Overview
Ketoacidosis in Type 2 diabetes is a serious metabolic condition that can be overwhelming. It is characterized by high levels of ketones in the blood, which may arise from inadequate insulin treatment, illness, dehydration, poor dietary management, or stress. Recognizing the symptoms, such as excessive thirst and confusion, is crucial. It's understandable to feel concerned about these signs.
Implementing effective management strategies can make a significant difference. Regular monitoring and adhering to your treatment plan are essential steps to prevent severe complications associated with this condition. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; support is available to help you navigate these challenges.
If you or someone you know is facing this situation, consider reaching out for guidance and resources. Together, we can work toward a healthier future, and there are many who understand what you're going through. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
Ketoacidosis, especially within the context of Type 2 Diabetes, represents a significant health challenge that often goes unnoticed. While it is more frequently linked to Type 1 Diabetes, the occurrence of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in Type 2 patients can lead to serious complications if not managed appropriately.
This article aims to explore the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies for ketoacidosis, equipping you with the knowledge to recognize warning signs and take proactive measures.
How can you, as an individual with Type 2 Diabetes, safeguard your health against this potentially life-threatening condition? Understanding the intricate relationship between diabetes management and ketoacidosis is crucial to addressing this important question.
You're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
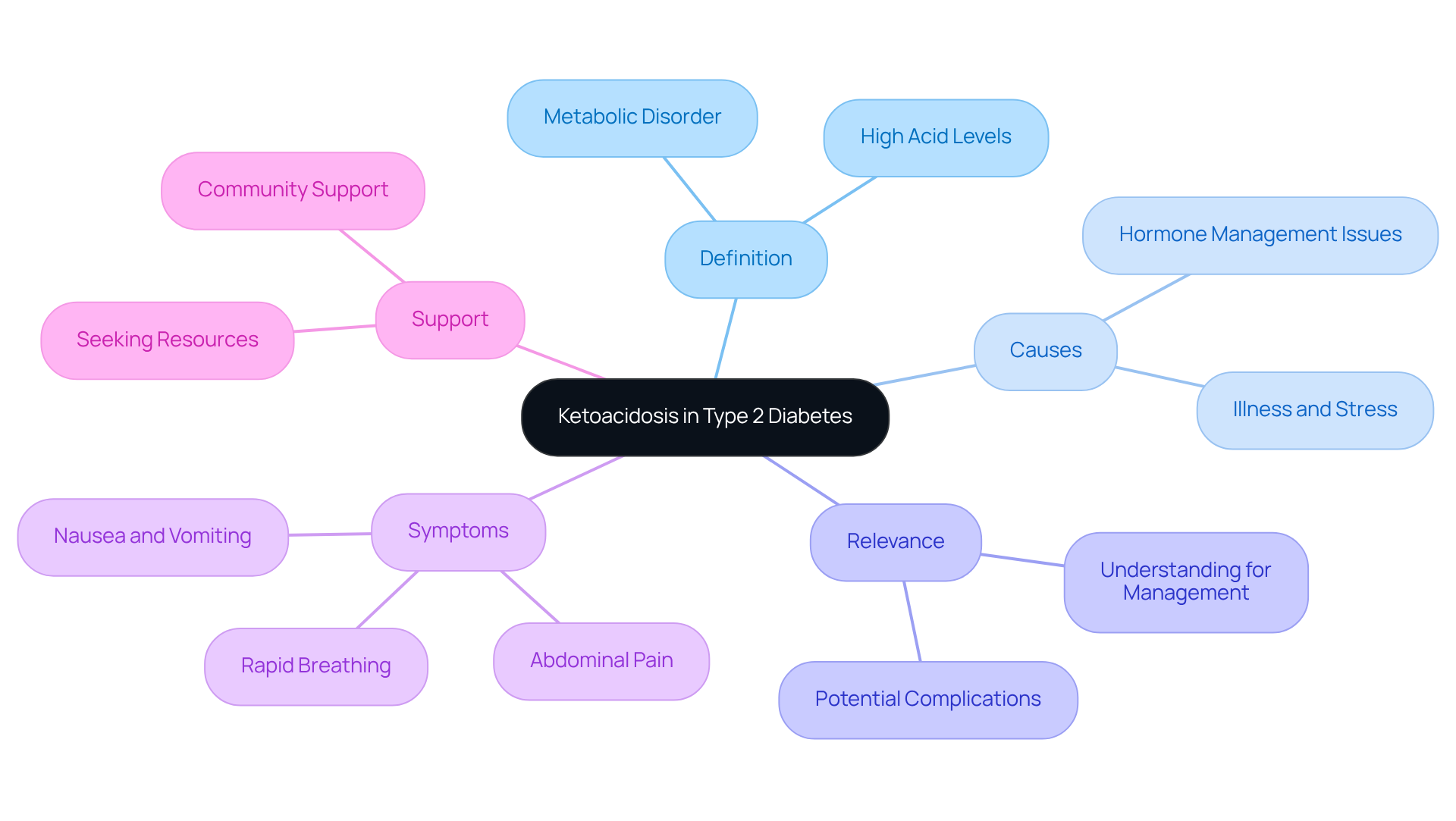
Define Ketoacidosis and Its Relevance to Type 2 Diabetes
Ketoacidosis, especially diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), is a serious metabolic disorder that can be concerning. It is characterized by high levels of acids in the blood, leading to acidosis. This condition arises when the body lacks sufficient amounts of a specific hormone, causing it to use fat for energy instead of glucose. As a result, ketones are produced, which can reach dangerous levels.
While ketoacidosis type 2 diabetes is less common than in Type 1 diabetes, it can still occur—particularly during times of illness, stress, or if hormone management is lacking. It's understandable to feel worried about this, but understanding ketoacidosis is crucial for individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. If not addressed promptly, it can lead to severe complications.
Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Seeking support and resources can make a significant difference in managing your health. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Explore the Causes of Ketoacidosis in Type 2 Diabetes
Explore the Causes of Ketoacidosis in Type 2 Diabetes
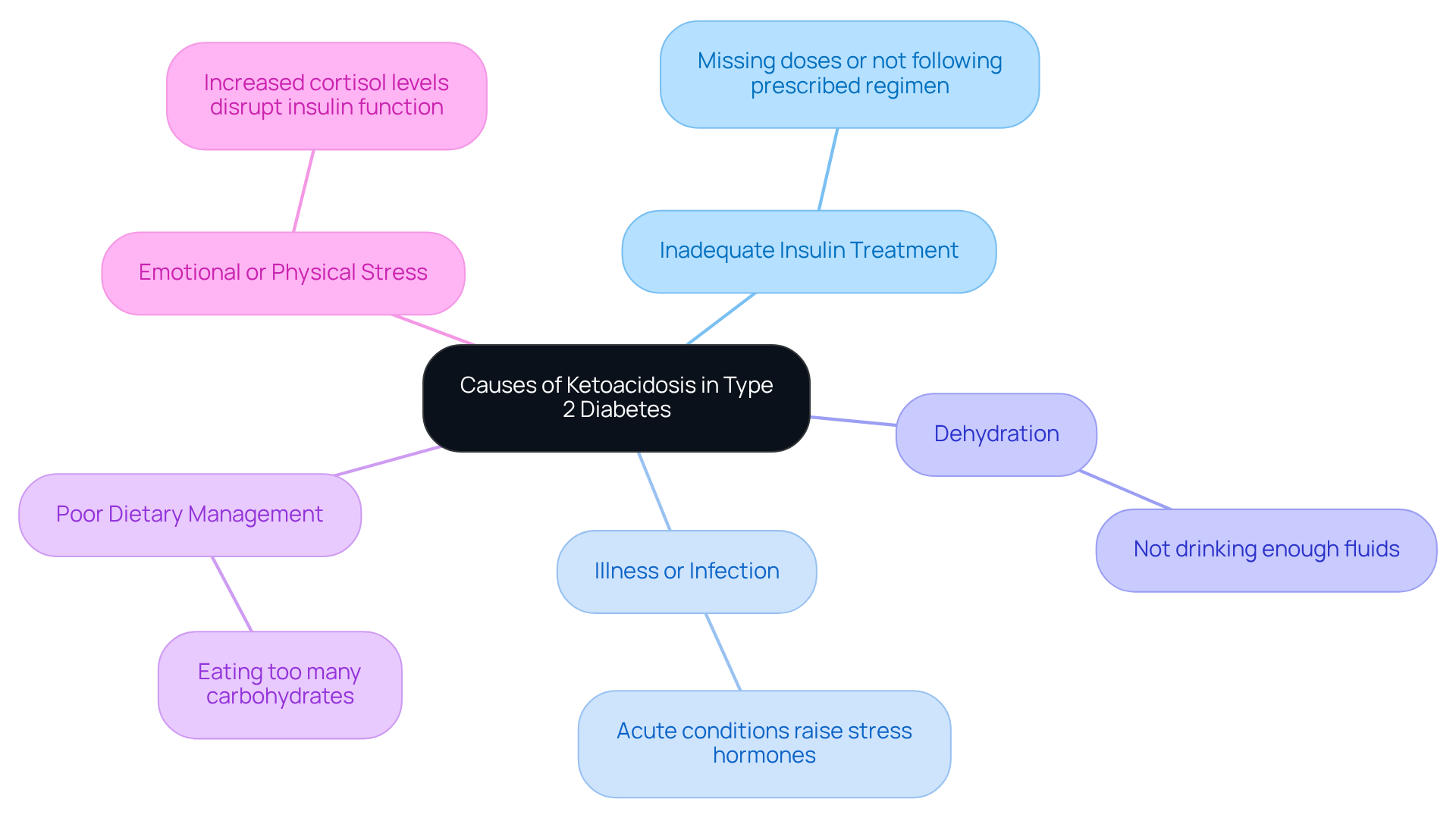
Ketoacidosis in Type 2 Diabetes can be triggered by several factors, and understanding these can help you manage your condition more effectively. Here are some key causes:
- Inadequate Insulin Treatment: Missing doses or not following your prescribed insulin regimen can lead to insufficient insulin levels. This may prompt your body to produce ketones, which can be concerning.
- Illness or Infection: Acute conditions, such as pneumonia or urinary tract infections, can raise stress hormones. These hormones oppose glucose regulation, leading to increased blood sugar and the production of byproducts.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough fluids can worsen your condition. Dehydration can result in elevated blood sugar levels and increased ketone production, which is something to be mindful of.
- Poor Dietary Management: Eating too many carbohydrates without adequate hormone support can also induce diabetic acidosis. It’s important to be aware of your dietary choices and their impact on your health.
- Emotional or Physical Stress: Stress can increase cortisol levels, which may disrupt insulin function and lead to metabolic acidosis. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed at times, but recognizing this can help you take proactive steps.
Recognizing these causes is crucial for individuals dealing with ketoacidosis type 2 diabetes. You're not alone in this journey. At T2DSolutions, we aim to provide comprehensive resources and support to help you understand these triggers. Together, we can empower you in your diabetes management journey. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Identify Symptoms and Warning Signs of Ketoacidosis
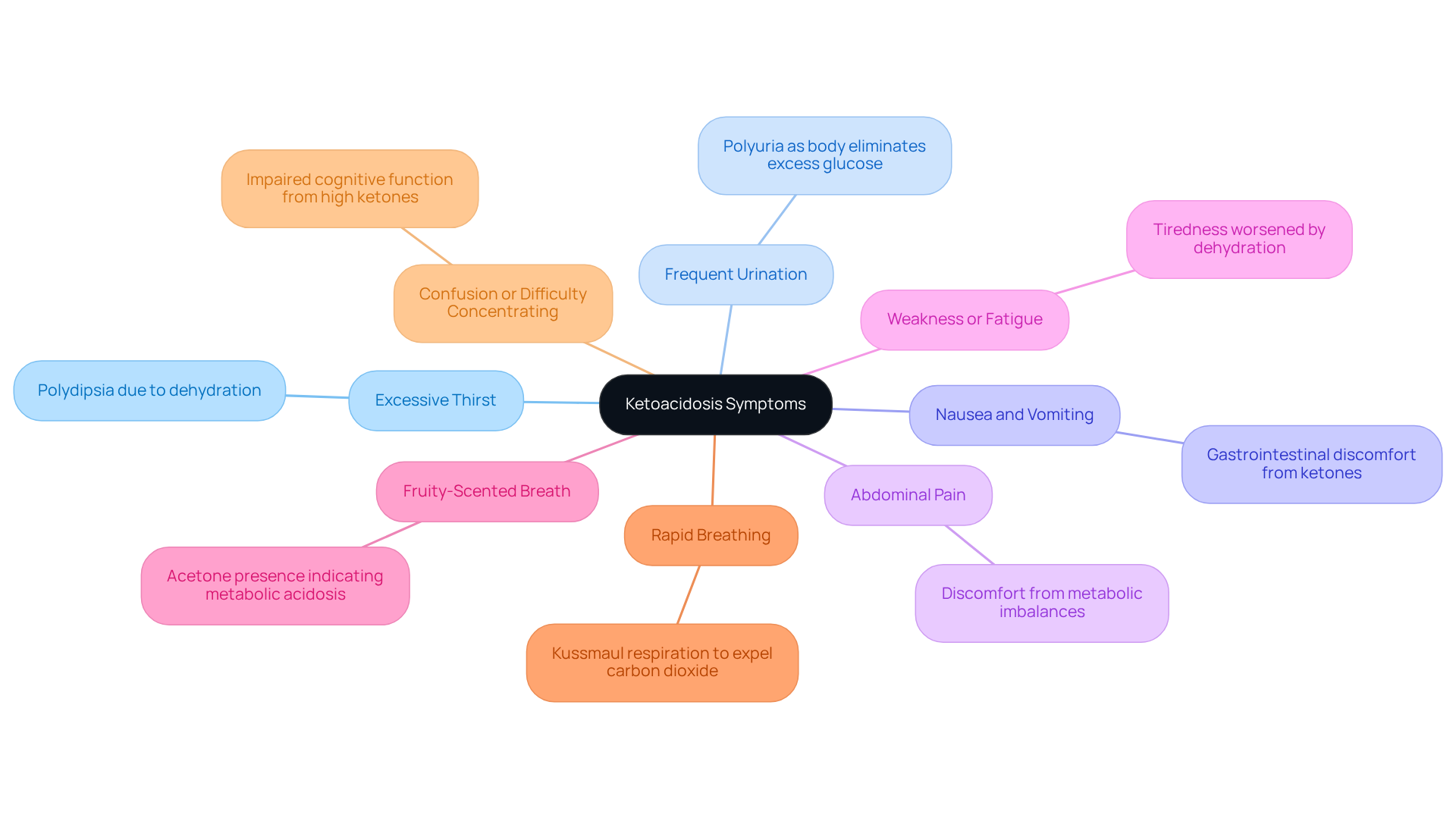
Symptoms of ketoacidosis can develop rapidly, often within hours, and recognizing them is crucial for your health. Here are some signs to watch for:
- Excessive Thirst: You may experience a strong urge to drink fluids due to dehydration, often leading to polydipsia.
- Frequent Urination: Increased urination occurs as your body works to eliminate excess glucose and acids, known as polyuria.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Gastrointestinal discomfort is common as your body responds to increased concentrations of ketones, which can lead to further dehydration.
- Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or pain in the stomach area may arise due to metabolic imbalances.
- Weakness or Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness or lack of energy is prevalent, often worsened by dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
- Fruity-Scented Breath: A unique smell resulting from acetone, a type of carbonyl compound, is a key indicator of metabolic acidosis.
- Rapid Breathing: Deep, labored breathing, known as Kussmaul respiration, may occur as your body tries to correct acidosis by expelling carbon dioxide.
- Confusion or Difficulty Concentrating: High ketone levels can impair cognitive function, leading to confusion or altered mental status.
Identifying these warning signs is essential for prompt medical intervention. Untreated ketoacidosis type 2 diabetes can lead to serious complications. At T2DSolutions, we focus on self-management and monitoring strategies that can significantly lower the occurrence of diabetic complications among patients. It’s important to observe these symptoms, especially if you have Type 2 Diabetes and may be at risk for ketoacidosis type 2 diabetes due to factors like infections or overlooked medication therapies.
We are here to support you every step of the way. T2DSolutions provides resources and guidance to help you recognize and respond to these symptoms promptly, significantly improving outcomes and preventing hospitalization. Remember, DKA accounts for 14% of all hospital admissions for diabetes and 16% of diabetes-related fatalities. This highlights the importance of recognizing symptoms quickly. Additionally, the impact of COVID-19 on DKA incidence underscores the need for heightened awareness and preventive measures during these challenging times.
Implement Management Strategies for Ketoacidosis
Managing ketoacidosis effectively is crucial for your health, and there are several key strategies that can help you navigate this challenge with confidence:
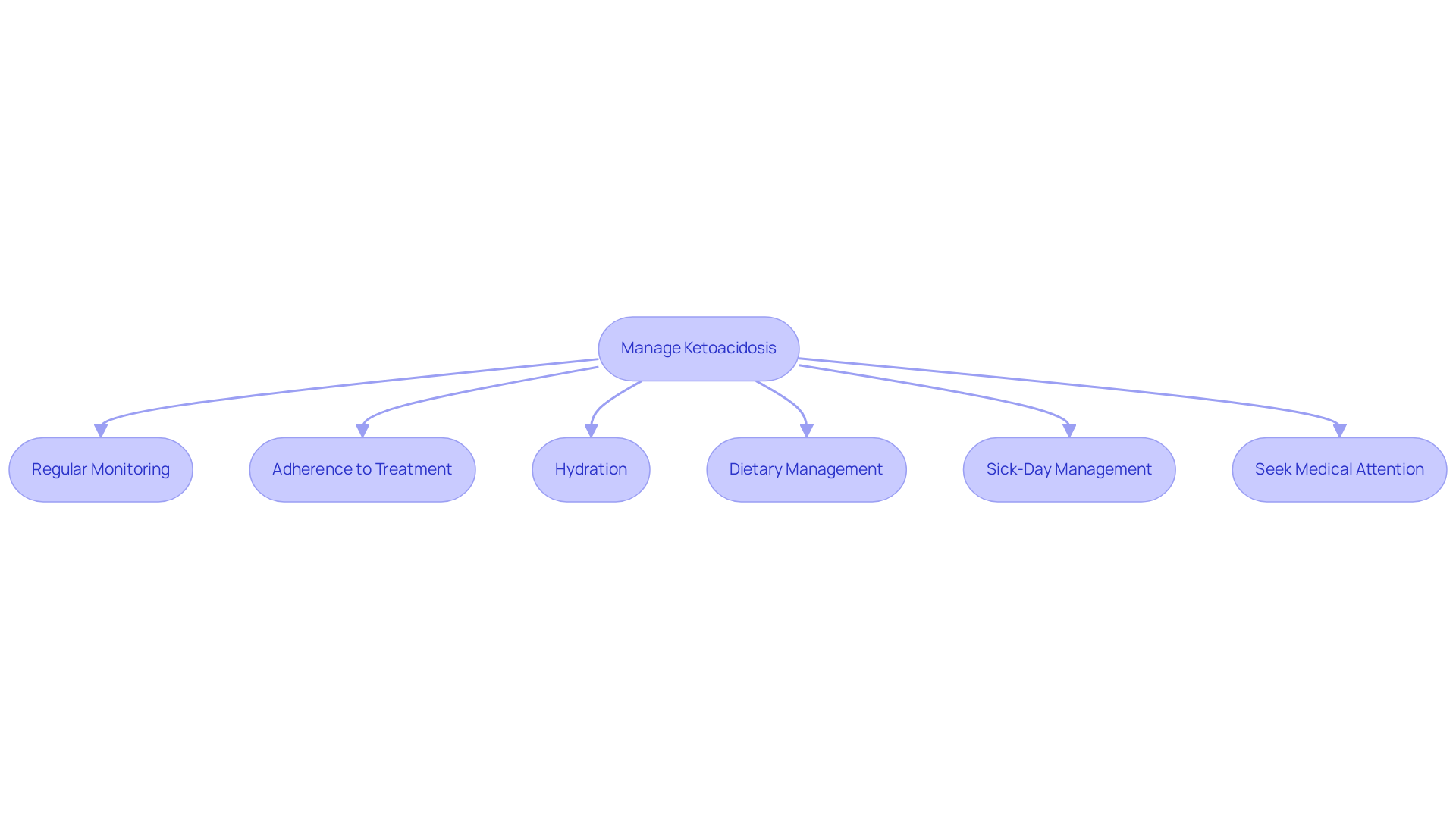
- Regular Monitoring: It's important to check your blood glucose and ketone levels frequently, especially during times of illness or stress. This practice can help you stay informed about your condition.
- Adherence to Treatment: Following your prescribed regimens and medications diligently is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; support is available.
- Hydration: Consuming ample liquids is vital to avoid dehydration, particularly if you're experiencing signs of metabolic imbalance. Staying hydrated can make a significant difference.
- Dietary Management: Maintaining a balanced diet with appropriate carbohydrate intake is key. If you feel uncertain, consulting with a dietitian can provide you with tailored guidance.
- Sick-Day Management: Having a plan for managing your diabetes during illness is crucial. This includes adjusting insulin doses and monitoring your blood sugar more frequently.
- Seek Medical Attention: If you notice signs of metabolic acidosis, don’t hesitate to seek immediate medical care. Early intervention can prevent complications.
By implementing these strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing ketoacidosis and manage your Type 2 Diabetes more effectively. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way. You are not alone in this journey, and together, we can work towards a healthier future.
Conclusion
Ketoacidosis, particularly in the context of Type 2 Diabetes, is a significant health concern that deserves careful understanding and management. While this condition is less common than in Type 1 Diabetes, it can have serious implications if not addressed promptly. By recognizing the factors that contribute to ketoacidosis and the symptoms that signal its onset, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your health.
Several critical aspects of ketoacidosis are essential to understand. Causes include:
- Inadequate insulin treatment
- Illness
- Dehydration
- Dietary mismanagement
Symptoms to be vigilant for are:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Nausea
- Confusion
Effective management strategies are equally important; these include:
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose and ketone levels
- Adhering to treatment plans
- Maintaining hydration
- Seeking medical attention when necessary
Ultimately, awareness and education are key in preventing ketoacidosis in individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. By understanding the connections between your condition and the potential risks of ketoacidosis, you can take informed actions to manage your health effectively. Engaging with healthcare providers and utilizing available resources can empower you in your diabetes management journey. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way, leading to better health outcomes and a more confident approach to living with Type 2 Diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ketoacidosis?
Ketoacidosis, particularly diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), is a serious metabolic disorder characterized by high levels of acids in the blood, leading to acidosis. It occurs when the body lacks sufficient amounts of a specific hormone, causing it to use fat for energy instead of glucose, resulting in the production of dangerous levels of ketones.
Is ketoacidosis common in Type 2 diabetes?
While ketoacidosis is less common in Type 2 diabetes compared to Type 1 diabetes, it can still occur, especially during times of illness, stress, or if hormone management is inadequate.
Why is it important to understand ketoacidosis for individuals with Type 2 diabetes?
Understanding ketoacidosis is crucial for individuals with Type 2 diabetes because if not addressed promptly, it can lead to severe complications.
What should individuals with Type 2 diabetes do if they are concerned about ketoacidosis?
Individuals with Type 2 diabetes should seek support and resources to help manage their health, as understanding and addressing ketoacidosis can significantly improve their well-being.



