the importance of addressing the diverse needs and experiences of patients.
The differences between diabetes GMI and HbA1c extend beyond mere numbers; they represent distinct methods of assessment and management. Diabetes GMI offers a real-time snapshot that can empower you and your healthcare provider to make timely adjustments to your treatment plan, while HbA1c remains a dependable indicator of long-term control. Together, these metrics provide a holistic view of your sugar management journey.
Experts agree on the importance of integrating both diabetes GMI and HbA1c into care strategies for effectively managing blood sugar conditions. The American Diabetes Association suggests that "standardized, single-page glucose reports from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices with visual cues, such as the ambulatory glucose profile, should be considered as a standard summary for all CGM devices." By harnessing the strengths of each metric, healthcare providers can better support you in reaching your health goals.
This collaborative approach aligns with T2DSolutions' commitment to empowering individuals through shared knowledge and community support, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes for those managing diabetes. Additionally, case studies like 'Challenges in Achieving Optimal Glycemic Management' illustrate the real-world hurdles individuals face in reaching their goals, further emphasizing the need for a multifaceted strategy in managing your condition.
Remember, you're not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Applying GMI in Daily Diabetes Management
To effectively incorporate diabetes GMI into your daily management of diabetes, it's important to consistently track your sugar levels using a continuous monitoring (CGM) device. This regular monitoring helps you identify patterns in your sugar levels, enabling you to make informed decisions about your diet, exercise, and medication adjustments. For instance, if you notice a spike in diabetes GMI after specific meals, you can modify your dietary choices or insulin dosages accordingly.
Research indicates that greater protein and fiber consumption is linked to more frequent monitoring of blood sugar levels, highlighting how your dietary selections can significantly influence diabetes GMI. A study titled 'Correlation Between Nutritional Variables and Scanning Frequency' found that individuals who consume more protein and fiber tend to scan their levels more often, emphasizing the importance of making thoughtful dietary choices for blood sugar control. Engaging in discussions about your diabetes GMI outcomes with healthcare professionals can help develop personalized treatment strategies, ultimately leading to better blood sugar management.
Moreover, the Ziegler algorithm has shown promise in enhancing sugar management for patients using CGM, suggesting that algorithmic methods may further improve daily management strategies. However, more research is needed to determine the long-term benefits of such algorithms in managing blood sugar conditions. As the landscape of blood sugar management evolves, staying informed about real-time glucose monitoring updates and expert advice is crucial for improving your health outcomes.
Notably, M.G.C. states, "Our findings endorse the use of the CGM system in all patients irrespective of the kind of condition or treatment approach as an educational resource for altering lifestyle and attaining improved disease control."
Incorporating diabetes GMI into your daily routine not only assists with dietary and medication adjustments but also empowers you to take charge of your health. By understanding the connection between your daily decisions and diabetes GMI, you can adopt a proactive approach to managing your condition effectively. Additionally, for adults with a BMI of 30.0–34.9 kg/m who struggle to achieve sustainable weight loss, metabolic surgery may be considered as a treatment option, highlighting the various approaches available for health management.
As T2DSolutions launches as a new resource hub for education on blood sugar management, it aims to provide valuable information and support for those newly diagnosed. By offering insights on diabetes GMI and its impact on controlling blood sugar levels, T2DSolutions seeks to empower you to make informed choices regarding your health. Stay tuned for upcoming resources and content designed to enhance your understanding of diabetes care.
Limitations of GMI: What You Need to Know
While the Diabetes GMI is a valuable tool for assessing sugar management, it’s important to recognize its limitations. One significant concern is that GMI may not accurately reflect sugar levels in individuals with specific medical conditions, such as anemia or hemoglobinopathies, which can skew HbA1c results. Additionally, GMI is derived from average sugar levels, potentially overlooking significant fluctuations that can occur throughout the day.
This limitation underscores the necessity for individuals to utilize diabetes GMI alongside other metrics and clinical assessments to gain a holistic understanding of their diabetes care. You're not alone in feeling overwhelmed by this information; many share similar concerns.
Recent studies have highlighted accuracy concerns surrounding GMI, particularly regarding physiological and pathophysiological factors. For instance, a study examining continuous sugar monitoring (CGM) data from 497 adults showed that while 68% of participants reached a GMI below 7%, only 39% met all seven glycemic objectives established by international agreement. This suggests that relying solely on diabetes GMI may not provide a comprehensive view of an individual’s glucose control.
Specialist perspectives further emphasize the need for a comprehensive strategy to manage blood sugar control. Conditions such as obesity, kidney disease, and hormonal disorders can also affect GMI accuracy, making it crucial for healthcare providers to consider these factors when interpreting GMI results. As Dr. Mefferd mentioned, 'We wish to convey our appreciation to the Research Department, Sunrise Health, GME Consortium, Mountain View Hospital, Las Vegas, Nevada, and Dr. Mefferd,' highlighting the collaborative efforts in managing blood sugar.
By combining diabetes GMI with other clinical indicators, patients can navigate their health journey more effectively, ensuring they are not solely reliant on a single metric for their health choices. Furthermore, ongoing research indicates that further studies are needed to examine diabetes GMI and HbA1c in relation to physiological and pathophysiological factors, underscoring the evolving understanding of diabetes GMI's clinical implications. It’s also essential to recognize that the average lifespan of a glycemic sensor is 7–14 days, which provides context on the instruments utilized in glucose oversight.
As T2DSolutions introduces itself as a new resource center for education and community support related to blood sugar issues, it’s crucial to consider how diabetes GMI fits into the broader context of resources available for managing these conditions. We encourage you to subscribe for updates on the latest management resources offered by T2DSolutions. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
The Future of GMI in Diabetes Care
The future of diabetes GMI in glucose management is bright and filled with hope, thanks to ongoing advancements in technology and research aimed at enhancing precision and expanding its applications. As continuous monitoring devices improve, we can expect more accurate readings, greatly enhancing the reliability of calculations related to diabetes GMI. With healthcare practitioners increasingly recognizing its significance, diabetes GMI is set to become a standard measure within blood sugar care protocols.
This shift could lead to better patient outcomes through personalized care strategies tailored to individual needs. It’s understandable to feel overwhelmed by these changes, but know that you are not alone in this journey.
Recent studies show that integrating connected digital health tools, such as smart pens and advanced CGM systems, can help develop personalized treatment plans. For instance, Dexcom provided continuous sugar monitoring systems at a discount during the HYPNOS trial, making CGM technology more accessible. These tools not only assist healthcare providers in tracking sugar levels but also empower patients to actively manage their condition.
Utilizing CGM data can reveal patterns in blood sugar variations, allowing for timely adjustments in treatment strategies. This is an important step toward feeling more in control of your health.
Moreover, experts predict that as GMI becomes more widely adopted, we may see a significant reduction in severe hypoglycemic events. This could lead to cost savings for both users and healthcare systems. Elizabeth Selvin from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health emphasizes the importance of establishing CGM average sugar levels as treatment goals, providing a crucial perspective on the evolving landscape of health management. The ongoing research into improving diabetes GMI accuracy and its applications in diabetes care underscores a commitment to enhancing the quality of life for individuals managing diabetes.
With a focus on community and collaboration, these advancements promise to foster shared knowledge and support, ultimately improving health outcomes for everyone involved. Additionally, the case study titled "Personalized Treatment Plans" highlights how various continuous glucose monitors and connected digital health apps contribute to tailored treatment strategies, showcasing the practical application of these technologies. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) is essential for effective diabetes management. It offers a real-time perspective on average blood glucose levels derived from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data. This innovative metric not only approximates traditional HbA1c levels but also empowers you to make informed decisions about your health. The advantages of GMI, such as its ability to detect fluctuations in glucose levels and its responsiveness to lifestyle changes, highlight its significance in enhancing treatment plans and improving health outcomes for individuals managing diabetes.
However, it's important to acknowledge the limitations of GMI. There may be potential inaccuracies in certain medical conditions, and comprehensive assessments alongside other metrics are necessary. As diabetes care evolves, integrating GMI with traditional measurements like HbA1c will be vital in providing a holistic view of your health. Ongoing research and advancements in technology promise to refine the accuracy of GMI, making it an increasingly valuable tool in diabetes management.
The future of GMI looks promising. It has the potential to revolutionize how diabetes care is approached. By fostering a collaborative environment among healthcare providers and patients, GMI can lead to more personalized treatment strategies that enhance glucose control and overall well-being. Embracing this innovative metric will not only empower you in your diabetes management journey but also contribute to a healthier, more informed community. As resources like T2DSolutions continue to evolve, they will play a crucial role in supporting you in navigating your diabetes management effectively, ensuring that you’re not alone in this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Diabetes GMI?
The Diabetes GMI (Glucose Management Indicator) is a metric that approximates an individual's average blood sugar levels over time, derived from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data. It estimates the laboratory-measured HbA1c level, reflecting average sugar levels over the past two to three months.
How is the GMI calculated?
The formula for calculating GMI is: GMI (%) = 3.31 + 0.02392 × (mean glucose in mg/dL).
Why is the Diabetes GMI important for individuals managing blood sugar levels?
The Diabetes GMI provides a dynamic and real-time perspective on glucose control, which is more informative than traditional methods. It helps individuals better manage their blood sugar levels and has been shown to decrease significantly within weeks without increasing hypoglycemia risk.
What does a lower Diabetes GMI indicate?
A lower Diabetes GMI indicates better sugar management, which is associated with a reduced risk of complications related to blood sugar disorders.
How can healthcare providers use the Diabetes GMI?
Healthcare providers can utilize the Diabetes GMI to tailor treatment plans, monitor patient progress, and make timely adjustments to therapies as needed.
What challenges exist in achieving optimal diabetes management?
Achieving optimal management of diabetes is complex, with only about 10% of adults with type 1 diabetes likely to be optimally managed. This highlights the challenges faced in care and the need for careful interpretation of the GMI in clinical practice.
What factors can influence glycemic control according to recent studies?
Various physiological factors, including age and comorbidities, can significantly affect glycemic levels, emphasizing the need for personalized strategies in diabetes management.
What role does T2DSolutions play in diabetes education?
T2DSolutions is dedicated to providing comprehensive resources and educational materials to help patients understand and effectively apply the Diabetes GMI in their blood sugar management.
What is the cost of laboratory HbA testing for diabetes management?
Laboratory HbA testing typically costs around $10 per test, which is an important consideration for patients managing their diabetes.
