Overview
Understanding your blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes, and it's important to know the difference between the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) and A1C. While GMI reflects your average blood sugar over just 10 to 14 days, A1C provides insight into your levels over the past two to three months. This distinction can be confusing, and it's completely understandable to feel a bit overwhelmed.
Discrepancies between these two metrics can arise due to various factors, which is why it's crucial to grasp both concepts. By doing so, you gain different insights into your glycemic control, helping you make informed decisions about your health. You're not alone in this journey; many people find it helpful to seek support and resources to better understand their diabetes management.
If you're feeling uncertain, consider reaching out to a healthcare professional or support group. They can provide the guidance you need to navigate your health effectively. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
Understanding the nuances of diabetes management can be challenging, especially when it comes to interpreting key metrics like the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) and A1C. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by these terms. These two measurements serve distinct purposes in monitoring blood sugar levels, yet many individuals grapple with the question: is GMI the same as A1C?
By exploring the definitions, calculations, and implications of these indicators, you can uncover valuable insights that empower you to take control of your health. However, the discrepancies between GMI and A1C can lead to confusion and raise critical questions about their reliability in clinical practice.
Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Define GMI and A1C: Key Metrics in Diabetes Management
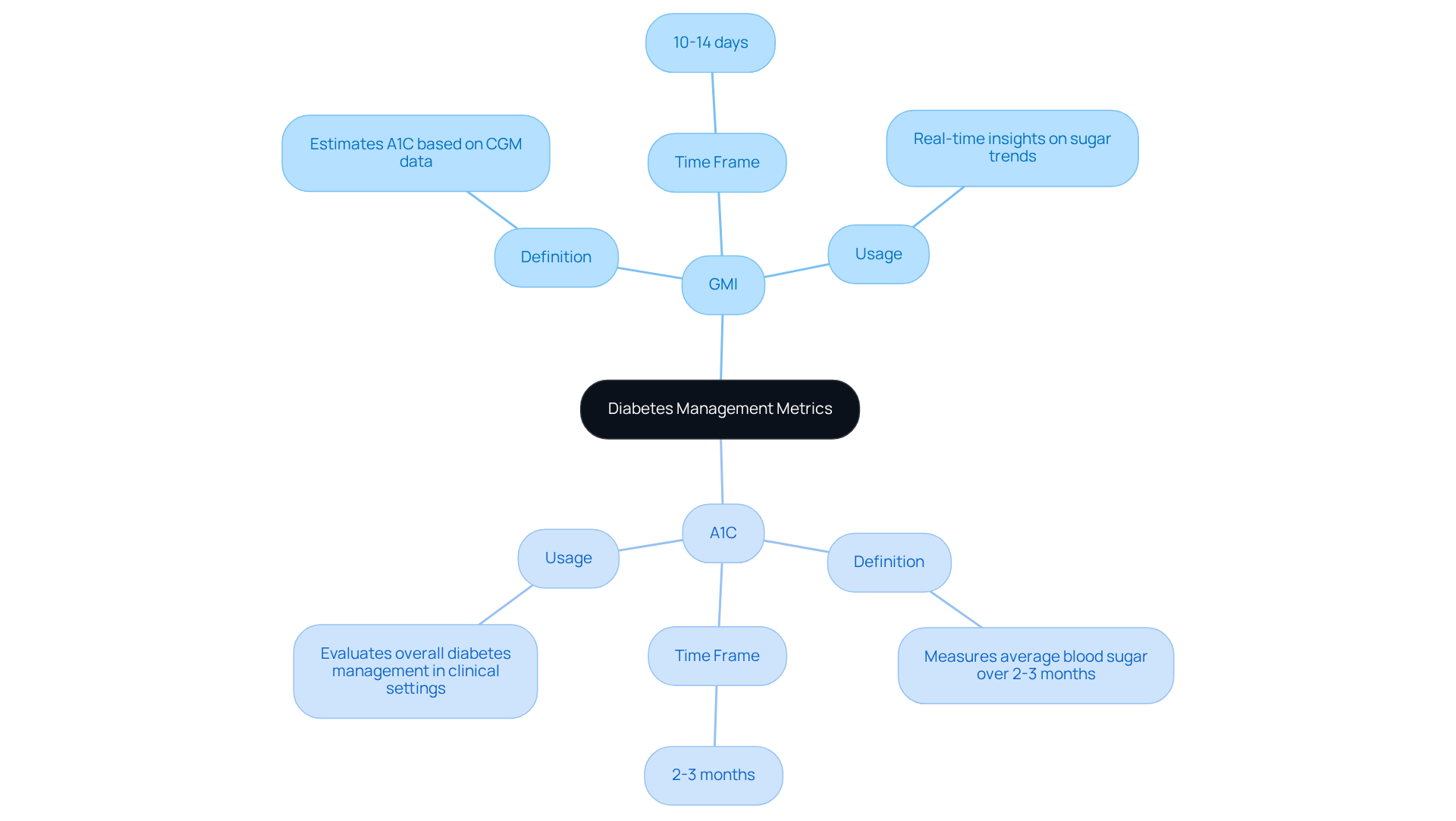
The Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) is a relatively new metric that estimates a person's A1C level based on continuous blood sugar monitoring (CGM) data, and it raises the question, is GMI same as A1C? This innovative tool reflects average sugar levels over a shorter duration, usually the last 10 to 14 days. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by these terms, but grasping their definitions is vital for effective diabetes oversight.
In contrast, A1C assesses the average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, offering a longer-term perspective on sugar control. Both metrics provide insights into a patient's glycemic control, and a key question is gmi same as a1c, considering their different time perspectives. For those utilizing CGM technology, GMI is especially beneficial as it can offer real-time insights on sugar trends. Meanwhile, A1C is frequently employed in clinical environments to evaluate overall diabetes management.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Understanding these tools can empower you to take charge of your health and make informed decisions. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Calculate and Interpret GMI and A1C: Understanding the Numbers
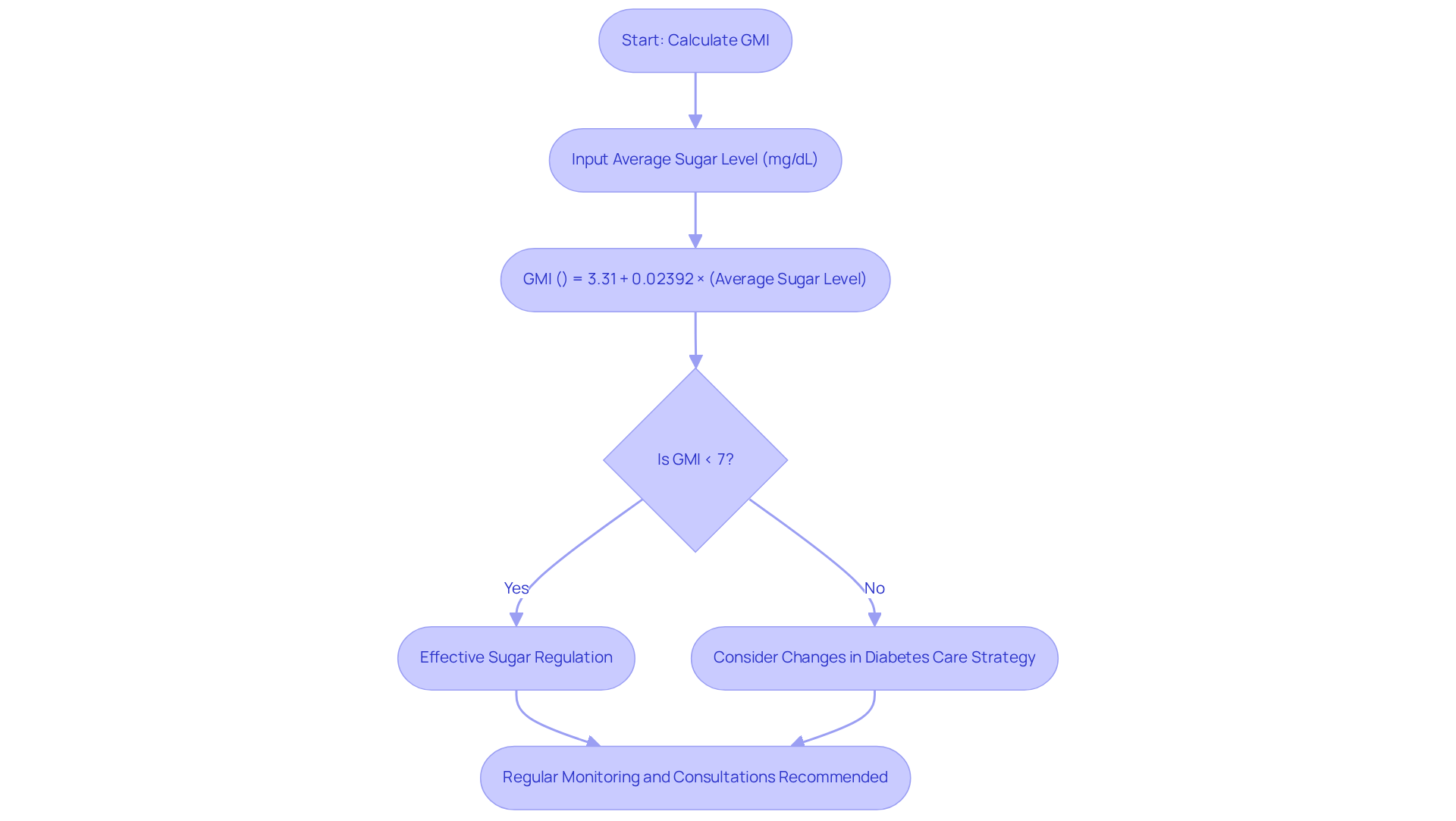
Understanding whether GMI is gmi same as A1C is essential for managing your diabetes effectively. To calculate your GMI, you can use the formula:
- GMI (%) = 3.31 + 0.02392 × (average sugar level in mg/dL).
For instance, if your average blood sugar level is 150 mg/dL, your GMI would be about 6.9%. This figure is significant, as a GMI of 6.9% indicates effective sugar regulation.
In contrast, the A1C value comes directly from a standard laboratory test. It’s important to comprehend these metrics together to determine if gmi is the same as a1c. An A1C of 7% or above may suggest that you need to consider changes in your diabetes care strategy. Regularly monitoring these values is crucial for identifying trends and facilitating timely interventions. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; many individuals share similar experiences.
Statistics reveal that achieving target levels for GMI is gmi same as A1C levels, which is vital for effective diabetes control. Studies indicate that between 26% and 68% of individuals experience clinically significant differences between these two metrics. It’s understandable to feel overwhelmed by these numbers, but knowing them can empower you to take charge of your health.
The root mean squared error for GMI has been reported to be between 0.66 and 0.69 percentage points, highlighting the variability in these measurements. It’s important to note that GMI may not always be a reliable measure of glycemic control for patients with type 2 diabetes. Therefore, it should be interpreted cautiously in clinical practice. Regular consultations with healthcare providers can enhance your diabetes control and provide the support you need. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Identify Discrepancies Between GMI and A1C: Implications for Management
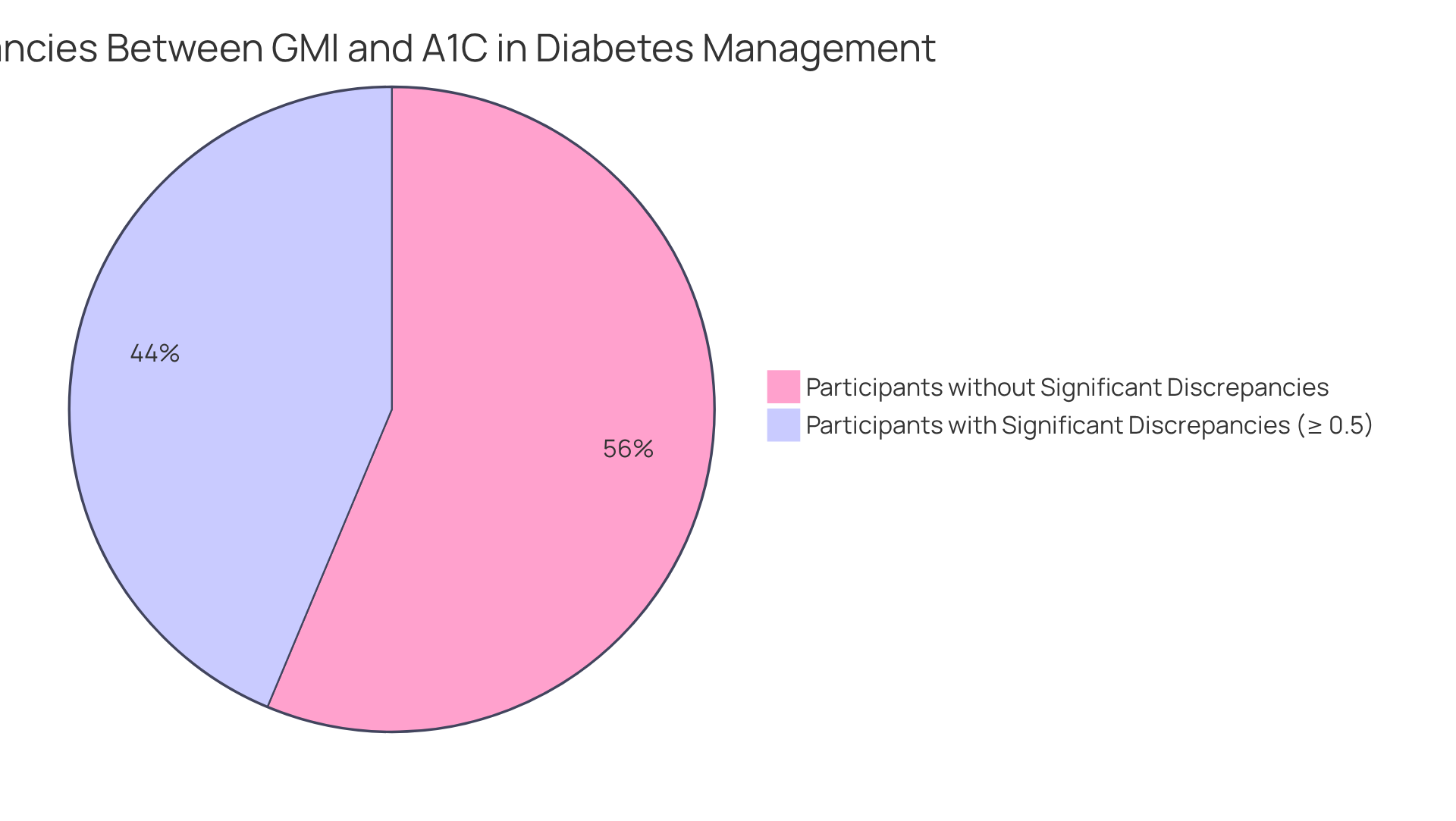
Many people may understandably experience confusion due to discrepancies, as they wonder if GMI is gmi same as A1C. Various factors contribute to these differences, including measurement methods and individual physiological responses. For example, a patient might have a GMI of 6.5% while their A1C is 7.5%, leading to the question of whether is GMI same as A1C. This indicates that their average sugar levels are actually more favorable than what the A1C suggests. Factors such as red blood cell turnover, hemoglobin variants, or recent changes in glucose control strategies can lead to such discrepancies.
Understanding whether is gmi same as A1C is essential. They can alert healthcare providers to potential complications or the need for treatment adjustments. Research shows that approximately 43.7% of participants in studies experience significant differences of 0.5% or more between GMI and A1C. This highlights the importance of these metrics in clinical practice.
Regular conversations with healthcare professionals about these measurements can lead to more personalized and effective diabetes control approaches. Ultimately, this can enhance patient outcomes. Furthermore, case studies reveal that discrepancies can significantly impact treatment decisions. It’s crucial for healthcare professionals to consider both GMI and A1C in their assessments. By integrating insights from both metrics, patients can achieve better glycemic control and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
You're not alone in this journey. Engaging with your healthcare team and discussing these vital numbers can empower you to take charge of your health.
Apply GMI and A1C in Daily Management: Practical Steps for Patients
To effectively apply GMI and A1C in your daily management, consider these supportive steps:
-
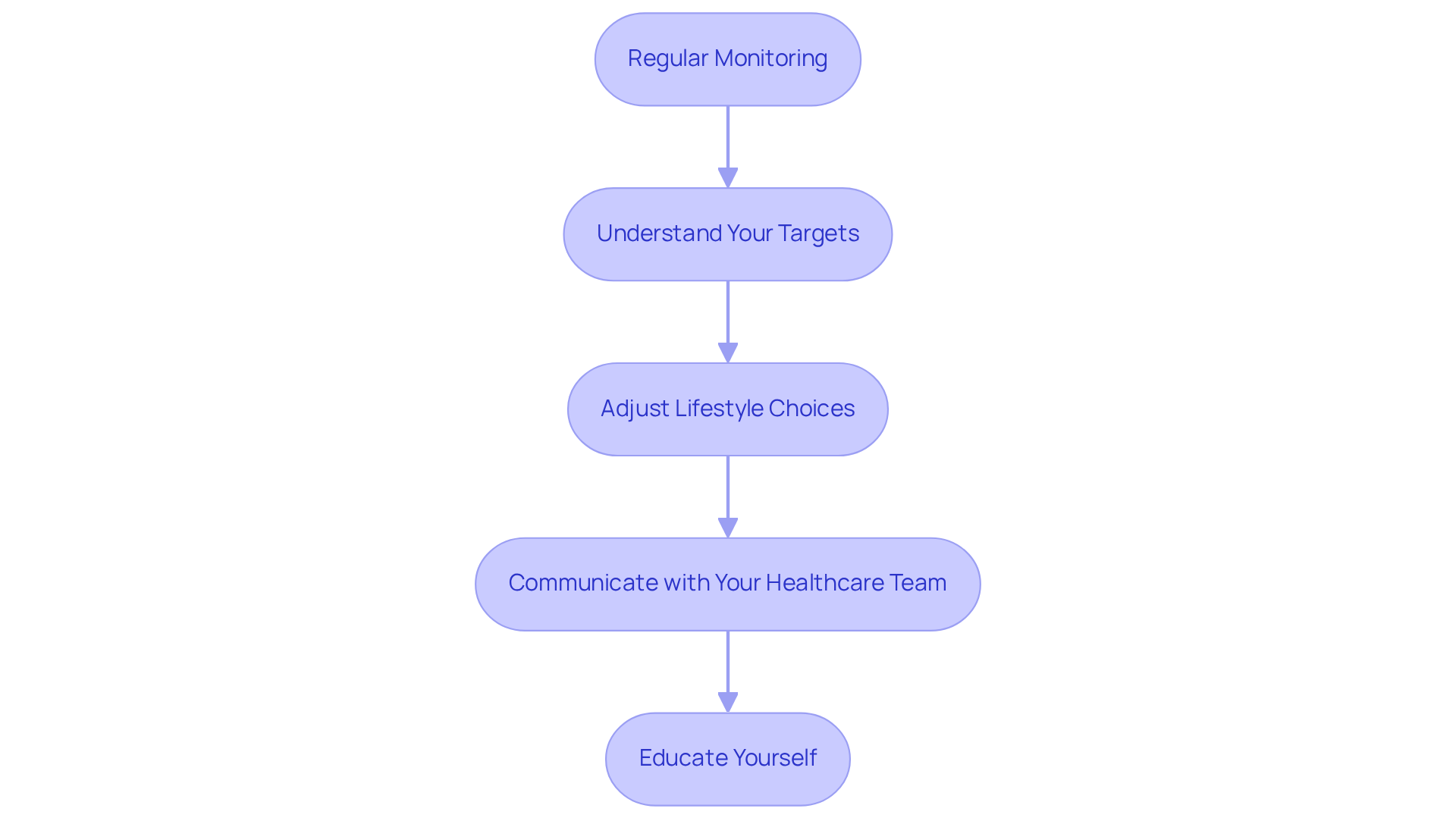
Regular Monitoring: It's important to employ a continuous monitor (CGM) to track your sugar levels and consistently calculate your GMI. Studies show that CGM users experience significant improvements in glycemic control, with reductions in A1C levels by an average of 0.62% compared to non-users. You're not alone in this journey; many have found success through regular monitoring.
-
Understand Your Targets: Collaborate with your healthcare provider to establish personalized targets for both GMI and A1C based on your health goals. This tailored approach can lead to improved results. In fact, a 13.2% rise in patients reaching A1C levels below 7% has been noted after just three months of CGM use. Remember, your goals are unique to you, and having a clear target can be empowering.
-
Adjust Lifestyle Choices: Incorporate healthy eating, regular physical activity, and stress control techniques to help maintain your glucose levels within target ranges. Recent guidelines emphasize the importance of lifestyle changes in effectively managing conditions, as it raises the question of whether is gmi same as A1C. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but small adjustments can lead to significant improvements.
-
Communicate with Your Healthcare Team: Share your GMI and A1C results during appointments to discuss any necessary adjustments to your diabetes care plan. Effective communication has been linked to improved patient outcomes, including a higher percentage of patients meeting their treatment targets. We are here to support you every step of the way.
-
Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest research and guidelines concerning diabetes care to make educated decisions about your health. Engaging with educational resources can empower you to take charge of your diabetes care. Remember, knowledge is a powerful tool in your journey.
By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can enhance your diabetes control and improve your overall quality of life. Real-life examples show that patients who actively monitor and adjust their management strategies based on GMI and A1C data report better health outcomes and a greater sense of control over their condition. You're not alone in this journey; many have walked this path and found success.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) and A1C is crucial for effective diabetes management. You're not alone in this journey, and recognizing these differences can empower you to make informed decisions about your health. While both metrics provide valuable insights into blood sugar control, they serve different purposes and timeframes. GMI offers a more immediate picture based on recent glucose levels, whereas A1C reflects a longer-term view of glycemic control, spanning two to three months.
Throughout this article, we’ve highlighted the importance of both GMI and A1C in monitoring diabetes. Calculating GMI from average blood sugar levels and understanding how it correlates with A1C can help identify potential discrepancies that may impact treatment plans. Regular monitoring and effective communication with healthcare providers are essential steps in managing diabetes effectively. Moreover, lifestyle adjustments and personalized targets can lead to improved outcomes.
Ultimately, integrating GMI and A1C into your daily diabetes management is vital for achieving better health. By actively engaging in monitoring, educating yourself about these metrics, and collaborating with healthcare professionals, you can take charge of your diabetes care. Embracing these practices not only enhances glycemic control but also fosters a greater sense of empowerment and wellbeing in your journey toward better health.
- Remember, it’s understandable to feel overwhelmed at times.
- Regular check-ins with your healthcare team can provide reassurance and guidance.
- Sharing your experiences with others can create a supportive community.
Together, we can navigate this path to better health, ensuring you feel supported every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI)?
The Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) is a metric that estimates a person's A1C level based on continuous blood sugar monitoring (CGM) data, reflecting average sugar levels over the last 10 to 14 days.
How does GMI differ from A1C?
GMI reflects average blood sugar levels over a shorter duration (10 to 14 days), while A1C assesses average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, providing a longer-term perspective on glucose control.
Why is understanding GMI and A1C important for diabetes management?
Understanding GMI and A1C is vital for effective diabetes oversight, as both metrics provide insights into a patient's glycemic control and help inform health decisions.
How can GMI be beneficial for those using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology?
GMI offers real-time insights on sugar trends for individuals utilizing CGM technology, helping them manage their blood sugar levels more effectively.
In what settings is A1C commonly used?
A1C is frequently employed in clinical environments to evaluate overall diabetes management.



