Overview
This article highlights the important conversion of fructosamine to A1C, a process that plays a crucial role in diabetes management for healthcare providers. Fructosamine is a valuable biomarker for understanding recent glycemic control, especially in situations where A1C results may not tell the whole story. This understanding allows for more timely and personalized treatment strategies for individuals living with diabetes.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by the complexities of diabetes management. You're not alone in this journey. By recognizing the significance of fructosamine, healthcare providers can better support you in achieving optimal health outcomes. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
In the journey of managing diabetes, understanding the differences between various testing methods is essential for achieving the best possible outcomes. Fructosamine, a glycated protein that reflects average blood glucose levels over the past two to three weeks, is a vital biomarker alongside the more commonly known A1C test. While the A1C test provides a long-term perspective on glycemic control, fructosamine offers a more immediate snapshot. This can be particularly helpful in certain clinical situations where A1C may not provide the full picture.
This article explores the significance of fructosamine testing and its role in diabetes care. We will discuss how fructosamine and A1C work together to create effective treatment strategies tailored to individual needs. By looking into current research, practical applications, and best practices for patient education, we aim to empower healthcare providers to enhance their approach to diabetes management. Ultimately, this can lead to improved health outcomes for those living with this condition. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
What is Fructosamine and Its Role in Diabetes Management?
Fructosamine is a glycated protein that serves as a crucial biomarker for assessing average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 weeks. It forms when glucose binds to proteins in the blood, predominantly albumin. This measurement can be especially helpful in situations where A1C testing may not provide precise results, such as in individuals with hemoglobinopathies or those experiencing rapid fluctuations in blood glucose levels.
By employing this type of analysis, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into an individual's recent glycemic control, thereby improving management strategies for blood sugar levels. You might find it comforting to know that recent studies suggest these levels can offer a more immediate indication of glycemic changes compared to A1C, which generally reflects a longer-term average. This is particularly relevant in clinical settings where timely adjustments to treatment plans are necessary.
For instance, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has shown that a 15-minute lag time in glucose readings is significantly more effective than the four-hour lag associated with traditional self-monitoring methods. This underscores the importance of incorporating specific assessments into the regular management of blood sugar conditions, enabling quicker reactions to changes in a person's health.
Moreover, the standardization of the approach for measuring glycated albumin (GA) has enhanced its dependability, making it less vulnerable to preanalytical variables compared to similar tests. This reliability is crucial for clinical management, as it allows for more consistent observation of individuals' glycemic control.
In practical applications, healthcare providers have reported that incorporating fructosamine testing into their management protocols has led to improved outcomes for those with the condition. For example, David Harlan, MD, from the Diabetes Branch of NIDDK, emphasized the importance of addressing individuals' concerns regarding the management of their condition, especially in light of funding difficulties for research. Additionally, insurance providers such as John Hancock have created specialized programs that reward healthy lifestyle choices for individuals facing blood sugar management challenges.
These programs illustrate the potential for reduced premiums and improved management through proactive health measures. Engaging in such initiatives can greatly enhance the standard of care for individuals, aligning financial motivations with positive health results.
At T2DSolutions, we recognize the vital role of fructosamine testing and its conversion to A1C in tracking blood glucose levels and managing blood sugar issues, particularly for those who may not respond effectively to conventional A1C testing. By understanding and utilizing this biomarker, healthcare providers can better tailor their strategies to meet the unique needs of those they serve. We are here to support newly diagnosed patients in navigating these testing options and enhancing their management strategies.
Understanding the A1C Test: Importance and Comparison with Fructosamine
The A1C test is a vital tool in managing blood sugar, measuring the percentage of glycated hemoglobin to provide an average glucose level over the last 2 to 3 months. This test is essential for identifying blood sugar disorders and tracking long-term glycemic control, as it reflects the cumulative effects of glucose levels on hemoglobin. In contrast, this type of testing offers a shorter-term perspective, indicating average glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 weeks.
This distinction can be particularly beneficial in situations where A1C results may not accurately reflect a patient's glycemic status, such as in individuals with conditions that influence red blood cell turnover, like anemia or recent blood transfusions.
Understanding the differences between these two tests is crucial for healthcare providers who aim to enhance management strategies for blood sugar control. While A1C is widely recognized for its role in assessing chronic glycemic control, the fructosamine conversion to A1C can serve as a valuable adjunct in monitoring fluctuations in glucose levels, especially during periods of significant lifestyle changes or medication adjustments. At T2D Solutions, we understand the importance of regular A1C testing, recommending that individuals at risk or diagnosed with prediabetes undergo follow-up tests at least annually. This proactive approach is vital for taking prompt actions that can halt the progression of the condition.
The American Diabetes Association advocates for comprehensive diabetes management, emphasizing the need for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) coverage to reduce barriers to necessary diabetes technology, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
Real-life examples illustrate the significance of these tests in clinical practice. For instance, an individual with fluctuating blood glucose levels may present with a normal A1C, which can lead to a false sense of security. However, a specific test could reveal elevated glucose levels, prompting necessary adjustments in their management plan. Such insights highlight the importance of employing both tests to gain a thorough understanding of an individual's glycemic control.
Furthermore, T2D Solutions strives to improve management strategies for glucose regulation by providing access to independent life insurance agents who can present a wider array of quotes and options tailored to the needs of individuals with high blood sugar. Diabetes Care and Education Specialists (DCESs) also play a vital role in lowering healthcare costs and improving access to quality care through their interdisciplinary approach. Despite their potential, DCESs are often underutilized in U.S. healthcare models, yet they offer extensive self-management education and support (DSMES) that addresses clinical, educational, psychosocial, and behavioral aspects of care.
In summary, incorporating A1C testing alongside fructosamine conversion into management not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also enables healthcare providers to customize treatment plans that meet the unique needs of their clients. T2D Solutions is dedicated to being a valuable resource for newly diagnosed patients, providing educational content and tools that aid in understanding and managing their condition effectively.
When to Use Fructosamine Testing Instead of A1C
The conversion of fructosamine to A1C is vital in various clinical scenarios, enhancing the accuracy of diabetes management. Understanding when fructosamine testing is particularly beneficial can empower you in your health journey.
Unreliable A1C Outcomes: It's understandable to feel concerned if factors like anemia or hemoglobin disorders distort A1C results. In these situations, an alternative measurement may be more dependable for evaluating your glycemic control. For instance, the ICD-10 code D58 relates to hereditary hemolytic anemias, which can significantly affect A1C accuracy. Given that anemia and hemoglobin disorders are common among individuals with elevated blood sugar levels, using fructosamine conversion to A1C can provide a clearer picture for monitoring and treatment adjustments.
Rapidly Changing Glucose Levels: If you're undergoing intensive insulin treatment and your glucose levels fluctuate significantly, you might find that alternative testing offers a more immediate representation of your glycemic control. This is crucial for timely interventions and optimizing your treatment plan.
Pregnancy Monitoring: For expectant mothers, A1C may not fully capture short-term changes in glucose levels. Fructosamine conversion to A1C testing can provide a clearer understanding of glycemic control during pregnancy, which is essential for both your health and your baby's well-being. Current studies emphasize the importance of precise testing techniques during this critical period.
By recognizing these situations, healthcare providers can effectively incorporate blood sugar assessments into their practice, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and ensuring more personalized management strategies for metabolic conditions. As Karen Pulford, Editor in Chief, notes, "The HbA1c is a precise and straightforward test with immediate results availability and can be a valuable instrument in determining the diagnosis of diabetes-related conditions, particularly in low- and middle-income nations and hard-to-reach communities." This underscores the need for a balanced approach to blood sugar regulation, where both A1C and blood sugar testing are essential.
Moreover, case studies such as the OmniPod 5 illustrate effective diabetes management techniques, highlighting the significance of precise testing approaches. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
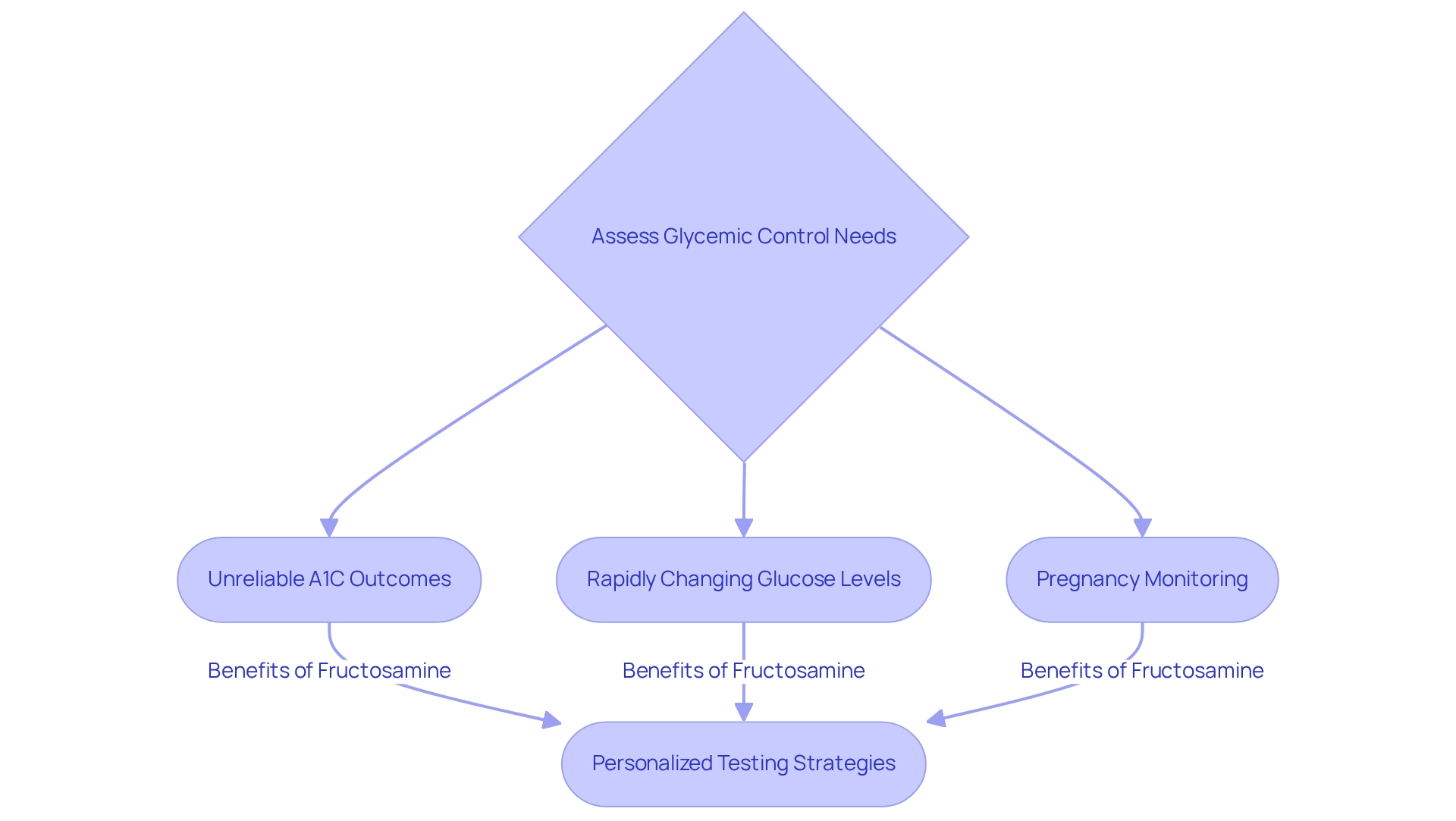
Converting Fructosamine Levels to A1C: Methods and Calculations
Understanding how to convert certain sugar levels to A1C is vital for your health journey. Healthcare providers typically use the formula:
- HbA1c (%) = (Sugar level in µmol/L × 0.017) + 1.61.
For instance, if your blood sugar level is measured at 300 µmol/L, the estimated A1C can be calculated as follows:
- (300 × 0.017) + 1.61 = 6.61%.
This conversion is crucial because it helps you comprehend how your recent glycemic control relates to long-term regulation, represented by A1C.
This conversion is particularly important as it provides a more timely representation of your glycemic status, especially for those whose standard A1C assessments may not be as reliable. For example, if you experience rapid fluctuations in glucose levels or have hemoglobinopathies, this method can serve as a valuable alternative.
Current methods for converting this compound to A1C have been validated by various studies, underscoring their accuracy in clinical practice. Research indicates that certain levels can reliably assess average blood glucose levels over the previous two to three weeks. This makes it a valuable resource for tracking individuals with blood sugar concerns. In Germany alone, more than 7.2 million cases of this metabolic disorder were recorded as of 2014, highlighting the importance of precise glycemic monitoring in managing this widespread condition.
Moreover, the reliability of these conversion techniques has been confirmed through practical cases and studies. For instance, the IN CONTROL Trial revealed that individuals with Type 1 diabetes and hypoglycemia unawareness benefited from continuous glucose monitoring, which can be complemented by related measurements. A recent study also showed that individuals with levels consistently above 300 µmol/L had A1C readings that matched the expected values from the conversion formula, reinforcing the method's usefulness in clinical settings.
When interpreting A1C results, it’s essential to consider findings from Khan et al., which suggest that individuals with HbA1c between 6.0% and 6.5% should have their status confirmed by combined FPG and HbA1c criteria. This enhances the credibility of discussions surrounding A1C interpretation.
Additionally, innovations in blood sugar management tools, such as smart insulin pens, are transforming how healthcare providers and individuals approach glycemic control. These devices assist in insulin dosing and can be integrated into electronic health records, improving overall management of the condition.
In summary, understanding how to convert fructosamine to A1C is essential for healthcare providers. It enhances their ability to evaluate and manage your condition effectively. By incorporating these conversion methods into practice, providers can offer more personalized care, ensuring that both recent and long-term glycemic control are adequately monitored. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. For more resources and tools related to diabetes management, visit T2DSolutions, your comprehensive hub for diabetes education and support.
Limitations and Considerations in Fructosamine and A1C Testing
Both fructosamine conversion to A1C and A1C tests come with significant limitations that healthcare providers must navigate with care. It's important to understand that levels of a specific glycation marker are particularly sensitive to serum albumin levels. When albumin concentrations are reduced, this can lead to inaccurately high readings of the marker, complicating the evaluation of glycemic control. Additionally, renal failure can significantly affect the accuracy of fructosamine measurements, as impaired kidney function may result in misleading results.
In a study, it was discovered that collecting samples in tubes containing citrate buffer doubled the diagnostic sensitivity for gestational metabolic disorder (GDM) compared to sodium fluoride-containing tubes. This finding underscores the importance of sample handling in ensuring testing accuracy.
However, A1C testing presents its own challenges. Factors like hemoglobin variants, recent blood transfusions, and certain types of anemia can distort A1C results, potentially leading to misdiagnosis. For example, a case study on glycation and glycated hemoglobin testing highlights the necessity of using standardized assay methods to guarantee accurate reporting of A1C levels.
Standardization is crucial for aligning results across clinical studies, which is essential for assessing the impacts of metabolic control on complications related to blood sugar disorders. Given these complexities, it’s vital for healthcare providers to consider these influencing factors when analyzing test results. Misinterpretation can lead to unsuitable management strategies, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive understanding of the limitations of fructosamine conversion to A1C and A1C testing in managing blood sugar.
By being aware of these nuances, providers can better assist their clients in achieving optimal health outcomes. As T2DSolutions aims to be a thorough resource center for diabetes-related education, understanding these testing limitations empowers recently diagnosed individuals to engage actively in their health management. Ultimately, the emphasis on community and collaboration in managing this condition highlights that this journey is collective. Shared knowledge and support can lead to improved health outcomes for everyone involved.
Current Research and Guidelines on Fructosamine and A1C Testing
Recent studies have highlighted the importance of this compound in the context of fructosamine conversion to A1C, serving as a complementary tool in diabetes management. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines recommend considering tests for advanced glycation end products, especially for individuals with conditions that affect red blood cell turnover, such as hemolytic anemia or recent blood transfusions. This is crucial, as the specific compound reflects average blood glucose levels over the past two to three weeks, providing a more timely evaluation of glycemic control compared to A1C, which measures levels over the preceding two to three months.
Current research continues to explore the connection between glycemic control measures and the conversion of fructosamine to A1C. Results suggest a strong association that could enhance evaluations of treatment effectiveness. For instance, a recent study titled 'Correlation Between HbA1c and Fructosamine Levels' demonstrated that the fructosamine conversion to A1C serves as a reliable indicator of recent treatment changes, particularly beneficial in managing conditions like fulminant diabetes and juvenile diabetes mellitus. This correlation is backed by a 95% confidence interval for the area under the curve (AUC) of serum glucose in identifying Type 2 Diabetes, ranging from 0.89 to 0.95, underscoring its diagnostic potential.
At T2DSolutions, we recognize the importance of integrating fructosamine testing into regular evaluations to enhance care for individuals. By offering resources and tools, including calculators for fructosamine conversion to A1C, we strive to provide a comprehensive approach to managing blood sugar levels. This ensures that newly diagnosed individuals receive personalized care that aligns with their unique health profiles.
As Debra Manzella, RN, pointed out, "The A1C test results show higher levels in Black, Asian, and Hispanic populations compared to tests in White individuals, even when their blood sugar levels are similar." This highlights the necessity of considering demographic factors in managing diabetes, which is vital for newly diagnosed individuals to understand. You're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Educating Patients on Fructosamine and A1C: Best Practices for Healthcare Providers
Informing individuals about glycosylated proteins and A1C assessments is crucial for effective diabetes management. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by medical jargon, but healthcare providers should clearly articulate the purpose of each test. By highlighting their differences and the implications of the results for treatment plans, we can foster a greater understanding. For instance, the fructosamine conversion to A1C can provide insights into glycemic control over a shorter period compared to A1C, which reflects average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months.
This distinction is vital, particularly for individuals experiencing fluctuations in glucose levels or modifications in their treatment plan. Offering clear, accessible information enables individuals to take an active role in their care. Research shows that when you comprehend your test results, you are more inclined to participate in your treatment plans, leading to improved health outcomes. A recent study discovered that fructosamine levels ≥ 250 umol/L were linked to the onset of retinopathy in individuals with an HbA1c < 7.0% (53 mmol/mol). This highlights the significance of monitoring the fructosamine conversion to A1C alongside both metrics.
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to improving engagement by discussing how test results influence lifestyle choices, medication adherence, and ongoing monitoring. Optimal methods for instructing individuals involve utilizing visual aids, supplying written resources, and encouraging inquiries to ensure understanding. Real-world examples of effective education strategies show that personalized conversations about test results can greatly enhance your understanding and management of diabetes.
Furthermore, integrating expert guidance into educational initiatives can bolster knowledge even further. For example, glycated albumin has been acknowledged as a more dependable marker than HbA1c for evaluating glucose control in individuals with chronic kidney disease, which can be especially pertinent for those undergoing dialysis. By incorporating such insights into patient education, healthcare providers can promote a cooperative strategy for managing diabetes-related conditions, ultimately resulting in enhanced health outcomes for their patients.
Additionally, the concept of the glycosylation gap serves as a useful clinical research tool for evaluating variations in diabetic complications beyond glycemic control. This emphasizes the importance of comprehensive monitoring. Precise assessment of biomarkers associated with the condition, as highlighted in recent case studies, is essential for effective monitoring and management of this illness and its complications. Together, we can navigate this health issue within a supportive community. For more resources and tools related to the fructosamine conversion to A1C and A1C testing, we encourage you to explore T2DSolutions, your comprehensive resource for diabetes education and support.
Conclusion
Understanding the interplay between fructosamine and A1C testing is crucial for effective diabetes management. It's important to recognize how fructosamine provides valuable insights into recent glycemic control, especially when A1C results might be misleading due to rapid glucose fluctuations or specific medical conditions. By integrating both tests into diabetes care, healthcare providers can develop personalized and responsive treatment strategies that truly cater to the unique needs of each patient.
The advantages of fructosamine testing go beyond simple diagnostics; they empower both patients and providers to make informed decisions regarding treatment adjustments. As research continues to affirm the reliability and relevance of fructosamine levels, it becomes clear that these two testing methods complement each other, enhancing the overall quality of diabetes management.
Ultimately, fostering an environment of education and collaboration around these testing methods can lead to improved health outcomes for individuals living with diabetes. By embracing a comprehensive approach that includes both A1C and fructosamine testing, healthcare providers can better support their patients in navigating the complexities of diabetes management. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; effective care is a shared journey that we can embark on together.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is fructosamine and its significance in blood glucose monitoring?
Fructosamine is a glycated protein that serves as a crucial biomarker for assessing average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 weeks. It forms when glucose binds to proteins in the blood, predominantly albumin, and provides valuable insights into an individual's recent glycemic control.
When is fructosamine testing particularly useful?
Fructosamine testing is especially helpful in situations where A1C testing may not provide precise results, such as in individuals with hemoglobinopathies or those experiencing rapid fluctuations in blood glucose levels.
How does fructosamine compare to A1C in terms of glycemic monitoring?
While A1C testing reflects average glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months, fructosamine provides a shorter-term perspective, indicating average glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 weeks. This makes fructosamine particularly relevant for timely adjustments to treatment plans.
What advancements have been made in fructosamine testing?
The standardization of measuring glycated albumin (GA) has enhanced its reliability, making it less vulnerable to preanalytical variables compared to similar tests, which is crucial for consistent observation of glycemic control.
What impact has fructosamine testing had on diabetes management?
Healthcare providers have reported that incorporating fructosamine testing into management protocols has led to improved outcomes for individuals with diabetes, allowing for better-tailored strategies to meet unique patient needs.
How do insurance programs relate to blood sugar management?
Insurance providers, such as John Hancock, have created specialized programs that reward healthy lifestyle choices for individuals facing blood sugar management challenges, potentially leading to reduced premiums and improved health outcomes.
What role does T2DSolutions play in diabetes management?
T2DSolutions recognizes the importance of fructosamine testing and its conversion to A1C in managing blood glucose levels, particularly for those who may not respond effectively to conventional A1C testing. They provide support for newly diagnosed patients in navigating testing options and enhancing management strategies.
