Overview
This article offers a compassionate overview of the diagnosis and management of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. It highlights essential concepts such as insulin resistance, risk factors, symptoms, and effective management strategies. By understanding these elements—like the importance of diet and exercise, the value of regular monitoring, and the effects of genetics and obesity—you can feel empowered to manage your condition and enhance your overall health outcomes.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but remember, you’re not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way. By exploring these key topics, you can gain valuable insights that will help you take control of your health and well-being. Together, let’s navigate this path toward a healthier future.
Introduction
In a world where chronic conditions like Type 2 Diabetes are becoming increasingly common, understanding the nuances of this complex disease is more important than ever. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by the challenges that come with it. Characterized by insulin resistance and fluctuating blood glucose levels, Type 2 Diabetes not only impacts physical health but also intertwines with mental well-being. Many individuals face heightened risks of depression and other complications, which can feel daunting.
Recognizing key symptoms and risk factors is the first step toward taking control. Implementing effective management strategies through diet, exercise, and monitoring can make a significant difference. This comprehensive exploration delves into the essential aspects of living with Type 2 Diabetes, providing you with the knowledge and resources you need. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
By empowering individuals with information and practical strategies, we pave the way for better health outcomes and a more proactive approach to managing this prevalent condition. Together, we can navigate the complexities of Type 2 Diabetes, fostering a supportive community where everyone feels heard and understood.
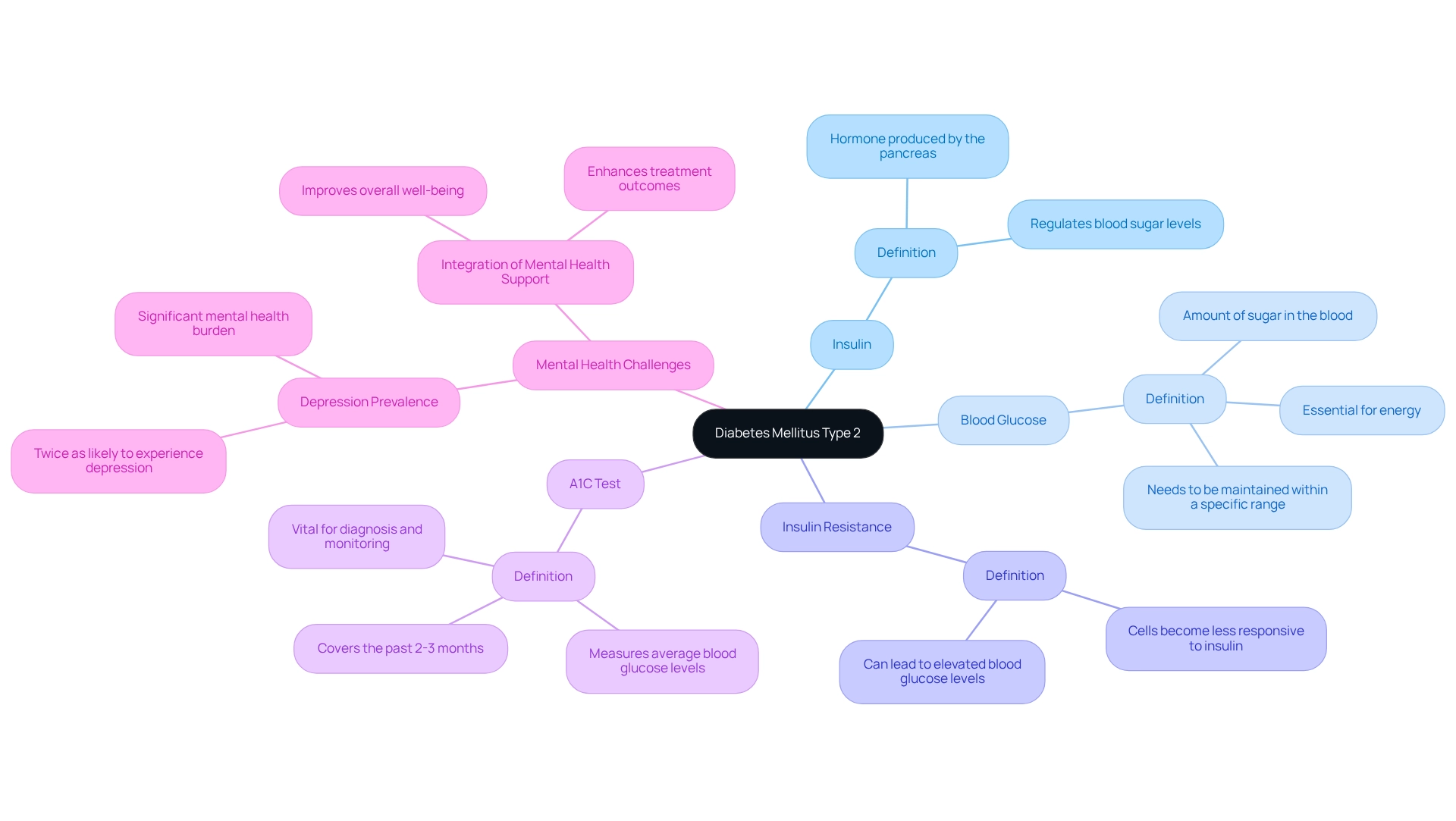
Define Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: Key Concepts and Terminology
Mellitus Type 2 is a chronic condition that can feel overwhelming, and a diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosis is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body struggles to utilize insulin effectively. Understanding some key terms can help you navigate this journey toward a diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosis:
- Insulin: This hormone, produced by the pancreas, plays a crucial role in regulating your blood sugar levels.
- Blood Glucose: This refers to the amount of sugar in your blood, essential for energy but needing to be maintained within a specific range for your health.
- Insulin Resistance: This condition occurs when your body's cells become less responsive to insulin, which can lead to elevated blood glucose levels.
- A1C Test: This blood test measures your average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months and is vital for a diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosis and monitoring diabetes.
It's understandable to feel a bit lost with all this information, but knowing these terms is vital for effective communication with your healthcare providers and for managing your condition.
According to the CDC’s National Statistics Report on Diabetes, this condition affects various demographic groups differently, with prevalence rates of 7.4% among non-Hispanic whites, 8.0% among Asian Americans, 12.1% among Hispanics, 12.7% among non-Hispanic blacks, and 15.1% among American Indians and Alaska Natives. Furthermore, individuals with Type 2 Diabetes are twice as likely to experience depression compared to those without it, as highlighted in the case study titled 'Mental Health Challenges in Diabetes.' This underscores the importance of incorporating mental health support into your blood sugar management plan. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; seeking help can enhance your overall well-being and treatment outcomes. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Explore Causes and Risk Factors: Understanding Your Diagnosis
Explore Causes and Risk Factors: Understanding Your Diagnosis
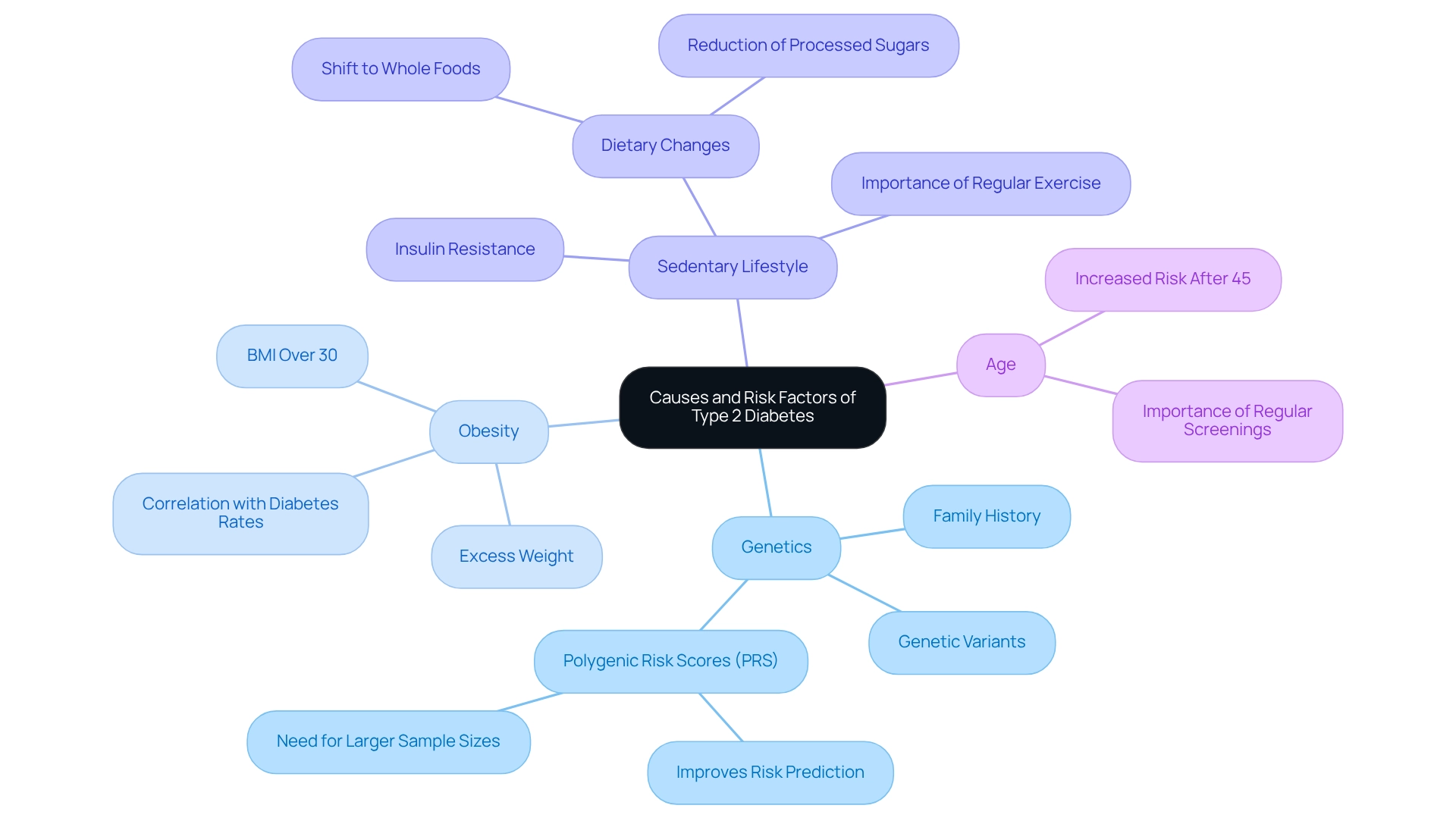
At T2DSolutions, we genuinely care about supporting individuals on their health journey. Understanding the factors that influence diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosis is crucial for effective management and prevention. This condition is shaped by various interconnected elements, including:
-
Genetics: If you have a family history of Type 2 Diabetes, it's understandable to feel concerned, as this significantly increases your risk. Recent studies reveal that genetic variants are vital in predicting the likelihood of developing this condition. A significant meta-analysis involving around 55,000 individuals monitored for over 15 years underscores the importance of these genetic factors. Additionally, research on Polygenic Risk Scores (PRS) aims to improve predictions of Type 2 Diabetes risk by integrating genetic variants into clinical models, although larger sample sizes are needed to fully harness these insights.
-
Obesity: Carrying excess weight, especially around the abdomen, is a major risk factor. The current obesity rates are alarming, with many individuals classified as overweight or obese, which correlates directly with the rising rates of diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosis. For instance, research shows that individuals with a body mass index (BMI) over 30 face a significantly higher risk of a diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosis.
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by the demands of daily life, but a lack of physical activity can lead to insulin resistance. Regular exercise is key for the prevention and management of conditions related to diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosis. Even moderate activities, like daily walks, can greatly reduce your risk of a diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosis. Many individuals have found that incorporating exercise into their routines leads to noticeable improvements in their blood sugar levels, especially for those with a diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosis. Transitioning to a balanced diet rich in whole foods is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar, especially following a diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosis. For example, those who shift from a diet heavy in processed sugars to one focused on whole grains, fruits, and vegetables often report positive health changes.
-
Age: As we age, particularly after 45, the likelihood of developing chronic conditions increases. This highlights the importance of regular screenings and proactive health management in the context of diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosis. Understanding these factors can empower you to take proactive steps in managing your health and reducing your risk.
For additional resources and support in managing your health, we invite you to explore what T2DSolutions has to offer. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Identify Symptoms and Complications: Recognizing the Impact of Type 2 Diabetes
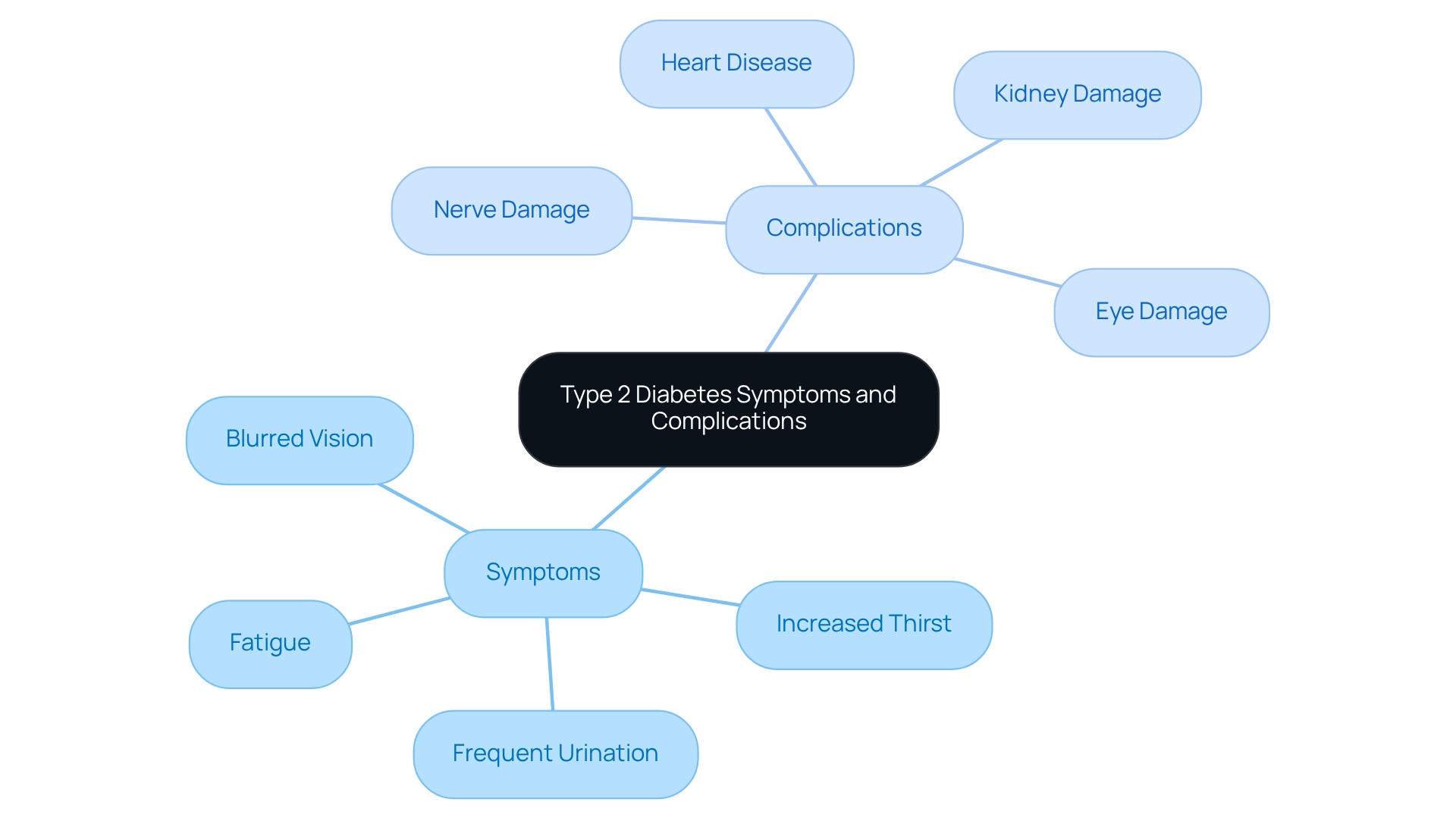
Common symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes can be concerning, and it's important to recognize them:
- Increased Thirst: You might find yourself feeling excessively thirsty, which often stems from elevated blood sugar levels, prompting your body to seek hydration.
- Frequent Urination: As your kidneys work to eliminate excess glucose, you may notice more frequent trips to the bathroom.
- Fatigue: It's understandable to feel persistently tired as your body struggles to effectively utilize glucose for energy.
- Blurred Vision: Fluctuating blood sugar levels can lead to temporary changes in vision, making it difficult to focus.
If these symptoms are left unmanaged, Type 2 Diabetes can lead to serious complications, which can be alarming:
- Heart Disease: Those with this condition face a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular problems, which can be life-threatening.
- Nerve Damage: This condition may result in pain, tingling, or loss of sensation, particularly in your extremities.
- Kidney Damage: Over time, this health issue can impair kidney function, potentially leading to kidney failure.
- Eye Damage: Diabetic retinopathy is a serious condition that can result in vision loss or blindness.
Awareness of these symptoms and potential complications is essential for effective management and prevention. Statistics indicate that uncontrolled blood sugar levels significantly increase the risk of severe health issues, including cardiovascular disease and kidney failure. Furthermore, individuals with the disease are twice as likely to experience depression compared to those without the condition, highlighting the need for comprehensive care that addresses both physical and mental health. You're not alone in this journey—recognizing these signs early can lead to timely interventions, improving your overall health outcomes. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Implement Management Strategies: Diet, Exercise, and Monitoring
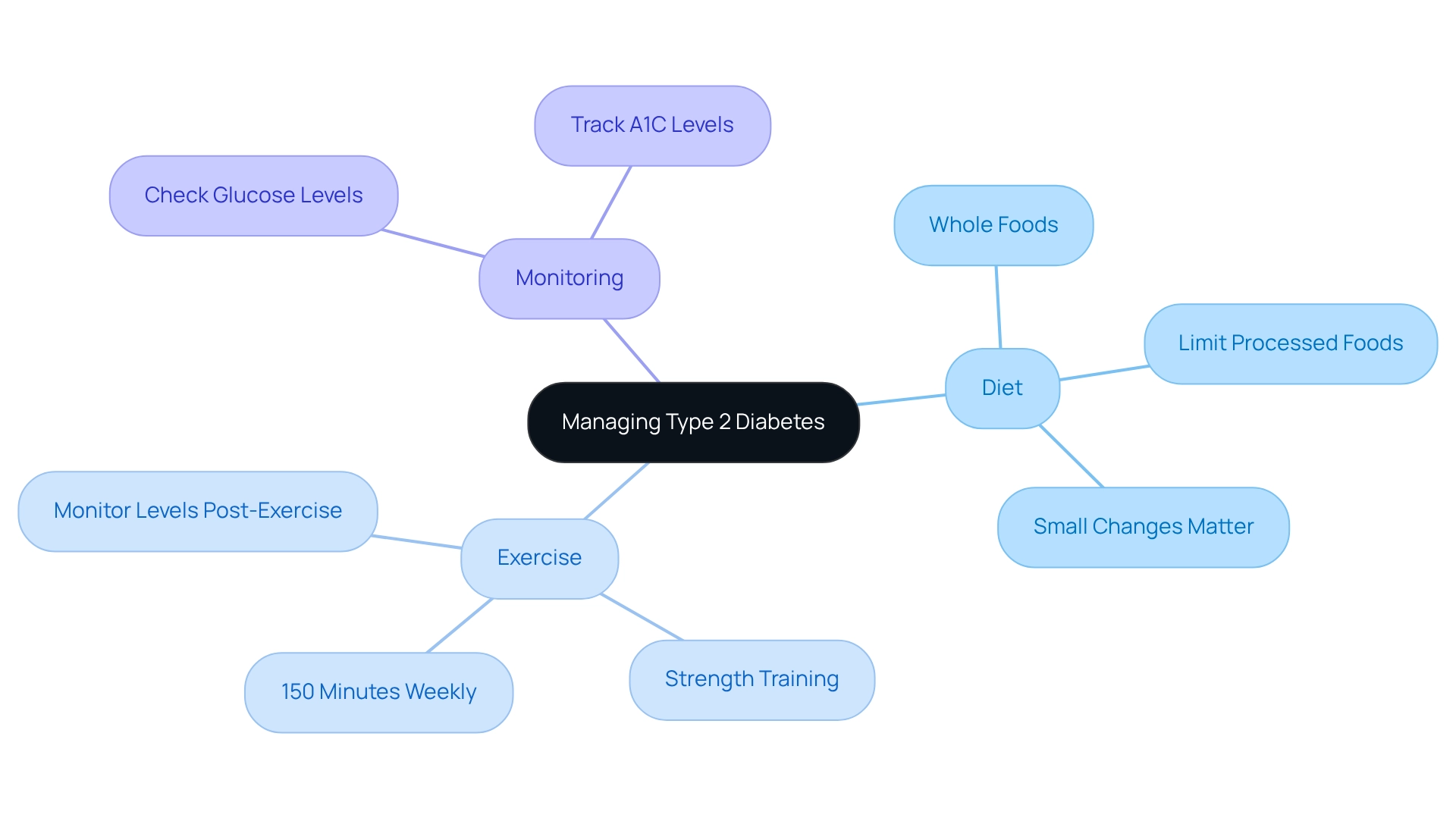
Managing Type 2 Diabetes effectively requires a compassionate and multifaceted approach. It’s important to understand that you’re not alone in this journey, and there are practical steps you can take to improve your health.
Diet: Focus on a balanced diet filled with whole foods like vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Research shows that what you eat plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. It’s essential to limit processed foods and sugars to help maintain stable glucose levels. Remember, every small change can make a difference.
Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week—think walking, swimming, or cycling. Incorporating strength training exercises at least twice a week is also beneficial. Studies indicate that moderate exercise can enhance insulin action and glucose tolerance, with benefits lasting up to 72 hours after your workout. It’s understandable to feel concerned about exercise-induced temporary hyperglycemia; just know that monitoring your levels can help you manage this effectively.
Oversight: Regularly checking your glucose levels is vital. It helps you understand how your food choices, activity levels, and medications impact your body. Keeping track of your A1C levels, as advised by your healthcare provider, is essential for assessing your long-term glucose control.
By embracing these strategies, you can significantly improve your blood sugar control and overall health. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way. Take action today and reach out for resources that can help you on this journey.
Conclusion
Living with Type 2 Diabetes can feel overwhelming, but understanding your condition and committing to proactive management can make a significant difference. Key concepts like insulin resistance, blood glucose monitoring, and the A1C test are essential for effective communication with your healthcare providers. By recognizing the various causes and risk factors—including genetics, obesity, and lifestyle choices—you empower yourself to take charge of your health.
It's crucial to identify the symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes early on. Unmanaged diabetes can lead to serious complications, such as heart disease and nerve damage. Acknowledging the profound impact on both your physical and mental health underscores the importance of integrated care that addresses these interconnected aspects.
Implementing effective management strategies—such as focusing on a balanced diet, regular exercise, and diligent monitoring—can significantly improve your blood sugar control and overall well-being. By adopting these practices, you can manage your condition more effectively and enhance your quality of life.
Ultimately, the journey of managing Type 2 Diabetes is one that requires support, education, and resilience. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. With the right resources and a proactive approach, you can navigate the complexities of this condition, fostering a healthier future and a supportive community along the way. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Diabetes Mellitus Type 2?
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 is a chronic condition characterized by insulin resistance, where the body struggles to utilize insulin effectively, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
What role does insulin play in the body?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels, ensuring that glucose is used for energy.
What is blood glucose?
Blood glucose refers to the amount of sugar in your blood, which is essential for energy but must be maintained within a specific range for health.
What is insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance occurs when the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, resulting in elevated blood glucose levels.
What is the A1C test?
The A1C test is a blood test that measures average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months, and it is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring Diabetes Mellitus Type 2.
How does Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 affect different demographic groups?
According to the CDC’s National Statistics Report, prevalence rates of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 vary by demographic groups, with 7.4% among non-Hispanic whites, 8.0% among Asian Americans, 12.1% among Hispanics, 12.7% among non-Hispanic blacks, and 15.1% among American Indians and Alaska Natives.
What is the relationship between Type 2 Diabetes and mental health?
Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes are twice as likely to experience depression compared to those without the condition, highlighting the importance of incorporating mental health support into blood sugar management plans.
How can individuals manage their condition effectively?
Understanding key terms related to Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and seeking support can enhance overall well-being and treatment outcomes for individuals managing the condition.



